Introduction
The incidence rate of fetal cardiac abnormalities is
reported to be 4–10% (1). By
clarifying the diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities and
improving the domestic use of such a diagnosis, in addition to
taking corresponding preventive measures and intervention
strategies, the incidence rate of fetal and infant congenital
cardiac malformations is likely to be reduced significantly.
The early diagnosis of complex fetal cardiac
abnormalities has become a frontier subject in the prenatal
diagnosis field (2). Traditional
two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography indicates anatomical details
clearly; it has become the gold standard in the prenatal diagnosis
of fetal cardiac abnormalities (3–5) and
remains the main non-invasive diagnostic method used in the
screening and diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities (6). The World Society of Ultrasound in
Obstetrics and Gynecology proposes that the necessary views for
screening fetal hearts include the four chamber view, the left
ventricular outflow tract view, the right ventricular outflow tract
view and the three vessel-trachea view (7). However, these views would miss the
diagnosis of certain fetal cardiac abnormalities, despite the fact
that they include the scanning views of the left ventricular
outflow tract, the right ventricular outflow tract and the three
vessel-trachea on the basis of the reference four-chamber view.
Furthermore, fetal echocardiography has the limitations of a long
examination time and high technical difficulty.
Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC) is a newly
developed three-dimensional (3D) imaging technology for fetal
hearts and arteries. STIC is able to scan the whole fetal heart
within a short time and present the 3D ultrasound image in various
imaging modes, which may improve the understanding of the
anatomical configuration of the fetal heart. STIC technology may
improve the diagnosis rate of fetal cardiac abnormalities and
shorten the examination time, in addition to compensating for the
deficiencies of traditional 2D echocardiography. Therefore, STIC
technology has become a viable and effective method for the
diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities.
The current study applied STIC technology in the
echocardiographic examination of 1,286 fetuses (18–40 weeks) and
evaluated the accuracy of the technology in the diagnosis of fetal
cardiac abnormalities.
Subjects and methods
Subjects
A total of 1,286 fetuses, which were
echocardiographically examined in Beijing Anzhen Hospital (Beijing,
China) from September 2010 to September 2011, were selected for the
present study and the complete follow-up data of 1,080 fetuses were
collected. All the pregnant patients were informed of the details
and the agreements to take part in this study were secured from
these patients and their families. As for the subjects who were
given an autopsy following the termination of pregnancy due to
serious fetal cardiac abnormality, the autopsy was carried out in
the Pathology Department of the hospital once the pregnant patients
and their families had signed an autopsy consent document. This
study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki
and with approval from the Ethics Committee of Beijing Anzhen
Hospital, Capital Medical University. Written informed consent was
obtained from all participants.
STIC technology data collection and image
post-processing analysis method
The 2D mode, which was able to present the fetal
four chamber view or the main artery arch axis view, was shifted
into the 3D/4D mode, during which the pregnant patients were told
to hold their breath and the STIC function was initiated. Volume
data were collected by setting the collecting time as 7.5–15 sec
and the scanning angle as 25–40°, according to the number of
gestational weeks, following adjustment of the fields of interest
which were included in the volume window. The entire volume data
collection process followed the as low as reasonably achievable
(ALARA) principle, which meant minimizing the volume of data
collected to shorten the scanning time (8–12).
The volume probe scanned and collected the volume data of the whole
heart automatically and stored it on a hard disk for subsequent
off-line analysis.
The volume data images collected by applying STIC
technology underwent gray scale and contrast adjustment to achieve
satisfactory effects. The dynamic three-orthogonal-plane model,
surface imaging mode, reverse mode, tomographic ultrasound imaging
technology and vitreous body volume imaging technology were used
for off-line analysis according to the diagnostic requirements.
Statistic analysis
SPSS 16.0 statistical software was used for
statistical analysis. The 2×2 table of diagnostic test evaluation
was used for evaluating the effectiveness and applicability of 2D
ultrasound incorporating STIC technology in the diagnosis of fetal
cardiac abnormalities in addition to calculating an evaluating
indicator of the diagnostic test. The κ test was used to assess the
consistency of 2D ultrasound incorporating STIC technology in the
diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities.
Results
Clinical data of the subjects
Among the 1,286 subjects, 8 cases were twin
pregnancies and the rest were singleton pregnancies. The pregnant
patients were 17–43 years old (mean, 28.73±4.60 years) and the
fetal gestational age was 18–40 weeks (mean, 26.42±3.94 weeks).
Complete follow-up data were collected for 1,080 of the 1,286
subjects (84%), and 206 cases (16%) were missing follow-up data
(Table I).
 | Table IClinical data. |
Table I
Clinical data.
| Age at pregnancy,
years | Fetal gestational
age, weeks | | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| Cases, n | Range | Mean | SD | Range | Mean | SD | Follow-up, cases | Follow-up, % |
|---|
| 1286 | 17–43 | 28.73 | 4.60 | 19–37 | 26.42 | 3.94 | 1080 | 84.0 |
Comparison of 2D ultrasound incorporating
STIC technology with the standard diagnosis method in the diagnosis
of fetal cardiac abnormalities
For 2D ultrasound incorporating STIC technology, the
sensitivity was 97.4%, the specificity was 99.6%, the misdiagnosis
rate was 0.4% and the rate of missed diagnosis was 2.6%.
Furthermore, the total coincidence rate was 99.2%, the Youden’s
index was 97% and the positive and negative predictive values were
97.9 and 99.4%, respectively (Table
II).
 | Table IIComparison of 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology with postpartum recheck and autopsy
following induced labor in the diagnosis of fetal cardiac
abnormalities. |
Table II
Comparison of 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology with postpartum recheck and autopsy
following induced labor in the diagnosis of fetal cardiac
abnormalities.
| 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology | Postpartum recheck
and induced labor autopsy |
|---|
|
|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total |
|---|
| Positive | 184 | 4 | 188 |
| Negative | 5 | 887 | 892 |
| Total | 189 | 891 | 1080 |
The contrasting results of prenatal 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology and follow-up testing in false
positive and false negative cases of fetal cardiac abnormality are
shown in Tables III and IV, respectively. The fetal
echocardiography and follow-ups identified 184 true positive cases
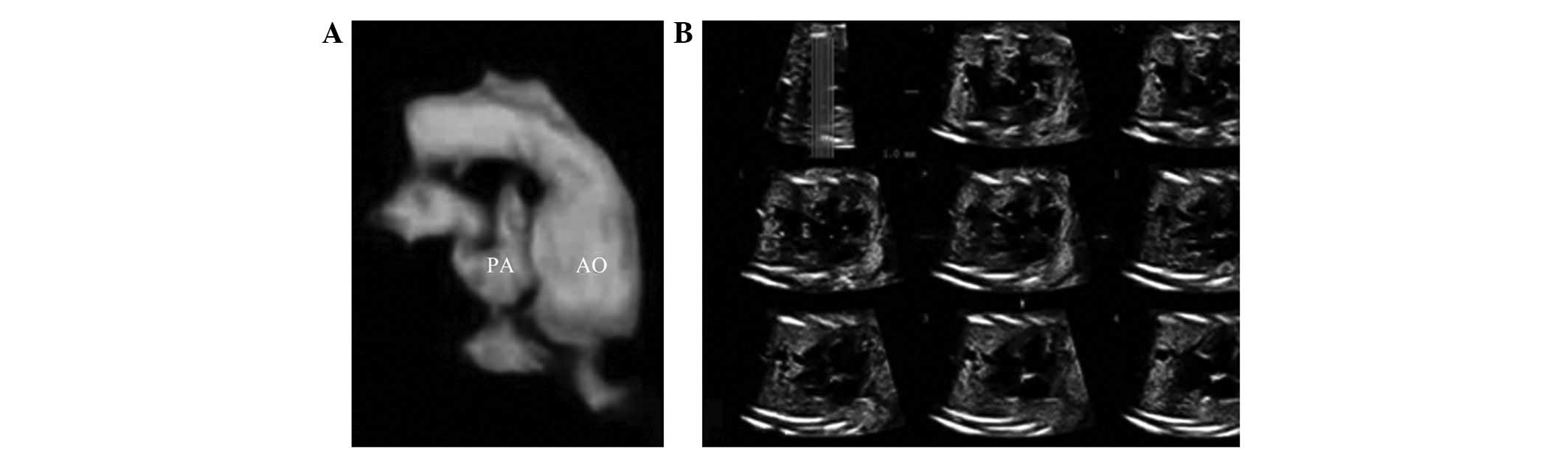
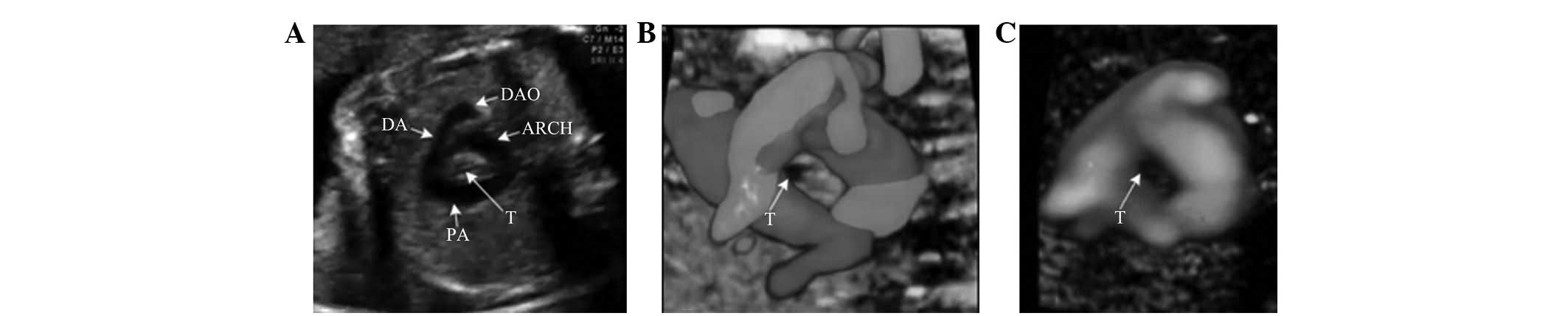
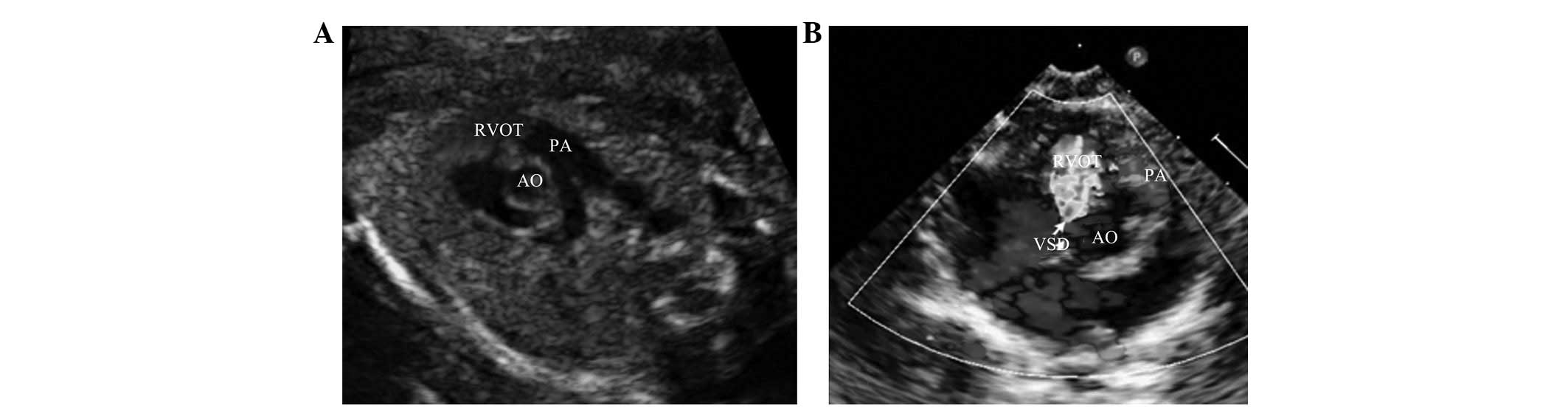
(17%) (Figs. 1–3), 887 true negative cases (82.1%), 5
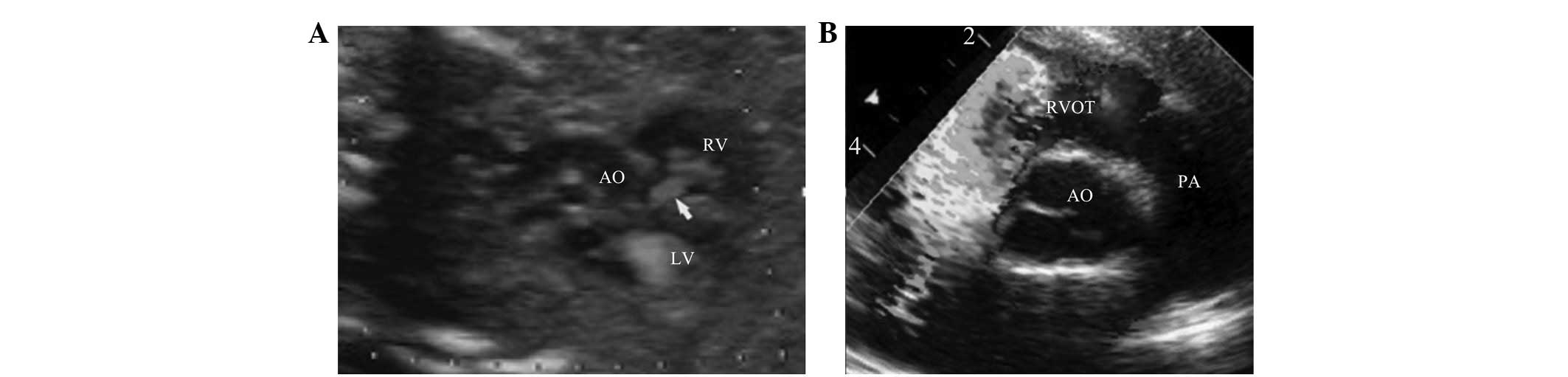
false negative cases (0.5%; Fig.
4) and 4 false positive cases (0.4%; Fig. 5).
 | Table IIIComparison of 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology in the diagnosis of false positive
cases of fetal cardiac abnormality with postpartum recheck and
autopsy following induced labor. |
Table III
Comparison of 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology in the diagnosis of false positive
cases of fetal cardiac abnormality with postpartum recheck and
autopsy following induced labor.
| Order | 2D incorporating STIC
technology | Postpartum recheck
and induced labor autopsy |
|---|
| 1 | Excluded ventricular
septal defect | Normal |
| 2 | Suspicion of
ventricular septal defect | Normal |
| 3 | Ventricular septal
defect (muscular part) | Normal |
| 4 | Ventricular septal
defect (muscular part) | Normal |
 | Table IVComparison of 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology in the diagnosis of false negative
cases of fetal cardiac abnormality with postpartum recheck and
autopsy following induced labor. |
Table IV
Comparison of 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology in the diagnosis of false negative
cases of fetal cardiac abnormality with postpartum recheck and
autopsy following induced labor.
| Order | 2D incorporating STIC
technology | Postpartum recheck
and induced labor autopsy |
|---|
| 1 | Normal | Ventricular septal
defect and membranous aneurysm formation, patent foramen ovale,
tricuspid regurgitation |
| 2 | Left ventricular
glare point | Pulmonary stenosis
(mild), atrial septal defect (II hole, central) |
| 3 | Left ventricular
glare point | Pulmonary stenosis
(mild), patent foramen ovale |
| 4 | Normal | Atrial septal defect
(II hole, central) |
| 5 | Normal | Ventricular septal
defect (membranous part) |
Consistency of 2D ultrasound
incorporating STIC technology in the diagnosis of fetal cardiac
abnormalities
2D ultrasound incorporating STIC technology was
compared with the standard diagnosis method in the diagnosis of
fetal cardiac abnormalities; the four table diagnostic test
evaluation is presented in Table
II.
The statistics for the consistency check of the STIC
technology were κ=0.991, P=0.000, which indicated that the
consistency of the STIC technology was as good as that of the
standard diagnostic method.
Discussion
A prenatal diagnosis is important for the prevention
of congenital heart diseases. At present, fetal cardiac ultra-sound
is the only effective imaging method for the prenatal diagnosis of
cardiac malformation, but misdiagnosed cases continue to occur.
Improvements in clinical techniques and the development of new
ultrasound technologies for prenatal diagnosis are currently
ongoing. STIC is a technology used for fetal echocardiography
(13–15), through which complete cardiac
information concerning 3D morphology and dynamic changes of the
heart structure may be obtained. At the same time, the adjacent
location and the spatial relation of the heart structure with the
lesion may be displayed. In theory, the 3D heart information is
more accessible in the fetal period due to atelectasis. STIC
technology may be used as a supplement to traditional ultrasound
technology and may replace traditional ultrasound technology to
enable the earlier diagnosis of fetal cardiac malformations in the
near future (11). STIC technology
is a significant method of fetal echocardiography, deserving
further study and clinical application. The present study has
confirmed the high sensitivity and accuracy of STIC technology
combined with traditional 2D ultrasound in the prenatal diagnosis
of congenital heart disease.
In this study, the fetal sequential
echocardiographic examination method combined with STIC technology
was performed on 1,286 fetuses. The results were compared with
those of post-natal echocardiography and autopsy following induced
labor due to complex cardiac malformation. The STIC technology was
identified as useful for displaying the spatial correlation of
anatomical structures in fetal cardiac malformations, and is a
process that affords high sensitivity and specificity as follows:
sensitivity, 97.4%; specificity, 99.6%; positive predictive value,
97.9%; and negative predictive value, 99.4%. In addition, STIC
technology also has a high consistency (κ=0.991) for the diagnosis
of complex fetal cardiac malformation.
In the cases with the application of STIC technology
combined with 2D ultrasound, the complex congenital heart
malformation includes infracardiac type pulmonary venous drainage,
type III common arterial trunk, coronary circulation dependent
right ventricular dysplasia and coronary artery abnormalities. The
advantages of STIC technology in the detection of venous drainage
terminals, coronary artery origins and tiny blood vessel pathways
may complement 2D ultrasound technology and avoid misdiagnosis.
Compared with 2D ultrasound, the STIC technology is able to obtain
more information with regard to the 3D structure of the heart by
reconstruction and superposition. The anatomical structure and
adjacent correlations and the lesion range may be observed by graph
rotation, translation and cutting. Therefore, the application of
STIC technology contributes to the diagnosis of complex fetal heart
malformations.
In the present study, 5 cases of false negative
heart malformations were identified by comparison of prenatal
echocardiography incorporating STIC technology with follow-up data.
The misdiagnosed heart malformations included small ventricular
septal defects, foramen primum atrial septal defects and mild
pulmonary valve stenosis. The retrieval of stored images and
retrospective analysis indicated that the 2D ultrasound
manifestation of the small ventricular septal defect was concealed.
Due to fetal atelectasis, a high pulmonary artery pressure and the
pressure balance of the bilateral ventricles, it is not possible
for the cross-valve blood flow signal to be displayed, even if
using color Doppler ultrasound, which leads to misdiagnosis
(16). The location of the atrial
septal defect of the primary septum is close to the
atrio-ventricular valve and coronary sinus outlet. It is easily
sheltered by the valve and confused with the coronary sinus outlet.
With STIC technology, the 3D image is recut and the atrial septum
may be observed without the sheltering effect of the
atrio-ventricular valve. The atrial and ventricular septal defects
may be identified by multi-slicing with one point of structure
confirmation using STIC technology. However, further experience of
the post-processing of STIC 3D images is required to further
improve the diagnostic accuracy (17,18).
The present study observed 2 misdiagnosed cases with
mild pulmonary valve stenosis. It may be concluded by a comparison
of prenatal and postnatal echocardiography that, when diagnosing
mild pulmonary valve stenosis by fetal echocardiography, the
morphological echo, opening and closing activity and pulmonary
valve loop size should be carefully observed to detect the color
mixing flow signal and high speed blood flow in the Doppler
spectrum. It should be noted that, due to a lower blood flow and
mild pulmonary valve stenosis during the fetal period, the stenosis
sign may be presented. Subsequent to birth, the increased pulmonary
blood flow and cross-valve blood flow may manifest as pulmonary
stenosis in the ultrasound image. Therefore, certain mild lesions,
including small ventricular septal defects and mild pulmonary valve
stenosis, may not be detected due to the technical level of the
instrument and the special circulatory status during the fetal
period. This should be explained to the patient.
In the present study, 4 false positive cases of
cardiac abnormality were identified with a ventricular septal
defect or suspicious ventricular septal defect in the fetal
echocardiogram and follow-up, but no abnormalities in the postnatal
echocardiogram. There is a cross connection between normal left and
right ventricular outflow tracts. The reasons for the misdiagnosis
with ventricular septal defects may be that there is a mixed blood
flow signal in the echocardiography, and the blood flow signal from
the right ventricular outflow tract is recognized as the shunting
signal from right to left in the ventricular septum or
perimembranous region. According to the comparison of prenatal and
postnatal echocardiography, it may be concluded that the 2D
structure of the ventricular septum should be observed carefully to
exclude echo loss in the diagnosis of ventricular septal defects.
The color flow gain and sensitivity should be adjusted to the
optimal status in the application of color Doppler ultrasound to
observe the shunting at the ventricular level. This is likely to
improve the accuracy of the prenatal ultrasound and reduce the
false positive rate.
The misdiagnosed patients included 2 cases of
pulmonary vein atresia and 1 case of left pulmonary hypoplasia. The
main cause of this misdiagnosis was the lack of knowledge
concerning these two diseases in the fetal period. Atresia with a
common arterial trunk is a rare congenital heart disease and is the
most serious type of ectopic pulmonary venous drainage. The newborn
rarely survives. There has been no experience accumulated in the
detection of Atresia by neonatal and adult echocardiography, which
thus leads to misdiagnosis. In the present study, the cases with
lung agenesis were prenatally diagnosed with partial pulmonary
venous ectopic drainage combined with extracardiac malformation,
and right pulmonary agenesis combined with other heart defects. The
autopsy showed no abnormal cardiac structure. A lack of awareness
concerning the effects of extracardiac malformation on blood flow
abnormalities is the main cause of misdiagnosis. For cases without
a display of blood flow from the right pulmonary vein to the left
atrium, the main cause is likely to be pulmonary hypoplasia or an
ectopic connection of the pulmonary vein. Therefore, the mastering
of heart disease-related knowledge and correct and comprehensive
clinical thinking are the basis of improvements in the prenatal
diagnosis levels of fetal cardiac diseases.
The present study concluded that STIC technology
combined with fetal echocardiography may be used for the definite
diagnosis of fetal heart malformations, with high sensitivity and
specificity.
References
|
1.
|
Wieczorek A, Hernandez-Robles J, Ewing L,
Leshko J, Luther S and Huhta J: Prediction of outcome of fetal
congenital heart disease using a cardiovascular profile score.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 31:284–288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Bartel T, Müller S and Geibel A:
Preoperative assessment of cor triatriatum in an adult by dynamic
three dimensional echocardiography was more informative than
transesophageal echocardiography or magnetic resonance imaging. Br
Heart J. 72:498–499. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Allan LD, Sharland GK, Milburn A, et al:
Prospective diagnosis of 1,006 consecutive cases of congenital
heart disease in the fetus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 23:1452–1458. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Allan LD, Crawford DC, Chita SK and Tynan
MJ: Prenatal screening for congenital heart disease. Br Med J (Clin
Res Ed). 292:1717–1719. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Turan S, Turan O and Baschat AA: Three-and
four-dimensional fetal echocardiography. Fetal Diagn Ther.
25:361–372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Guo YX, Liang YY, Ma XY and Xiao DZ:
Clinic study of patio-temporal image correlation in fetal heart. J
Practical Medicine. 24:2270–2272. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
7.
|
International Society of Ultrasound in
Obstetrics and Gynecology: Cardiac screening examination of the
fetus: guidelines for performing the ‘basic’ and ‘extended basic’
cardiac scan. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 27:107–113. 2006.
|
|
8.
|
Bennasar M, Martínez JM, Olivella A, et
al: Feasibility and accuracy of fetal echocardiography using
four-dimensional spatiotemporal image correlation technology before
16 weeks’ gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 33:645–651.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Turan S, Turan OM, Ty-Torredes K, Harman
CR and Baschat AA: Standardization of the first-trimester fetal
cardiac examination using spatiotemporal image correlation with
tomographic ultrasound and color Doppler imaging. Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol. 33:652–656. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Gindes L, Hegesh J, Weisz B, Gilboa Y and
Achiron R: Three and four dimensional ultrasound: a novel method
for evaluating fetal cardiac anomalies. Prenat Diagn. 29:645–653.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Uittenbogaard LB, Haak MC, Spreeuwenberg
MD and Van Vugt JM: A systematic analysis of the feasibility of
four-dimensional ultrasound imaging using spatiotemporal image
correlation in routine fetal echocardiography. Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol. 31:625–632. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Hata T, Dai SY, Inubashiri E, et al:
Four-dimensional sonography with B-flow imaging and spatiotemporal
image correlation for visualization of the fetal heart. J Clin
Ultrasound. 36:204–207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
DeVore GR, Falkensammer P, Sklansky MS and
Platt LD: Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC): new technology
for evaluation of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol.
22:380–387. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Gonçalves LF, Lee W, Chaiworapongsa T, et
al: Four-dimensional ultrasonography of the fetal heart with
spatiotemporal image correlation. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
189:1792–1802. 2003.
|
|
15.
|
Viñals F, Poblete P and Giuliano A:
Spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC): a new tool for the
prenatal screening of congenital heart defects. Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol. 22:388–394. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Yagel S, Benachi A, Bonnet D, et al:
Rendering in fetal cardiac scanning: the intracardiac septa and the
coronal atrioventricular valve planes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol.
28:266–274. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yagel S, Valsky DV and Messing B: Detailed
assessment of fetal ventricular septal defect with 4D color Doppler
ultrasound using spatio-temporal image correlation technology.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 25:97–98. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Chaoui R, Hoffmann J and Heling KS:
Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography
using spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC). Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol. 23:535–545. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|