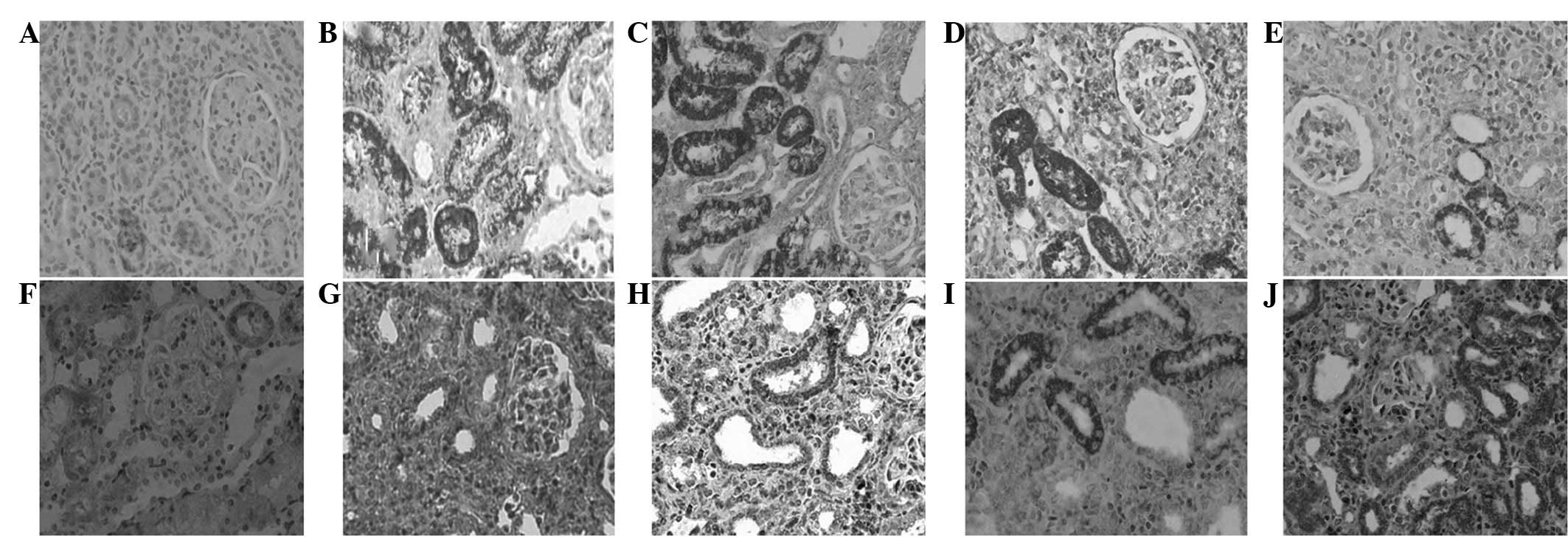
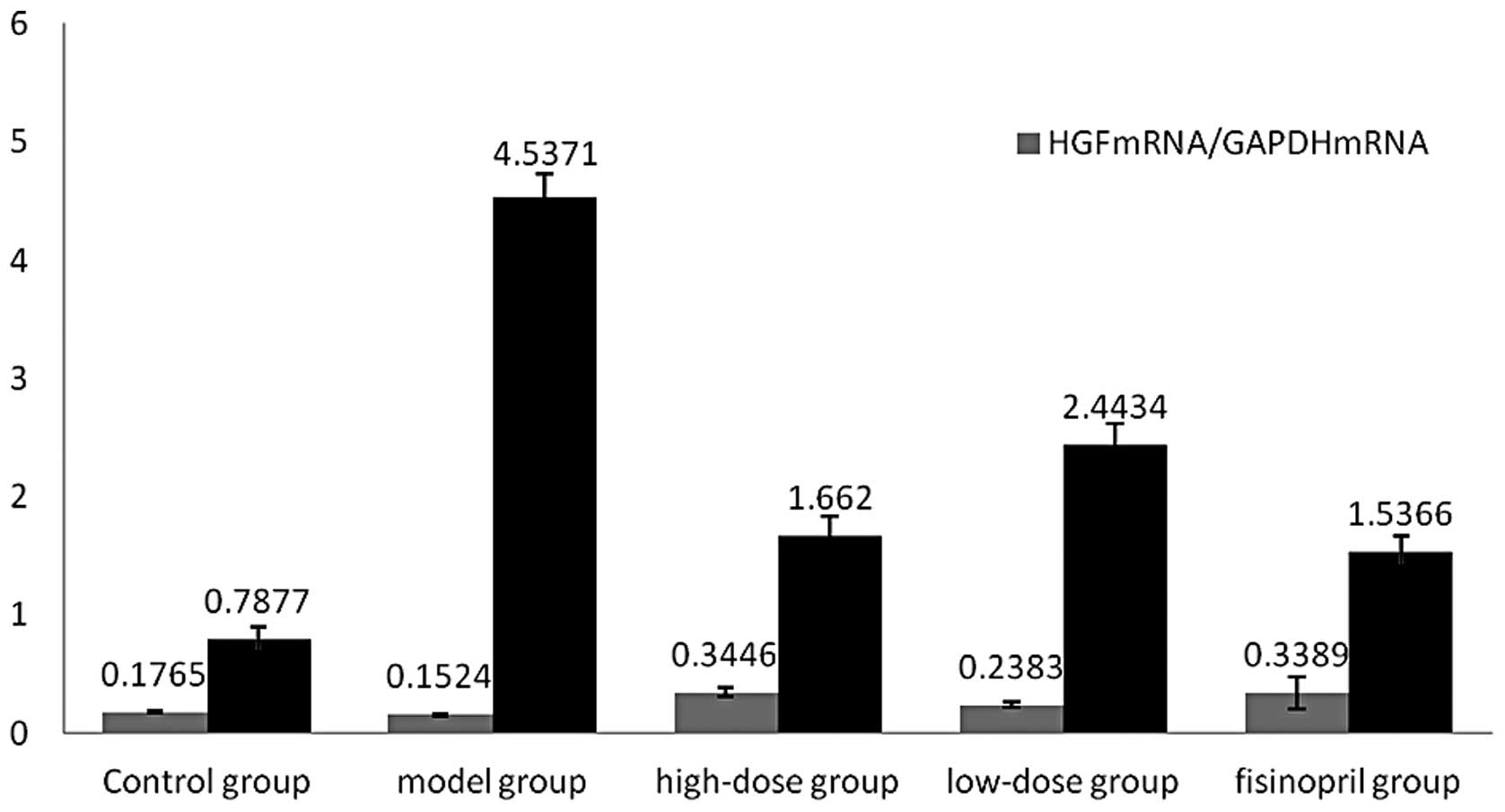
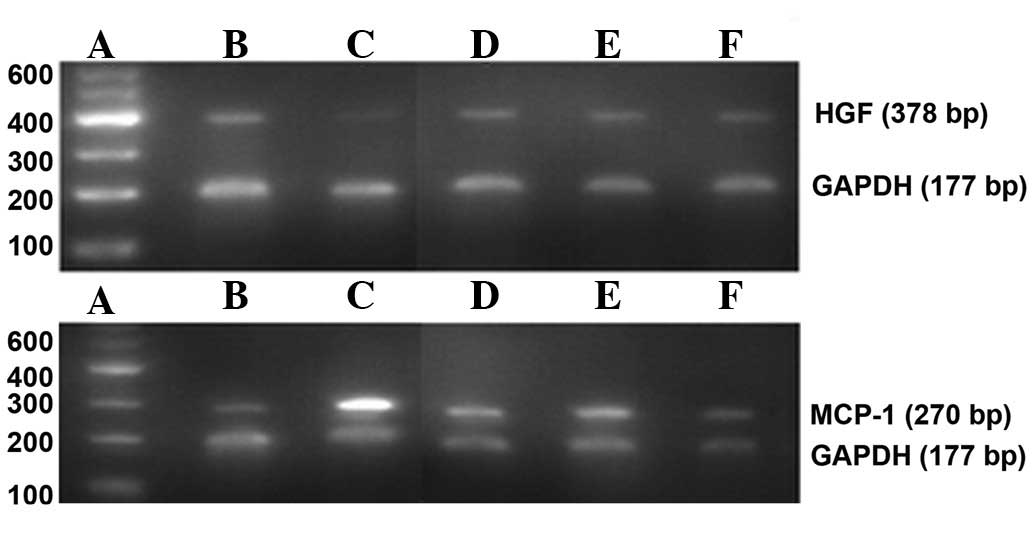
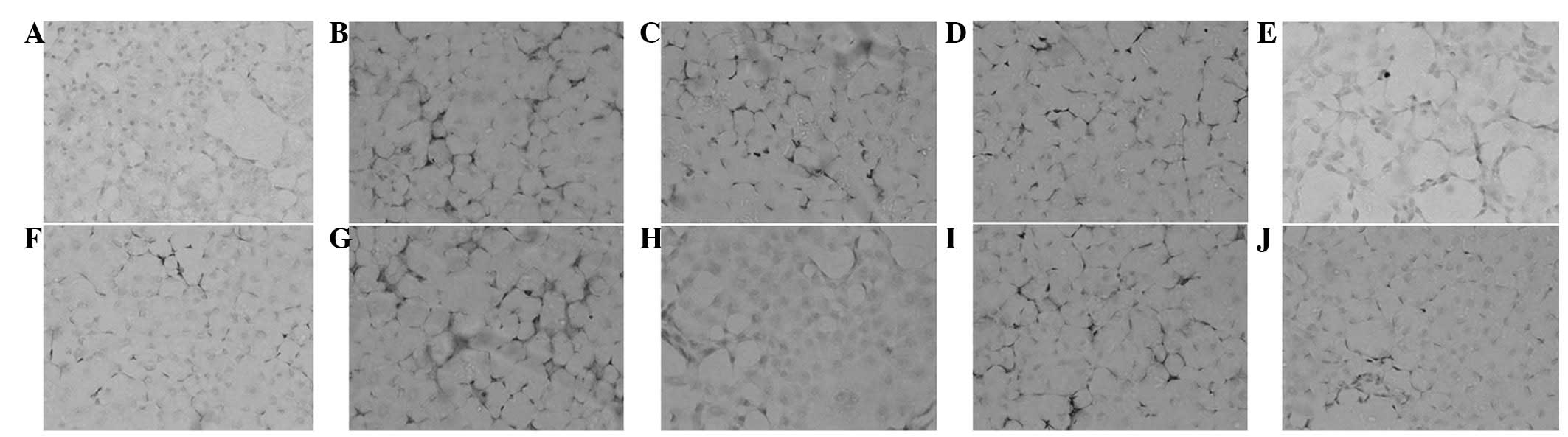
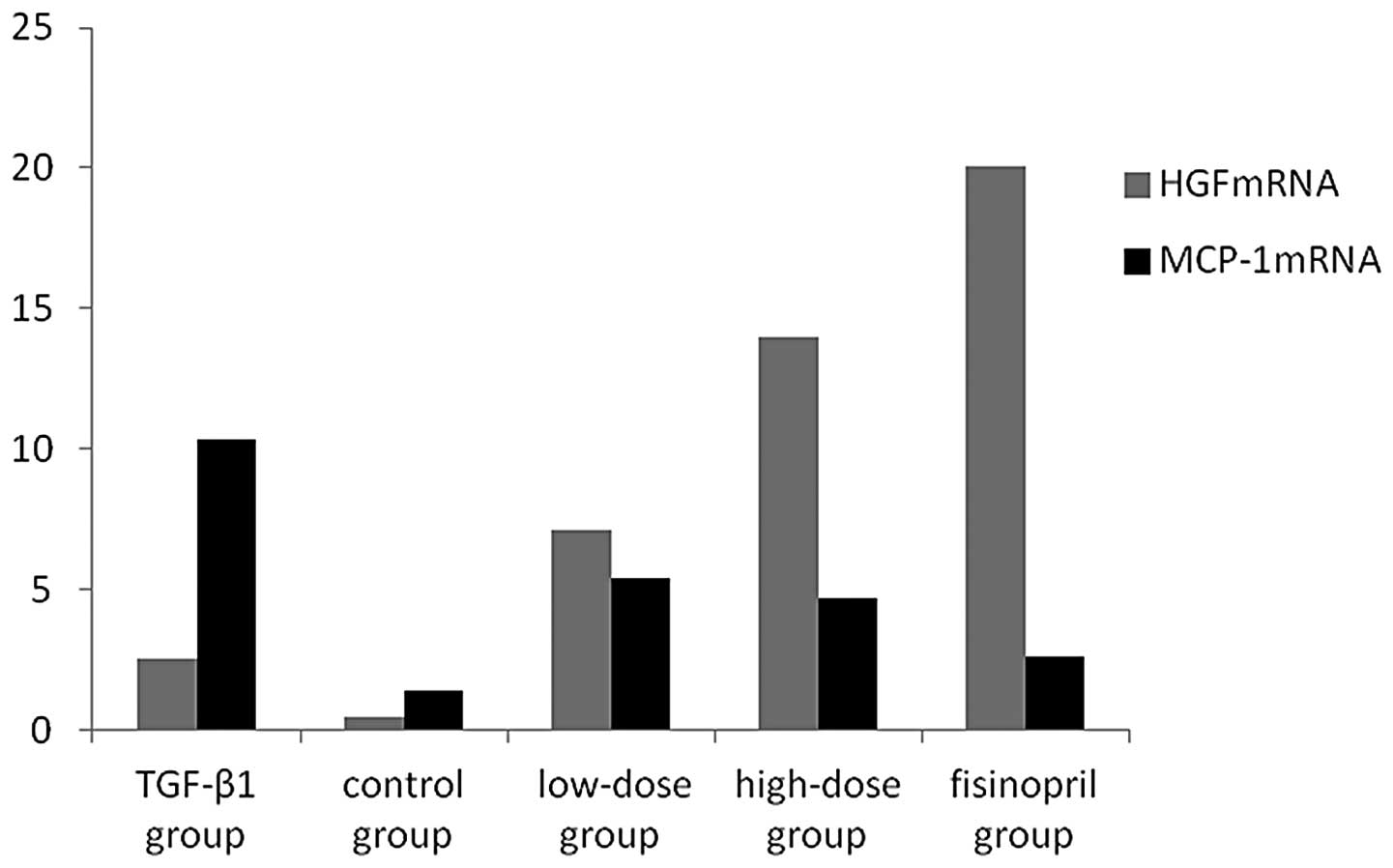
|
1.
|
Eddy AA: Molecular basis of renal
fibrosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 15:290–301. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Klahr S and Morrissey J: Obstructive
nephropathy and renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
283:F861–F875. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Kobayashi E, Sasamura H, Mifune M, et al:
Hepatocyte growth factor regulates proteoglycan synthesis in
interstitial fibroblasts. Kidney Int. 64:1179–1788. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada
H and Neilson EG: Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium
during tissue fibrosis. J Clin lnvest. 11:341–350. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Wada T, Furuichi K, Sakai N, et al: Gene
therapy via blockade of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 for
renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:940–948. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Liu Y: Epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in renal fibrogenesis: pathologic significance,
molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 15:1–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Zhang Z, Wan JY, Luo FL, Li HZ and Zhou
QX: Studies on analgesic effect and mechanism of asiaticoside on
lipopolysaccharide induced hyperalgesia in mice. Clin Pharm J.
43:751–753. 2008.
|
|
8.
|
Liu ZF, Zhao HN and Nie SL: Progress in
the research on the mechanism of the pharmacological effects of
asiaticoside. Guangdong Med J. 30:649–651. 2009.
|
|
9.
|
Dadfar E, Lundahl J and Jacobson SH:
Monocyte adhesion molecule expression in interstitial inflammation
in patients with renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
19:614–622. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ranieri E, Gesualdo L, Petrarulo F and
Schena FP: Urinary IL-6/EGF ratio: a useful prognostic marker for
the progression of renal damage in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int.
50:1990–2001. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Chevalier RL, Forbes MS and Thornhill BA:
Ureteral obstruction as a model of renal interstitial fibrosis and
obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int. 75:1145–1152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Bohle A, Müller GA, Wehrmann M,
Mackensen-Haen S and Xiao JC: Pathogenesis of chronic renal failure
in the primary glomerulopathies, renal vasculopathies and chronic
interstitial nephritides. Kidney Int Suppl. 54:S2–S9.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Zeisberg M, Maeshima Y, Mosterman B and
Kalluri R: Renal fibrosis: extracellular matrix microenvironment
regulates migratory behavior of activated tubular epithelial cells.
Am J Pathol. 160:2001–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Okada H and Kalluri R: Cellular and
molecular pathways that lead to progression and regression of renal
fibrogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 5:467–474. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kroening S, Solomovitch S, Sachs M,
Wullich B and Goppelt-Struebe M: Regulation of connective tissue
growth factor (CTGF) by hepatocyte growth factor in human tubular
epithelial cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 24:755–762. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Yang J, Dai C and Liu Y: A novel mechanism
by which hepatocyte growth factor blocks tubular epithelial to
mesenchymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:68–78. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Yang J, Dai C and Liu Y: Hepatocyte growth
factor suppresses renal interstitial myofibroblast activation and
intercepts Smad signal transduction. Am J Pathol. 163:621–632.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kaschina E and Unger T: Pathophysiologic
link between atherosclerosis and nephrosclerosis. Cardiorenal
Syndrome. 5:245–253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Panzer U, Thaiss F, Zahner G, et al:
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and osteopontin differentially
regulate monocytes recruitment in experimental glomerulonephritis.
Kidney Int. 59:1762–1769. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Huang YY, Xu AP, Zhou SS, Fu JZ and Du H:
Effect of losartan on renal expression of monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 and transforming growth factor-β(1) in rats after
unilateral ureteral obstruction. J South Med Univ. 31:1405–1410.
2011.
|
|
21.
|
Zhang Z, Zhao L, Wang B, et al: Effects of
Centella asiatica on expression of connective colledge
tissue growth factor in UUO rats. Chin J Integr Tradit Western
Nephrol. 9:118–120. 2008.
|
|
22.
|
Zhang Z, Wang SG, Wang B, et al: Effects
of Centella asiatica Granule on renal tissue in rats with
unilateral ureteral obstruction alpha-smooth muscle actin
expression. Tradit Chin Med Res. 22:15–18. 2009.
|
|
23.
|
Wang LL, Liu PN, Ma JW, et al: Effect of
Centella asiatica granula on TGF-β1-induced expression of
bone morphogenetic protein-7 in renal tubular epithelial cells.
Shandong Med J. 49:13–15. 2009.
|