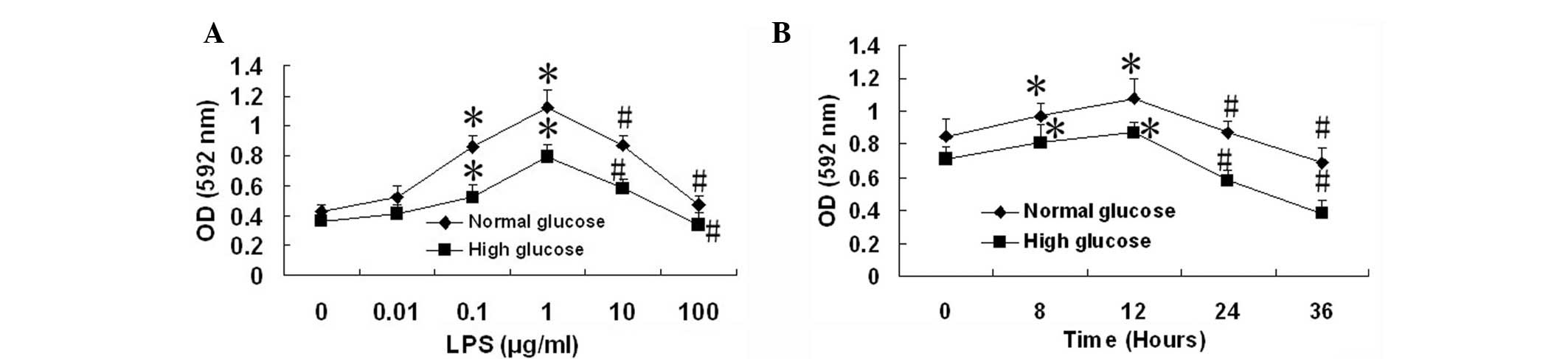
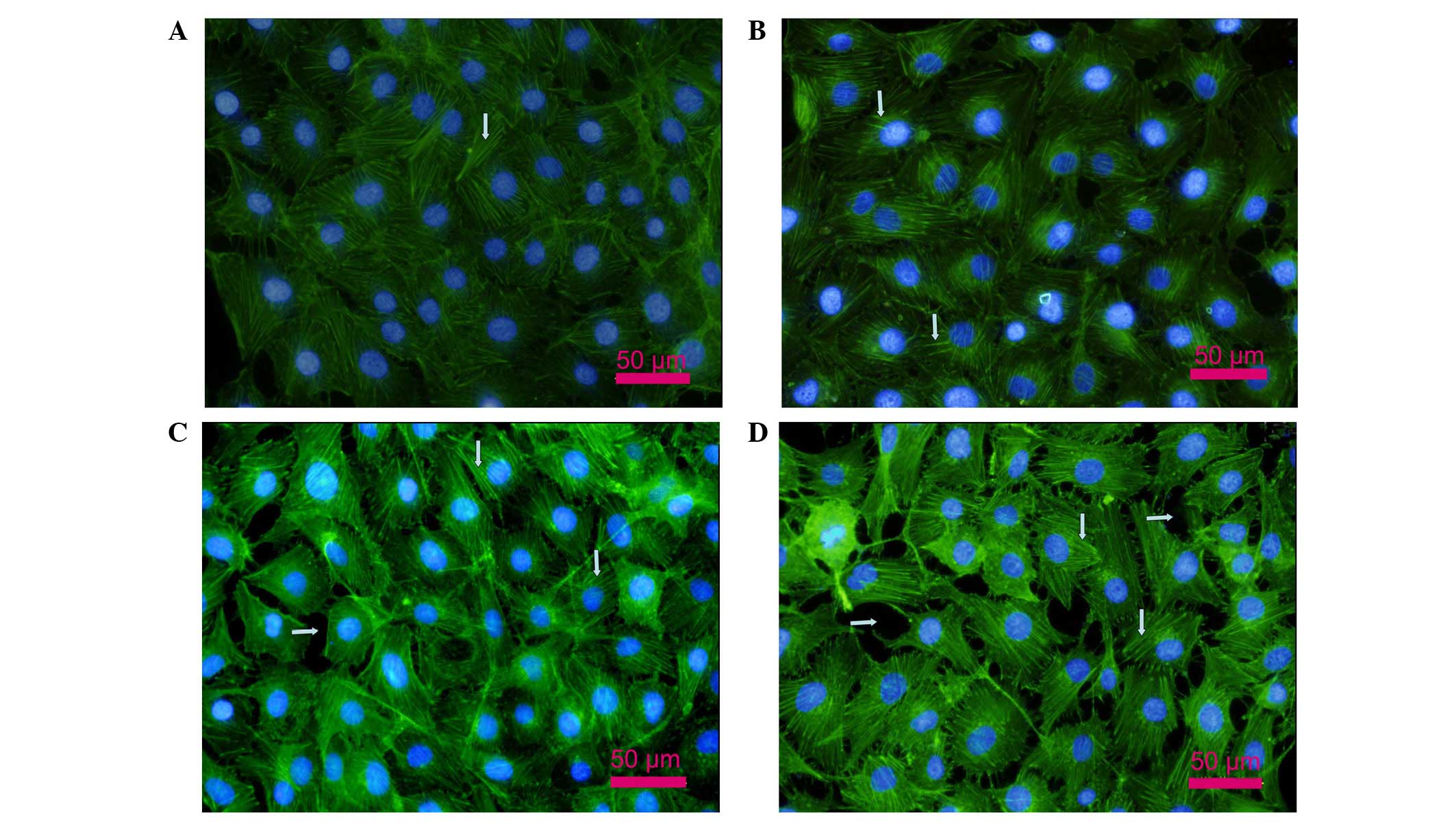
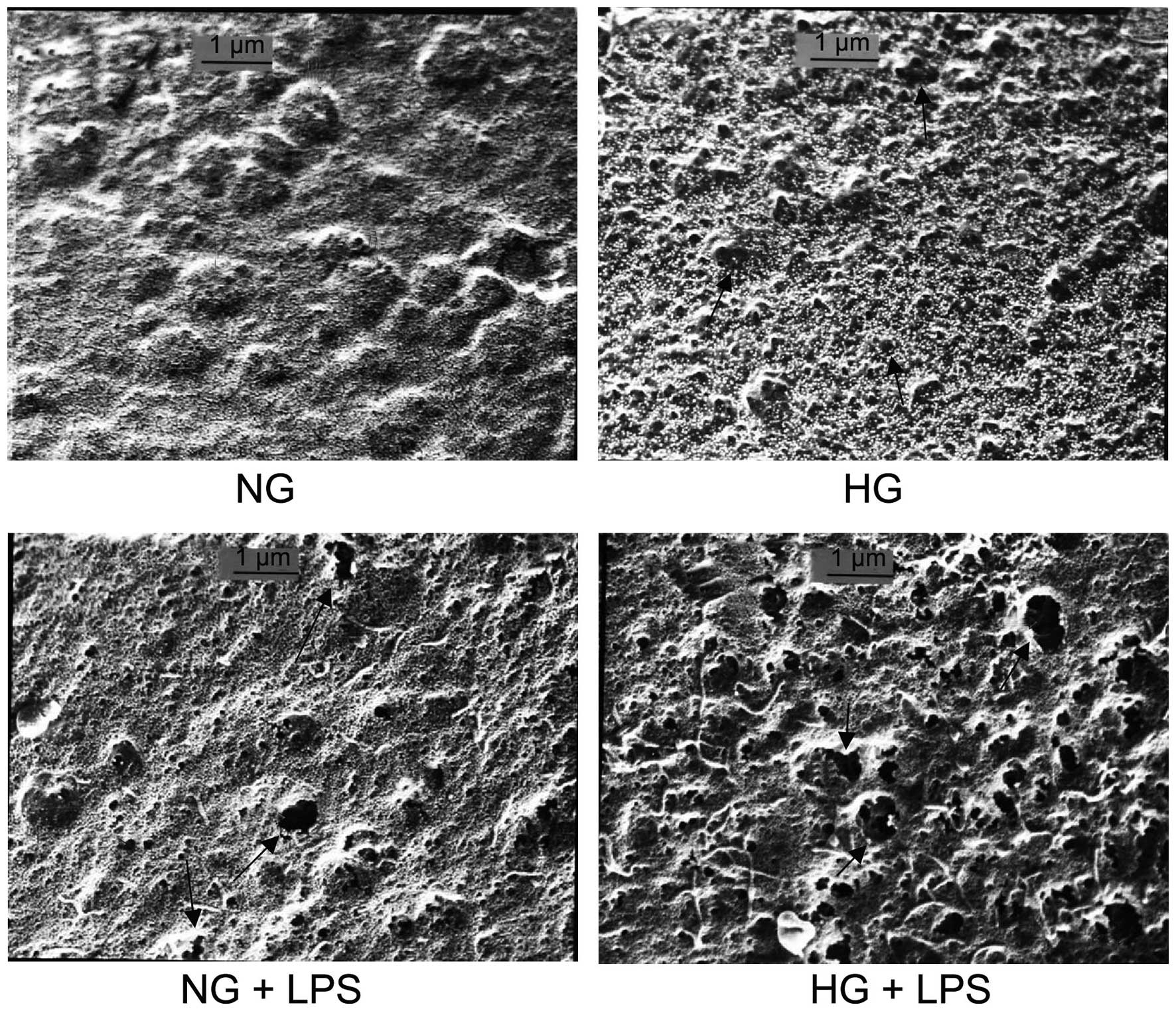
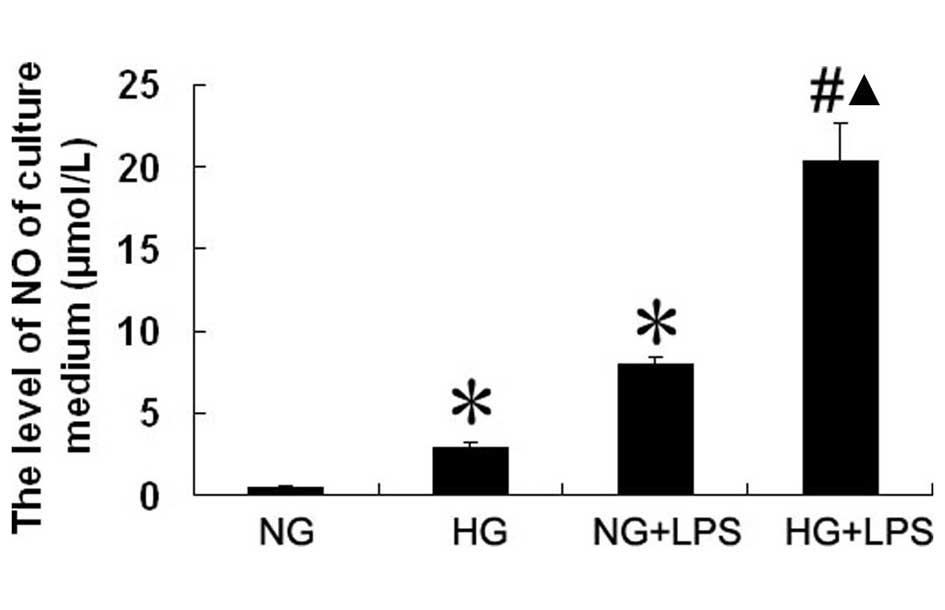
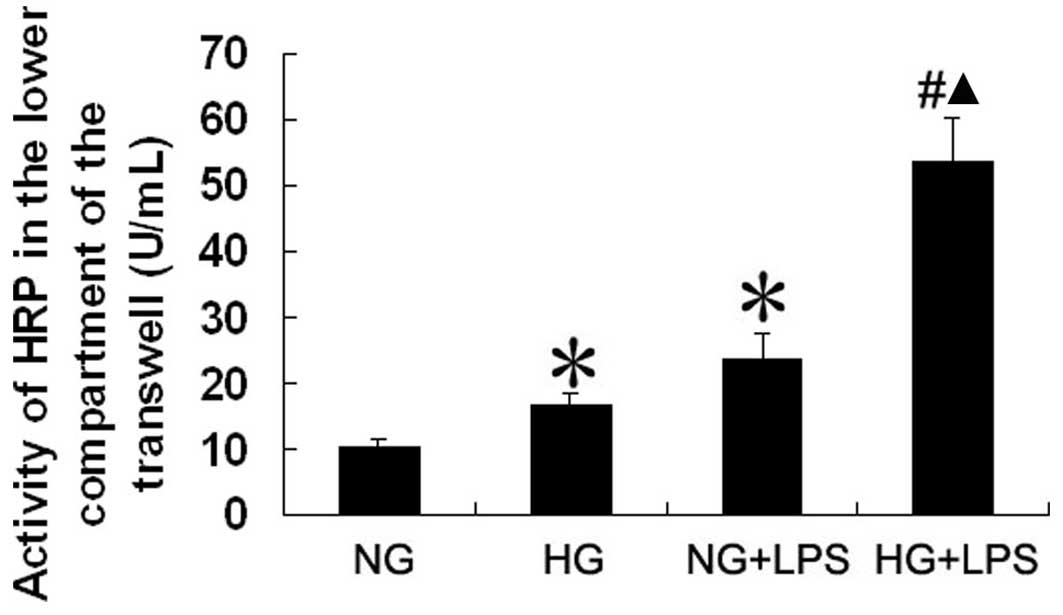
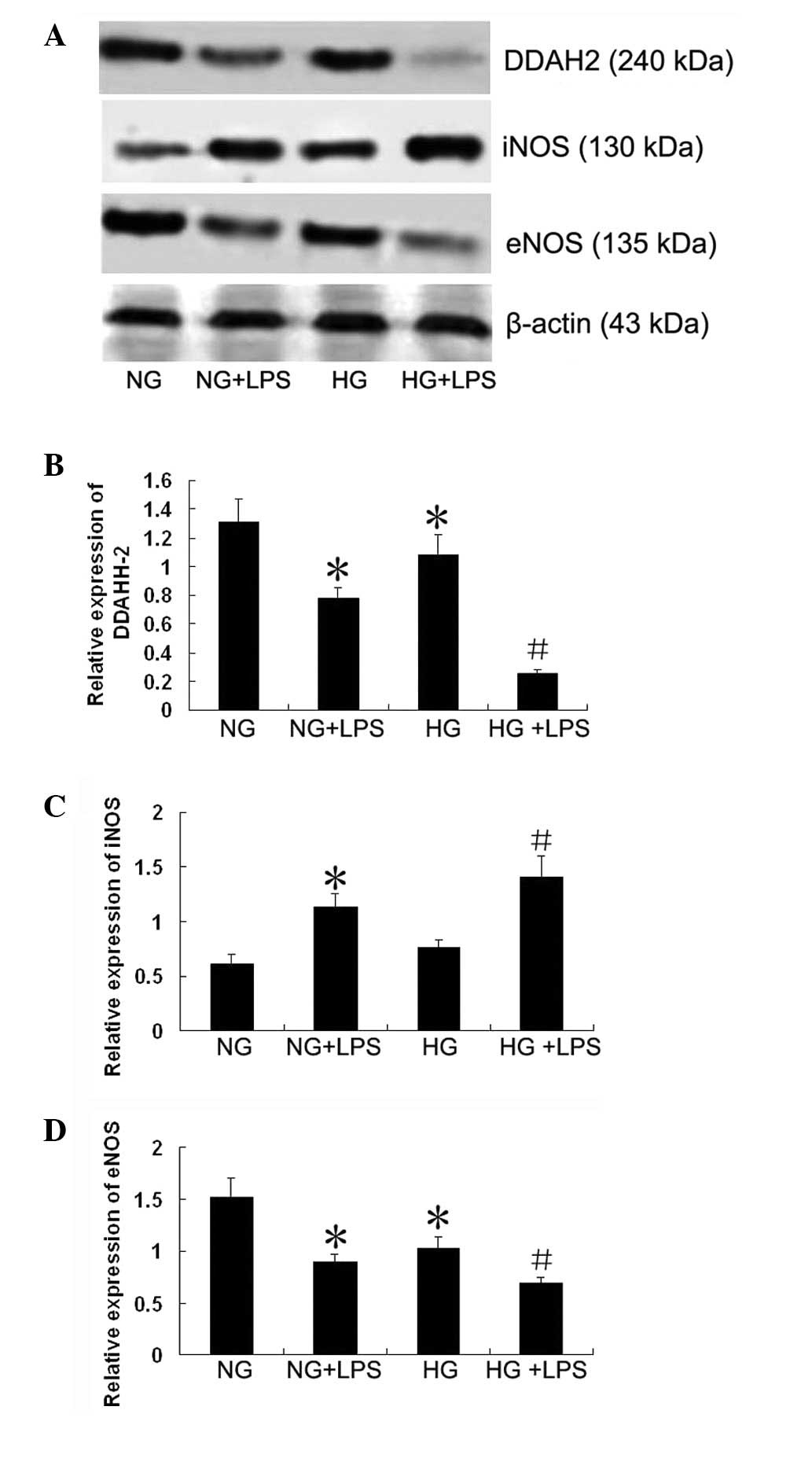
|
1.
|
Shapiro NI, Schuetz P, Yano K, et al: The
association of endothelial cell signaling, severity of illness, and
organ dysfunction in sepsis. Crit Care. 14:R1822010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Muller LM, Gorter KJ, Hak E, et al:
Increased risk of common infections in patients with type 1 and
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Infect Dis. 41:281–288. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Shah BR and Hux JE: Quantifying the risk
of infectious diseases for people with diabetes. Diabetes Care.
26:510–513. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Nareika A, Im YB, Game BA, et al: High
glucose enhances lipopolysaccharide stimulated CD14 expression in
U937 mono-nuclear cells by increasing nuclear factor kappaB and
AP-1 activities. J Endocrinol. 196:45–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Maldonado A, He L, Game BA, et al:
Pre-exposure to high glucose augments lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression by human U937 histiocytes. J
Periodontal Res. 39:415–423. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Song MK, Um JY, Jang HJ and Lee BS:
Beneficial effect of dietary Ephedra sinica on obesity and
glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice. Exp Ther Med.
3:707–712. 2012.
|
|
7.
|
Sherry CL, O’Connor JC, Kramer JM and
Freund GG: Augmented lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha
production by peritoneal macrophages in type 2 diabetic mice is
dependent on elevated glucose and requires p38 MAPK. J Immunol.
178:663–670. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Noda A, Kinoshita K, Sakurai A, et al:
Hyperglycemia and lipopolysaccharide decrease depression effect of
interleukin 8 production by hypothermia: an experimental study with
endothelial cells. Intensive Care Med. 34:109–115. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
de Souza LF, Barreto F, da Silva EG, et
al: Regulation of LPS stimulated ROS production in peritoneal
macrophages from alloxan-induced diabetic rats: involvement of high
glucose and PPARgamma. Life Sci. 81:153–192. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Stegenga ME, van der Crabben SN, Blümer
RM, et al: Hyperglycemia enhances coagulation and reduces
neutrophil degranulation, whereas hyperinsulinemia inhibits
fibrinolysis during human endotoxemia. Blood. 112:82–89. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Durán WN, Breslin JW and Sánchez FA: The
NO cascade, eNOS location, and microvascular permeability.
Cardiovasc Res. 87:254–261. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Akaike T and Maeda H: Nitric oxide and
virus infection. Immunology. 101:300–308. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Jiang WG, Sanders AJ, Ruge F and Harding
KG: Influence of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and IL-8 receptors on the
migration of human keratinocytes, the role of PLC-γ and potential
clinical implications. Exp Ther Med. 3:231–236. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
van der Vliet A, Eiserich JP, Shigenaga MK
and Cross CE: Reactive nitrogen species and tyrosine nitration in
the respiratory tract: epiphenomena or a pathobiologic mechanism of
disease? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 160:1–9. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Pope AJ, Karuppiah K and Cardounel AJ:
Role of the PRMT-DDAH-ADMA axis in the regulation of endothelial
nitric oxide production. Pharmacol Res. 60:461–465. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Sharma S, Smith A, Kumar S, et al:
Mechanisms of nitric oxide synthase uncoupling in endotoxin-induced
acute lung injury: Role of asymmetric dimethylarginine. Vascul
Pharmacol. 52:182–190. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Vu DM, Yokoyama TA, Sawada K, et al:
Enhancement of permeability in endothelial cells for the
development of an anti-thrombogenic bioartificial hemofilter.
Biotechnol Bioeng. 101:634–641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Birukova AA, Arce FT, Moldobaeva N, et al:
Endothelial permeability is controlled by spatially defined
cytoskeletal mechanics: atomic force microscopy force mapping of
pulmonary endothelial monolayer. Nanomedicine. 5:30–41. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
Schwarz MA: Acute lung injury: cellular
mechanisms and derangements. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2:3–9. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Yang B, Huang W, Han J and Liang Z: Study
of the role of epidermal growth factor on lung fluid transport in
rabbits with acute lung injury caused by endotoxin. Exp Ther Med.
4:611–614. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Groeneveld AB: Vascular pharmacology of
acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Vascul
Pharmacol. 39:247–256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Vallance BA, Dijkstra G, Qiu B, et al:
Relative contributions of NOS isoforms during experimental colitis:
endothelial-derived NOS maintains mucosal integrity. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G865–G874. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Nuszkowski A, Gräbner R, Marsche G, et al:
Hypochlorite-modified low density lipoprotein inhibits nitric oxide
synthesis in endothelial cells via an intracellular dislocalization
of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 276:14212–14221.
2001.
|
|
24.
|
Chatterjee A, Snead C, Yetik-Anacak G, et
al: Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors attenuate LPS-induced
endothelial hyperpermeability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
294:L755–L763. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Han X, Fink MP, Yang R and Delude RL:
Increased iNOS activity is essential for intestinal epithelial
tight junction dysfunction in endotoxemic mice. Shock. 21:261–270.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Forsyth CB, Banan A, Farhadi A, et al:
Regulation of oxidant-induced intestinal permeability by
metalloprotease-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor
signaling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 321:84–97. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Farley KS, Wang LF, Law C and Mehta S:
Alveolar macrophage inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent
pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell septic barrier
dysfunction. Microvasc Res. 76:208–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Huffman LJ, Prugh DJ, Millecchia L, et al:
Nitric oxide production by rat bronchoalveolar macrophages or
polymorphonuclear leukocytes following intratracheal instillation
of lipopolysaccharide or silica. J Biosci. 28:29–37. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Farley KS, Wang LF, Razavi HM, et al:
Effects of macrophage inducible nitric oxide synthase in murine
septic lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
290:L1164–L1172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Wojciak-Stothard B, Torondel B, Zhao L, et
al: Modulation of Rac1 activity by ADMA/DDAH regulates pulmonary
endothelial barrier function. Mol Biol Cell. 20:33–42. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|