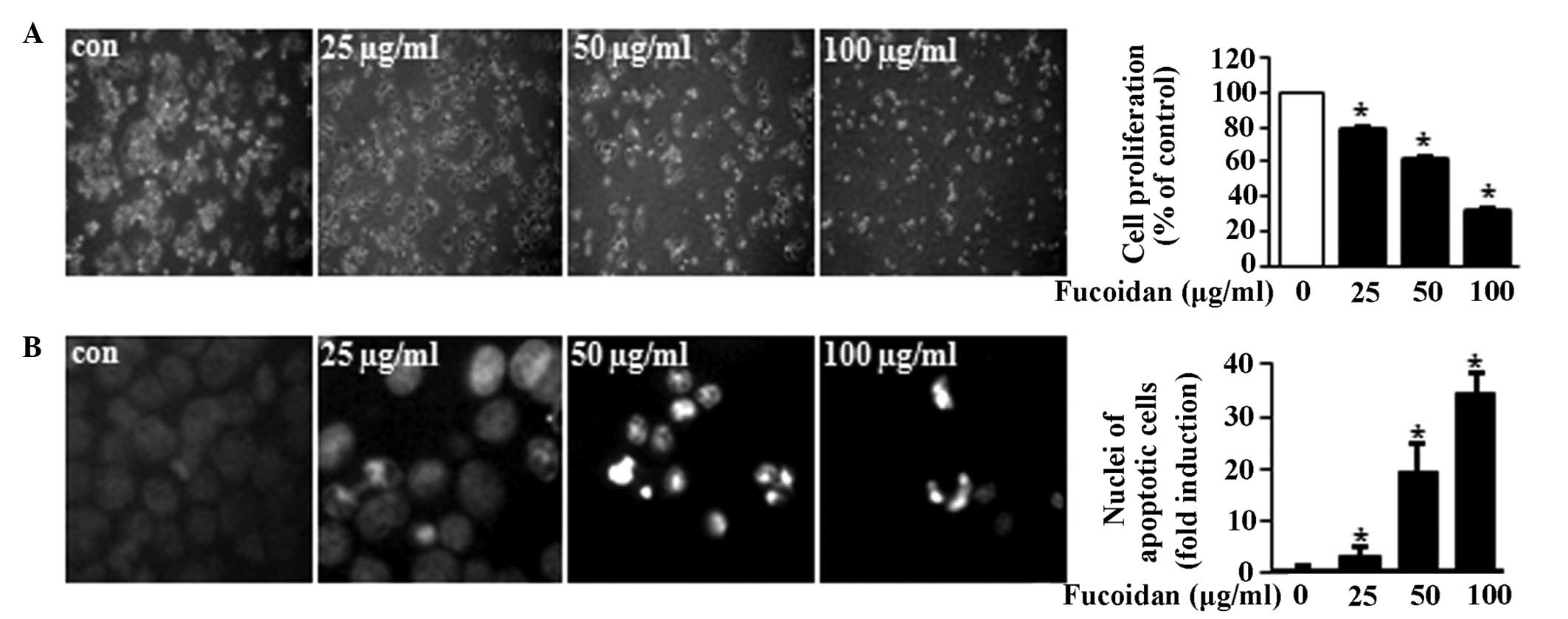
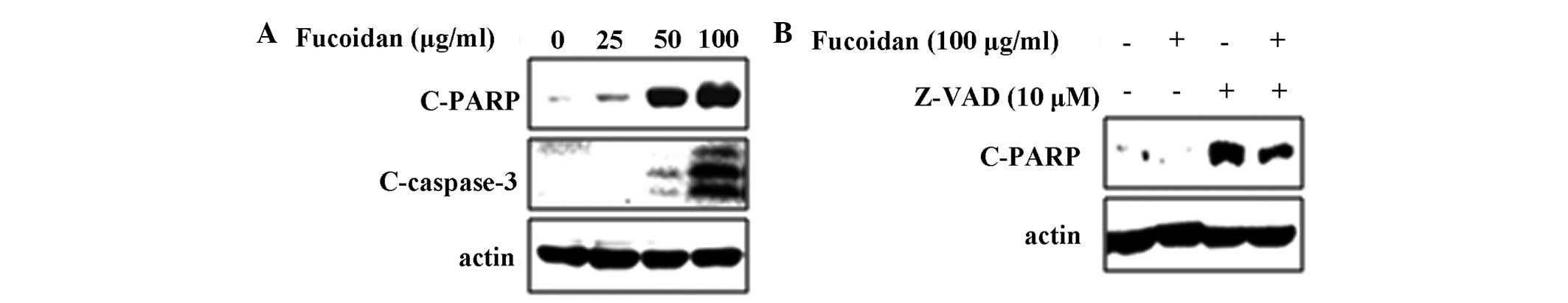
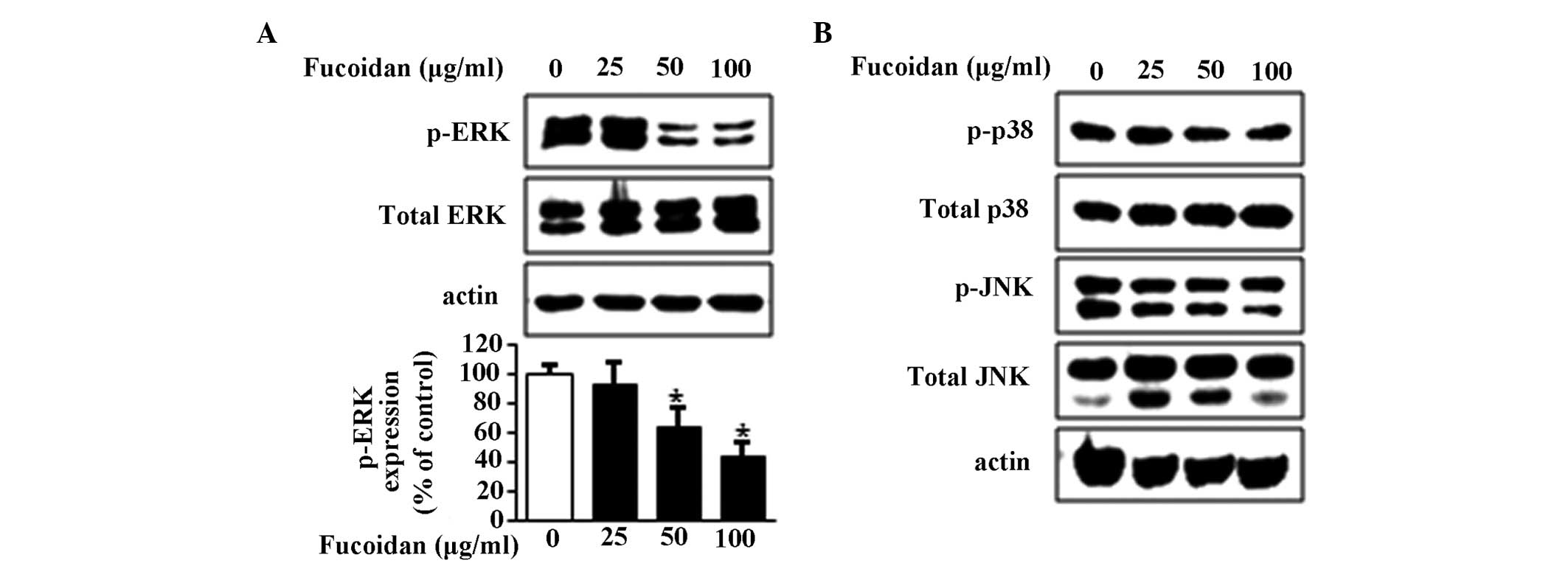
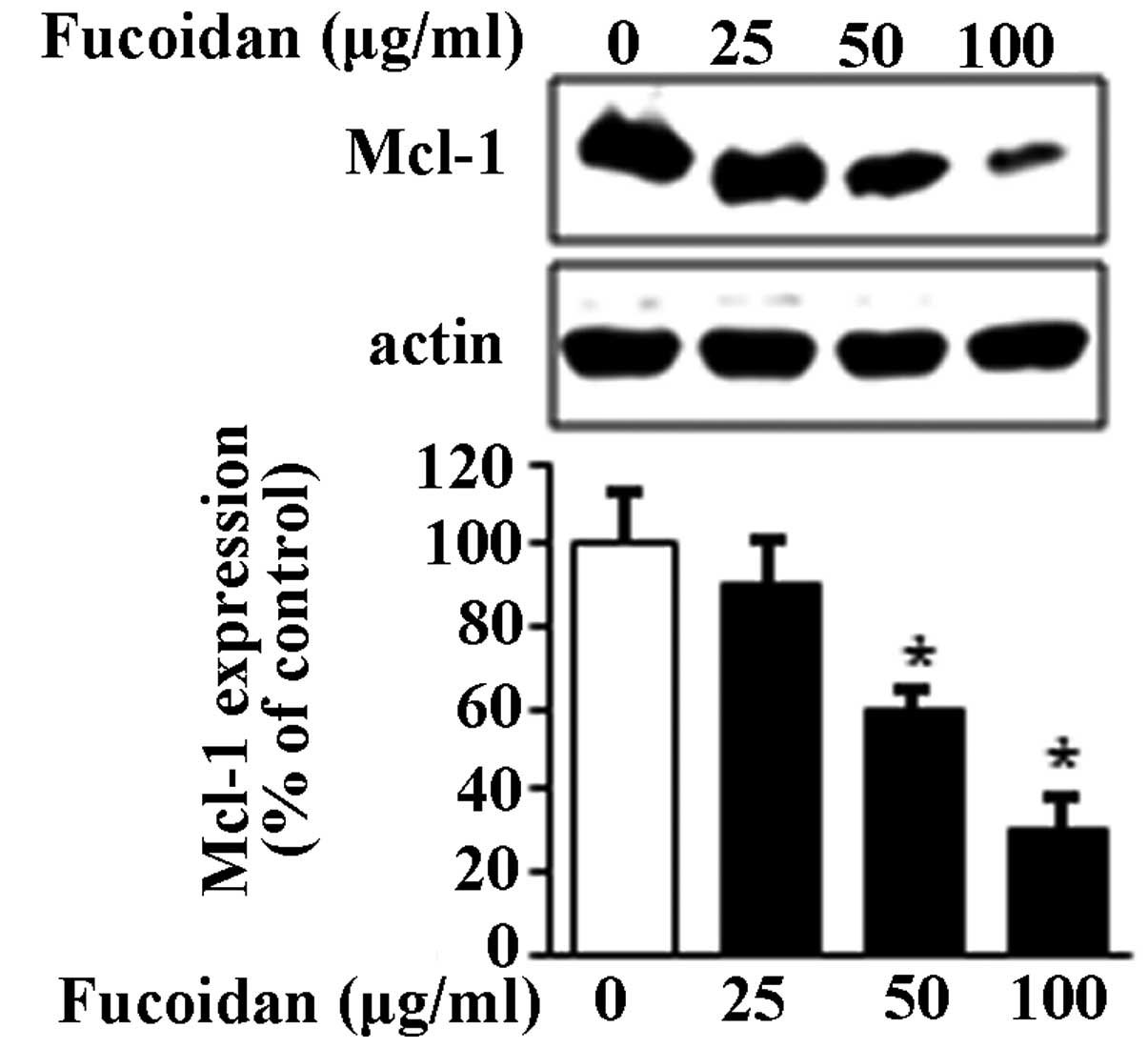
|
1
|
Zhang Z, Teruya K, Yoshida T, Eto H and
Shirahata S: Fucoidan extract enhances the anti-cancer activity of
chemotherapeutic agents in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Mar Drugs. 11:81–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cumashi A, Ushakova NA, Preobrazhenskaya
ME, et al: A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory,
anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine
different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology. 17:541–552.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ye J, Li Y, Teruya K, et al:
Enzyme-digested fucoidan extracts derived from seaweed Mozuku of
Cladosiphon novae-caledoniae kylin inhibit invasion and
angiogenesis of tumor cells. Cytotechnology. 47:117–126. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang J, Zhang Q, Zhang Z and Li Z:
Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions extracted
from Laminaria japonica. Int J Biol Macromol. 42:127–132.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alekseyenko TV, Zhanayeva SY, Venediktova
AA, et al: Antitumor and antimetastatic activity of fucoidan, a
sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the Okhotsk Sea Fucus
evanescens brown alga. Bull Exp Biol Med. 143:730–732. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maruyama H, Tamauchi H, Iizuka M and
Nakano T: The role of NK cells in antitumor activity of dietary
fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida sporophylls (Mekabu).
Planta Med. 72:1415–1417. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Z, Teruya K, Eto H and Shirahata S:
Fucoidan extract induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells via a mechanism
involving the ROS-dependent JNK activation and
mitochondria-mediated pathways. PLoS One. 6:e274412011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Koyanagi S, Tanigawa N, Nakagawa H, Soeda
S and Shimeno H: Oversulfation of fucoidan enhances its
anti-angiogenic and antitumor activities. Biochem Pharmacol.
65:173–179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aisa Y, Miyakawa Y, Nakazato T, et al:
Fucoidan induces apoptosis of human HS-sultan cells accompanied by
activation of caspase-3 and down-regulation of ERK pathways. Am J
Hematol. 78:7–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schroeter H, Boyd CS, Ahmed R, et al:
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-mediated modulation of brain
mitochondria function: new target proteins for JNK signalling in
mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis. Biochem J. 372:359–369. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aoki H, Kang PM, Hampe J, et al: Direct
activation of mitochondrial apoptosis machinery by c-Jun N-terminal
kinase in adult cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 277:10244–10250.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun NK, Huang SL, Chang TC and Chao CC:
Sorafenib induces endometrial carcinoma apoptosis by inhibiting
Elk-1-dependent Mcl-1 transcription and inducing
Akt/GSK3β-dependent protein degradation. J Cell Biochem.
114:1819–1831. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang-Yen HF: Mcl-1: a highly regulated
cell death and survival controller. J Biomed Sci. 13:201–204. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death - apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aquilano K, Baldelli S, Rotilio G and
Ciriolo MR: trans-Resveratrol inhibits
H2O2-induced adenocarcinoma gastric cells
proliferation via inactivation of MEK1/2-ERK1/2-c-Jun signalling
axis. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:337–347. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rahman MS, Yamasaki A, Yang J, Shan L,
Halayko AJ and Gounni AS: IL-17A induces eotaxin-1/CC chemokine
ligand 11 expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: role of
MAPK (Erk1/2, JNK, and p38) pathways. J Immunol. 177:4064–4071.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sawatzky DA, Willoughby DA, Colville-Nash
PR and Rossi AG: The involvement of the apoptosis-modulating
proteins ERK 1/2, Bcl-xL and Bax in the resolution of acute
inflammation in vivo. Am J Pathol. 168:33–41. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun HL, Tsai AC, Pan SL, et al: EPOX
inhibits angiogenesis by degradation of Mcl-1 through ERK
inactivation. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4904–4914. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Philchenkov A, Zavelevich M, Imbs T,
Zvyagintseva T and Zaporozhets T: Sensitization of human malignant
lymphoid cells to etoposide by fucoidan, a brown seaweed
polysaccharide. Exp Oncol. 29:181–185. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Párrizas M, Saltiel AR and LeRoith D:
Insulin-like growth factor 1 inhibits apoptosis using the
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways. J Biol Chem. 272:154–161. 1997.
|
|
24
|
Anderson P: Kinase cascades regulating
entry into apoptosis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 61:33–46.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin JO, Song MG, Kim YN, Park JI and Kwak
JY: The mechanism of fucoidan-induced apoptosis in leukemic cells:
involvement of ERK1/2, JNK, glutathione, and nitric oxide. Mol
Carcinog. 49:771–782. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hyun JH, Kim SC, Kang JI, et al: Apoptosis
inducing activity of fucoidan in HCT-15 colon carcinoma cells. Biol
Pharm Bull. 32:1760–1764. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boo HJ, Hyun JH, Kim SC, et al: Fucoidan
from Undaria pinnatifida induces apoptosis in A549 human
lung carcinoma cells. Phytother Res. 25:1082–1086. 2011.
|
|
28
|
Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH, Reed
JC, Lainé J and Rivard N: MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the
expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of
human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 79:355–369. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Balmanno K and Cook SJ: Tumour cell
survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ.
16:368–377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Akgul C: Mcl-1 is a potential therapeutic
target in multiple types of cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
66:1326–1336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Domina AM, Vrana JA, Gregory MA, Hann SR
and Craig RW: MCL1 is phosphorylated in the PEST region and
stabilized upon ERK activation in viable cells, and at additional
sites with cytotoxic okadaic acid or taxol. Oncogene. 23:5301–5315.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|