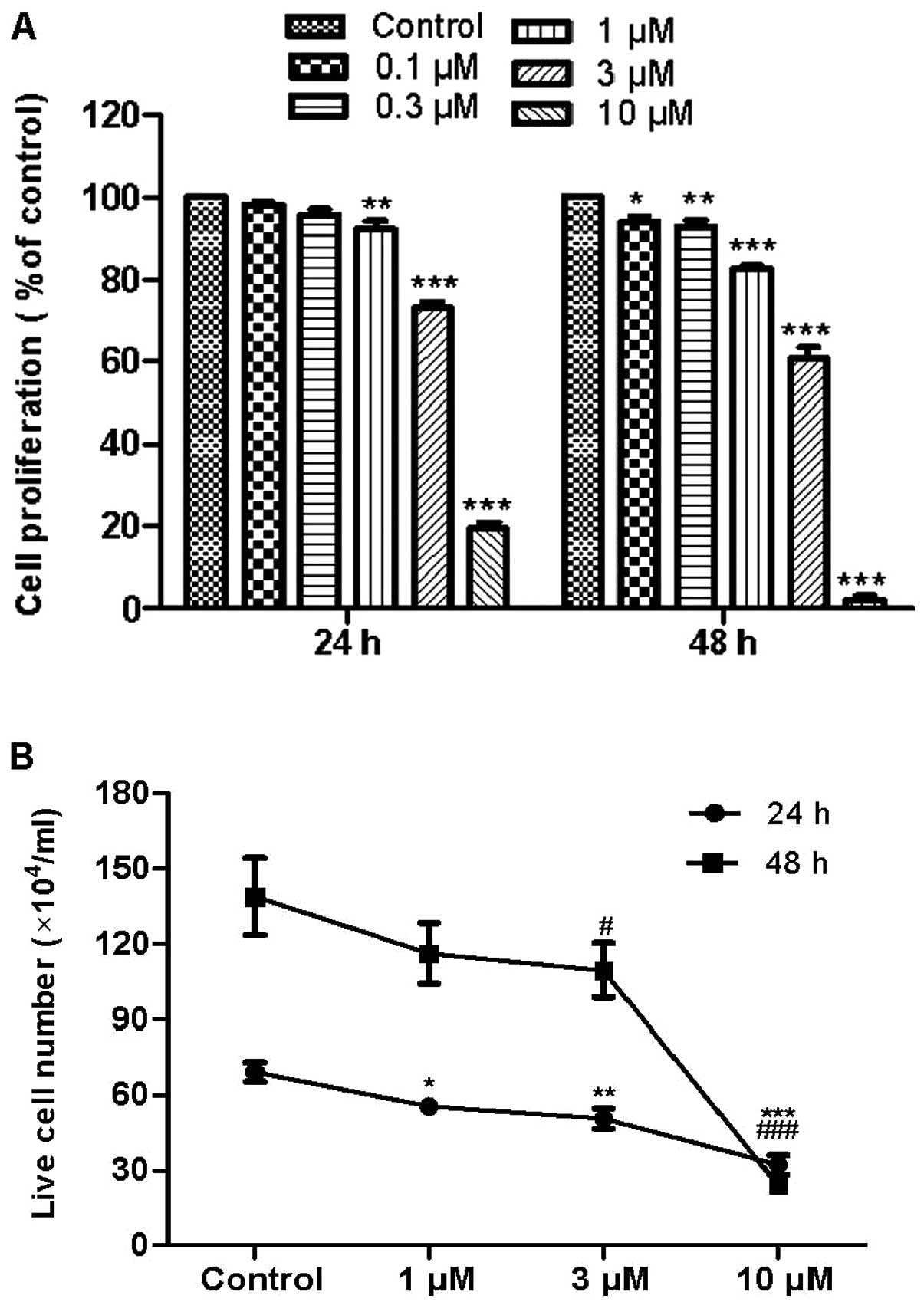
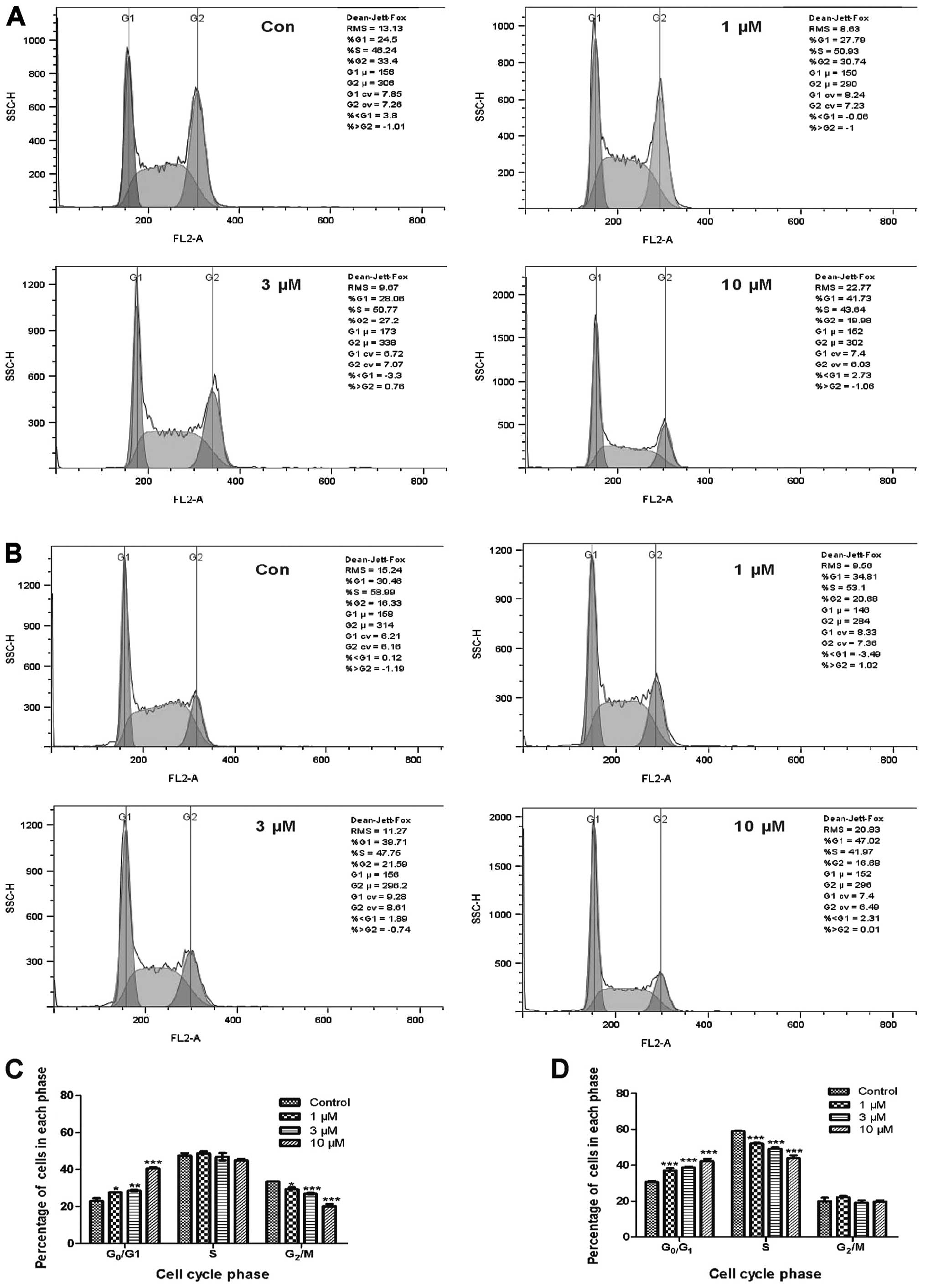
|
1
|
Barr RD and Fialkow PJ: Clonal origin of
chronic myelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 289:307–309. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giles FJ, Cortes JE, Kantarjian HM and
O’Brien SM: Accelerated and blastic phases of chronic myelogenous
leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 18:753–774. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baccarani M, Saglio G, Goldman J, et al:
Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia.
Recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European
LeukemiaNet. Blood. 108:1809–1820. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
von BN and Duyster J: Chronic myelogenous
leukemia: treatment and monitoring. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 107:114–121.
2010.
|
|
5
|
Nowell PC and Hungerford DA: Chromosome
studies on normal and leukemic human leukocytes. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 25:85–109. 1960.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rowley JD: Letter: A new consistent
chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified
by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature.
243:290–293. 1973. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Barnes DJ and Melo JV: Management of
chronic myeloidleukemia: targets for molecular therapy. Semin
Hematol. 40:34–49. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamdane M, David-Cordonnier M and
D’Halluin JC: Activation of p65NF-kB protein by p210BCR-ABL in a
myeloid cell line. Oncogene. 15:2267–2275. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deininger MW, Goldman JM and Melo JV: The
molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 10:3343–3356.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, et
al: Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase
in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute
lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J
Med. 344:1038–1042. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roskoski RJ: STI-571: an anticancer
protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
309:709–717. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Druker BJ: Perspectives on the development
of imatinib and the future of cancer research. Nat Med.
15:1149–1152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, et al:
Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine
kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 344:1031–1037.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Azam M, Latek RR and Daley GQ: Mechanisms
of autoinhibition and STI-571/imatinib resistance revealed by
mutagenesis of BCR-ABL. Cell. 112:831–843. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Konig H, Holyoake TL and Bhatia R:
Effective and selective inhibition of chronic myeloid leukemia
primitive hematopoietic progenitors by the dual Src/Abl kinase
inhibitor SKI-606. Blood. 111:2329–2338. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura K, Tsuchiya S, Sugimoto Y,
Sugimura Y and Yamada Y: Histamine release inhibition activity of
bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Planta Med. 58:505–508. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HS, Zhang YH, Oh KW and Ahn HY:
Vasodilating and hypotensive effects of fangchinoline and
tetrandrine on the rat aorta and the stroke-prone spontaneously
hypertensive rat. J Ethnopharmacol. 58:117–123. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hristova M and Istatkova R:
Complement-mediated antiinflammatory effect of
bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid fangchinoline. Phytomedicine.
6:357–362. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi HS, Kim HS, Min KR, Kim Y, Lim HK,
Chang YK and Chung MW: Anti-inflammatory effects of fangchinoline
and tetrandrine. J Ethnopharmacol. 69:173–179. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shen YC, Chou CJ, Chiou WF and Chen CF:
Anti-inflammatory effects of the partially purified extract of
radix Stephaniae tetrandrae: comparative studies of its
active principles tetrandrine and fangchinoline on human
polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions. Mol Pharmacol. 60:1083–1090.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HS, Zhang YH and Yun YP: Effects of
tetrandrine and fangchinoline on experimental thrombosis in mice
and human platelet aggregation. Planta Med. 65:135–138. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsutsumi T, Kobayashi S, Liu YY and
Kontani H: Anti-hyperglycemic effect of fangchinoline isolated from
Stephania tetrandra Radix in streptozotocin-diabetic mice.
Biol Pharm Bull. 26:313–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma W, Nomura M, Takahashi-Nishioka T and
Kobayashi S: Combined effects of fangchinoline from Stephania
tetrandra Radix and formononetin and calycosin from
Astragalus membranaceus Radix on hyperglycemia and
hypoinsulinemia in streptozotocin-diabetic mice. Biol Pharm Bull.
30:2079–2083. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin TY, Lu CW, Tien LT, Chuang SH, Wang
YR, Chang WH and Wang SJ: Fangchinoline inhibits glutamate release
from rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals (synaptosomes). Neurochem
Int. 54:506–512. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gülçin I, Elias R, Gepdiremen A, Chea A
and Topal F: Antioxidant activity of bisbenzylisoquinoline
alkaloids from Stephania rotunda: cepharanthine and fangchinoline.
J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 25:44–53. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sekiya N, Hikiami H, Yokoyama K, Kouta K,
Sakakibara I, Shimada Y and Terasawa K: Inhibitory effects of
Stephania tetrandra S. Moore on free radical-induced lysis
of rat red blood cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:667–670. 2005.
|
|
27
|
Xing ZB, Yao L, Zhang GQ, Zhang XY, Zhang
YX and Pang D: Fangchinoline inhibits breast adenocarcinoma
proliferation by inducing apoptosis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
59:1476–1480. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang CD, Huang JG, Gao X, et al:
Fangchinoline induced G1/S arrest by modulating expression of p27,
PCNA and cyclin D in human prostate carcinoma cancer PC3 cells and
tumor xenograft. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 74:488–493. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang N, Pan W, Zhu M, Zhang M, Hao X,
Liang G and Feng Y: Fangchinoline induces autophagic cell death via
p53/sestrin2/AMPK signalling in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Br J Pharmacol. 164:731–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He L, Yang J and Hu L: Transmembrane
transport activity of paclitaxel regulated by fangchinoline in
MDR1-mDCK II cells. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 35:1478–1481.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
He P, Sun H, Jian XX, Chen QH, Chen DL,
Liu GT and Wang FP: Partial synthesis and biological evaluation of
bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids derivatives: potential modulators
of multidrug resistance in cancer. J Asian Nat Prod Res.
14:564–576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kenneth JL and Thomas DS: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2–ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sherr CJ: G1 phase progression: Cycling on
cue. Cell. 79:551–555. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Johnson DG and Schneider-Broussard R: Role
of E2F in cell cycle control and cancer. Front Biosci. 3:447–448.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bischoff JR: Cdk inhibitors in cancer
therapy: What is next? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 29:16–21. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J,
Stone A and Sutherland RL: Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:558–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ando K, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F and
Griffin JD: Regulation of G1/S transition by cyclins D2 and D3 in
hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:9571–9575. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gartel AL and Tyner AL: The role of the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis. Mol Cancer
Ther. 1:639–649. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Weiss RH: p21Waf1/Cip1 as a therapeutic
target in breast and other cancers. Cancer Cell. 4:425–429. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zu K, Bihani T, Lin A, Park YM, Mori K and
Ip C: Enhanced selenium effect on growth arrest by BiP/GRP78
knockdown in p53-null human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene.
25:546–554. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Romanov VS, Pospelov VA and Pospelova TV:
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 (Waf1): contemporary view on
its role in senescence and oncogenesis. Biochemistry (Mosc).
77:575–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gorospe M, Wang X, Guyton K and Holbrook
N: Protective role of p21 (WAF1/CIP1) against prostaglandin
A2-mediated apoptosis of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell
Biol. 16:6654–6660. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hitomi M, Shu J, Strom D, Harter ML and
Stacey DW: Prostaglandin A2 blocks the activation of G1 phase
cyclin dependent kinase without altering mitogen-activated protein
kinase stimulation. J Biol Chem. 271:9376–9383. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Forster K, Obermeier A, Mitina O, Simon N,
Warmuth M, Krause G and Hallek M: Role of p21(WAF1/CIP1) as an
attenuator of both proliferative and drug-induced apoptotic signals
in BCR-ABL-transformed hematopoietic cells. Ann Hematol.
87:183–193. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
van Delft MF and Huang DC: How the Bcl-2
family of proteins interact to regulate apoptosis. Cell Res.
16:203–213. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Labi V, Erlacher M, Kiessling S and
Villunger A: BH3-only proteins in cell death initiation, malignant
disease and anticancer therapy. Cell Death Differ. 13:1325–1338.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Leber B, Lin J and Andrews DW: Embedded
together: the life and death consequences of interaction of the
Bcl-2 family with membranes. Apoptosis. 12:897–911. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, et al:
Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial
dysfunction and death. Science. 292:727–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Aichberger KJ, Mayerhofer M, Krauth MT,
Skvara H, Florian S and Sonneck K: Identification of mcl-1 as a
BCR/ABL-dependent target in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML):
evidence for cooperative antileukemic effects of imatinib and mcl-1
antisense oligonucleotides. Blood. 105:3303–3311. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhou P, Qian L, Kozopas KM and Craig RW:
Mcl-1, a Bcl-2 family member, delays the death of hematopoietic
cells under a variety of apoptosis-inducing conditions. Blood.
89:630–643. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Opferman JT, Iwasaki H, Ong CC, Suh H,
Mizuno S and Akashi K: Obligate role of anti-apoptotic MCL-1 in the
survival of hematopoietic stem cells. Science. 307:1101–1104. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Thallinger C, Wolschek MF, Wacheck V,
Maierhofer H, Gunsberg P and Polterauer P: Mcl-1 antisense therapy
chemosensitizes human melanoma in a SCID mouse xenotransplantation
model. J Invest Dermatol. 120:1081–1086. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Germain M, Milburn J and Duronio V: MCL-1
inhibits BAX in the absence of MCL-1/BAX Interaction. J Biol Chem.
283:6384–6392. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Coqueret O: New roles for p21 and p27
cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends
Cell Biol. 13:65–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Asada M, Yamada T, Ichijo H, Delia D,
Miyazono K, Fukumuro K and Mizutani S: Apoptosis inhibitory
activity of cytoplasmic p21(Cip1/WAF1) in monocytic
differentiation. EMBO J. 18:1223–1234. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Suzuki A, Tsutomi Y, Akahane K, Araki T
and Miura M: Resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis: activation of
caspase 3 is regulated by cell cycle regulator p21WAF1 and IAP gene
family ILP. Oncogene. 17:931–939. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|