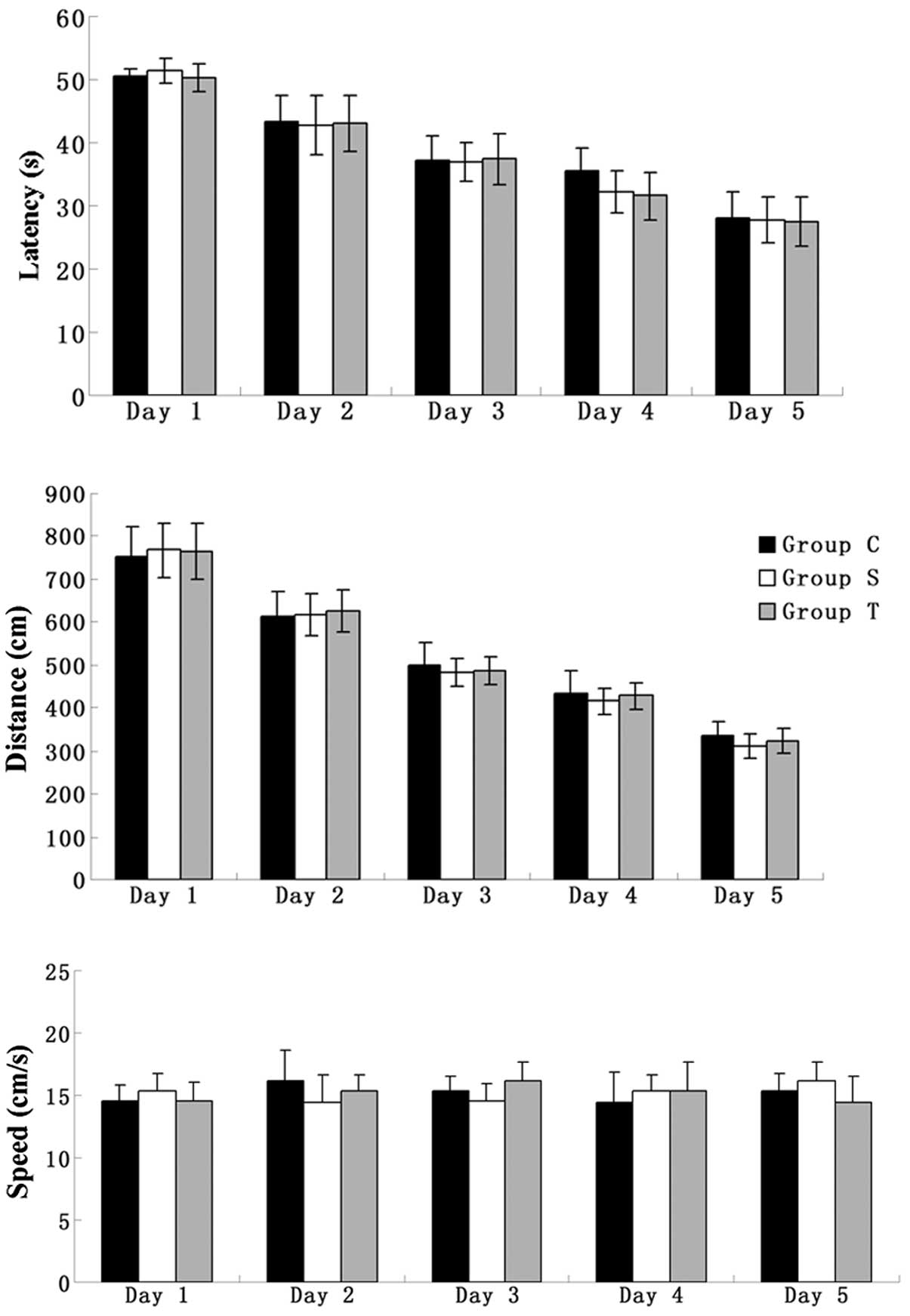
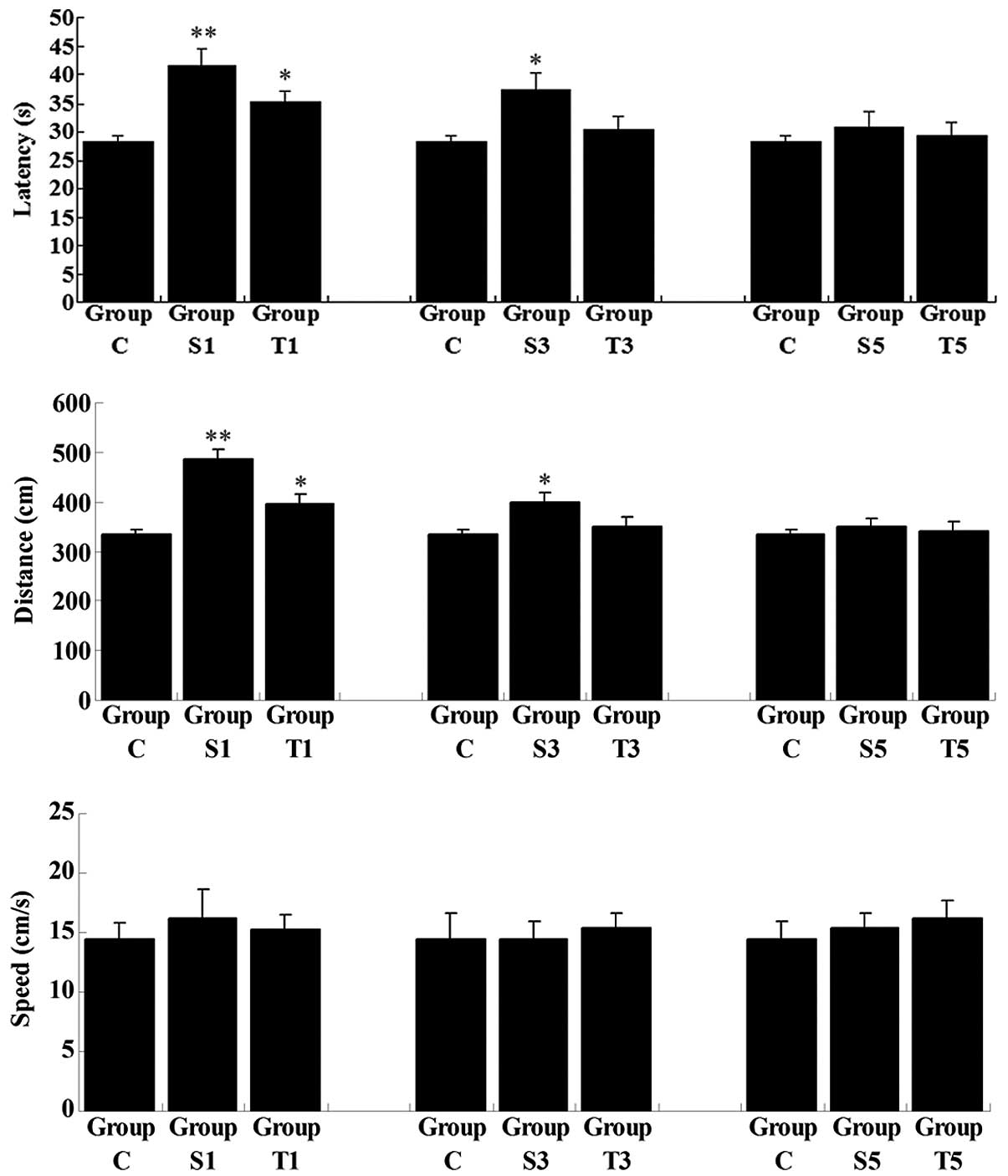
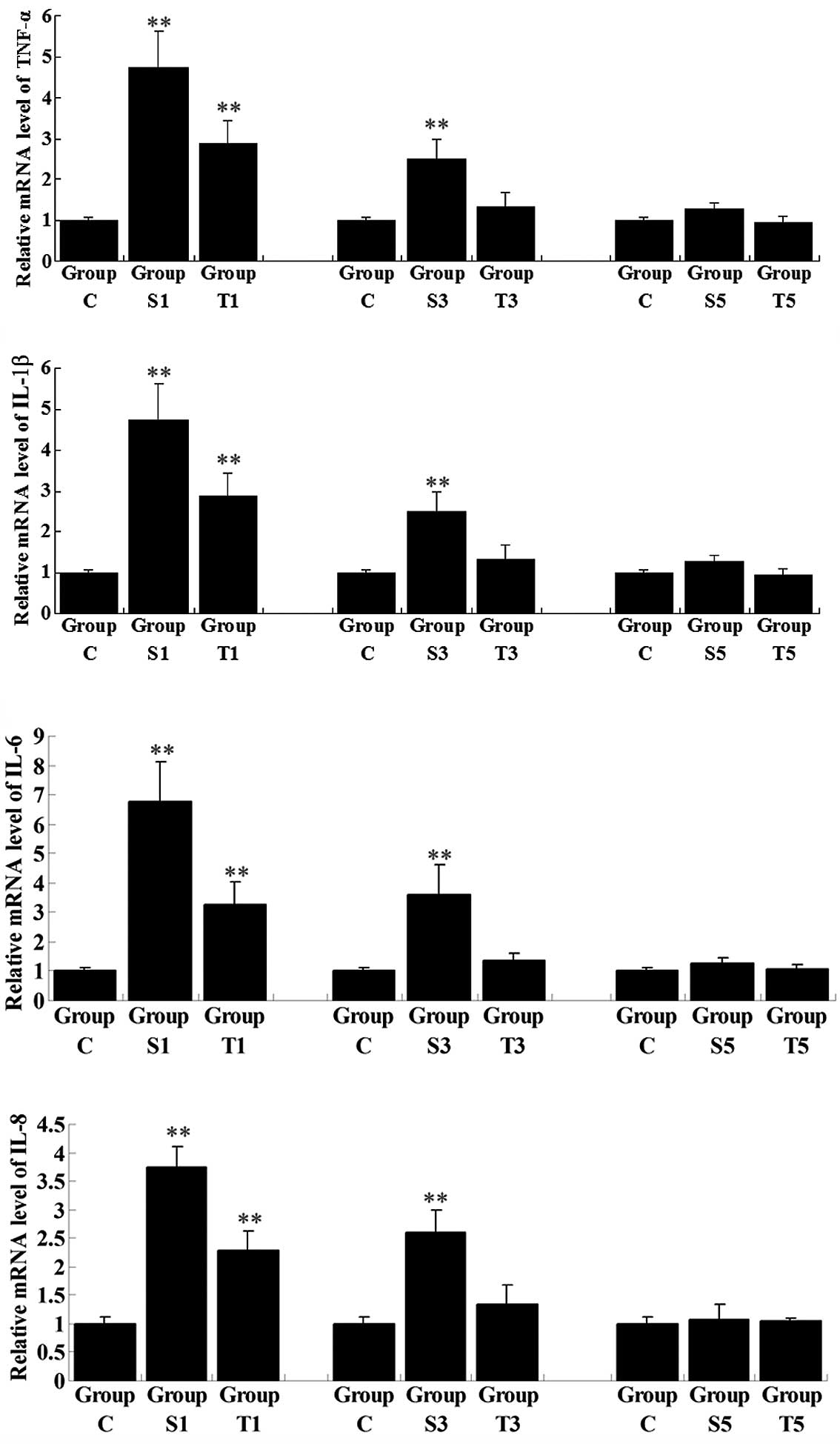
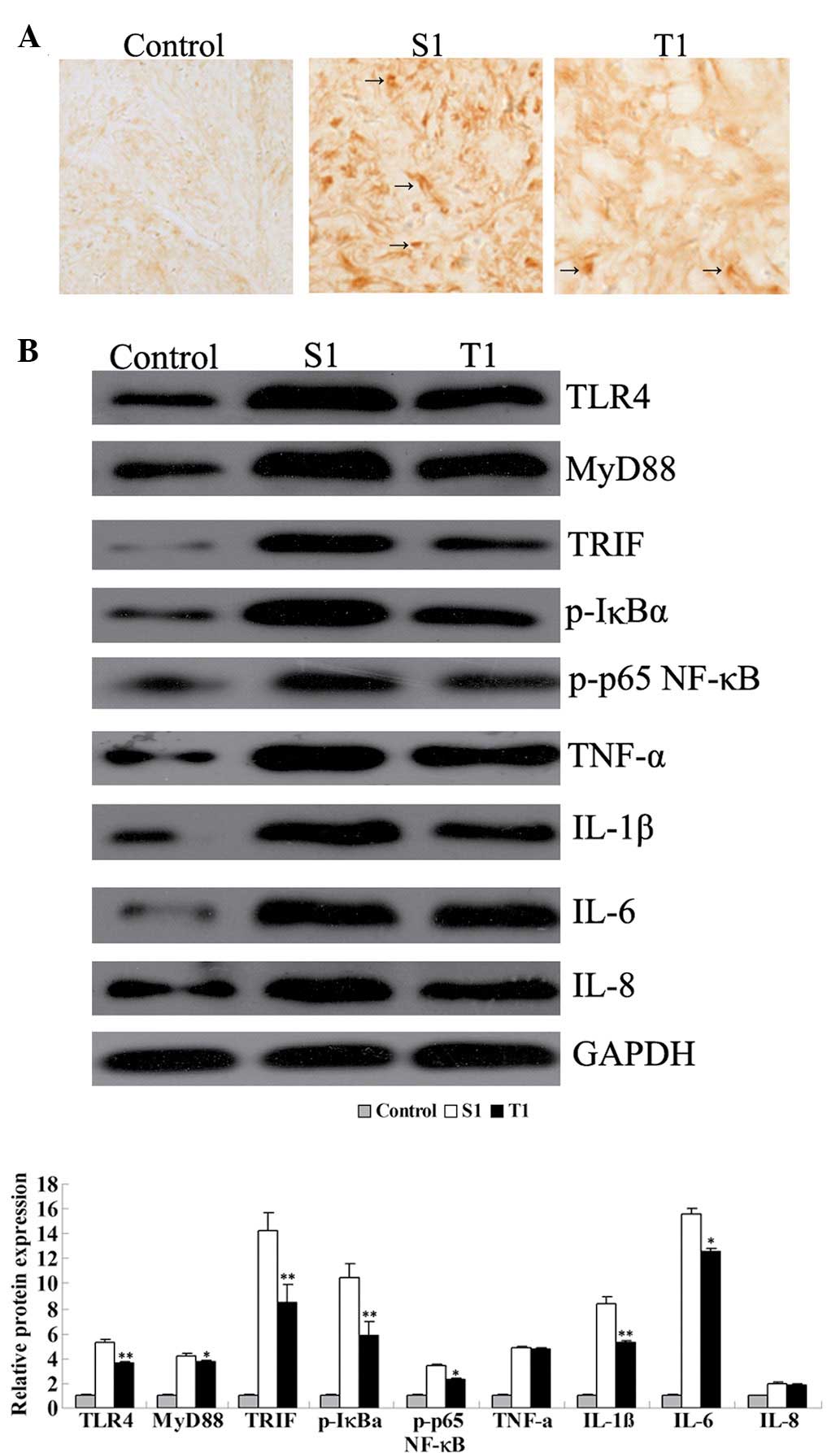
|
1
|
Coburn M, Fahlenkamp A, Zoremba N and
Schaelte G: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: Incidence and
prophylaxis. Anaesthesist. 59:177–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deiner S and Silverstein JH: Postoperative
delirium and cognitive dysfunction. Br J Anaesth. 103(Suppl 1):
i41–i46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu Z, Ou Y, Duan K and Jiang X:
Inflammation: a bridge between postoperative cognitive dysfunction
and Alzheimer’s disease. Med Hypotheses. 74:722–724.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosczyk HA, Sparkman NL and Johnson RW:
Neuroinflammation and cognitive function in aged mice following
minor surgery. Exp Gerontol. 43:840–846. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Terrando N, Monaco C, Ma D, Foxwell BM,
Feldmann M and Maze M: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers a
cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:20518–20522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Teeling JL and Perry VH: Systemic
infection and inflammation in acute CNS injury and chronic
neurodegeneration: underlying mechanisms. Neuroscience.
158:1062–1073. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park CH, Choi SH, Koo JW, et al: Novel
cognitive improving and neuroprotective activities of Polygala
tenuifolia Willdenow extract, BT-11. J Neurosci Res.
70:484–492. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ikeya Y, Takeda S, Tunakawa M, et al:
Cognitive improving and cerebral protective effects of acylated
oligosaccharides in Polygala tenuifolia. Biol Pharm Bull.
27:1081–1085. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie W, Yang Y, Gu X, et al: Senegenin
attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion induced cognitive
dysfunction by increasing hippocampal NR2B expression in rats. PLoS
One. 7:e455752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F and Karin M: NF-κB
and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev.
246:379–400. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Hartholt KA, van der Cammen TJ and Klimek
M: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in geriatric patients. Z
Gerontol Geriatr. 45:411–416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shin KY, Lee JY, Won BY, et al: BT-11 is
effective for enhancing cognitive functions in the elderly humans.
Neurosci Lett. 465:157–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee JY, Kim KY, Shin KY, Won BY, Jung HY
and Suh YH: Effects of BT-11 on memory in healthy humans. Neurosci
Lett. 454:111–114. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Haseneder R, Kochs E and Jungwirth B:
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Possible neuronal mechanisms
and practical consequences for clinical routine. Anaesthesist.
61:437–443. 2012.(In German).
|
|
15
|
Hua F, Ma J, Ha T, et al: Activation of
Toll-like receptor 4 signaling contributes to hippocampal neuronal
death following global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. J
Neuroimmunol. 190:101–111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barrientos RM, Hein AM, Frank MG, Watkins
LR and Maier SF: Intracisternal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist
prevents postoperative cognitive decline and neuroinflammatory
response in aged rats. J Neurosci. 32:14641–14648. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Crack PJ and Bray PJ: Toll-like receptors
in the brain and their potential roles in neuropathology. Immunol
Cell Biol. 85:476–480. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Okun E, Griffioen KJ, Lathia JD, Tang SC,
Mattson MP and Arumugam TV: Toll-like receptors in
neurodegeneration. Brain Res Rev. 59:278–292. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sohn KH, Jo MJ, Cho WJ, et al:
Bojesodok-eum, a herbal prescription, ameliorates acute
inflammation in association with the inhibition of NF-κB-mediated
nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokine production. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:4573702012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cortez M, Carmo LS, Rogero MM, Borelli P
and Fock RA: A high-fat diet increases IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α
production by increasing NF-κB and attenuating PPAR-γ expression in
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Inflammation. 36:379–386.
2013.
|
|
21
|
Iwai K: Diverse ubiquitin signaling in
NF-κB activation. Trends Cell Biol. 22:355–364. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Dyson HJ and Komives EA: Role of disorder
in IκB-NFκB interaction. IUBMB Life. 64:499–505. 2012.
|