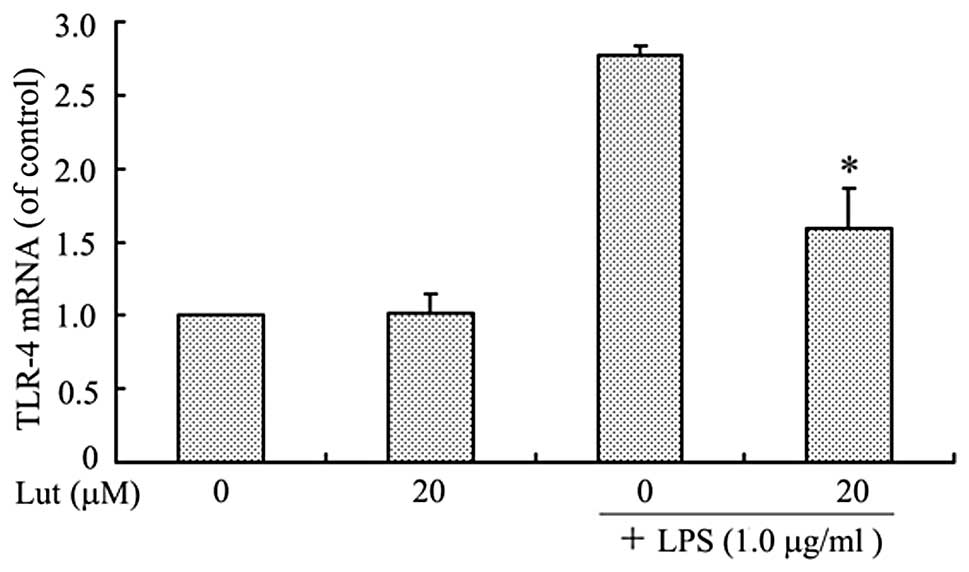
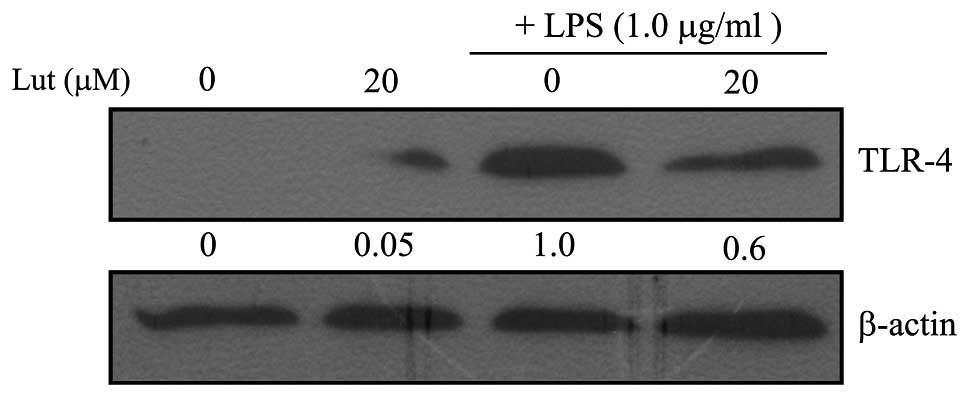
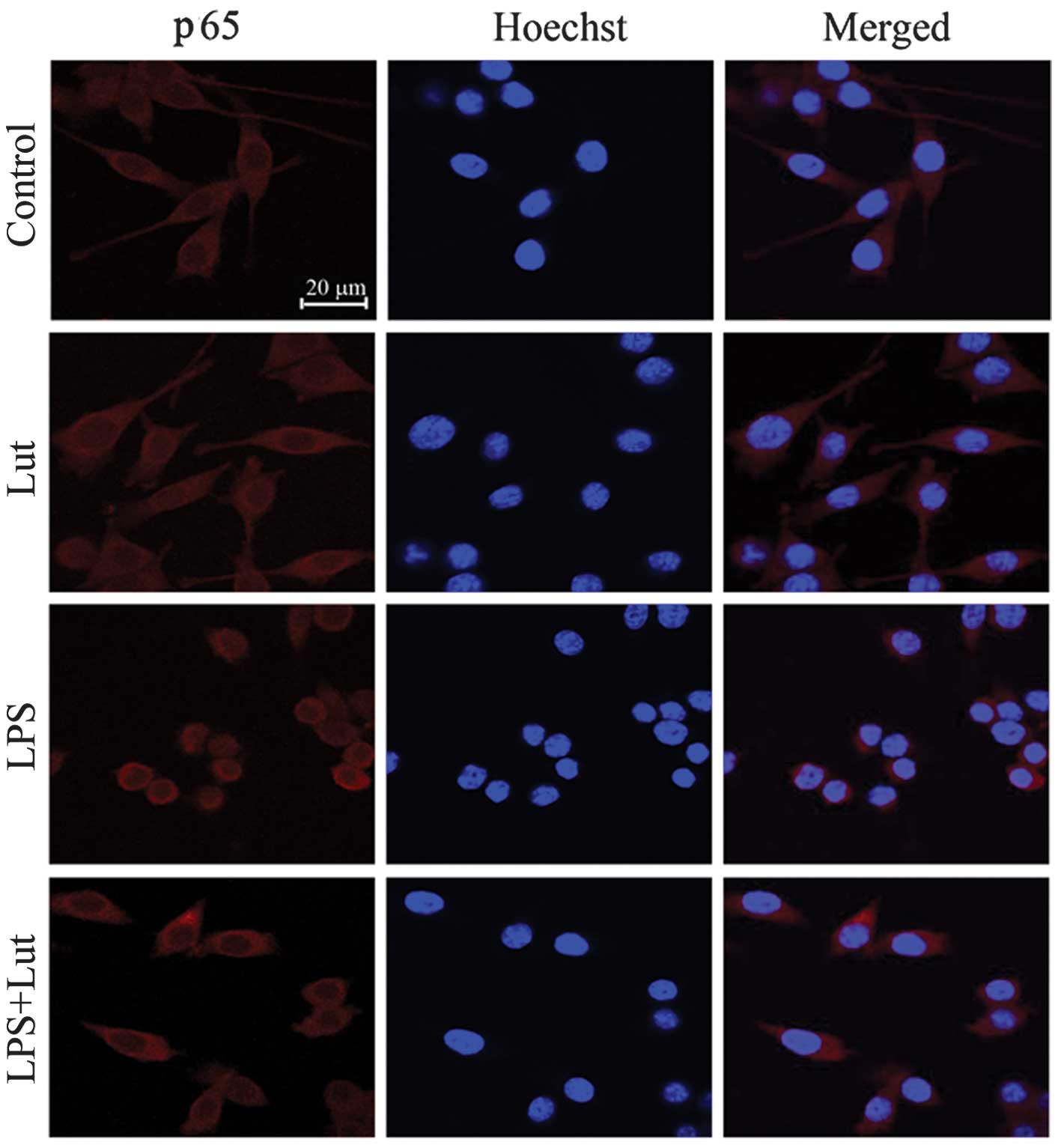
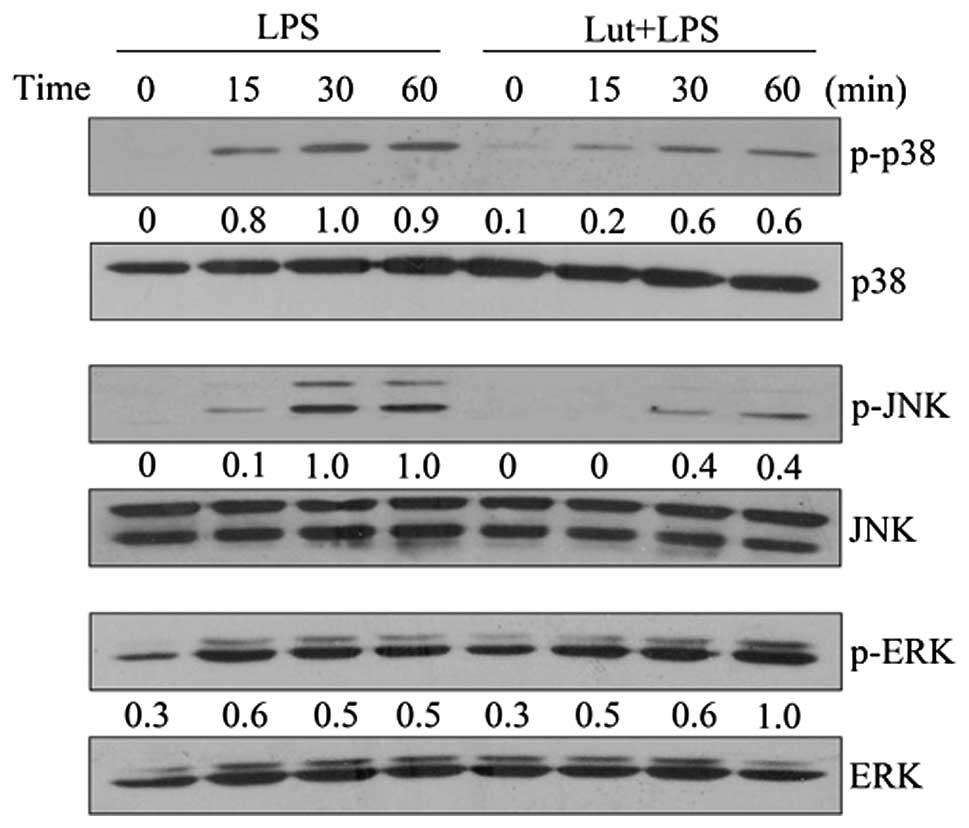
|
1
|
Bernardi A, Frozza RL, Meneghetti A, Hoppe
JB, Battastini AM, Pohlmann AR, Guterres SS and Salbego CG:
Indomethacin-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules reduce the damage
triggered by Aβ1–42 in Alzheimer’s disease models. Int J
Nanomedicine. 7:4927–4942. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yokoyama H, Uchida H, Kuroiwa H, Kasahara
J and Araki T: Role of glial cells in neurotoxin-induced animal
models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci. 32:1–7. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dibaj P, Zschüntzsch J, Steffens H,
Scheffel J, Göricke B, Weishaupt JH, Le Meur K, Kirchhoff F,
Hanisch UK, Schomburg ED and Neusch C: Influence of methylene blue
on microglia-induced inflammation and motor neuron degeneration in
the SOD1(G93A) model for ALS. PLoS One. 7:e439632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McGeer EG and McGeer PL: Neuroinflammation
in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a field in
its infancy. J Alzheimers Dis. 19:355–361. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Mrak RE and Griffin WS: Glia and their
cytokines in progression of neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging.
26:349–354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anisman H: Cascading effects of stressors
and inflammatory immune system activation: implications for major
depressive disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 34:4–20.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ha SK, Lee P, Park JA, Oh HR, Lee SY, Park
JH, et al: Apigenin inhibits the production of NO and PGE2 in
microglia and inhibits neuronal cell death in a middle cerebral
artery occlusion-induced focal ischemia mice model. Neurochem Int.
52:878–886. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lyons A, Downer EJ, Crotty S, Nolan YM,
Mills KH and Lynch MA: CD 200 ligand receptor interaction modulates
microglial activation in vivo and in vitro: a role for IL-4. J
Neurosci. 27:8309–8313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qian L, Flood PM and Hong JS:
Neuroinflammation is a key player in Parkinson’s disease and a
prime target for therapy. J Neural Transm. 117:971–979. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Krause DL and Müller N: Neuroinflammation,
microglia and implications for anti-inflammatory treatment in
Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2010:7328062010.
|
|
11
|
Park E, Kum S, Wang C, Park SY, Kim BS and
Schuller-Levis G: Anti-inflammatory activity of herbal medicines:
Inhibition of nitric oxide production and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha secretion in an activated macrophage-like cell line.
Am J Chin Med. 33:415–424. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JS and Jobin C: The flavonoid luteolin
prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB signaling and gene
expression by blocking IκB kinase activity in intestinal epithelial
cells and bone-marrow derived dendritic cells. Immunology.
115:375–387. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim SH, Shin KJ, Kim D, Kim YH, Han MS,
Lee TG, et al: Luteolin inhibits the nuclear factor-κB
transcriptional activity in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol.
66:955–963. 2003.
|
|
14
|
Gutiérrez-Venegas G, Kawasaki-Cárdenas P,
Arroyo-Cruz SR and Maldonado-Frías S: Luteolin inhibits
lipopolysaccharide actions on human gingival fibroblasts. Eur J
Pharmacol. 541:95–105. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu LH, Bi W, Qi RB, Wang HD and Lu DX:
Luteolin inhibits microglial inflammation and improves neuron
survival against inflammation. Int J Neurosci. 121:329–336. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bureau G, Longpré F and Martinoli MG:
Resveratrol and quercetin, two natural polyphenols, reduce
apoptotic neuronal cell death induced by neuroinflammation. J
Neurosci Res. 86:403–410. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jang S, Kelley KW and Johnson RW: Luteolin
reduces IL-6 production in microglia by inhibiting JNK
phosphorylation and activation of AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:7534–7539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rezai-Zadeh K, Ehrhart J, Bai Y, Sanberg
PR, Bickford P, Tan J and Shytle RD: Apigenin and luteolin modulate
microglial activation via inhibition of STAT1-induced CD40
expression. J Neuroinflammation. 5:412008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dirscherl K, Karlstetter M, Ebert S, Kraus
D, Hlawatsch J, Walczak Y, Moehle C, Fuchshofer R and Langmann T:
Luteolin triggers global changes in the microglial transcriptome
leading to a unique anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective
phenotype. J Neuroinflammation. 7:32010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jang S, Dilger RN and Johnson RW: Luteolin
inhibits microglia and alters hippocampal-dependent spatial working
memory in aged mice. J Nutr. 140:1892–1898. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Willis LM, Bielinski DF, Fisher DR,
Matthan NR and Joseph JA: Walnut extract inhibits LPS-induced
activation of BV-2 microglia via internalization of TLR4: Possible
involvement of phospholipase D2. Inflammation. 33:325–333. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Medzhitov R: Toll-like receptors and
innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:135–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ozato K, Tsujimura H and Tamura T:
Toll-like receptor signaling and regulation of cytokine gene
expression in the immune system. Biotechniques. 33(4 Suppl):
S66–S75. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bi W, Jing X, Zhu L, Liang Y, Liu J, Yang
L, Xiao S, Xu A, Shi Q and Tao E: Inhibition of 26S protease
regulatory subunit 7 (MSS1) suppresses neuroinflammation. Plos One.
7:e361422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bi W, Zhu L, Wang C, Liang Y, Liu J, Shi Q
and Tao E: Rifampicin inhibits microglial inflammation and improves
neuron survival against inflammation. Brain Res. 1395:12–20. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xie Z, Smith CJ and Van Eldik LJ:
Activated glia induce neuron death via MAP kinase signaling
pathways involving JNK and p38. Glia. 45:170–179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC and Hogan EL:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of
mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide
synthase and tumor necrosis factor-α gene expression in
endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J Neurosci.
18:1633–1641. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Madrid LV, Wang CY, Guttridge DC,
Schottelius AJ, Baldwin AS Jr and Mayo MW: Akt suppresses apoptosis
by stimulating the transactivation potential of the Rel A/p65
subunit of NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. 20:1626–1638. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Downward J: Lipid-regulated kinases: some
common themes at last. Science. 279:673–674. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Liu L, Barger SW, Mrak RE and
Griffin WS: Vitamin E suppression of microglial activation is
neuroprotective. J Neurosci Res. 15:163–170. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Brown GC and Neher JJ: Inflammatory
neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons.
Mol Neurobiol. 41:242–247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bi W, Zhu L, Jing X, Liang Y and Tao E:
Rifampicin and Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci. 34:137–141.
2013.
|