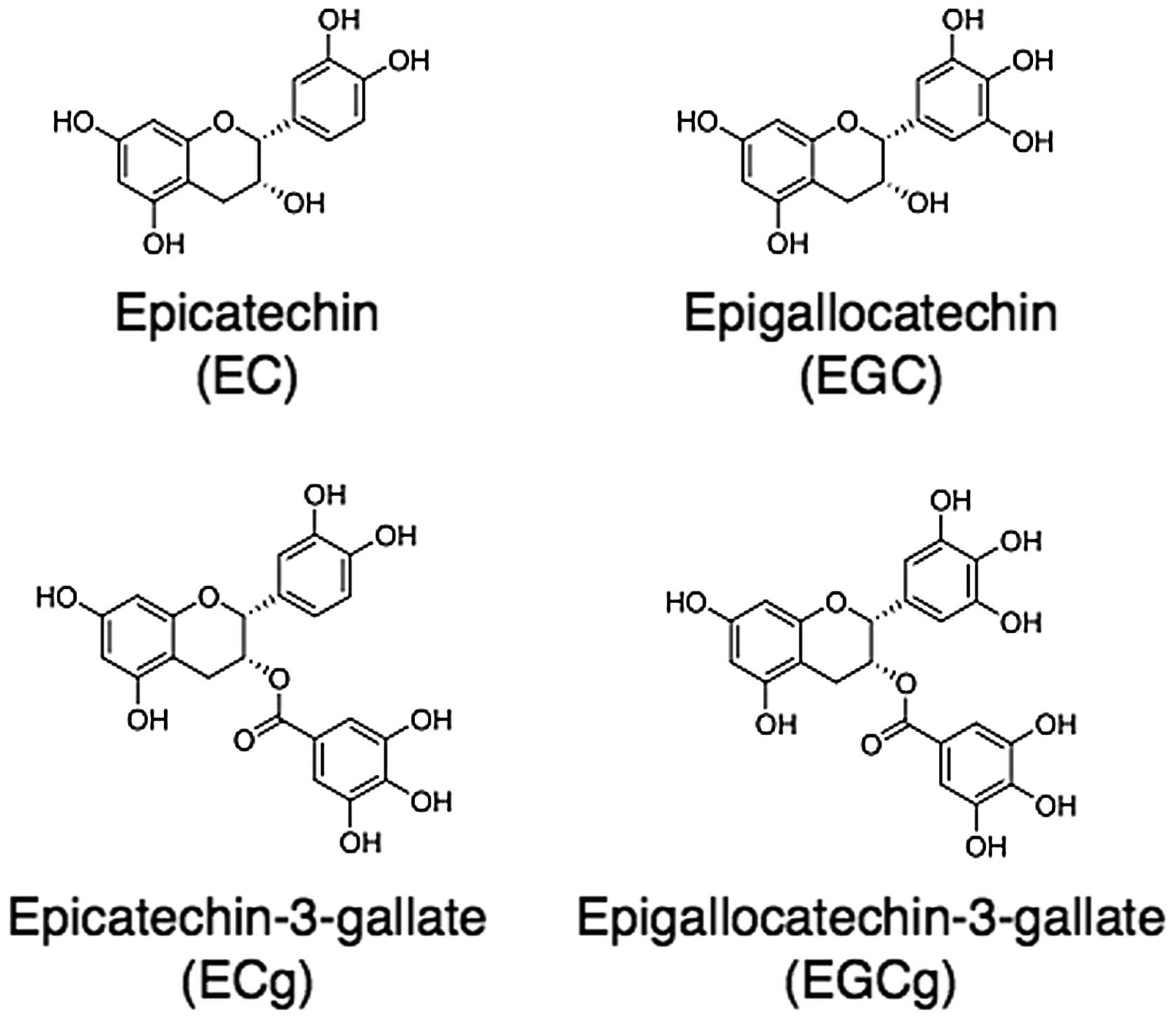
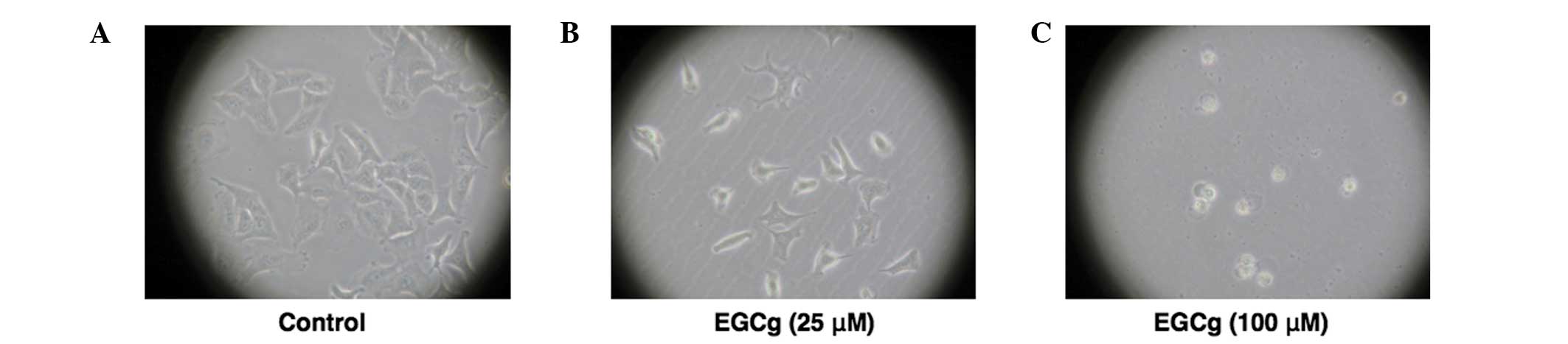
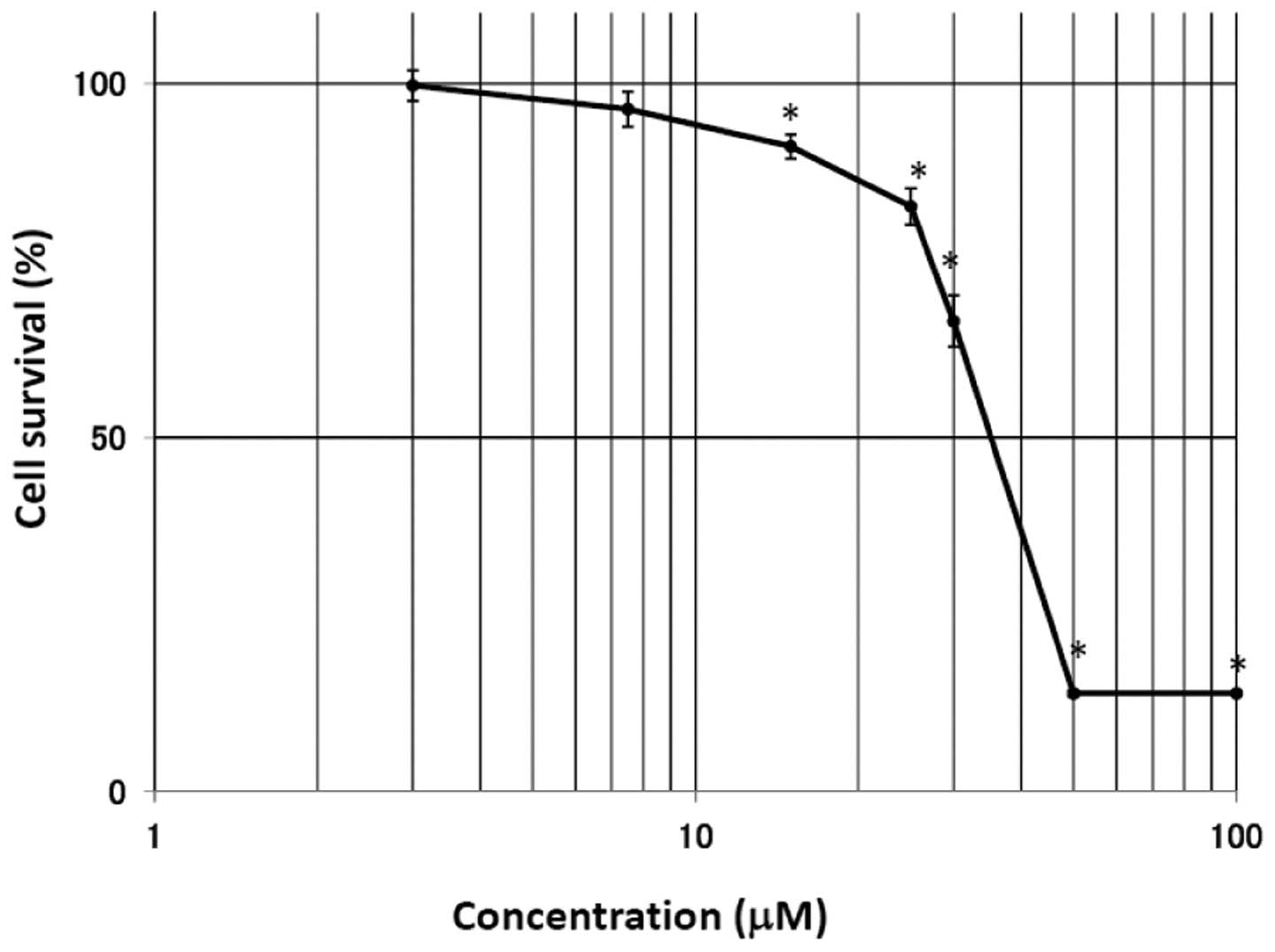
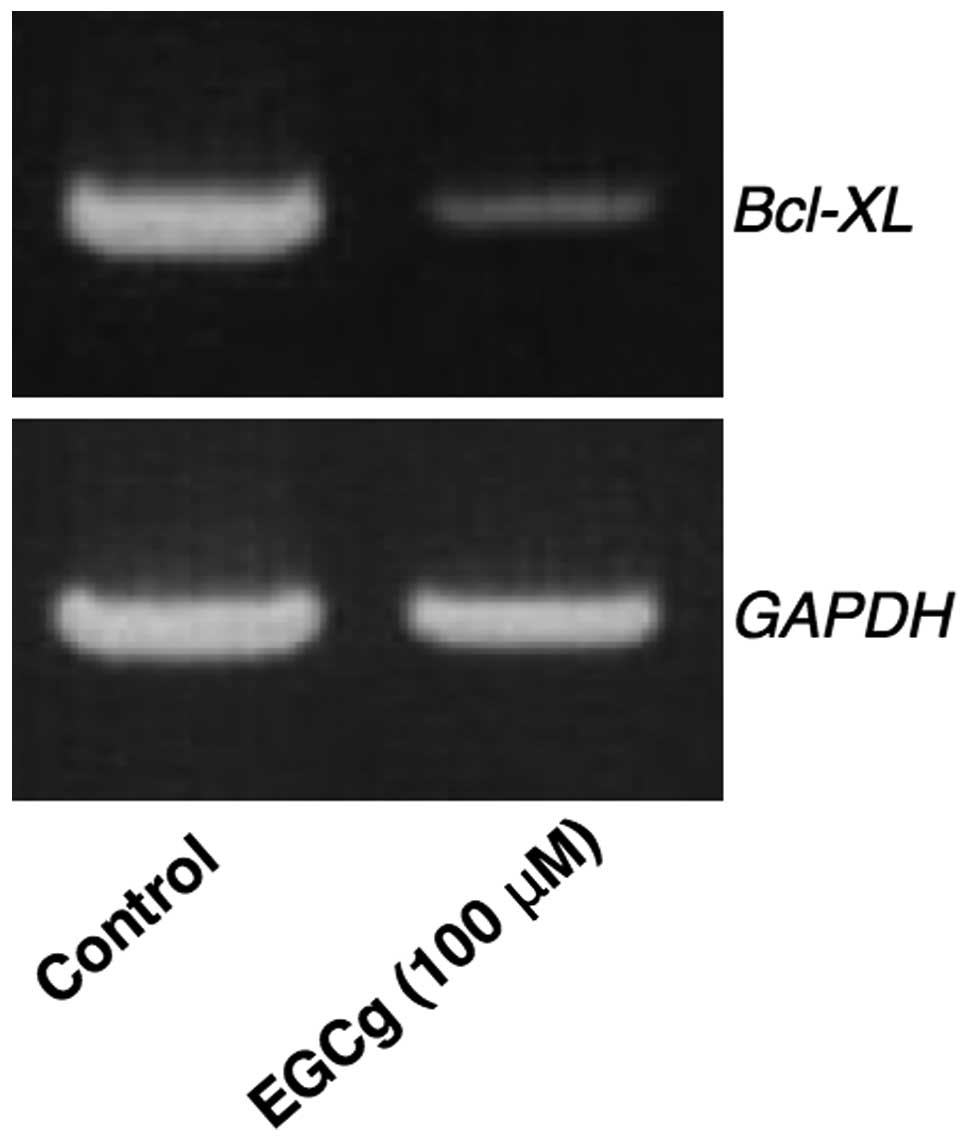
|
1
|
Baba Y, Sonoda JI, Hayashi S, et al:
Reduction of oxidative stress in liver cancer patients by oral
green tea polyphenol tablets during hepatic arterial infusion
chemotherapy. Exp Ther Med. 4:452–458. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee IP, Kim YH, Kang MH, et al:
Chemopreventive effect of green tea (Camellia sinensis)
against cigarette smoke-induced mutations (SCE) in humans. J Cell
Biochem Suppl. 27:68–75. 1997.
|
|
3
|
Shimizu M, Fukutomi Y, Ninomiya M, et al:
Green tea extracts for the prevention of metachronous colorectal
adenomas: a pilot study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
17:3020–3025. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan N, Adhami VM and Mukhtar H: Review:
green tea polyphenols in chemoprevention of prostate cancer:
preclinical and clinical studies. Nutr Cancer. 61:836–841. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suganuma M, Saha A and Fujiki H: New
cancer treatment strategy using combination of green tea catechins
and anticancer drugs. Cancer Sci. 102:317–323. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Imai K, Suga K and Nakachi K:
Cancer-preventive effects of drinking green tea among a Japanese
population. Prev Med. 26:769–775. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inoue M, Tajima K, Mizutani M, et al:
Regular consumption of green tea and the risk of breast cancer
recurrence: follow-up study from the Hospital-based Epidemiologic
Research Program at Aichi Cancer Center (HERPACC), Japan. Cancer
Lett. 167:175–182. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bettuzzi S, Brausi M, Rizzi F, et al:
Chemoprevention of human prostate cancer by oral administration of
green tea catechins in volunteers with high-grade prostate
intraepithelial neoplasia: a preliminary report from a one-year
proof-of-principle study. Cancer Res. 66:1234–1240. 2006.
|
|
9
|
Naganuma T, Kuriyama S, Kakizaki M, et al:
Green tea consumption and hematologic malignancies in Japan: the
Ohsaki study. Am J Epidemiol. 170:730–738. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nishikawa T, Nakajima T, Moriguchi M, et
al: A green tea polyphenol, epigalocatechin-3-gallate, induces
apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma, possibly through
inhibition of Bcl-2 family proteins. J Hepatol. 44:1074–1082. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yamauchi R, Sasaki K and Yoshida K:
Identification of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in green tea
polyphenols as a potent inducer of p53-dependent apoptosis in the
human lung cancer cell line A549. Toxicol In Vitro. 23:834–839.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li HC, Yashiki S, Sonoda J, et al: Green
tea polyphenols induce apoptosis in vitro in peripheral blood T
lymphocytes of adult T-cell leukemia patients. Jap J Cancer Res.
91:34–40. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsukahara T, Kannagi M, Ohashi T, et al:
Induction of Bcl-x(L) expression by human T-cell leukemia virus
type 1 Tax through NF-kappaB in apoptosis-resistant T-cell
transfectants with Tax. J Virol. 73:7981–7987. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ahmad N, Gupta S and Mukhtar H: Green tea
polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate differentially modulates
nuclear factor κB in cancer cells versus normal cells. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 376:338–346. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sonoda J, Koriyama C, Yamamoto S, et al:
HTLV-1 provirus load in peripheral blood lymphocytes of HTLV-1
carriers is diminished by green tea drinking. Cancer Sci.
95:596–601. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khoshnan A, Tindell C, Laux I, et al: The
NF-kappa B cascade is important in Bcl-xL expression and for the
anti-apoptotic effects of the CD28 receptor in primary human CD4+
lymphocytes. J Immunol. 165:1743–1754. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bui NT, Livolsi A, Peyron JF and Prehn JH:
Activation of nuclear factor kappaB and Bcl-x survival gene
expression by nerve growth factor requires tyrosine phosphorylation
of IkappaBalpha. J Cell Bio. 152:753–764. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carmichael J, De Graff WG, Gazdar AF,
Minna JD and Mitchell JB: Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based
semiautomated colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity
testing. Cancer Res. 47:936–942. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cabrera C, Artacho R and Giménez R:
Beneficial effects of green tea - a review. J Am Coll Nutr.
25:79–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yamamoto T, Staples J, Wataha J, et al:
Protective effects of EGCG on salivary gland cells treated with
gamma-radiation or cis-platinum(II)diammine dichloride. Anticancer
Res. 24:3065–3073. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng J, Lee HC, Bin Sattar MM, Huang Y
and Bian JS: Cardioprotective effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate
against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Eur J Pharmacol.
652:82–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ohe Y, Ohashi Y, Kubota K, et al:
Randomized phase III study of cisplatin plus irinotecan versus
carboplatin plus paclitaxel, cisplatin plus gemcitabine, and
cisplatin plus vinorelbine for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer:
Four-Arm Cooperative Study in Japan. Ann Oncol. 18:317–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liang G, Tang A, Lin X, et al: Green tea
catechins augment the antitumor activity of doxorubicin in an in
vivo mouse model for chemoresistant liver cancer. Int J Oncol.
37:111–123. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kurahashi N1, Sasazuki S, Iwasaki M, Inoue
M and Tsugane S; JPHC Study Group. Green tea consumption and
prostate cancer risk in Japanese men: a prospective study. Am J
Epidemiol. 167:71–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paschka AG, Butler R and Young CY:
Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines by the green
tea component, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Lett.
130:1–7. 1998.
|
|
26
|
Fujiki H: Two stages of cancer prevention
with green tea. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 125:589–597. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Inoue M, Tajima K, Mizutani M, Iwata H,
Iwase T, Miura S, Hirose K, Hamajima N and Tominaga S: Regular
consumption of green tea and the risk of breast cancer recurrence:
follow-up study from the Hospital-based Epidemiologic Research
Program at Aichi Cancer Center (HERPACC), Japan. Cancer Lett.
167:175–182. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Orner GA, Dashwood WM, Blum CA, Díaz GD,
Li Q and Dashwood RH: Suppression of tumorigenesis in the Apc(min)
mouse: down-regulation of beta-catenin signaling by a combination
of tea plus sulindac. Carcinogenesis. 24:263–267. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao YT, McLaughlin JK, Blot WJ, Ji BT, Dai
Q and Fraumeni JF Jr: Reduced risk of esophageal cancer associated
with green tea consumption. J Natl Cancer Inst. 86:855–858. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hibasami H, Komiya T, Achiwa Y, Ohnishi K,
Kojima T, Nakanishi K, Akashi K and Hara Y: Induction of apoptosis
in human stomach cancer cells by green tea catechins. Oncol Rep.
5:527–529. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takada M, Nakamura Y, Koizumi T, Toyama H,
Kamigaki T, Suzuki Y, Takeyama Y and Kuroda Y: Suppression of human
pancreatic carcinoma cell growth and invasion by
epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Pancreas. 25:45–48. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fujimoto N, Sueoka N, Sueoka E, Okabe S,
Suganuma M, Harada M and Fujiki H: Lung cancer prevention with
(−)-epigallocatechin gallate using monitoring by heterogeneous
nuclear ribonucleoprotein B1. Int J Oncol. 20:1233–1239. 2002.
|
|
33
|
Okabe S, Suganuma M, Hayashi M, Sueoka E,
Komori A and Fujiki H: Mechanisms of growth inhibition of human
lung cancer cell line, PC-9, by tea polyphenols. Jap J Cancer Res.
88:639–643. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee MH, Han DW, Hyon SH and Park JC:
Apoptosis of human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells by
epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate via induction of p53 and caspases as
well as suppression of Bcl-2 and phosphorylated nuclear factor-κB.
Apoptosis. 16:75–85. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hong J, Lambert JD, Lee SH, Sinko PJ and
Yang CS: Involvement of multidrug resistance-associated proteins in
regulating cellular levels of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and
its methyl metabolites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 310:222–227.
2003.
|
|
36
|
Ahn SC, Kim GY, Kim JH, et al:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, constituent of green tea, suppresses
the LPS-induced phenotypic and functional maturation of murine
dendritic cells through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein
kinases and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 313:148–155.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee HH, Dadgostar H, Cheng Q, Shu J and
Cheng G: NF-kappaB-mediated up-regulation of Bcl-x and Bfl-1/A1 is
required for CD40 survival signaling in B lymphocytes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci U S A. 96:9136–9141. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|