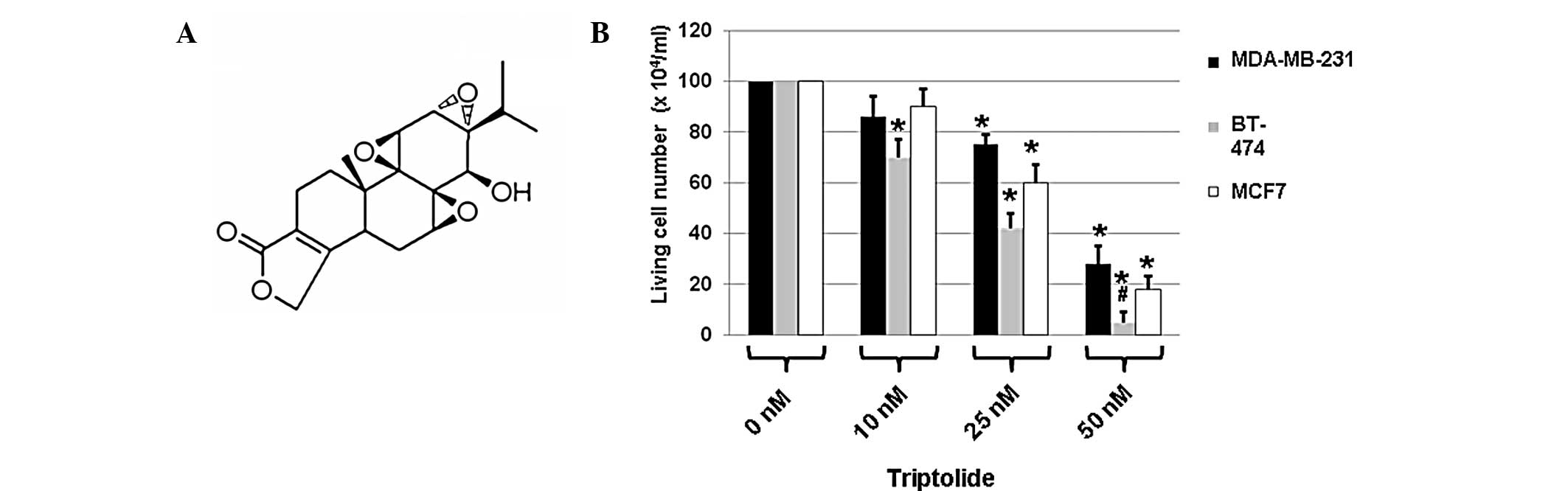
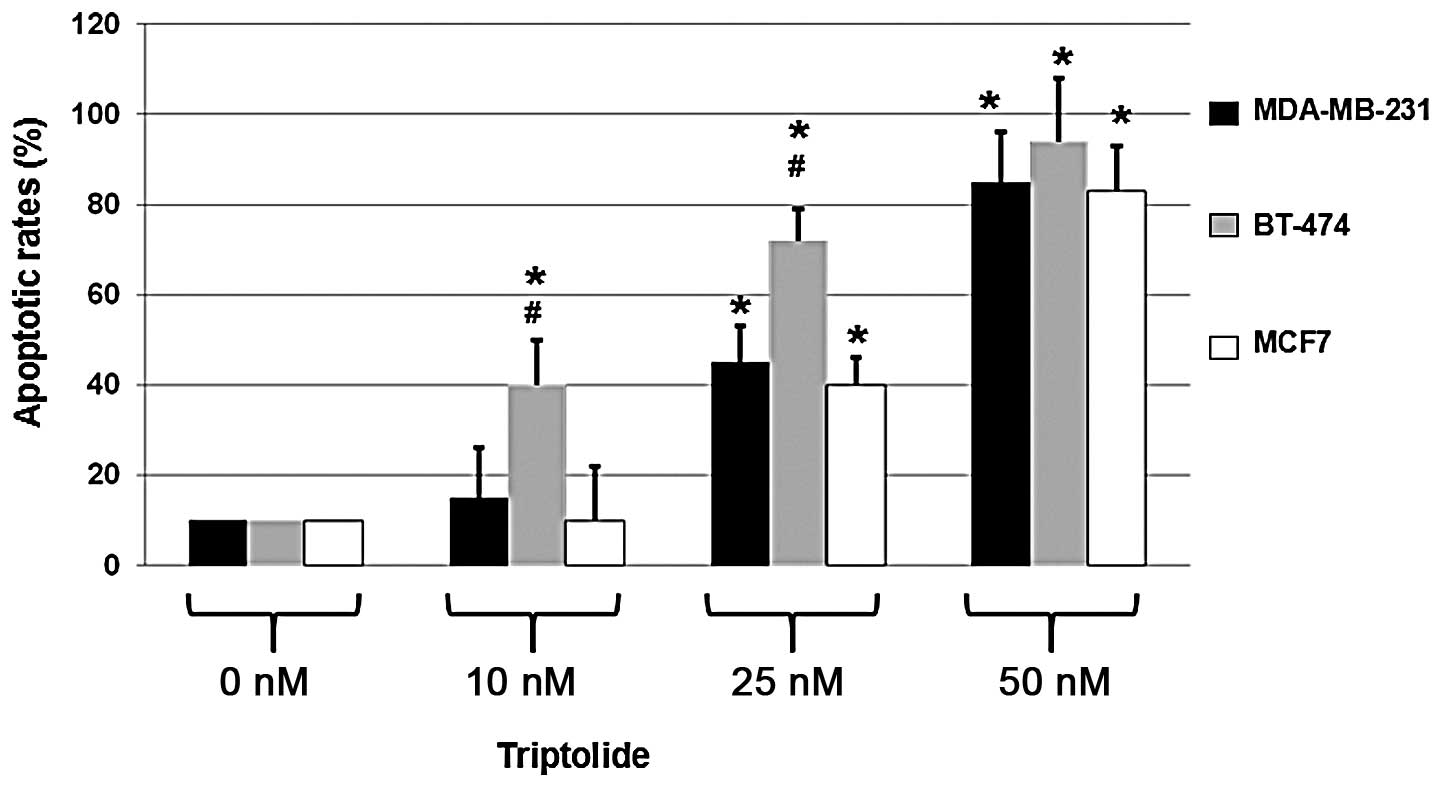
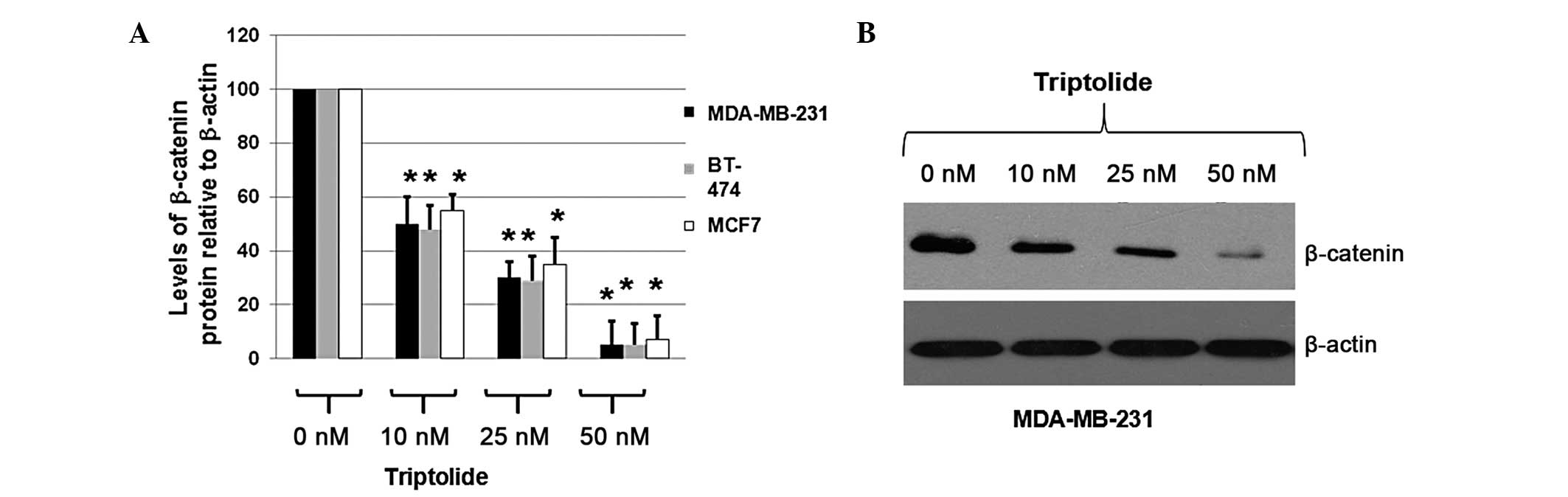
|
1
|
Chen F and Huang K: Effects of the Chinese
medicine matrine on experimental C. parvum infection in
BALB/c mice and MDBK cells. Parasitol Res. 111:1827–1832. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jong TT, Lee MR, Chiang YC and Chiang ST:
Using LC/MS/MS to determine matrine, oxymatrine, ferulic acid,
mangiferin, and glycyrrhizin in the Chinese medicinal preparations
Shiau-feng-saan and Dang-guei-nian-tong-tang. J Pharm Biomed Anal.
40:472–477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wen HL, Liang ZS, Zhang R and Yang K:
Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide improve left ventricular
function in a rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 12:502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xue M, Jiang ZZ, Liu JP, et al:
Comparative study on the anti-inflammatory and immune suppressive
effect of Wilforlide A. Fitoterapia. 81:1109–1112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhong YY, Chen HP, Tan BZ, Yu HH and Huang
XS: Triptolide avoids cisplatin resistance and induces apoptosis
via the reactive oxygen species/nuclear factor-κB pathway in
SKOV3PT platinum-resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Lett.
6:1084–1092. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rousalova I, Banerjee S, Sangwan V, et al:
Minnelide: a novel therapeutic that promotes apoptosis in non-small
cell lung carcinoma in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e774112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cai YY, Lin WP, Li AP and Xu JY: Combined
effects of curcumin and triptolide on an ovarian cancer cell line.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4267–4271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma JX, Sun YL, Wang YQ, Wu HY, Jin J and
Yu XF: Triptolide induces apoptosis and inhibits the growth and
angiogenesis of human pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating
COX-2 and VEGF. Oncol Res. 20:359–368. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu C, Zhang Y, Kong X, et al: Triptolide
prevents bone destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model
of rheumatoid arthritis by targeting RANKL/RANK/OPG signal Pathway.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:6260382013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Straughn JM Jr
and Buchsbaum DJ: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: a
review. Gynecol Oncol. 131:772–779. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Huang GL, Luo Q, Rui G, Zhang W, Zhang QY,
Chen QX and Shen DY: Oncogenic activity of retinoic acid receptor γ
is exhibited through activation of the Akt/NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin
pathways in cholangiocarcinoma. Mol Cell Biol. 33:3416–3425.
2013.
|
|
12
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Minde DP, Radli M, Forneris F, Maurice MM
and Rüdiger SG: Large extent of disorder in adenomatous polyposis
coli offers a strategy to guard Wnt signalling against point
mutations. PLoS One. 8:e772572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rahmani M, Read JT, Carthy JM, et al:
Regulation of the versican promoter by the beta-catenin-T-cell
factor complex in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem.
280:13019–13028. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin T, George Fantus I and Sun J: Wnt and
beyond Wnt: multiple mechanisms control the transcriptional
property of beta-catenin. Cell Signal. 20:1697–1704. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tarapore RS, Siddiqui IA and Mukhtar H:
Modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by bioactive food
components. Carcinogenesis. 33:483–491. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Kim JH, Kim B, Cai L, et al:
Transcriptional regulation of a metastasis suppressor gene by Tip60
and beta-catenin complexes. Nature. 434:921–926. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Essers MA, de Vries-Smits LM, Barker N, et
al: Functional interaction between beta-catenin and FOXO in
oxidative stress signaling. Science. 308:1181–1184. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Park SW and Kim YI: Triptolide induces
apoptosis of PMA-treated THP-1 cells through activation of
caspases, inhibition of NF-κB and activation of MAPKs. Int J Oncol.
43:1169–1175. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan BJ and Chiu GN: Role of oxidative
stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and ERK activation in
triptolide-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 42:1605–1612.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chueh FS, Chen YL, Hsu SC, et al:
Triptolide induced DNA damage in A375.S2 human malignant melanoma
cells is mediated via reduction of DNA repair genes. Oncol Rep.
29:613–618. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|