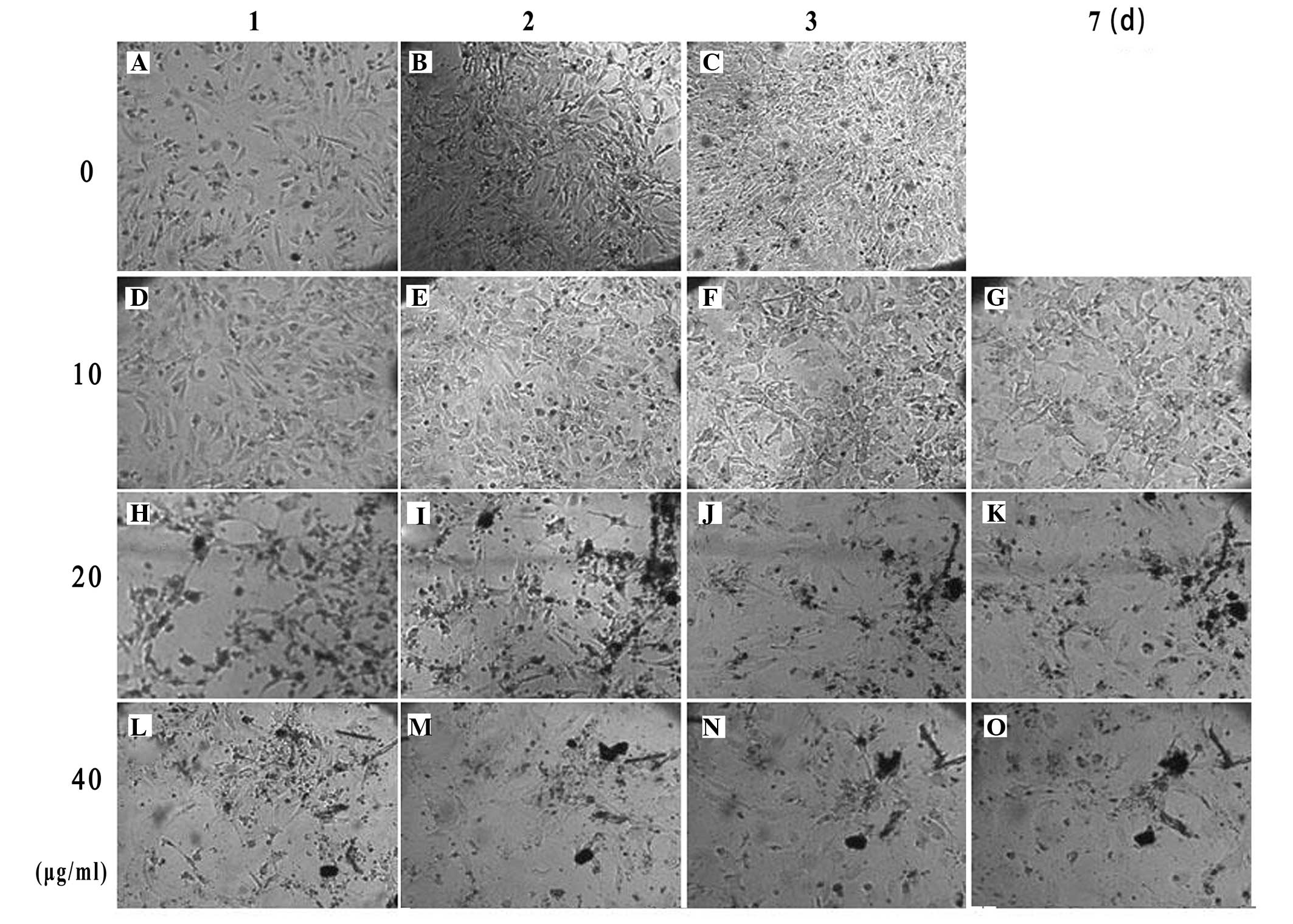
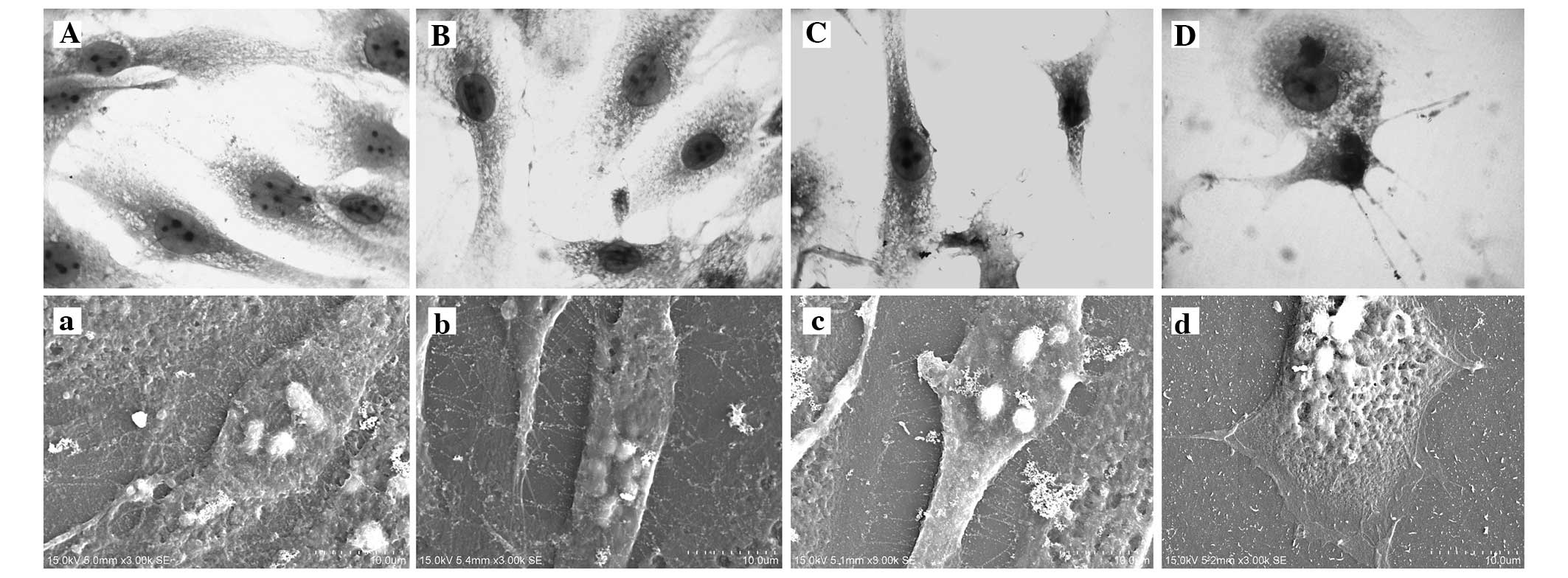
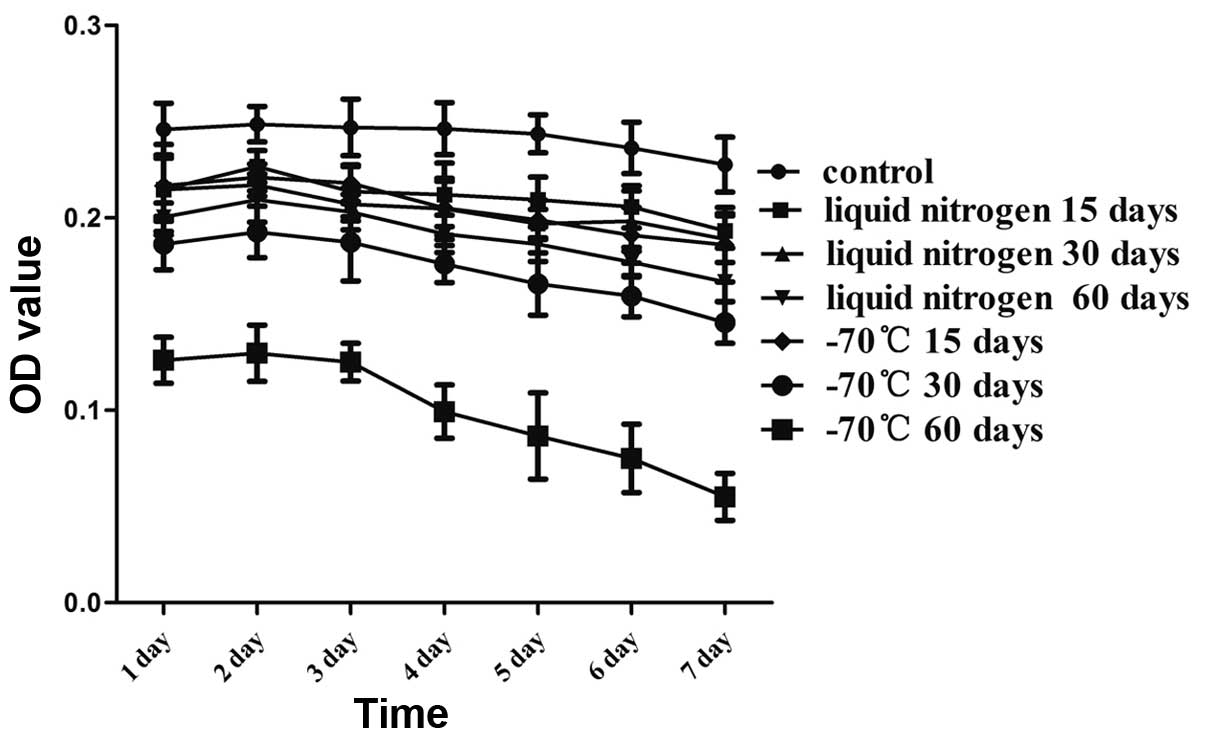
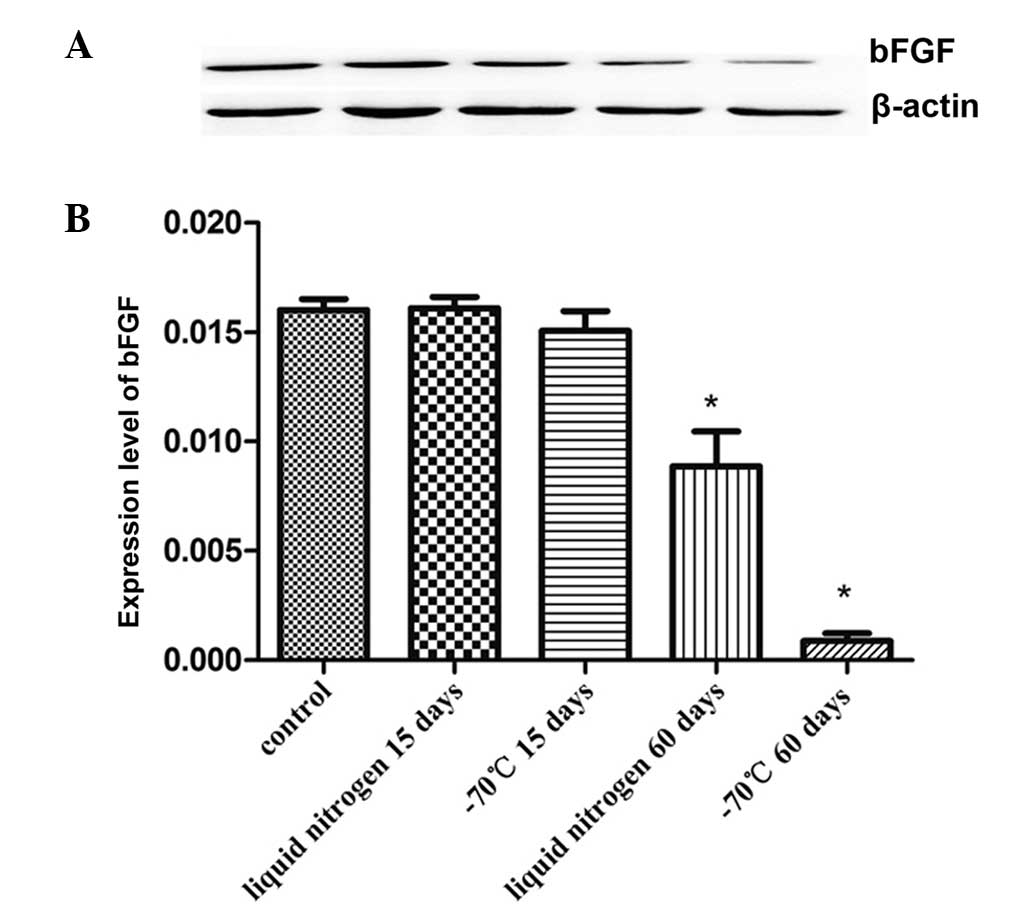
|
1
|
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS,
et al: Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts.
Science. 282:1145–1147. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Niwa H: How is pluripotency determined and
maintained? Development. 134:635–646. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Darabi R and Perlingeiro RC:
Lineage-specific reprogramming as a strategy for cell therapy. Cell
Cycle. 7:1732–1737. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, et al:
Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic
differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 18:399–404. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hovatta O, Mikkola M, Gertow K, et al: A
culture system using human foreskin fibroblasts as feeder cells
allows production of human embryonic stem cells. Hum Reprod.
18:1404–1409. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng L, Hammond H, Ye Z, et al: Human
adult marrow cells support prolonged expansion of human embryonic
stem cells in culture. Stem Cells. 21:131–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inzunza J, Gertow K, Strömberg MA, et al:
Derivation of human embryonic stem cell lines in serum replacement
medium using postnatal human fibroblasts as feeder cells. Stem
Cells. 23:544–549. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lim JW and Bodnar A: Proteome analysis of
conditioned medium from mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder layers
which support the growth of human embryonic stem cells. Proteomics.
2:1187–1203. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cai J, Chen J, Liu Y, et al: Assessing
self-renewal and differentiation in human embryonic stem cell
lines. Stem Cells. 24:516–530. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chin AC, Fong WJ, Goh LT, et al:
Identification of proteins from feeder conditioned medium that
support human embryonic stem cells. J Biotechnol. 130:320–328.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Levenstein ME, Ludwig TE, Xu RH, et al:
Basic fibroblast growth factor support of human embryonic stem cell
self-renewal. Stem Cells. 24:568–574. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang G, Zhang H, Zhao Y, et al: Noggin and
bFGF cooperate to maintain the pluripotency of human embryonic stem
cells in the absence of feeder layers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
330:934–942. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park Y, Kim JH, Lee SJ, et al: Human
feeder cells can support the undifferentiated growth of human and
mouse embryonic stem cells using their own basic fibroblast growth
factors. Stem Cells Dev. 20:1901–1910. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin S and Talbot P: Methods for culturing
mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 690:31–56.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu J, Hu S, Ma Q, et al: Immortalized
mouse fetal liver stromal cells support growth and maintenance of
human embryonic stem cells. Oncol Rep. 28:1385–1391.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Talbot MJ and White RG: Cell surface and
cell outline imaging in plant tissues using the backscattered
electron detector in a variable pressure scanning electron
microscope. Plant Methods. 9:402013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee DY, Lee MK, Kim GS, et al: Brazilin
inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells.
Molecules. 18:2449–2457. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang N, Ren GD, Zhou Z, et al: Cooperation
of myocardin and Smad2 in inducing differentiation of mesenchymal
stem cells into smooth muscle cells. IUBMB Life. 64:331–339. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li C, Yang Y, Lu X, et al: Efficient
derivation of Chinese human embryonic stem cell lines from frozen
embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 46:186–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brockbank KG, Carpenter JF and Dawson PE:
Effects of storage temperature on viable bioprosthetic heart
valves. Cryobiology. 29:537–542. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Galmes A, Besalduch J, Bargay J, et al:
Long-term storage at −80 degrees C of hematopoietic progenitor
cells with 5-percent dimethyl sulfoxide as the sole cryoprotectant.
Transfusion. 39:70–73. 1999.
|
|
22
|
Massie I, Selden C, Hodgson H and Fuller
B: Storage temperatures for cold-chain delivery in cell therapy: a
study of alginate-encapsulated liver cell spheroids stored at −80°C
or −170°C for up to 1 year. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 19:189–195.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu J, Hou R, Booth CJ, et al: Defined
culture conditions of human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:5688–5693. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murai T, Sato M, Nishiyama H, et al:
Ultrastructural analysis of nanogold-labeled cell surface
microvilli in liquid by atmospheric scanning electron microscopy
and their relevance in cell adhesion. Int J Mol Sci.
14:20809–20819. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ubelmann F, Chamaillard M, El-Marjou F, et
al: Enterocyte loss of polarity and gut wound healing rely upon the
F-actin-severing function of villin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:E1380–E1389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ozolek JA, Jane EP, Esplen JE, et al: In
vitro neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells using a
low-density mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder protocol. Methods Mol
Biol. 584:71–95. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heng BC, Liu H and Cao T: Feeder cell
density - a key parameter in human embryonic stem cell culture. In
Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 40:255–257. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park SP, Lee YJ, Lee KS, et al:
Establishment of human embryonic stem cell lines from frozen-thawed
blastocysts using STO cell feeder layers. Hum Reprod. 19:676–684.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hou P, Li Y, Zhang X, et al: Pluripotent
stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule
compounds. Science. 341:651–654. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maherali N and Hochedlinger K: Guidelines
and techniques for the generation of induced pluripotent stem
cells. Cell Stem Cell. 3:595–605. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|