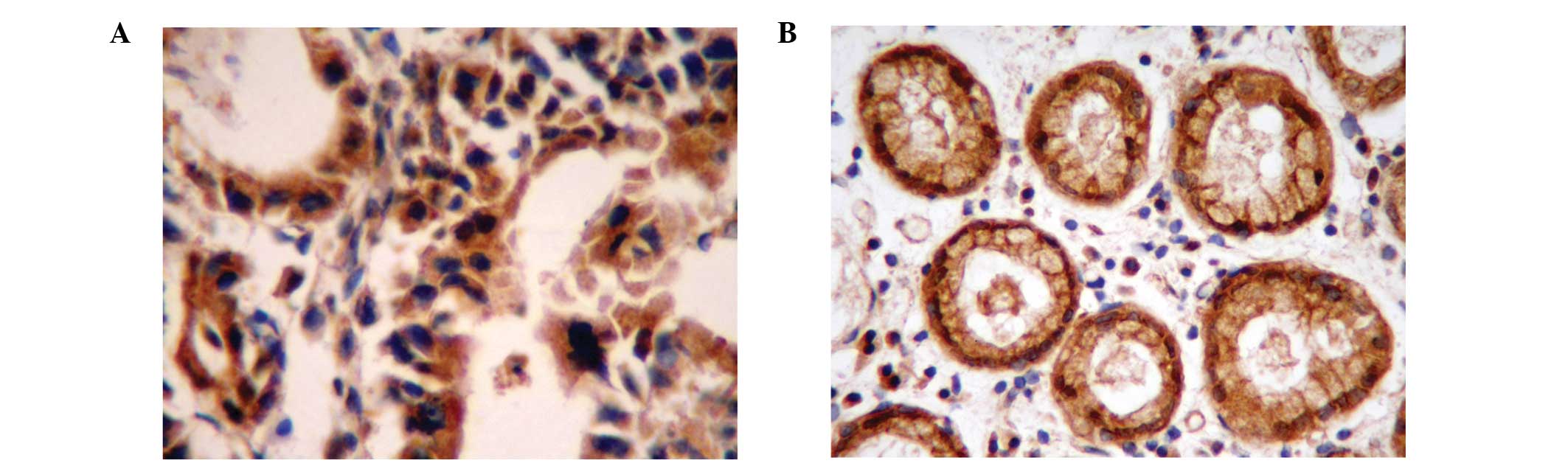
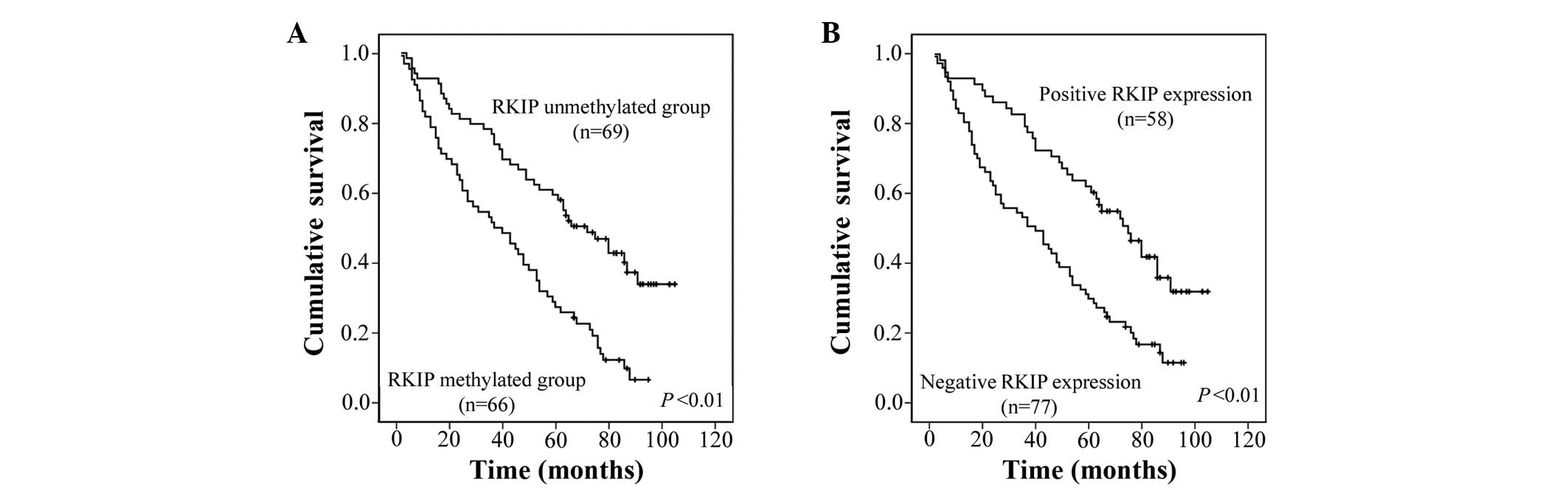
|
1
|
Begnami MD, Fukuda E, Fregnani JH, et al:
Prognostic implications of altered human epidermal growth factor
receptors (HERs) in gastric carcinomas: HER2 and HER3 are
predictors of poor outcome. J Clin Oncol. 29:3030–3036. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang L, Xu Z, Xu X, et al: SALL4, a novel
marker for human gastric carcinogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene.
Nov 25–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
3
|
Tang H, Deng M, Tang Y, et al: miR-200b
and miR-200c as prognostic factors and mediators of gastric cancer
cell progression. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5602–5612. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
You JS and Jones PA: Cancer genetics and
epigenetics: two sides of the same coin? Cancer Cell. 22:9–20.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baylin SB and Jones PA: A decade of
exploring the cancer epigenome - biological and translational
implications. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:726–734. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Taby R and Issa JP: Cancer epigenetics. CA
Cancer J Clin. 60:376–392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hu X, Sui X, Li L, et al: Protocadherin 17
acts as a tumour suppressor inducing tumour cell apoptosis and
autophagy, and is frequently methylated in gastric and colorectal
cancers. J Pathol. 229:62–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu J, Liang QY, Wang J, et al: Zinc-finger
protein 331, a novel putative tumor suppressor, suppresses growth
and invasiveness of gastric cancer. Oncogene. 32:307–317. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du W, Wang S, Zhou Q, et al: ADAMTS9 is a
functional tumor suppressor through inhibiting AKT/mTOR pathway and
associated with poor survival in gastric cancer. Oncogene.
32:3319–3328. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, et al: Suppression
of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature.
401:173–177. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fu Z, Smith PC, Zhang L, et al: Effects of
raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on suppression of prostate
cancermetastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:878–889. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Al-Mulla F, Bitar MS, Thiery JP, et al:
Clinical implications for loss or diminution of expression of Raf-1
kinase inhibitory protein and its phosphorylated form in ductal
breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 3:446–464. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zebisch A, Wölfler A, Fried I, et al:
Frequent loss of RAF kinase inhibitor protein expression in acute
myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 26:1842–1849. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Behbehani AI, et al:
Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression in a survival analysis of
colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 24:5672–5679. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Das SK, Bhutia SK, Sokhi UK, et al: Raf
kinase inhibitor RKIP inhibits MDA-9/syntenin-mediated metastasis
in melanoma. Cancer Res. 72:6217–6226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zlobec I, Baker K, Minoo P, et al:
Node-negative colorectal cancer at high risk of distant metastasis
identified by combined analysis of lymph node status, vascular
invasion, and Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein expression. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:143–148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Beach S, Tang H, Park S, et al: Snail is a
repressor of RKIP transcription in metastatic prostate cancer
cells. Oncogene. 27:2243–2248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Al-Mulla F, Bitar MS, Al-Maghrebi M, et
al: Raf kinase inhibitor protein RKIP enhances signaling by
glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Cancer Res. 71:1334–1343.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo W, Dong Z, Guo Y, et al: Aberrant
methylation and loss expression of RKIP is associated with tumor
progression and poor prognosis in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma.
Clin Exp Metastasis. 30:265–275. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hamilton SR and Aaltonen LA: Pathology and
genetics of tumours of the digestive system. World Health
Organization Classification of Tumours. IARC Press; Lyon: 2000
|
|
21
|
Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Al-Ali W, et al: Raf
kinase inhibitor protein: mechanism of loss of expression and
association with genomic instablility. J Clin Pathol. 61:524–529.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chatterjee D, Sabo E, Tavares R and
Resnick MB: Inverse association between Raf kinase inhibitory
protein and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3
expression in gastric adenocarcinoma patients: implications for
clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2994–3001. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hsu YL, Chen CY, Lin IP, et al: 4-Shogaol,
an active constituent of dietary ginger, inhibits metastasis of
MDA-MB-231 human breast adenocarcinoma cells by decreasing the
repression of NF-κB/Snail on RKIP. J Agric Food Chem. 60:852–861.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu SC and Zhang Y: Active DNA
demethylation: many roads lead to Rome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
11:607–620. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo W, Dong Z, Lin X, et al: Decreased
expression and aberrant methylation of Raf kinase inhibitory
protein gene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Invest.
30:703–711. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Poma P, Labbozzetta M, Vivona N, et al:
Analysis of possible mechanisms accounting for Raf-1 kinase
inhibitor protein downregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma.
OMICS. 16:579–588. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martinho O, Gouveia A, Silva P, et al:
Loss of RKIP expression is associated with poor survival in GISTs.
Virchows Arch. 455:277–284. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|