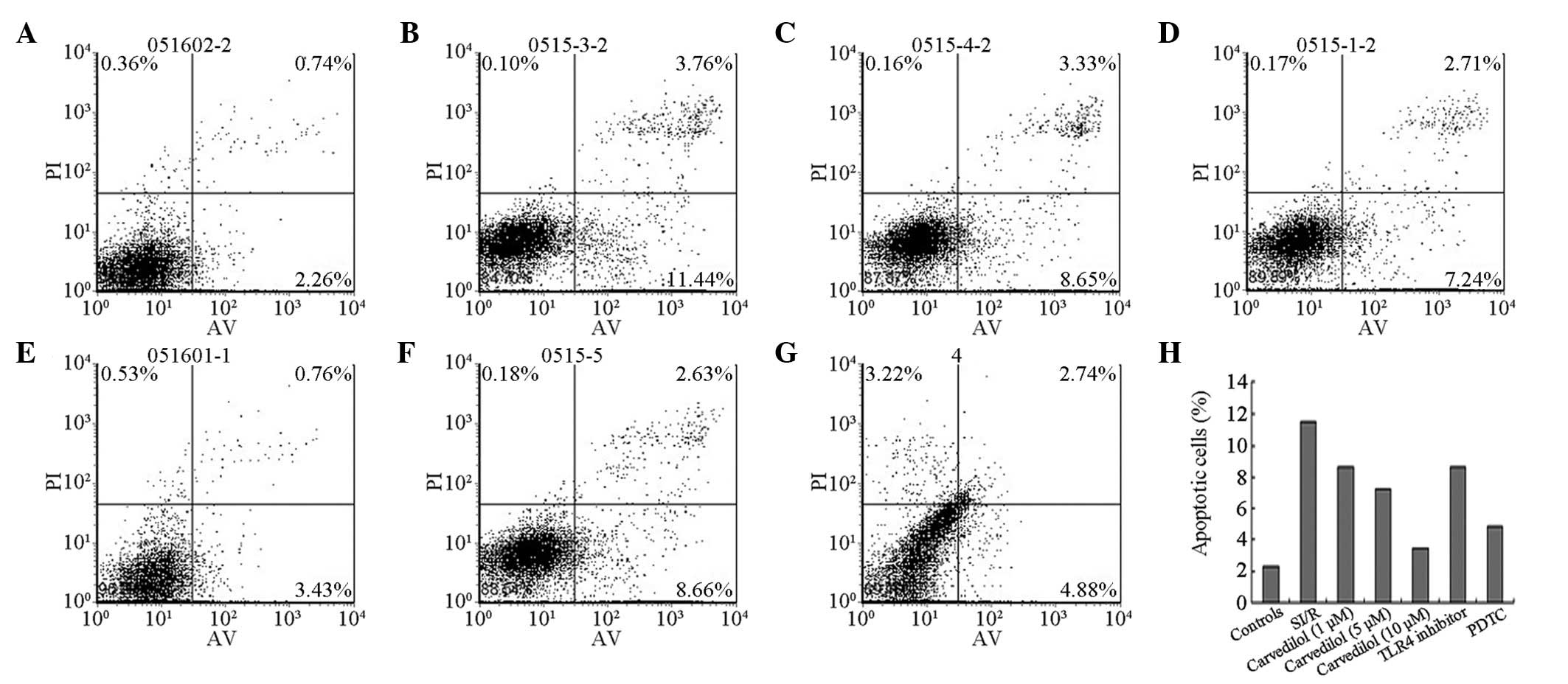
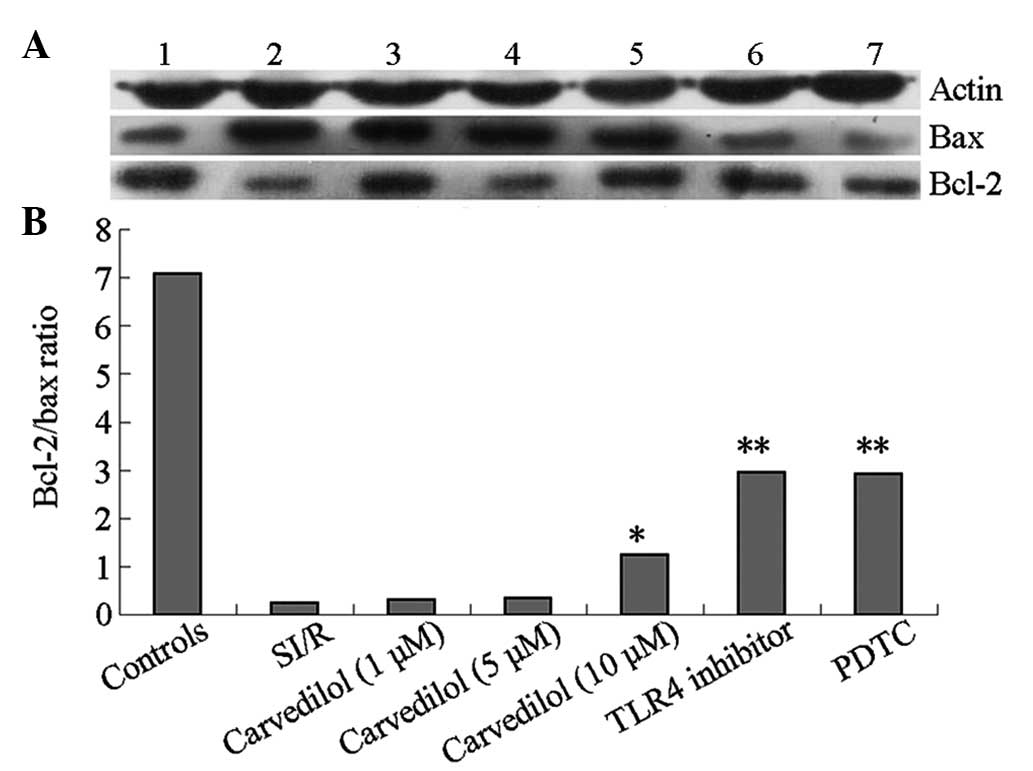
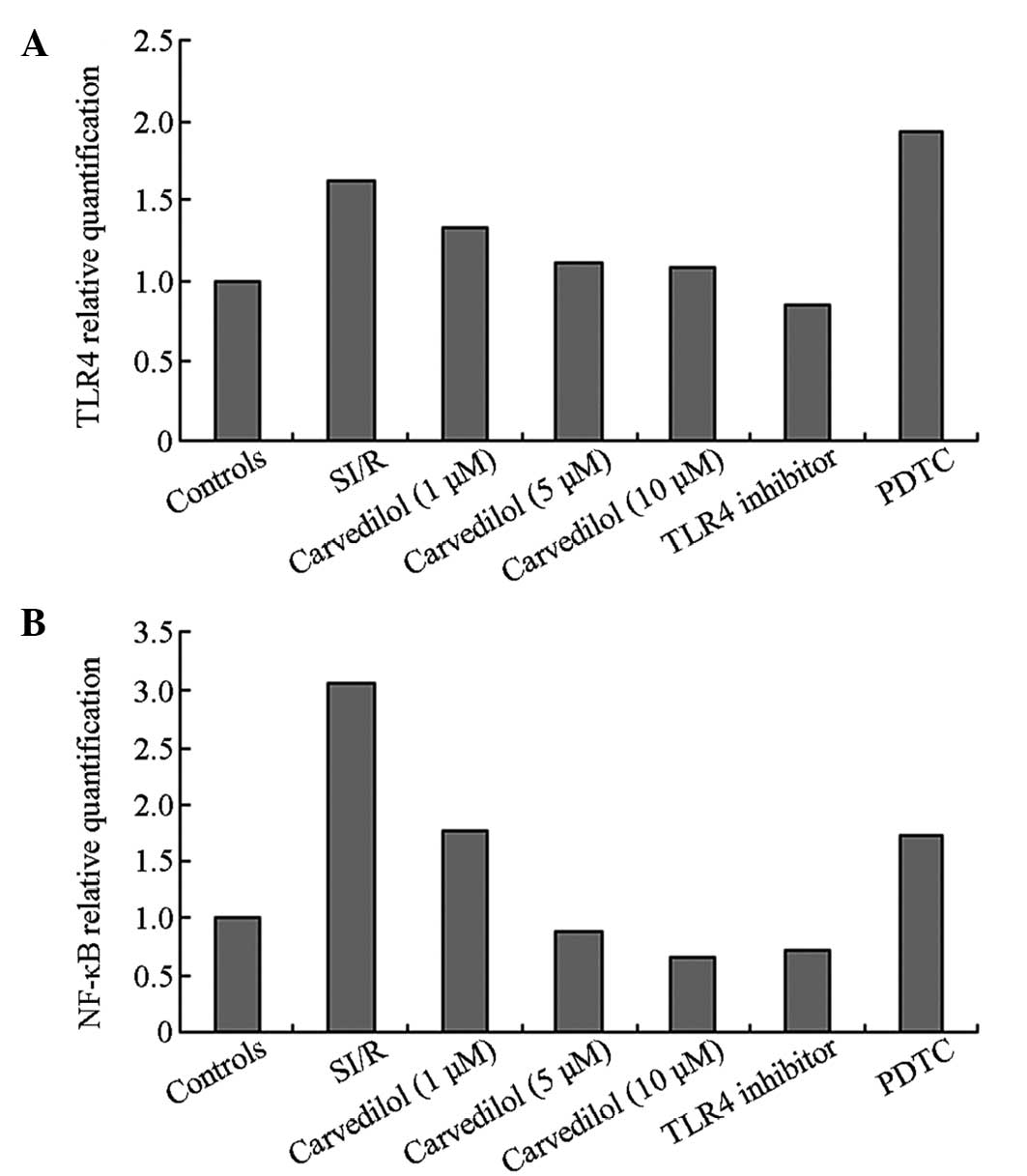
|
1
|
Jayachandran M, Brunn GJ, Karnicki K,
Miller RS, Owen WG and Miller VM: In vivo effects of
lipopolysaccharide and TLR4 on platelet production and activity:
implications for thrombotic risk. J Appl Physiol (1985).
102:429–433. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhong X, Li X, Qian L, et al: Glycine
attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting
myocardial apoptosis in rats. J Biomed Res. 26:346–354. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin J, Wang H, Li J, et al: κ-Opioid
receptor stimulation modulates TLR4/NF-κB signaling in the rat
heart subjected to ischemia-reperfusion. Cytokine. 61:842–848.
2013.
|
|
4
|
Kim SC, Stice JP, Chen L, et al:
Extracellular heat shock protein 60, cardiac myocytes, and
apoptosis. Circ Res. 105:1186–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao P, Wang J, He L, et al: Deficiency in
TLR4 signal transduction ameliorates cardiac injury and
cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction during ischemia. J Cell Mol
Med. 13:1513–1525. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Riad A, Jäger S, Sobirey M, et al:
Toll-like receptor-4 modulates survival by induction of left
ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice. J
Immunol. 180:6954–6961. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leonetti G and Egan CG: Use of carvedilol
in hypertension: an update. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 8:307–322.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kanoupakis EM, Manios EG, Mavrakis HE, et
al: Electrophysiological effects of carvedilol administration in
patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.
22:169–176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Le DE, Pascotto M, Leong-Poi H, Sari I,
Micari A and Kaul S: Anti-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic effects
of beta blockers in a canine model of chronic ischemic
cardiomyopathy: comparison between carvedilol and metoprolol. Basic
Res Cardiol. 108:3842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mori Y, Nishikawa Y, Kobayashi F and
Hiramatsu K: Clinical status and outcome of Japanese heart failure
patients with reduced or preserved ejection fraction treated with
carvedilol. Int Heart J. 54:15–22. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen-Scarabelli C, Saravolatz L Jr, Murad
Y, et al: A critical review of the use of carvedilol in ischemic
heart disease. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 12:391–401. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Q, Zhang J, Xu Y, Huang Y and Wu C:
Effect of carvedilol on cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a rat model of
myocardial infarction: a role for toll-like receptor 4. Indian J
Pharmacol. 45:458–463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Esumi K, Nishida M, Shaw D, Smith TW and
Marsh JD: NADH measurements in adult rat myocytes during simulated
ischemia. Am J Physiol. 260:H1743–1752. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dargie HJ: Effect of carvedilol on outcome
after myocardial infarction in patients with left-ventricular
dysfunction: the CAPRICORN randomised trial. Lancet. 357:1385–1390.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin YC, Kim CW, Kim YM, et al:
Cryptotanshinone, a lipophilic compound of Salvia
miltiorrriza root, inhibits TNF-alpha-induced expression of
adhesion molecules in HUVEC and attenuates rat myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol.
614:91–97. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin E, Freedman JE and Beaulieu LM: Innate
immunity and toll-like receptor antagonists: a potential role in
the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc Ther.
27:117–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ishikawa Y, Satoh M, Itoh T, Minami Y,
Takahashi Y and Akamura M: Local expression of Toll-like receptor 4
at the site of ruptured plaques in patients with acute myocardial
infarction. Clin Sci (Lond). 115:133–140. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Poole-Wilson PA, Swedberg K, Cleland JG,
et al: Carvedilol Or Metoprolol European Trial Investigators:
Comparison of carvedilol and metoprolol on clinical outcomes in
patients with chronic heart failure in the Carvedilol Or Metoprolol
European Trial (COMET): randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
362:7–13. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fiuzat M, Wojdyla D, Kitzman D, et al:
Relationship of beta-blocker dose with outcomes in ambulatory heart
failure patients with systolic dysfunction: results from the
HF-ACTION (Heart Failure: A Controlled Trial Investigating Outcomes
of Exercise Training) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 60:208–215. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Soriano ME and Scorrano L: Traveling Bax
and forth from mitochondria to control apoptosis. Cell. 145:15–17.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Condorelli G, Morisco C, Stassi G, et al:
Increased cardiomyocyte apoptosis and changes in proapoptotic and
antiapoptotic genes bax and bcl-2 during left ventricular
adaptations to chronic pressure overload in the rat. Circulation.
99:3071–3078. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shimamoto A, Chong AJ, Yada M, et al:
Inhibition of Toll-like receptor 4 with eritoran attenuates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulation. 114(1 Suppl):
I270–I274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|