Spandidos Publications style
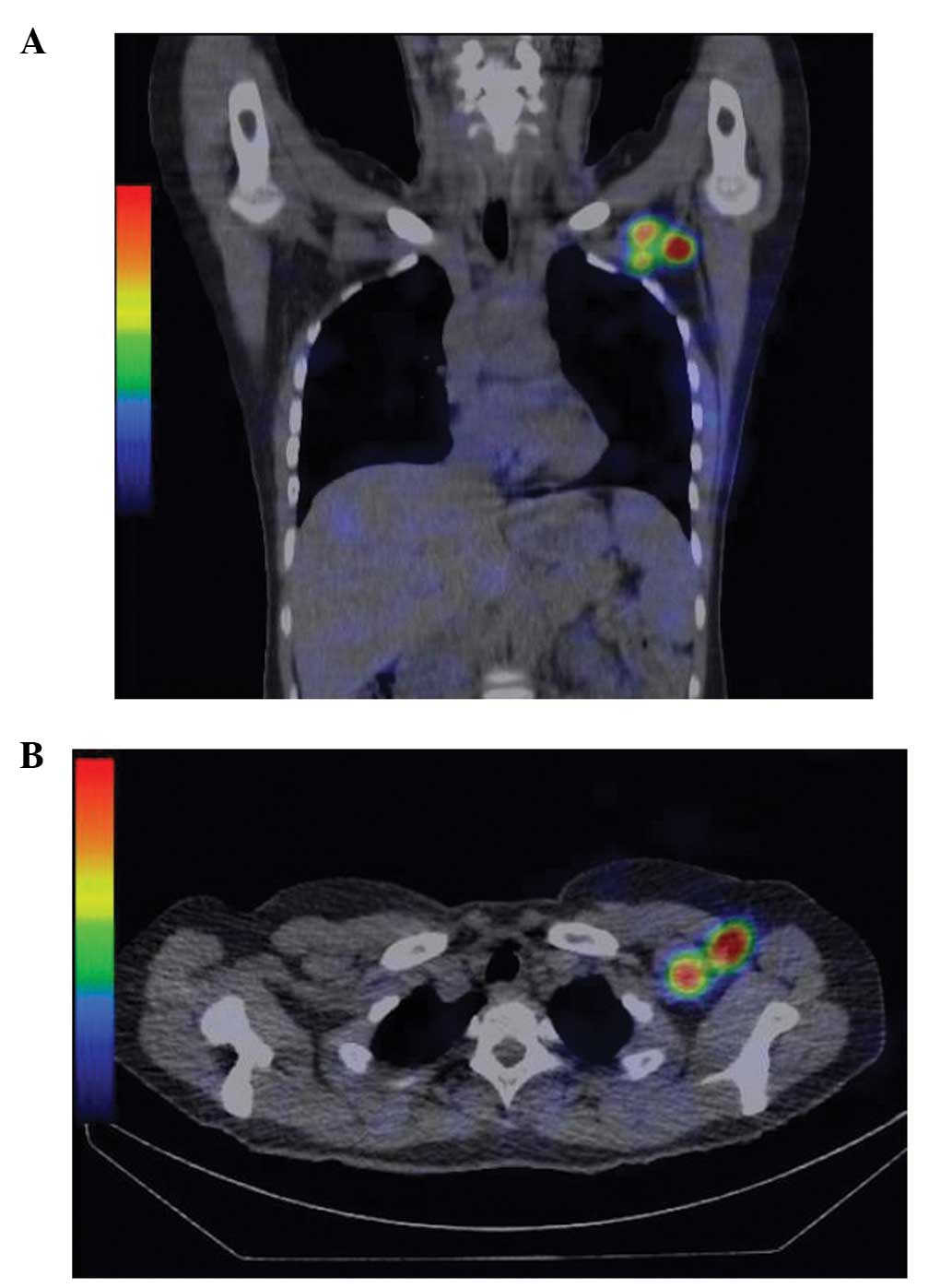
Shima H, Kutomi G, Satomi F, Maeda H, Takamaru T, Kameshima H, Omura T, Mori M, Hatakenaka M, Hasegawa T, Hasegawa T, et al: Risk of node metastasis of sentinel lymph nodes detected in level II/III of the axilla by single‑photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography. Exp Ther Med 8: 1447-1452, 2014.
APA
Shima, H., Kutomi, G., Satomi, F., Maeda, H., Takamaru, T., Kameshima, H. ... Hirata, K. (2014). Risk of node metastasis of sentinel lymph nodes detected in level II/III of the axilla by single‑photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 8, 1447-1452. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1968
MLA
Shima, H., Kutomi, G., Satomi, F., Maeda, H., Takamaru, T., Kameshima, H., Omura, T., Mori, M., Hatakenaka, M., Hasegawa, T., Hirata, K."Risk of node metastasis of sentinel lymph nodes detected in level II/III of the axilla by single‑photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 8.5 (2014): 1447-1452.
Chicago
Shima, H., Kutomi, G., Satomi, F., Maeda, H., Takamaru, T., Kameshima, H., Omura, T., Mori, M., Hatakenaka, M., Hasegawa, T., Hirata, K."Risk of node metastasis of sentinel lymph nodes detected in level II/III of the axilla by single‑photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 8, no. 5 (2014): 1447-1452. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1968