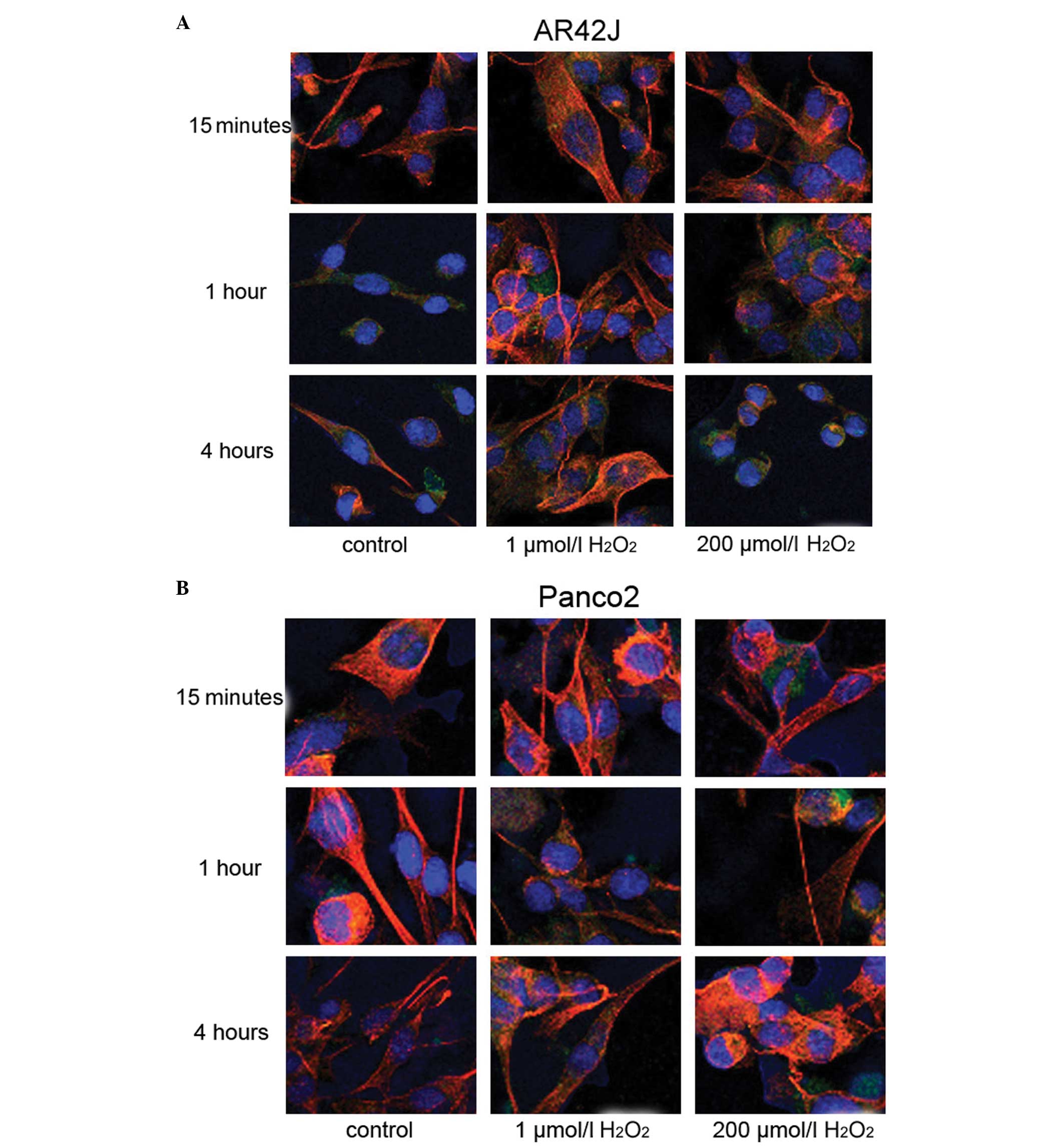
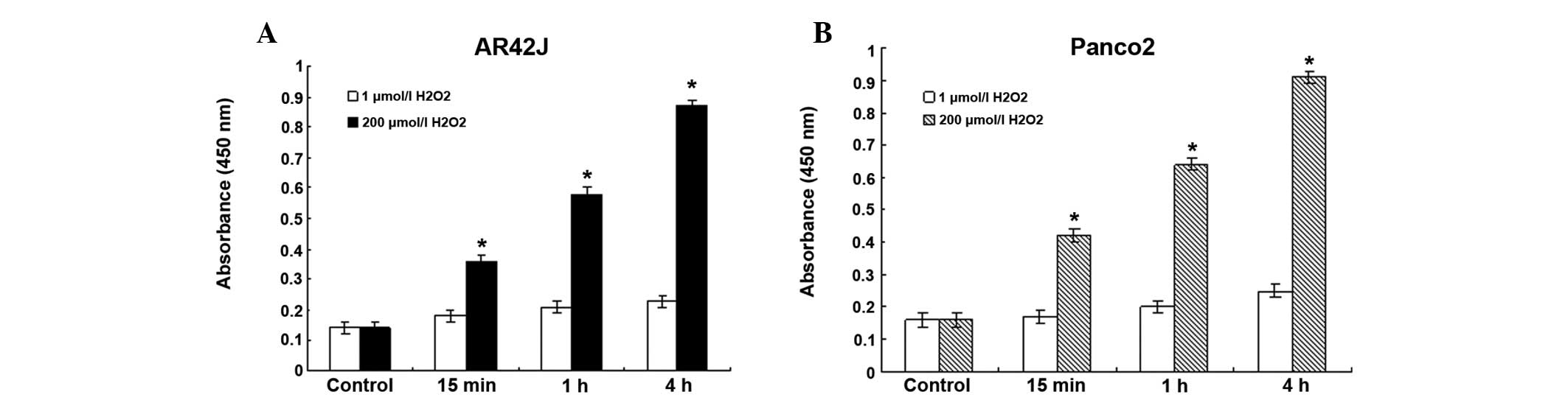
|
1
|
Schulz HU, Niederau C, Klonowski-Stumpe H,
et al: Oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis.
Hepatogastroenterology. 46:2736–2750. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Verlaan M, Roelofs HM, van-Schaik A, et
al: Assessment of oxidative stress in chronic pancreatitis
patients. World J Gastroenterol. 12:5705–5710. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li J, Lee JM and Johnson JA: Microarray
analysis reveals an antioxidant responsive element-driven gene set
involved in conferring protection from an oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis in IMR-32 cells. J Biol Chem. 277:388–394. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dandrea T, Hellmold H, Jonsson C, et al:
The transcriptosomal response of human A549 lung cells to a
hydrogen peroxide-generating system: relationship to DNA damage,
cell cycle arrest, and caspase activation. Free Radic Biol Med.
36:881–896. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Katsube T, Tsuji H and Onoda M: Nitric
oxide attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced barrier disruption and
protein tyrosine phosphorylation in monolayers of intestinal
epithelial cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1773:794–803. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tudek B, Winczura A, Janik J, et al:
Involvement of oxidatively damaged DNA and repair in cancer
development and aging. Am J Transl Res. 2:254–284. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jałoszyński P, Jaruga P, Oliński R, et al:
Oxidative DNA base modifications and polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbon DNA adducts in squamous cell carcinoma of larynx. Free
Radic Res. 37:231–240. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lim JW, Song JY, Seo JY, et al: Role of
pancreatitis-associated protein 1 on oxidative stress-induced cell
death of pancreatic acinar cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1171:545–548.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weber H, Hühns S, Jonas L, et al: Hydrogen
peroxide-induced activation of defense mechanisms against oxidative
stress in rat pancreatic acinar AR42J. Free Radic Biol Med.
42:830–841. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Etemad B and Whitcomb DC: Chronic
pancreatitis: diagnosis, classification, and new genetic
developments. Gastroenterology. 120:682–707. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weber H, Hühns S, Lüthen F and Joanas L:
Calpain-mediated breakdown of cytoskeletal proteins contributes to
cholecystokinin-induced damage of rat pancreatic acini. Int J Exp
Pathol. 90:387–399. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Banan A, Choudhary S, Zhang Y, et al:
Oxidant-induced intestinal barrier disruption and its prevention by
growth factors in a human colonic cell line: role of the
microtubule cytoskeleton. Free Radic Biol Med. 28:727–738. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fatokun AA, Stone TW and Smith RA:
Hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 cells: The
effects of glutamate and protection by purines. Bone. 39:542–551.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Valen G, Sondén A, Vaage J, et al:
Hydrogen peroxide induces endothelial cell atypia and cytoskeleton
depolymerization. Free Radic Biol Med. 26:1480–1488. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bijlsma MF, Borensztajn KS, Roelink H, et
al: Sonic hedgehog induces transcription-independent cytoskeletal
rearrangement and migration regulated by arachidonate metabolites.
Cell Signal. 19:2596–2604. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Banan A, Keshavarzian A, Zhang L, et al:
NF-kappaB activation as a key mechanism in ethanol-induced
disruption of the F-actin cytoskeleton and monolayer barrier
integrity in intestinal epithelium. Alcohol. 41:447–460. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nakashima H, Nakamura M, Yamaguchi H, et
al: Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to hedgehog signaling pathway
activation through sonic hedgehog induction in pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:7041–7049. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Arjona-Sánchez A, Ruiz-Rabelo J, Perea MD,
et al: Effects of capecitabine and celecoxib in experimental
pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 10:641–647. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|