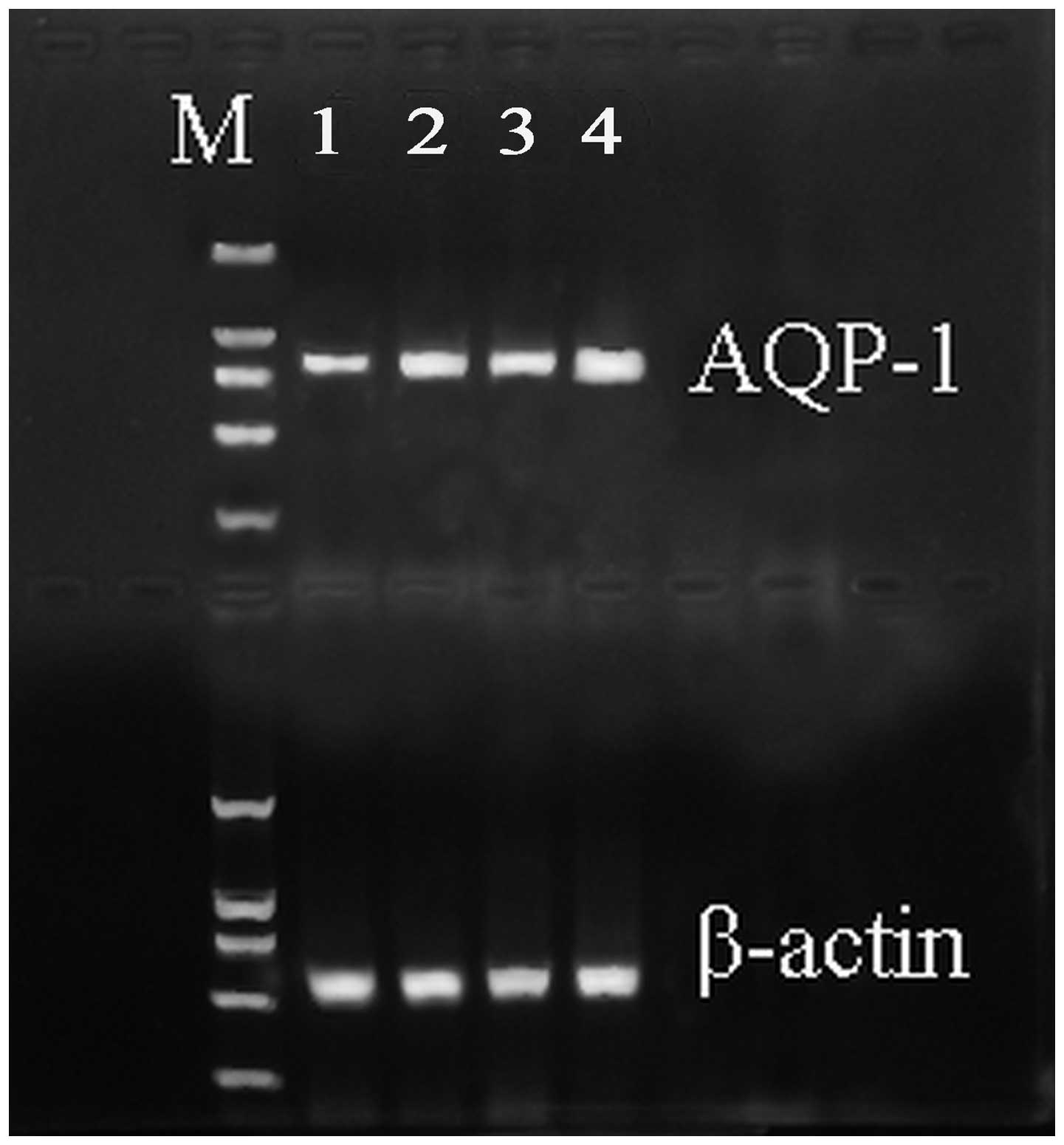
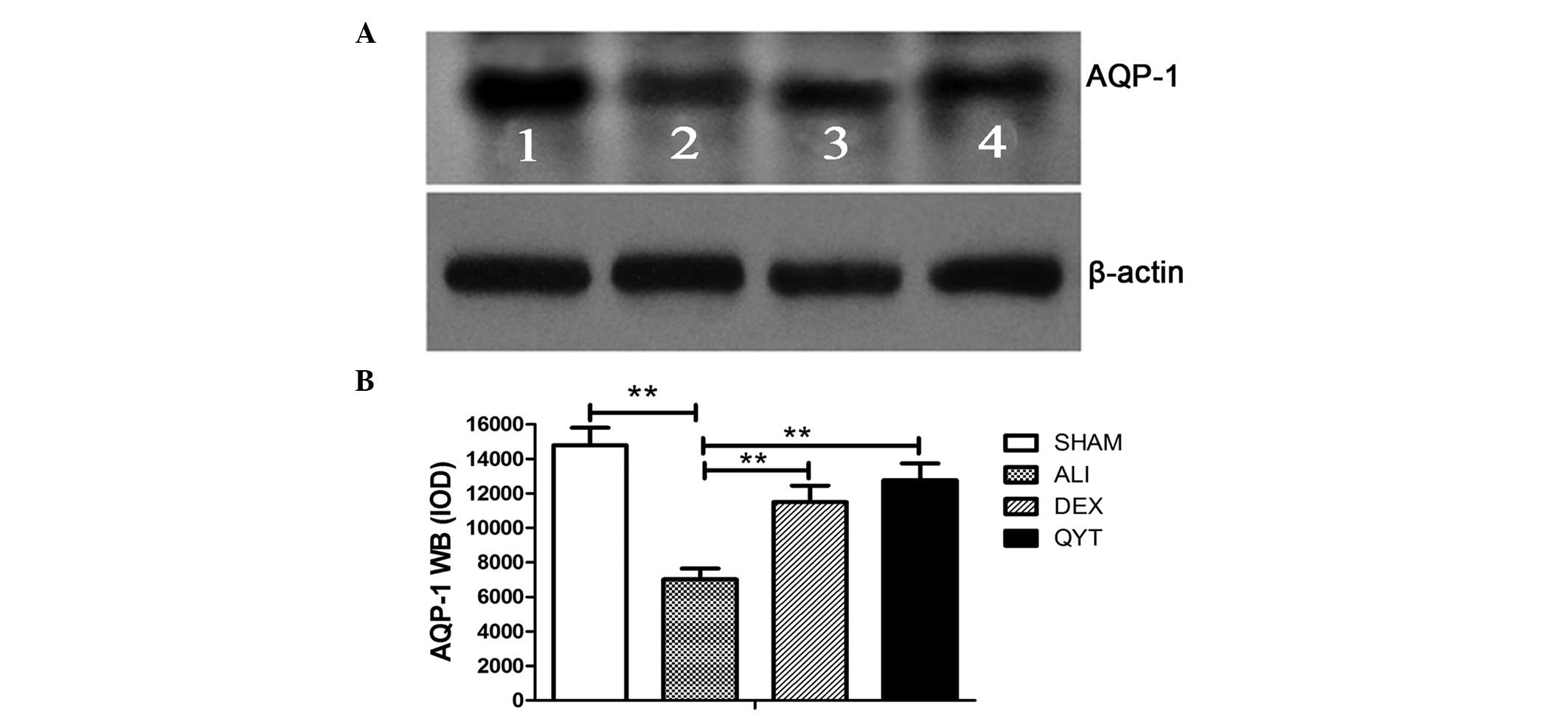
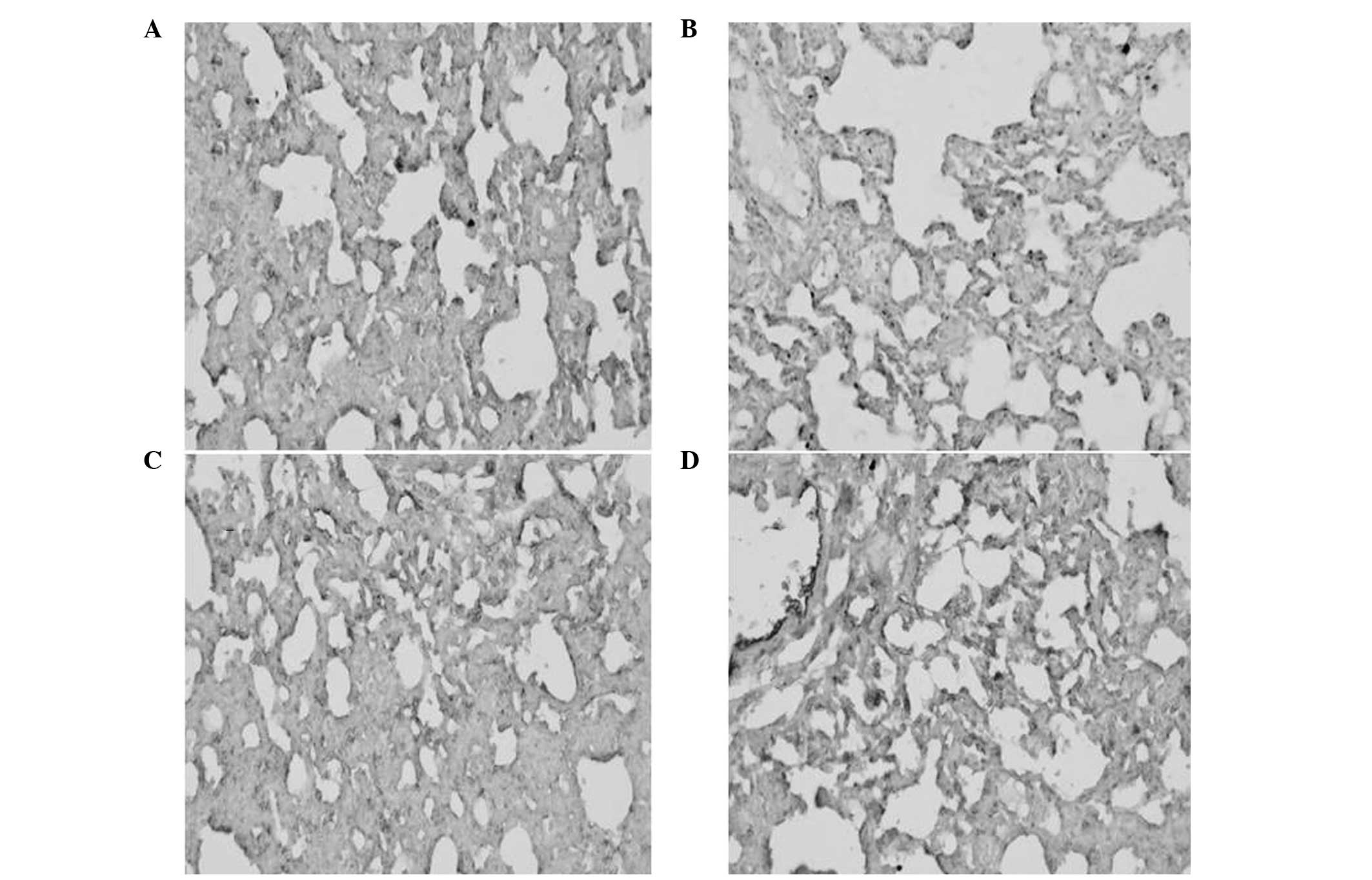
|
1
|
Verkman AS: Aquaporins in clinical
medicine. Annu Rev Med. 63:303–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Agre P, Bonhivers M and Borgnia MJ: The
aquaporins, blueprints for cellular plumbing systems. J Biol Chem.
273:14659–14662. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Benga G: On the definition, nomenclature
and classification of water channel proteins (aquaporins and
relatives). Mol Aspects Med. 33:514–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Denker BM, Smith BL, Kuhajda FP and Agre
P: Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a
novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and
renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 263:15634–15642. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Verkman AS: Mammalian aquaporins: diverse
physiological roles and potential clinical significance. Expert Rev
Mol Med. 10:e132008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mobasheri A and Marples D: Expression of
the AQP-1 water channel in normal human tissues: a semiquantitative
study using tissue microarray technology. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 286:C529–C537. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Hara-Chikuma M
and Verkman AS: Impairment of angiogenesis and cell migration by
targeted aquaporin-1 gene disruption. Nature. 434:786–792. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma T, Yang B, Gillespie A, et al: Severely
impaired urinary concentrating ability in transgenic mice lacking
aquaporin-1 water channels. J Biol Chem. 273:4296–4299. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li ZZ, Xing L, Zhao ZZ, et al: Decrease of
renal aquaporins 1–4 is associated with renal function impairment
in pediatric congenital hydronephrosis. World J Pediatr. 8:335–341.
2012.
|
|
10
|
Heinrich S, Schafer M, Rousson V and
Clavien PA: Evidence-based treatment of acute pancreatitis: a look
at established paradigms. Ann Surg. 243:154–168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Windsor JA and Petrov MS: Acute
pancreatitis reclassified. Gut. 62:4–5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shields CJ, Winter DC and Redmond HP: Lung
injury in acute pancreatitis: mechanisms, prevention, and therapy.
Curr Opin Crit Care. 8:158–163. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou MT, Chen CS, Chen BC, Zhang QY and
Andersson R: Acute lung injury and ARDS in acute pancreatitis:
mechanisms and potential intervention. World J Gastroenterol.
16:2094–2099. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Surbatović M, Jovanović K, Radaković S and
Filipović N: Pathophysiological aspects of severe acute
pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 133:76–81.
2005.(In Serbian).
|
|
15
|
Mayer J, Rau B, Gansauge F and Beger HG:
Inflammatory mediators in human acute pancreatitis: clinical and
pathophysiological implications. Gut. 47:546–552. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Neuhöfer P, Song L, et al: IL-6
trans-signaling promotes pancreatitis-associated lung injury and
lethality. J Clin Invest. 123:1019–1031. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Towne JE, Harrod KS, Krane CM and Menon
AG: Decreased expression of aquaporin (AQP)1 and AQP5 in mouse lung
after acute viral infection. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 22:34–44.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Burdick MD, et al:
Critical role for CXCR2 and CXCR2 ligands during the pathogenesis
of ventilator-induced lung injury. J Clin Invest. 110:1703–1716.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang YW, Bi LT, Hou SP, et al: Reduced
lung water transport rate associated with downregulation of
aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-5 in aged mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 36:734–738. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xue D, Zhang W, Zhang Y, et al: Adjusting
effects of baicalin for nuclear factor-kappaB and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha on rats with caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis.
Mediators Inflamm. 2006:262952006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li ZL, Wu CT, Lu LR, Zhu XF and Xiong DX:
Traditional Chinese medicine Qing Yi Tang alleviates oxygen free
radical injury in acute necrotizing pancreatits. World J
Gastroenterol. 4:357–359. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang XP, Shi Y and Zhang L: Progress in
the study of therapeutic effects of traditional Chinese medicine
and extracts in treating severe acute pancreatitis. JOP. 8:704–714.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao YQ, Liu XH, Ito T and Qian JM:
Protective effects of rhubarb on experimental severe acute
pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 10:1005–1009. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang MJ, Zhang GL, Yuan WB, Ni J and
Huang LF: Treatment of abdominal compartment syndrome in severe
acute pancreatitis patients with traditional Chinese medicine.
World J Gastroenterol. 14:3574–3578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sugiyama Y, Kato S, Abe M, Mitsufuji S and
Takeuchi K: Different effects of dexamethasone and the nitric oxide
synthase inhibitor L-NAME on caerulein-induced rat acute
pancreatitis, depending on the severity. Inflammopharmacology.
13:291–301. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kandil E, Lin YY, Bluth MH, et al:
Dexamethasone mediates protection against acute pancreatitis via
upregulation of pancreatitis-associated proteins. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:6806–6811. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang DY, Duan SB and Aili JT: Effect of
QYT in treating severe acute pancreatitis and its impacts on blood
level of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6 and
inteleukin-8. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 29:1122–1124.
2009.(In Chinese).
|