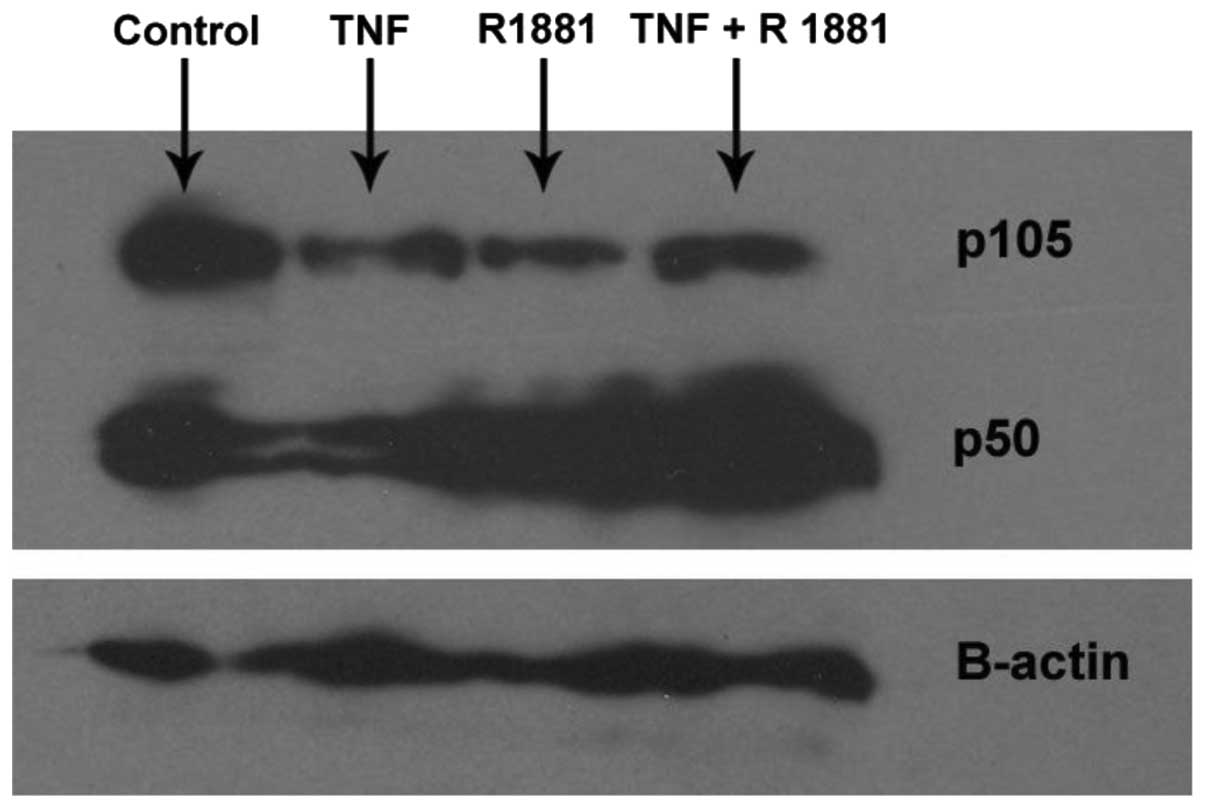
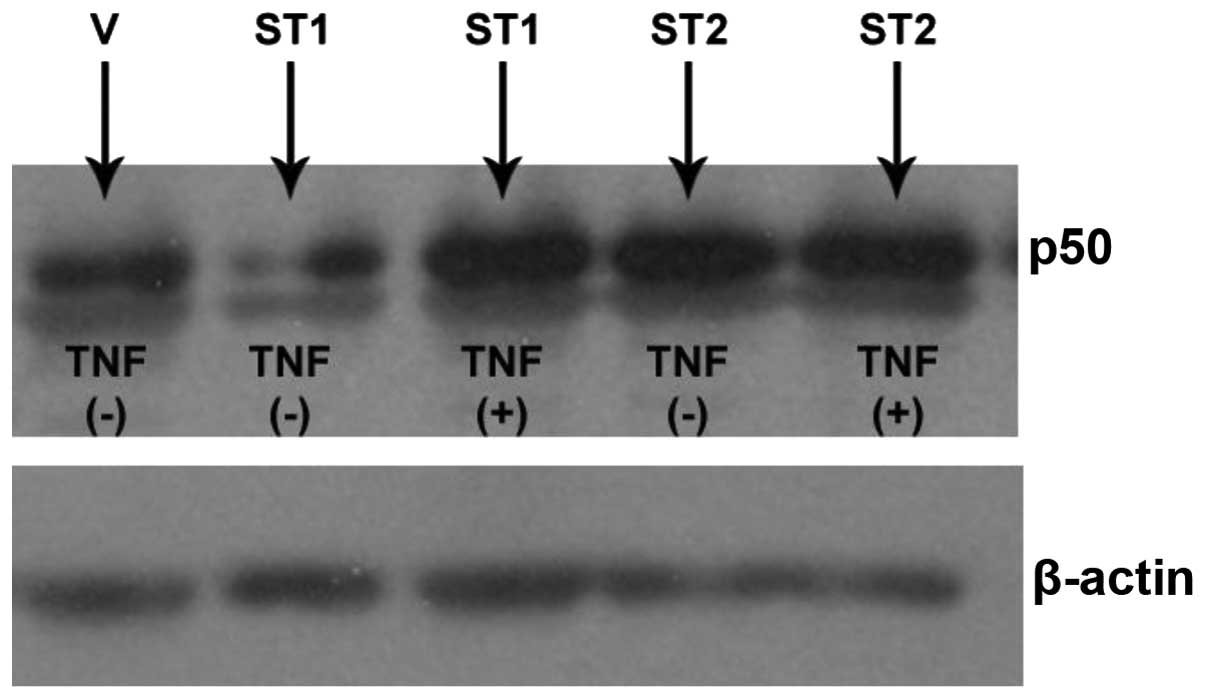
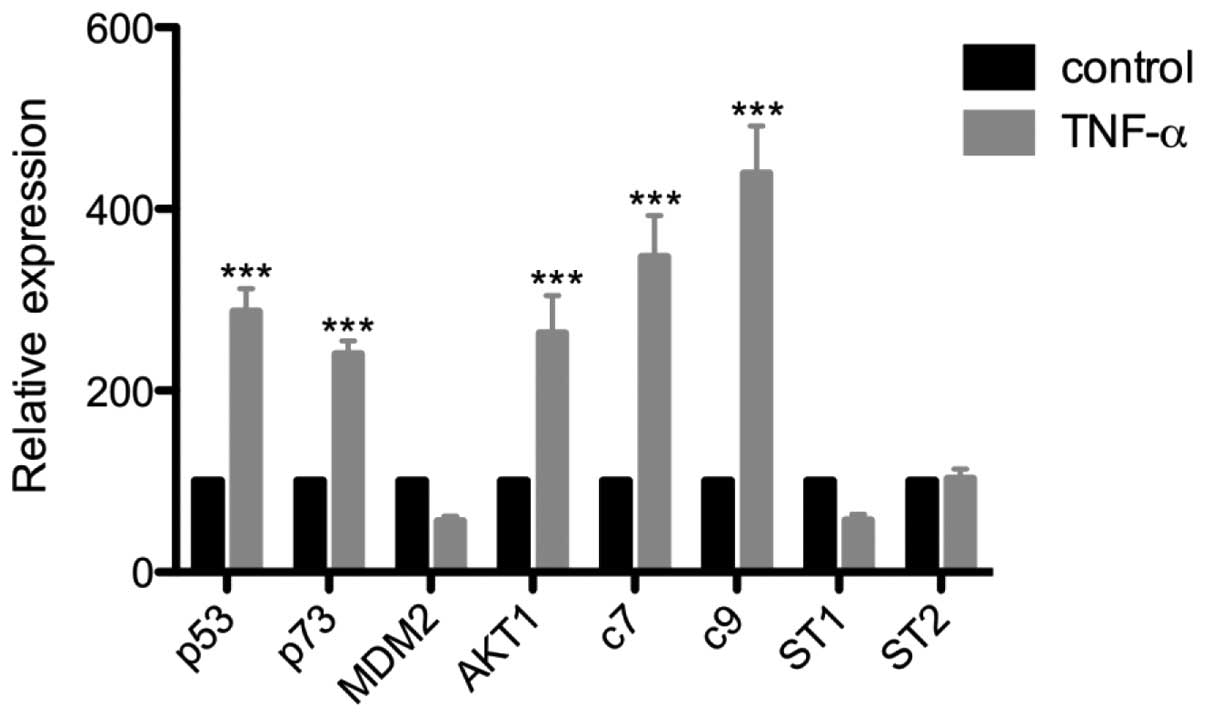
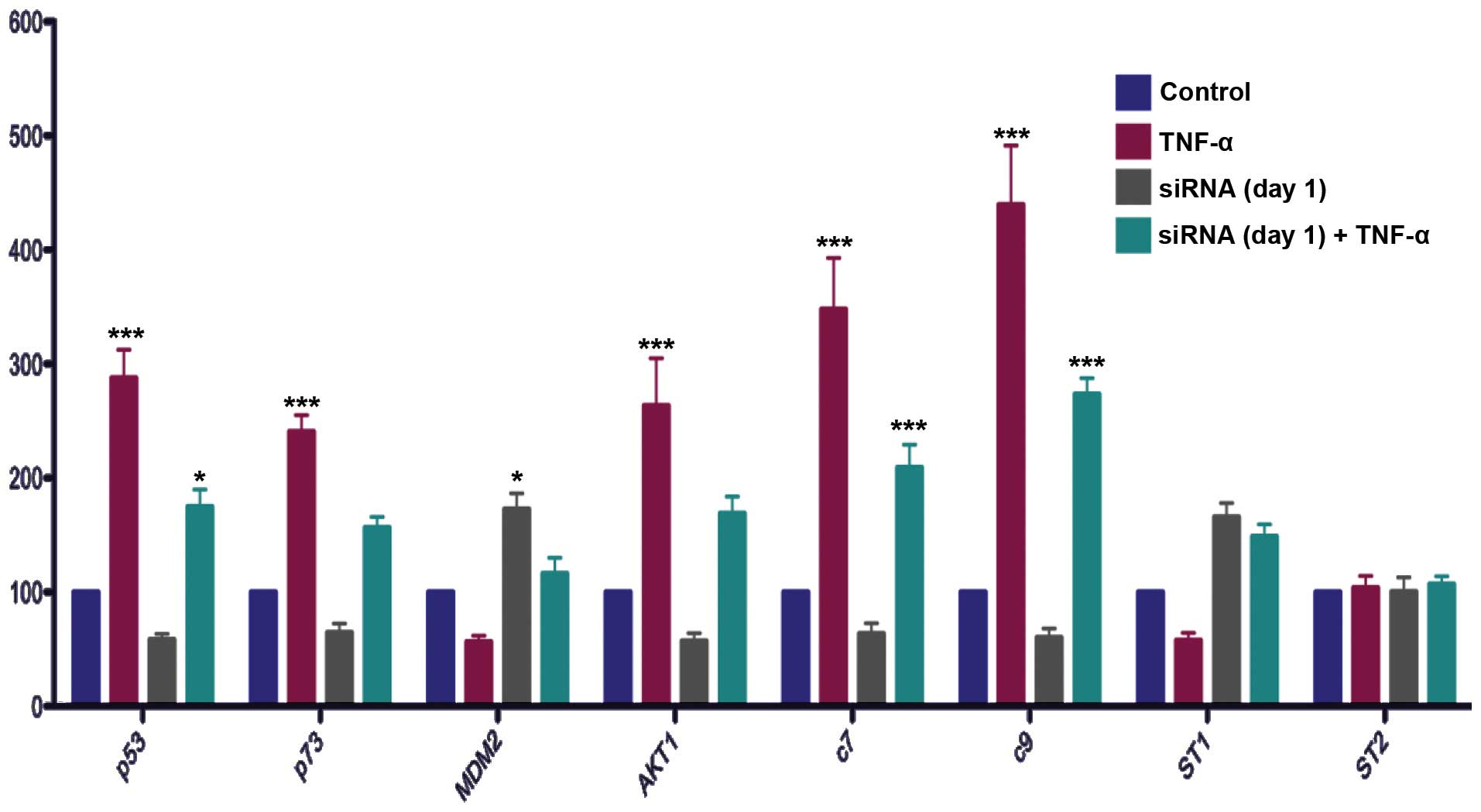
|
1
|
Lorenzo PI, Arnoldussen YJ and Saatcioglu
F: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in prostate cancer. Crit Rev
Oncog. 13:1–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hubert RS, Vivanco I, Chen E, Rastegar S,
Leong K, Mitchell SC, Madraswala R, et al: STEAP: a
prostate-specific cell-surface antigen highly expressed in human
prostate tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:14523–14528. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Korkmaz KS, Elbi C, Korkmaz CG, Loda M,
Hager GL and Saatcioglu F: Molecular cloning and characterization
of STAMP1, a highly prostate-specific six transmembrane protein
that is overexpressed in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem.
277:36689–36696. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Korkmaz CG, Korkmaz KS, Kurys P, Elbi C,
Wang L, Klokk TI, Hammarstrom C, et al: Molecular cloning and
characterization of STAMP2, an androgen-regulated six transmembrane
protein that is overexpressed in prostate cancer. Oncogene.
24:4934–4945. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wellen KE, Fucho R, Gregor MF, Furuhashi
M, Morgan C, Lindstad T, Vaillancourt E, et al: Coordinated
regulation of nutrient and inflammatory responses by STAMP2 is
essential for metabolic homeostasis. Cell. 129:537–548. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Steiner MS, Zhang X, Wang Y and Lu Y:
Growth inhibition of prostate cancer by an adenovirus expressing a
novel tumor suppressor gene, pHyde. Cancer Res. 60:4419–4425.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Passer BJ, Nancy-Portebois V, Amzallag N,
Prieur S, Cans C, Roborel de Climens A, et al: The p53-inducible
TSAP6 gene product regulates apoptosis and the cell cycle and
interacts with Nix and the Myt1 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:2284–2289. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang L, Jin Y, Arnoldussen YJ, Jonson I,
Qu S, Maelandsmo GM, Kristian A, et al: STAMP1 is both a
proliferative and an antiapoptotic factor in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 70:5818–5828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hussain SP and Harris CC: Inflammation and
cancer: an ancient link with novel potentials. Int J Cancer.
121:2373–2380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morgan MJ and Liu Z: Crosstalk of reactive
oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Morgan MJ, Kim YS and Liu ZG: TNFalpha and
reactive oxygen species in necrotic cell death. Cell Res.
18:343–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jablonska E, Piotrowski L and Grabowska Z:
Serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, sTNFR1 and CRP in patients with
oral cavity cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 3:126–129. 1997.
|
|
13
|
Mukhopadhyay A, Bueso-Ramos C, Chatterjee
D, Pantazis P and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin downregulates cell survival
mechanisms in human prostate cancer cell lines. Oncogene.
20:7597–7609. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen X, Kandasamy K and Srivastava RK:
Differential roles of RelA (p65) and c-Rel subunits of nuclear
factor kappa B in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand signaling. Cancer Res. 63:1059–1066. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Tajeddine
N and Kroemer G: Targeting p53 to mitochondria for cancer therapy.
Cell Cycle. 7:1949–1955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vikhanskaya F, Toh WH, Dulloo I, Wu Q,
Boominathan L, Ng HH, Vousden KH and Sabapathy K: p73 supports
cellular growth through c-Jun-dependent AP-1 transactivation. Nat
Cell Biol. 9:698–705. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deeb D, Jiang H, Gao X, Al-Holou S,
Danyluk AL, Dulchavsky SA and Gautam SC: Curcumin
[1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione;
C21H20O6] sensitizes human
prostate cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand/Apo2L-induced apoptosis by suppressing
nuclear factor-kappaB via inhibition of the prosurvival Akt
signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 321:616–625. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Wadgaonkar R and Collins T: Murine double
minute (MDM2) blocks p53-coactivator interaction, a new mechanism
for inhibition of p53-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem.
274:13760–13767. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lamkanfi M and Kanneganti TD: Caspase-7: a
protease involved in apoptosis and inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 42:21–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, Ladron
De Guevara R, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bharti AC and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappa B and cancer: its role in prevention and therapy.
Biochem Pharmacol. 64:883–888. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bharti AC and Aggarwal BB: Chemopreventive
agents induce suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB leading to
chemosensitization. Ann NY Acad Sci. 973:392–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Casanelles E, Gozzelino R,
Marqués-Fernández F, Iglesias-Guimarais V, Garcia-Belinchón M,
Sánchez-Osuna M, Solé C, et al: NF-κB activation fails to protect
cells to TNFα-induced apoptosis in the absence of Bcl-xL, but not
Mcl-1, Bcl-2 or Bcl-w. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:1085–1095.
2013.
|
|
24
|
Zhang L, Charron M, Wright WW, Chatterjee
B, Song CS, Roy AK and Brown TR: Nuclear factor-kappaB activates
transcription of the androgen receptor gene in Sertoli cells
isolated from testes of adult rats. Endocrinology. 145:781–789.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Murillo H, Huang H, Schmidt LJ, Smith DI
and Tindall DJ: Role of PI3K signaling in survival and progression
of LNCaP prostate cancer cells to the androgen refractory state.
Endocrinology. 142:4795–4805. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kikuchi E, Horiguchi Y, Nakashima J,
Kuroda K, Oya M, Ohigashi T, Takahashi N, et al: Suppression of
hormone-refractory prostate cancer by a novel nuclear factor kappaB
inhibitor in nude mice. Cancer Res. 63:107–110. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun HZ, Yang TW, Zang WJ and Wu SF:
Dehydroepiandrosterone-induced proliferation of prostatic
epithelial cell is mediated by NFKB via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
J Endocrinol. 204:311–318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|