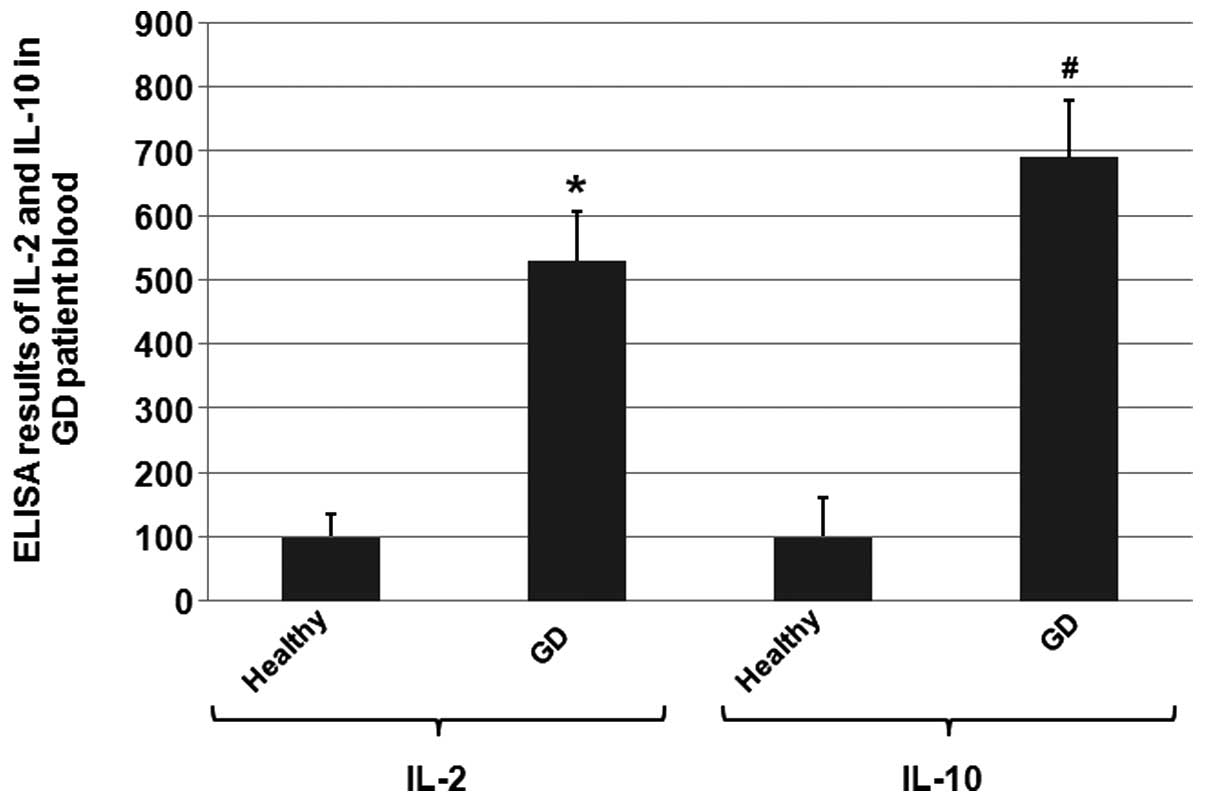
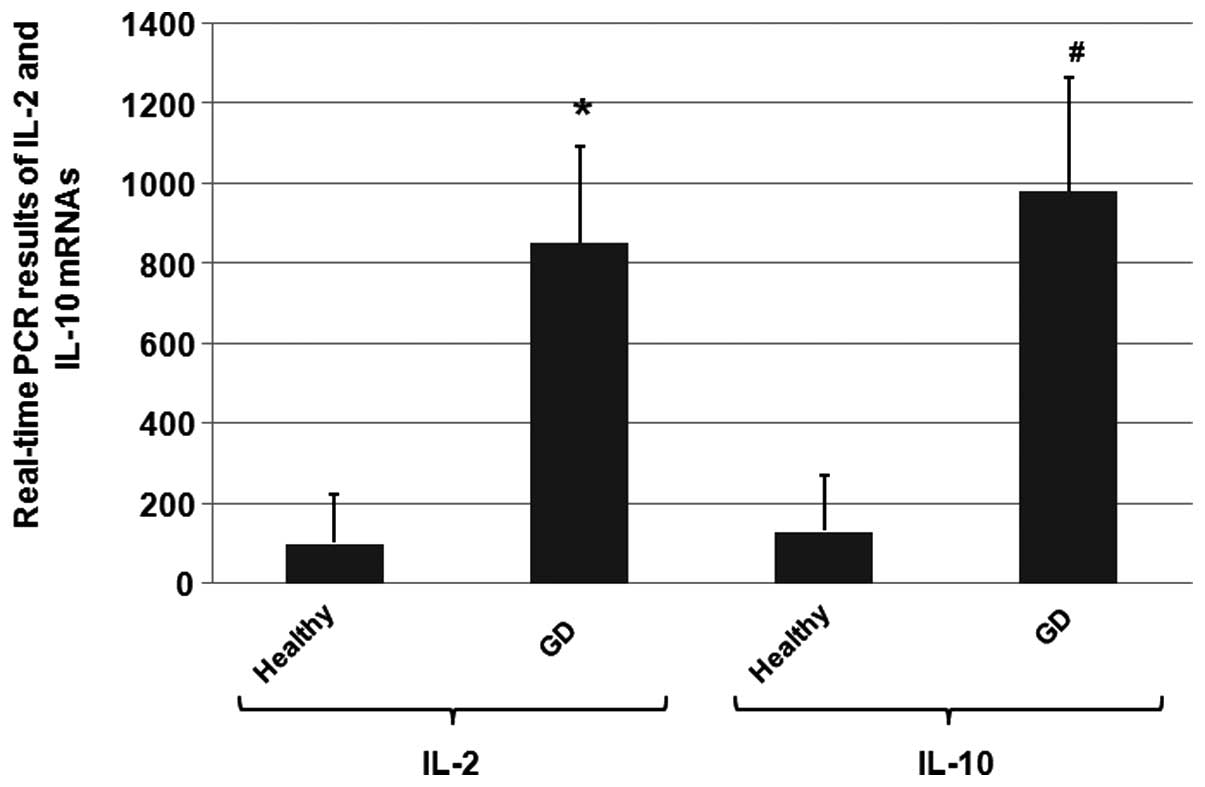
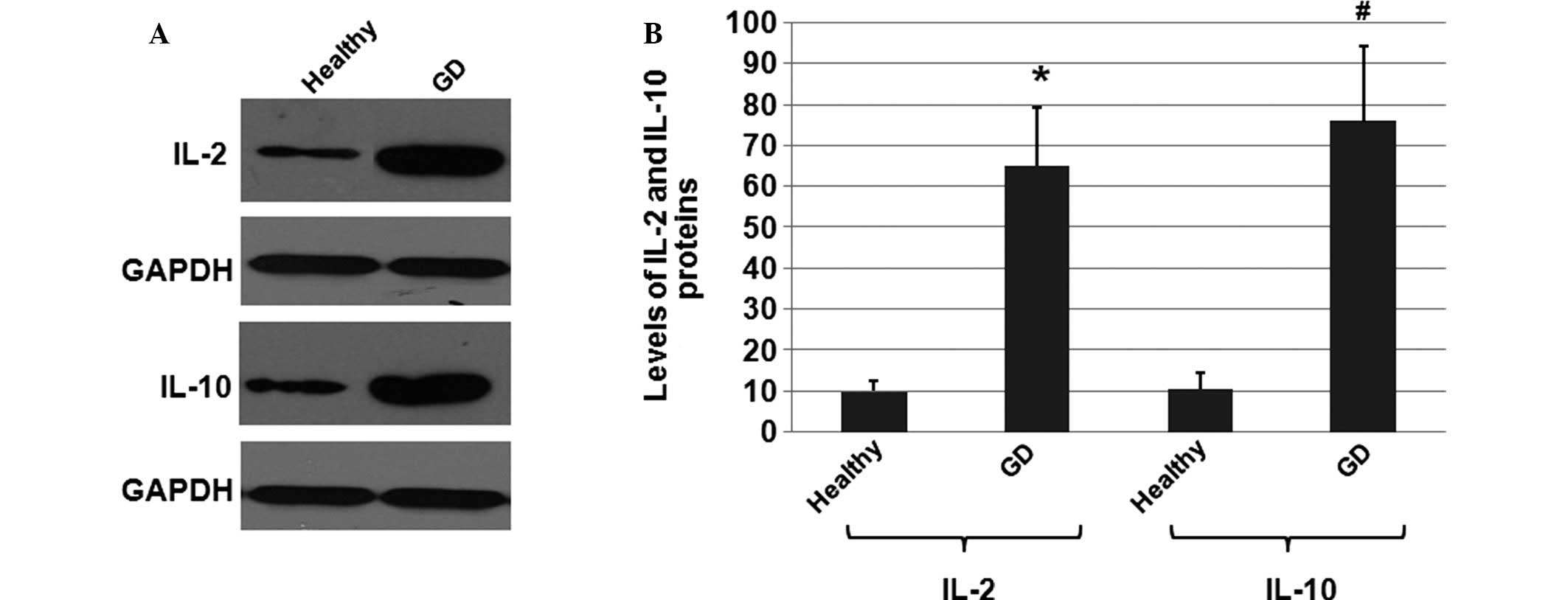
|
1
|
Menconi F, Marcocci C and Marinò M:
Diagnosis and classification of Graves’ disease. Autoimmun Rev.
13:398–402. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Park J, Kim JG, Park SP and Lee HW:
Asymmetric chorea as presenting symptom in Graves’ disease. Neurol
Sci. 33:343–345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mohaseb K, Linder M, Rootman J, Wilkins
GE, Schechter MT, Dolman PJ and Singer J: Development and
validation of a patient symptom questionnaire to facilitate early
diagnosis of thyroid-associated orbitopathy in graves’ disease.
Orbit. 27:419–425. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Imrie H, Vaidya B, Perros P, et al:
Evidence for Graves’ disease susceptibility locus at chromosome
Xp11 in a United Kingdom population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
86:626–630. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ngo ST, Stern FJ and McCombe PA: Gender
differences in autoimmune disease. Front Neuroendocrinol.
35:347–369. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rioux JD and Abbas AK: Paths to
understanding the genetic basis of autoimmune disease. Nature.
435:584–589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Prummel MF, Strieder T and Wiersinga WM:
The environment and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Eur J Endocrinol.
150:605–618. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sorrentino R: Genetics of autoimmunity: an
update. Immunol Lett. 158:116–119. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bordignon M, Bargagli E and Agostini Et Al
C: TLR7 Gln11Leu single nucleotide polymorphism in patients with
sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 30:157–161.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Esfahanian F, Naimi E, Doroodgar F and
Jadali Z: Th1/Th2 cytokines in patients with Graves’ disease with
or without ophthalmopathy. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol.
12:168–175. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qin Q, Liu P, Liu L, et al: The increased
but non-predominant expression of Th17- and Th1-specific cytokines
in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis but not in Graves’ disease. Braz J Med
Biol Res. 45:1202–1208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Frascerra S, et
al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α agonists modulate
Th1 and Th2 chemokine secretion in normal thyrocytes and Graves’
disease. Exp Cell Res. 317:1527–1533. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ribot JC, Ribeiro ST, Correia DV, Sousa AE
and Silva-Santos B: Human γδ thymocytes are functionally immature
and differentiate into cytotoxic type 1 effector T cells upon
IL-2/IL-15 signaling. J Immunol. 192:2237–2243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh S, Singh U and Pandey SS: Serum
concentration of IL-6, IL-2, TNF-α, and IFNγ in Vitiligo patients.
Indian J Dermatol. 57:12–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Das S, Banerjee S, Majumder S, et al:
Immune subversion by Mycobacterium tuberculosis through CCR5
mediated signaling: involvement of IL-10. PLoS One. 9:e924772014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koh SJ, Kim JM, Kim IK, Ko SH and Kim JS:
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of metformin and its effects in
intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated colon cancer. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:502–510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ueki I, Abiru N, Kawagoe K and Nagayama Y:
Interleukin 10 deficiency attenuates induction of anti-TSH receptor
antibodies and hyperthyroidism in a mouse Graves’ model. J
Endocrinol. 209:353–357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan JL, Wu YM, Zhao FJ and Liu SQ: The
expression of the recombinant protein for gpd gene from Treponema
Pallidum. Zhong Hua Pi Fu Ke Za Zhi. 40:301–302. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Stenszky V, Kozma L, Balazs C, Rochlitz S,
Bear JC and Farid NR: The genetics of Graves’ disease: HLA and
disease susceptibility. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 61:735–740. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Farid NR: Understanding the genetics of
autoimmune thyroid disease - still an illusive goal. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 74:495A–495B. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Świątkowska-Stodulska R, Kitowska A,
Skibowska-Bielińska A, Wiśniewski P and Sworczak K: Hageman factor
C46T promoter gene polymorphism in patients with hypercortisolism.
Horm Metab Res. 46:510–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsai KH, Chang CY, Tsai FJ, Lin HJ, Yang
YS, Lim YP, Liao CC and Wan L: Association of interleukin-16
polymorphisms with Graves’ disease in a Taiwanese population. Chin
J Physiol. 57:69–75. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kutluturk F, Yarman S, Sarvan FO and Kekik
C: Association of cytokine gene polymorphisms (IL6, IL10, TNF-α,
TGF-β and IFN-γ) and Graves’ disease in Turkish population. Endocr
Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 13:163–167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen ML, Liao N, Zhao H, Huang J and Xie
ZF: Association between the IL1B (−511), IL1B (+3954), IL1RN (VNTR)
polymorphisms and Graves’ disease risk: a meta-analysis of 11
case-control studies. PLoS One. 9:e860772014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Xiao WX, Zhu YF, et al:
Polymorphisms of interleukin-21 and interleukin-21-receptor genes
confer risk for autoimmune thyroid diseases. BMC Endocr Disord.
13:262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qiu LJ, Ni J, Cen H, et al: Relationship
between the IL-4 gene promoter −590C/T (rs2243250) polymorphism and
susceptibility to autoimmune diseases: a meta-analysis. J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. Mar 17–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|