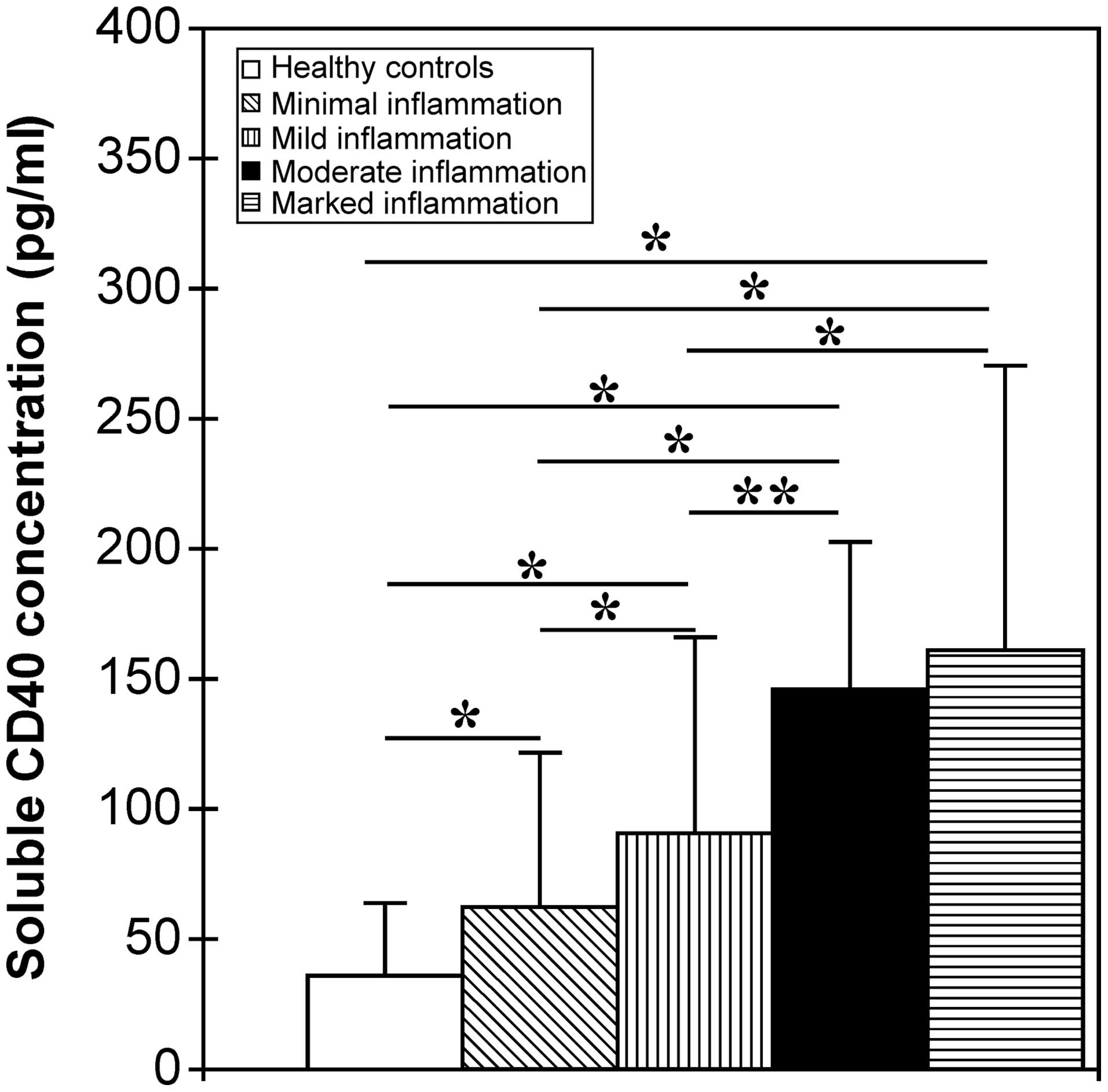
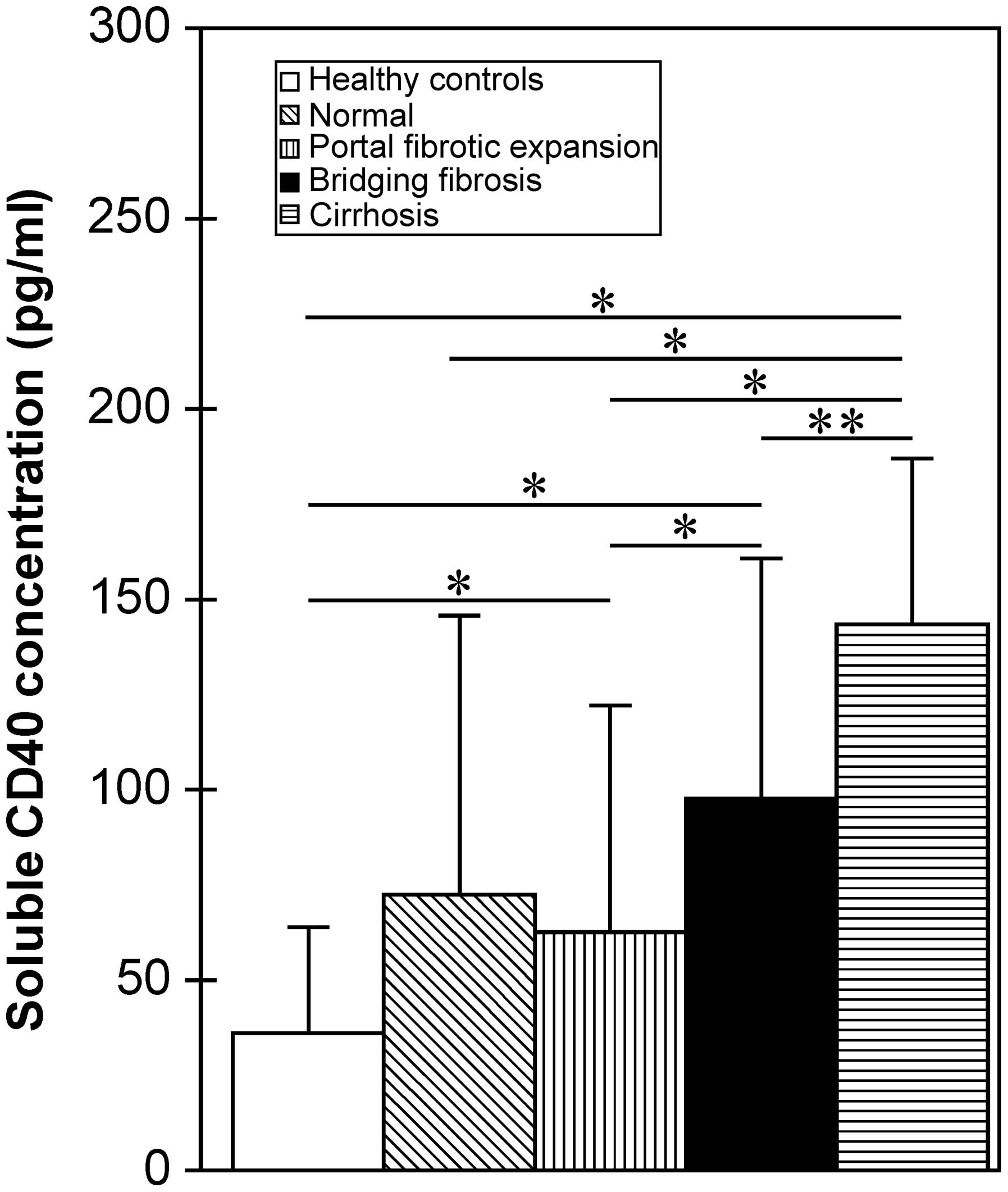
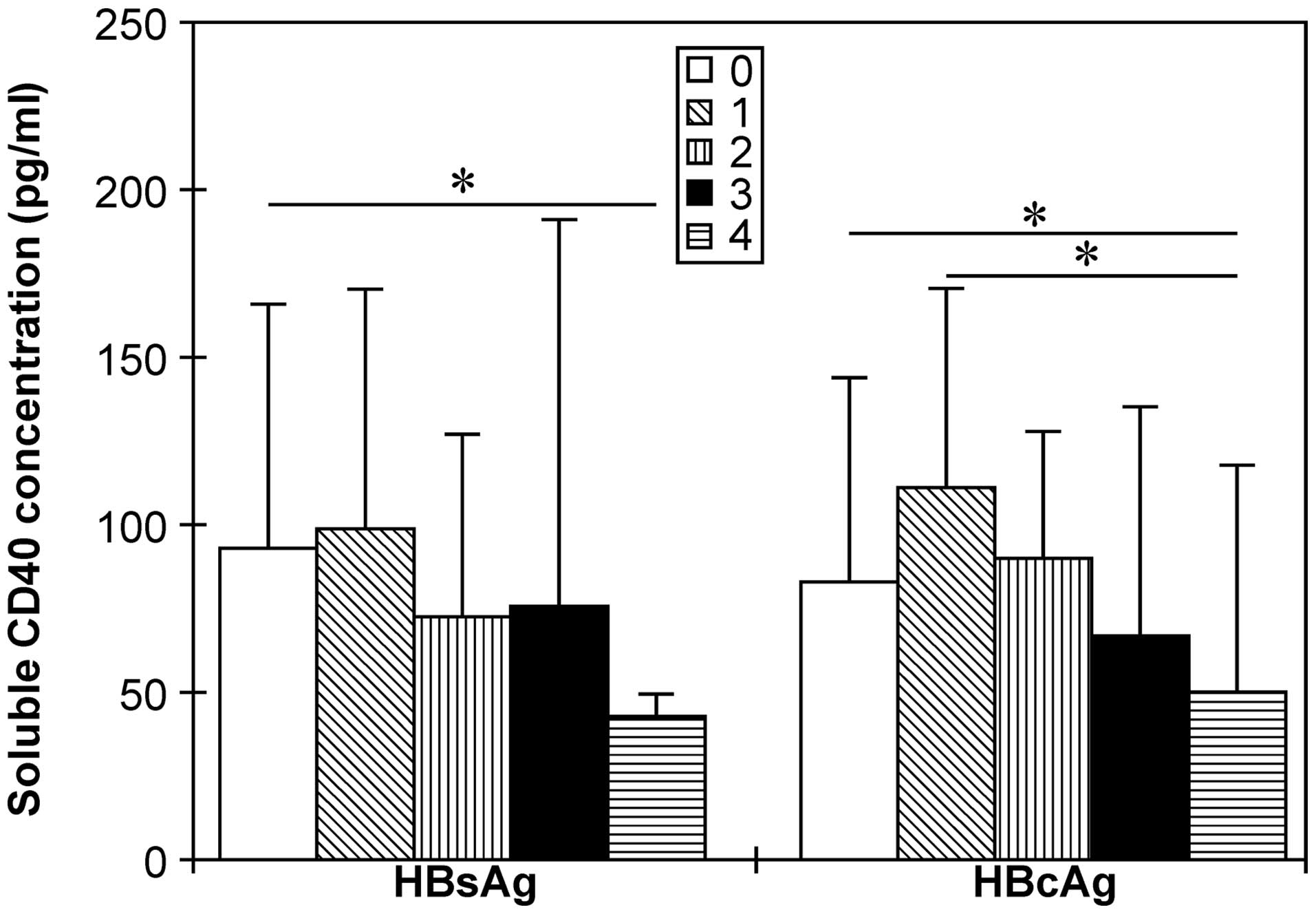
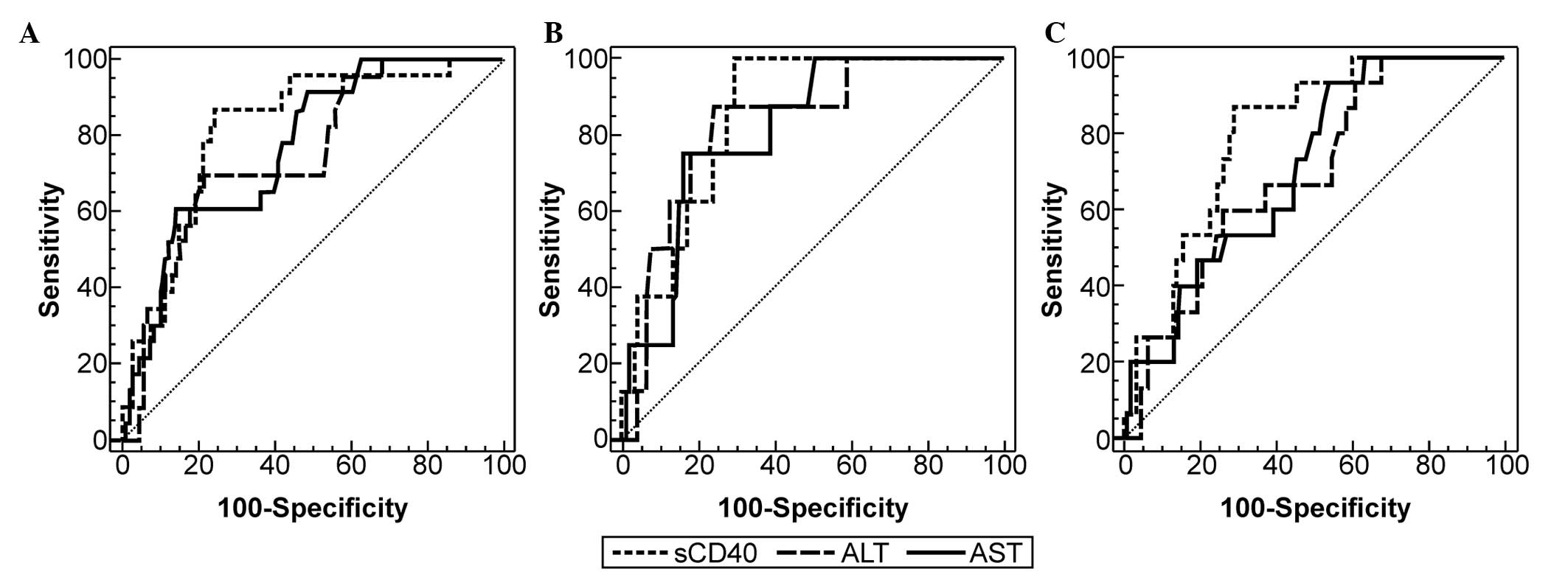
|
1
|
Quezada SA, Jarvinen LZ, Lind EF and
Noelle RJ: CD40/CD154 interactions at the interface of tolerance
and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 22:307–328. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma DY and Clark EA: The role of CD40 and
CD154/CD40L in dendritic cells. Semin Immunol. 21:265–272. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suttles J and Stout RD: Macrophage CD40
signaling: a pivotal regulator of disease protection and
pathogenesis. Semin Immunol. 21:257–264. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Danese S, Sans M and Fiocchi C: The
CD40/CD40L costimulatory pathway in inflammatory bowel disease.
Gut. 53:1035–1043. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peters AL, Stunz LL and Bishop GA: CD40
and autoimmunity: the dark side of a great activator. Semin
Immunol. 21:293–300. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
De Paoli P, Cozzi M, Tedeschi R, Gloghini
A, Cilia AM, van Kooten C, Gaidano G and Carbone A: High CD40
membrane expression in AIDS-related lymphoma B cell lines is
associated with the CD45RA+, CD45RO+,
CD95+ phenotype and high levels of its soluble form in
culture supernatants. Cytometry. 30:33–38. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Contin C, Pitard V, Itai T, Nagata S,
Moreau JF and Déchanet-Merville J: Membrane-anchored CD40 is
processed by the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme.
Implications for CD40 signaling. J Biol Chem. 278:32801–32809.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhuang Y, Huang J, Zhou Z, et al: A novel
blocking monoclonal antibody recognizing a distinct epitope of
human CD40 molecule. Tissue Antigens. 65:81–87. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fanslow WC, Anderson DM, Grabstein KH,
Clark EA, Cosman D and Armitage RJ: Soluble forms of CD40 inhibit
biologic responses of human B cells. J Immunol. 149:655–660.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Contin C, Pitard V, Delmas Y, et al:
Potential role of soluble CD40 in the humoral immune response
impairment of uraemic patients. Immunology. 110:131–140. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ait-ghezala G, Abdullah L, Volmar CH,
Paris D, Luis CA, Quadros A, Mouzon B, Mullan MA, Keegan AP,
Parrish J, Crawford FC, Mathura VS and Mullan MJ: Diagnostic
utility of APOE, soluble CD40, CD40L, and Abeta1-40 levels in
plasma in Alzheimer’s disease. Cytokine. 44:283–287. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Komura K, Fujimoto M, Matsushita T, et al:
Increased serum soluble CD40 levels in patients with systemic
sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 34:353–358. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hock BD, McKenzie JL, Patton NW, et al:
Circulating levels and clinical significance of soluble CD40 in
patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer. 106:2148–2157.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schmilovitz-Weiss H, Belinki A, Pappo O,
et al: Role of circulating soluble CD40 as an apoptotic marker in
liver disease. Apoptosis. 9:205–210. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ke B, Shen XD, Gao F, et al: The
CD154-CD40 T-cell co-stimulation pathway in liver ischemia and
reperfusion inflammatory responses. Transplantation. 79:1078–83.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kimura K, Kakimi K, Wieland S, Guidotti LG
and Chisari FV: Activated intrahepatic antigen-presenting cells
inhibit hepatitis B virus replication in the liver of transgenic
mice. J Immunol. 169:5188–5195. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kimura K, Nagaki M, Takai S, Satake S and
Moriwaki H: Pivotal role of nuclear factor kappaB signaling in
anti-CD40-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology. 40:1180–1189.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burgio VL, Ballardini G, Artini M,
Caratozzolo M, Bianchi FB and Levrero M: Expression of
co-stimulatory molecules by Kupffer cells in chronic hepatitis of
hepatitis C virus etiology. Hepatology. 27:1600–1606. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Okano H, et al:
CD40 expression in HCV-associated chronic liver diseases. Int J Mol
Med. 18:559–563. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kimura K, Moriwaki H, Nagaki M, et al:
Pathogenic role of B cells in anti-CD40-induced necroinflammatory
liver disease. Am J Pathol. 168:786–795. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese
Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases,
Chinese Medical Association. Guideline on prevention and treatment
of chronic hepatitis B in China (2005). Chin Med J (Engl).
120:2159–2173. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al:
Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol.
22:696–699. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan J, Jie Z, Hou L, et al: Parenchymal
expression of CD40 exacerbates adenovirus-induced hepatitis in
mice. Hepatology. 53:1455–1467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Connolly MK, Bedrosian AS, Mallen-St Clair
J, Mitchell AP, Ibrahim J, Stroud A, Pachter HL, Bar-Sagi D, Frey
AB and Miller G: In liver fibrosis, dendritic cells govern hepatic
inflammation in mice via TNF-alpha. J Clin Invest. 119:3213–3225.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Williams KT, Young SP, Negus A, Young LS,
Adams DH and Afford SC: C4b binding protein binds to CD154
preventing CD40-mediated cholangiocyte apoptosis: a novel link
between complement and epithelial cell survival. PLoS One.
2:e1592007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhou F, Ajuebor MN, Beck PL, Le T,
Hogaboam CM and Swain MG: CD154-CD40 interactions drive hepatocyte
apoptosis in murine fulminant hepatitis. Hepatology. 42:372–380.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schmitz V, Dombrowski F, Prieto J, et al:
Induction of murine liver damage by overexpression of CD40 ligand
provides an experimental model to study fulminant hepatic failure.
Hepatology. 44:430–439. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lunsford KE, Koester MA, Eiring AM, Horne
PH, Gao D and Bumgardner GL: Targeting LFA-1 and CD154 suppresses
the in vivo activation and development of cytolytic
(CD4-Independent) CD8+ T cells. J Immunol.
175:7855–7866. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Overall CM, Wrana JL and Sodek J:
Independent regulation of collagenase, 72-kDa progelatinase, and
metalloendoproteinase inhibitor expression in human fibroblasts by
transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 264:1860–1869.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takahara T, Furui K, Funaki J, et al:
Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-II in experimental
liver fibrosis in rats. Hepatology. 21:787–795. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Murphy G and Docherty AJ: The matrix
metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
7:120–125. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mach F, Schönbeck U, Fabunmi RP, et al: T
lymphocytes induce endothelial cell matrix metalloproteinase
expression by a CD40L-dependent mechanism: implications for tubule
formation. Am J Pathol. 154:229–238. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mach F, Schönbeck U, Bonnefoy JY, Pober JS
and Libby P: Activation of monocyte/macrophage functions related to
acute atheroma complication by ligation of CD40: induction of
collagenase, stromelysin, and tissue factor. Circulation.
96:396–399. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kuo WH, Chou FP, Lu SC, Chu SC and Hsieh
YS: Significant differences in serum activities of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and -9 between HCV- and HBV-infected patients
and carriers. Clin Chim Acta. 294:157–168. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Flisiak R, Al-Kadasi H, Jaroszewicz J,
Prokopowicz D and Flisiak I: Effect of lamivudine treatment on
plasma levels of transforming growth factor beta1, tissue inhibitor
of metalloproteinases-1 and metalloproteinase-1 in patients with
chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2661–2665.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ljumovic D, Diamantis I, Alegakis AK and
Kouroumalis EA: Differential expression of matrix
metalloproteinases in viral and non-viral chronic liver diseases.
Clin Chim Acta. 349:203–211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang BB, Cai WM, Weng HL, et al:
Diagnostic value of platelet derived growth factor-BB, transforming
growth factor-beta1, matrix metalloproteinase-1, and tissue
inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in serum and peripheral
blood mononuclear cells for hepatic fibrosis. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:2490–2496. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Flisiak R, Maxwell P, Prokopowicz D, Timms
PM and Panasiuk A: Plasma tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1
and transforming growth factor beta 1 - possible non-invasive
biomarkers of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic B and C
hepatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 49:1369–1372. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shu U, Kiniwa M, Wu CY, et al: Activated T
cells induce interleukin-12 production by monocytes via CD40-CD40
ligand interaction. Eur J Immunol. 25:1125–1128. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|