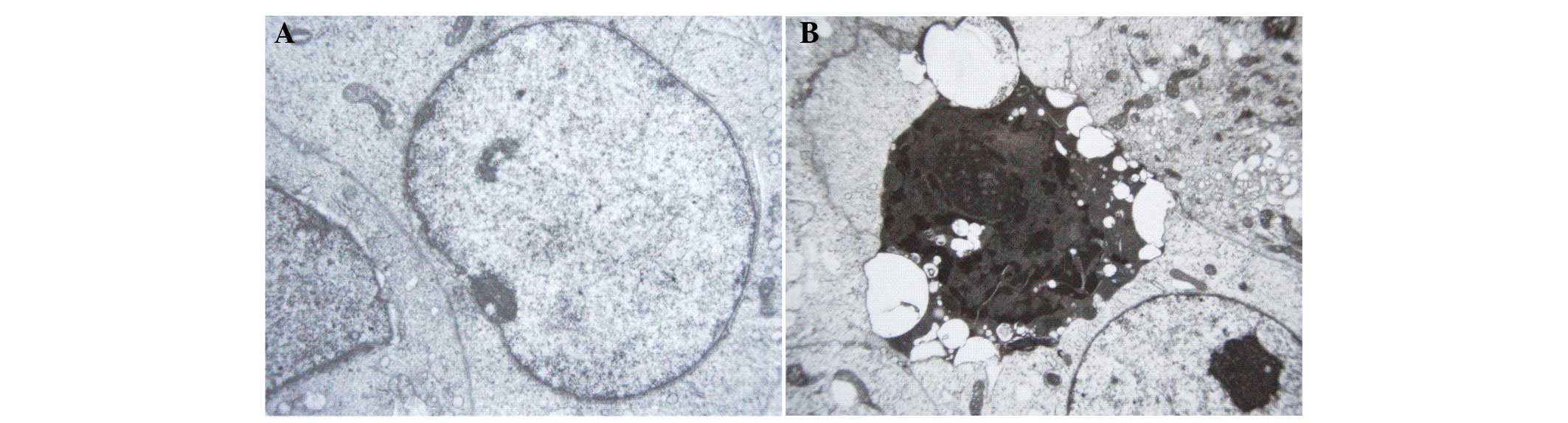
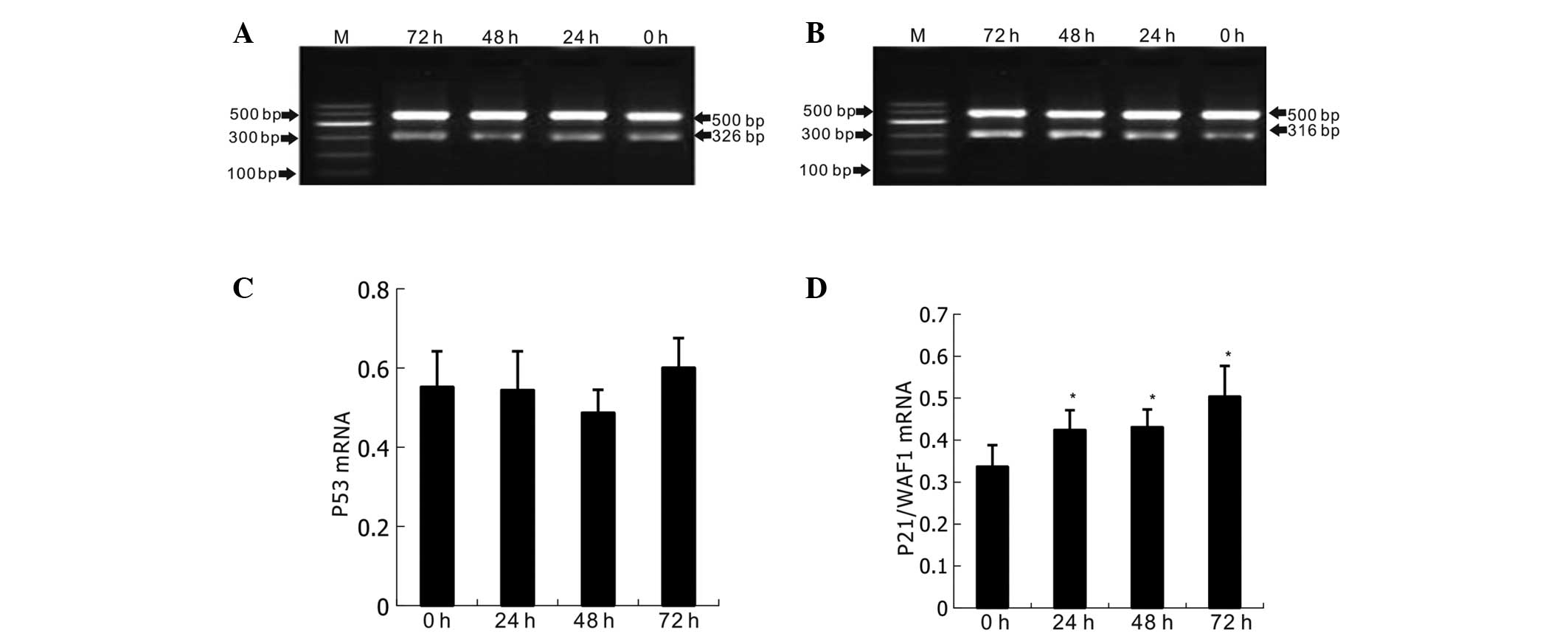
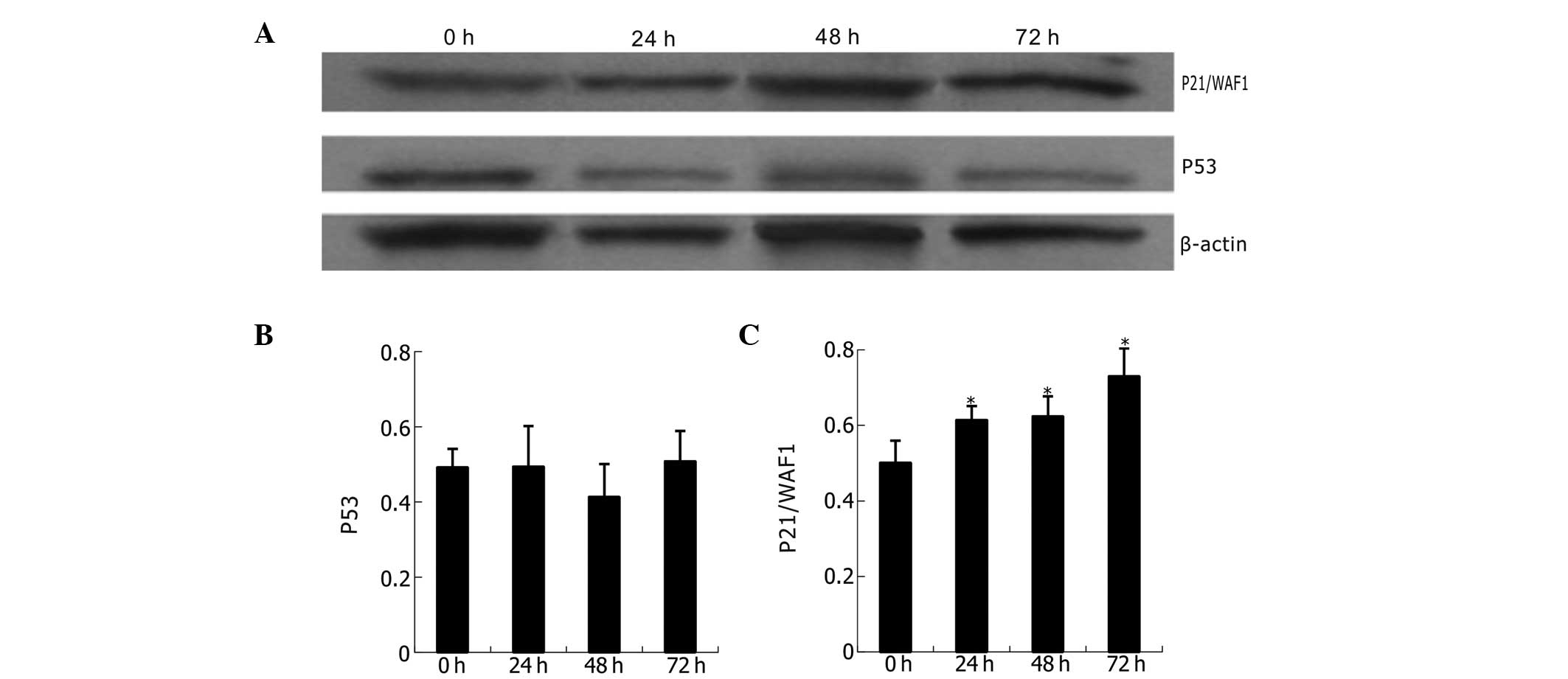
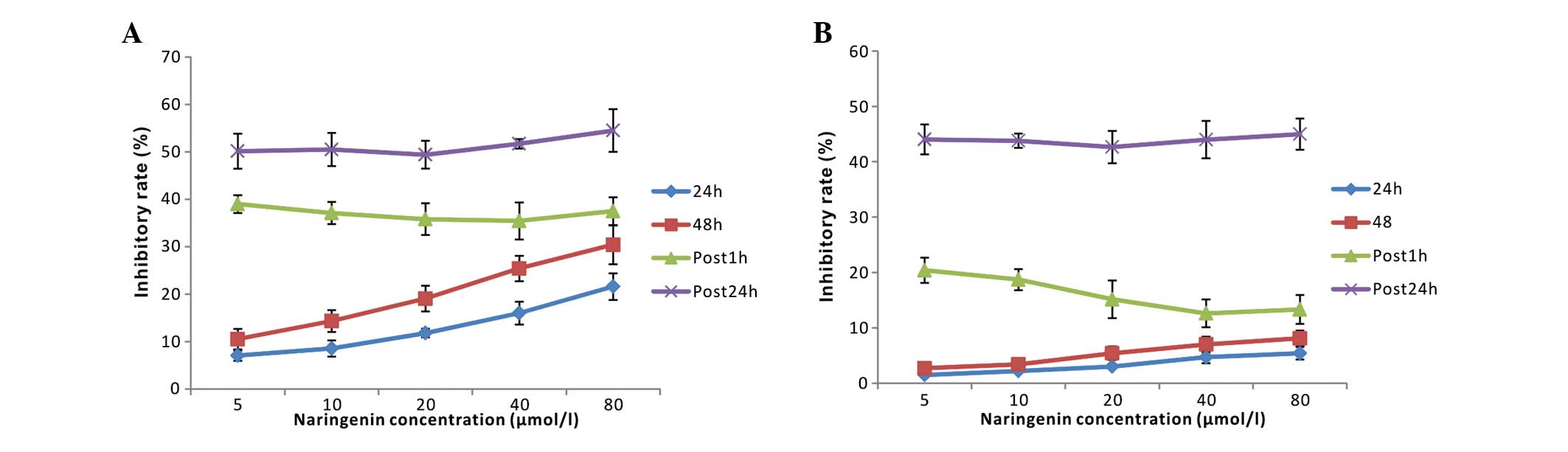
|
1
|
Yang C and Zhang X: Incidence survey of
leukemia in China. Chin Med Sci J. 6:65–70. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH and Debatin
KM: Involvement of the CD95 (APO-1/FAS) receptor/ligand system in
drug-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Nat Med. 2:574–577. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Durgo K, Koncar M, Komes D, et al:
Cytotoxicity of blended versus single medicinal mushroom extracts
on human cancer cell lines: contribution of polyphenol and
polysaccharide content. Int J Med Mushrooms. 15:435–448. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ravishankar D, Rajora AK, Greco F and
Osborn HM: Flavonoids as prospective compounds for anti-cancer
therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2821–2831. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ameer B, Weintraub RA, Johnson JV, Yost RA
and Rouseff RL: Flavanone absorption after naringin, hesperidin,
and citrus administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 60:34–40. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Galati G, Chan T, Wu B and O’Brien PJ:
Glutathione-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species by the
peroxidase-catalyzed redox cycling of flavonoids. Chem Res Toxicol.
12:521–525. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi Y, Dai J, Liu H, et al: Naringenin
inhibits allergen-induced airway inflammation and airway
responsiveness and inhibits NF-kappaB activity in a murine model of
asthma. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 87:729–735. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arul D and Subramanian P: Inhibitory
effect of naringenin (citrus flavonone) on N-nitrosodiethylamine
induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
434:203–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lv Y, Zhang B, Xing G, Wang F and Hu Z:
Protective effect of naringenin against acetaminophen-induced acute
liver injury in metallothionein (MT)-null mice. Food Funct.
4:297–302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tsai SJ, Huang CS, Mong MC, Kam WY, Huang
HY and Yin MC: Anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects of
naringenin in diabetic mice. J Agric Food Chem. 60:514–521. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Andrade JE and Burgess JR: Effect of the
citrus flavanone naringenin on oxidative stress in rats. J Agric
Food Chem. 55:2142–2148. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee S, Lee CH, Moon SS, et al: Naringenin
derivatives as anti-atherogenic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
13:3901–3903. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Totta P, Acconcia F, Leone S, Cardillo I
and Marino M: Mechanisms of naringenin-induced apoptotic cascade in
cancer cells: involvement of estrogen receptor alpha and beta
signalling. IUBMB Life. 56:491–499. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Harmon AW and Patel YM: Naringenin
inhibits glucose uptake in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: a mechanism
for impaired cellular proliferation. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
85:103–110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao K, Henning SM, Niu Y, et al: The
citrus flavonoid naringenin stimulates DNA repair in prostate
cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 17:89–95. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kanno S, Tomizawa A, Hiura T, et al:
Inhibitory effects of naringenin on tumor growth in human cancer
cell lines and sarcoma S-180-implanted mice. Biol Pharm Bull.
28:527–530. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sanderson JT, Hordijk J, Denison MS,
Springsteel MF, Nantz MH and van den Berg M: Induction and
inhibition of aromatase (CYP19) activity by natural and synthetic
flavonoid compounds in H295R human adrenocortical carcinoma cells.
Toxicol Sci. 82:70–79. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen YC, Shen SC and Lin HY: Rutinoside at
C7 attenuates the apoptosis-inducing activity of flavonoids.
Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1139–1150. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanno S, Shouji A, Hirata R, Asou K and
Ishikawa M: Effects of naringin on cytosine arabinoside
(Ara-C)-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in P388 cells. Life Sci.
75:353–365. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lozzio CB and Lozzio BB: Human chronic
myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia
chromosome. Blood. 45:321–334. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gewirtz AM, Burger D, Rado TA, Benz EJ Jr
and Hoffman R: Constitutive expression of platelet glycoproteins by
the human leukemia cell line K562. Blood. 60:785–789.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Iwabuchi K, Nagaoka I, Someya A and
Yamashita T: Type IV collagen-binding proteins of neutrophils:
possible involvement of L-selectin in the neutrophil binding to
type IV collagen. Blood. 87:365–372. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dalrymple S, Antony L, Xu Y, et al: Role
of notch-1 and E-cadherin in the differential response to calcium
in culturing normal versus malignant prostate cells. Cancer Res.
65:9269–9279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jeon SM, Kim HK, Kim HJ, et al:
Hypocholesterolemic and antioxidative effects of naringenin and its
two metabolites in high-cholesterol fed rats. Translat Res.
149:15–21. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dieckman LM, Freudenthal BD and Washington
MT: PCNA structure and function: insights from structures of PCNA
complexes and post-translationally modified PCNA. Subcell Biochem.
62:281–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gehen SC, Vitiello PF, Bambara RA, Keng PC
and O’Reilly MA: Downregulation of PCNA potentiates p21-mediated
growth inhibition in response to hyperoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 292:L716–L724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pedraza-Fariña LG: Mechanisms of oncogenic
cooperation in cancer initiation and metastasis. Yale J Biol Med.
79:95–103. 2006.
|
|
28
|
Croce CM: Oncogenes and cancer. New Engl J
Med. 358:502–511. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee EW, Lee MS, Camus S, et al:
Differential regulation of p53 and p21 by MKRN1 E3 ligase controls
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. EMBO J. 28:2100–2113. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gartel AL and Radhakrishnan SK: Lost in
transcription: p21 repression, mechanisms, and consequences. Cancer
Res. 65:3980–3985. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Insinga A, Cicalese A, Faretta M, et al:
DNA damage in stem cells activates p21, inhibits p53, and induces
symmetric self-renewing divisions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:3931–3936. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Panno ML, Giordano F, Mastroianni F, et
al: Evidence that low doses of Taxol enhance the functional
transactivatory properties of p53 on p21 waf promoter in MCF-7
breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 580:2371–2380. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Almond JB and Cohen GM: The proteasome: a
novel target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia. 16:433–443. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chinery R, Brockman JA, Peeler MO, Shyr Y,
Beauchamp RD and Coffey RJ: Antioxidants enhance the cytotoxicity
of chemotherapeutic agents in colorectal cancer: a p53-independent
induction of p21WAF1/CIP1 via C/EBPbeta. Nat Med. 3:1233–1241.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Waldman T, Zhang Y, Dillehay L, et al:
Cell-cycle arrest versus cell death in cancer therapy. Nat Med.
3:1034–1036. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu Q, Kirschmeier P, Hockenberry T, et al:
Transcriptional regulation during p21WAF1/CIP1-induced apoptosis in
human ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 277:36329–36337. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rodriguez R and Meuth M: Chk1 and p21
cooperate to prevent apoptosis during DNA replication fork stress.
Mol Biol Cell. 17:402–412. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Rodriguez RJ, Miranda CL, Stevens JF,
Deinzer ML and Buhler DR: Influence of prenylated and
non-prenylated flavonoids on liver microsomal lipid peroxidation
and oxidative injury in rat hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol.
39:437–445. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee MK, Bok SH, Jeong TS, et al:
Supplementation of naringenin and its synthetic derivative alters
antioxidant enzyme activities of erythrocyte and liver in high
cholesterol-fed rats. Bioorg Med Chem. 10:2239–2244. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Harrison C: Anticancer drugs: A double
strike at kinases. Nature reviews Drug Discov. 9:2702010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
van Acker FA, Schouten O, Haenen GR, van
der Vijgh WJ and Bast A: Flavonoids can replace alpha-tocopherol as
an antioxidant. FEBS Lett. 473:145–148. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Badary OA, Abdel-Maksoud S, Ahmed WA and
Owieda GH: Naringenin attenuates cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats.
Life Sci. 76:2125–2135. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Arafa HM, Abd-Ellah MF and Hafez HF:
Abatement by naringenin of doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in
rats. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 17:291–300. 2005.
|