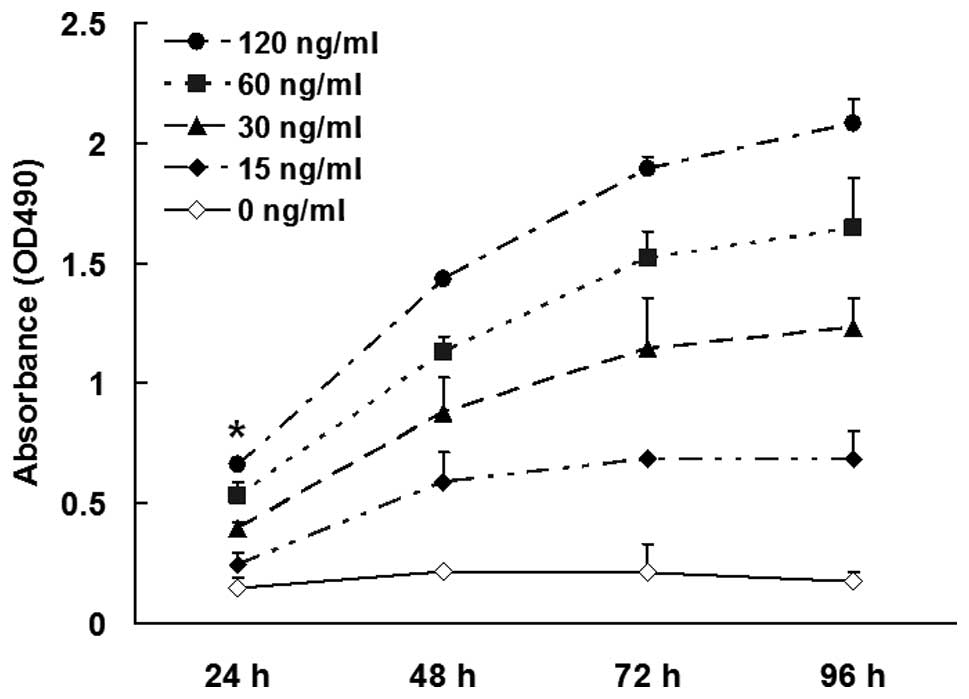
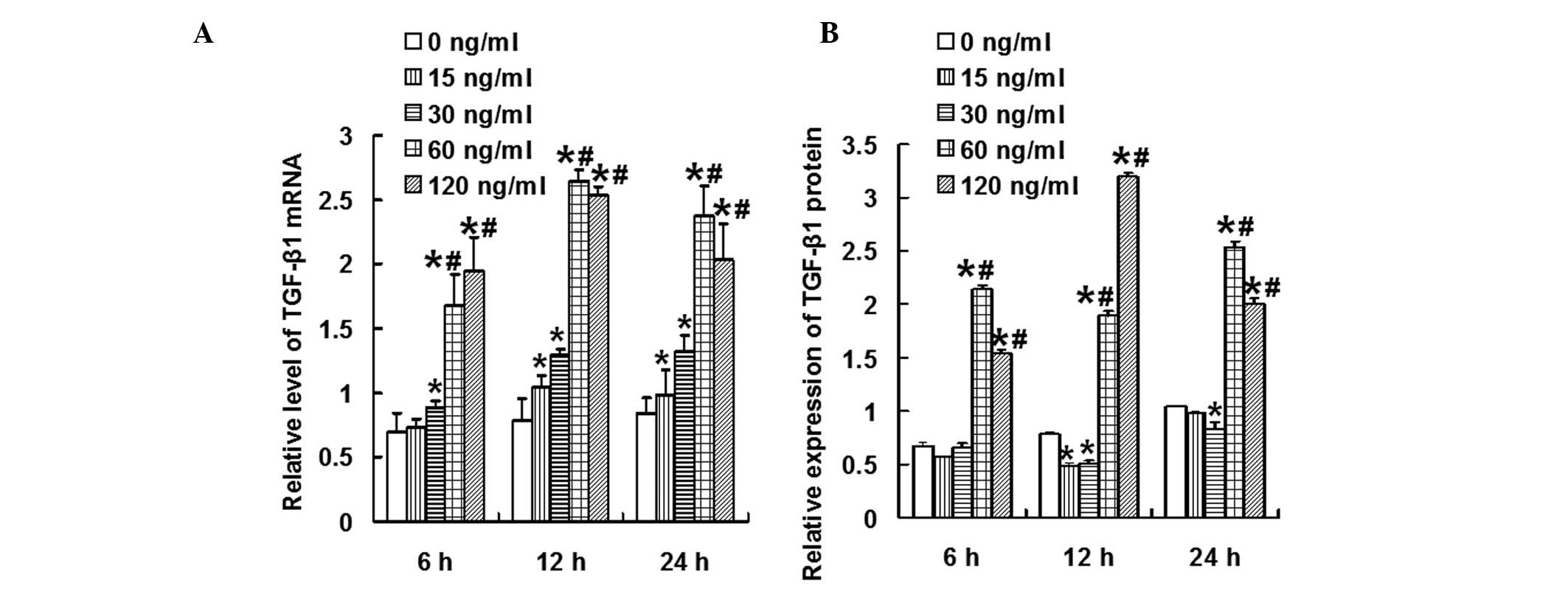
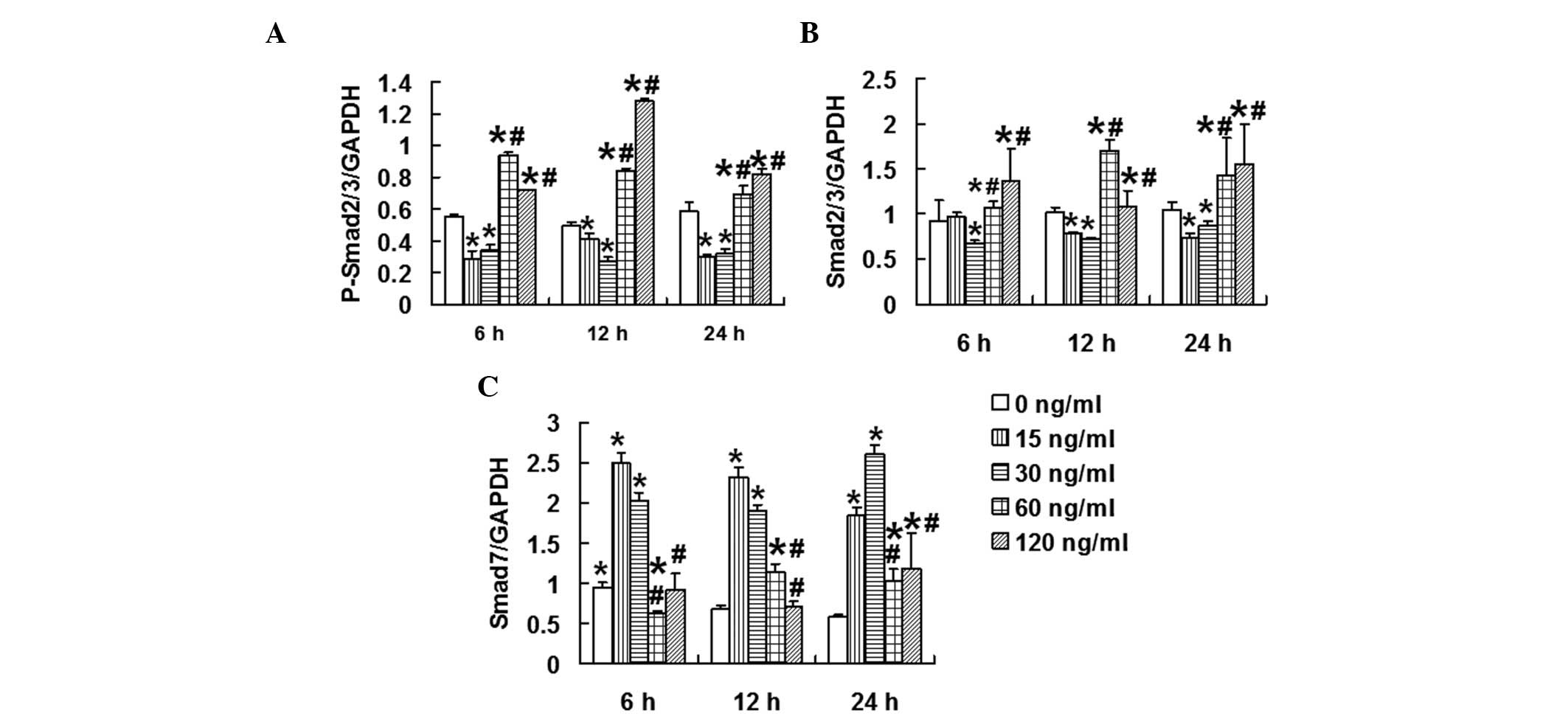
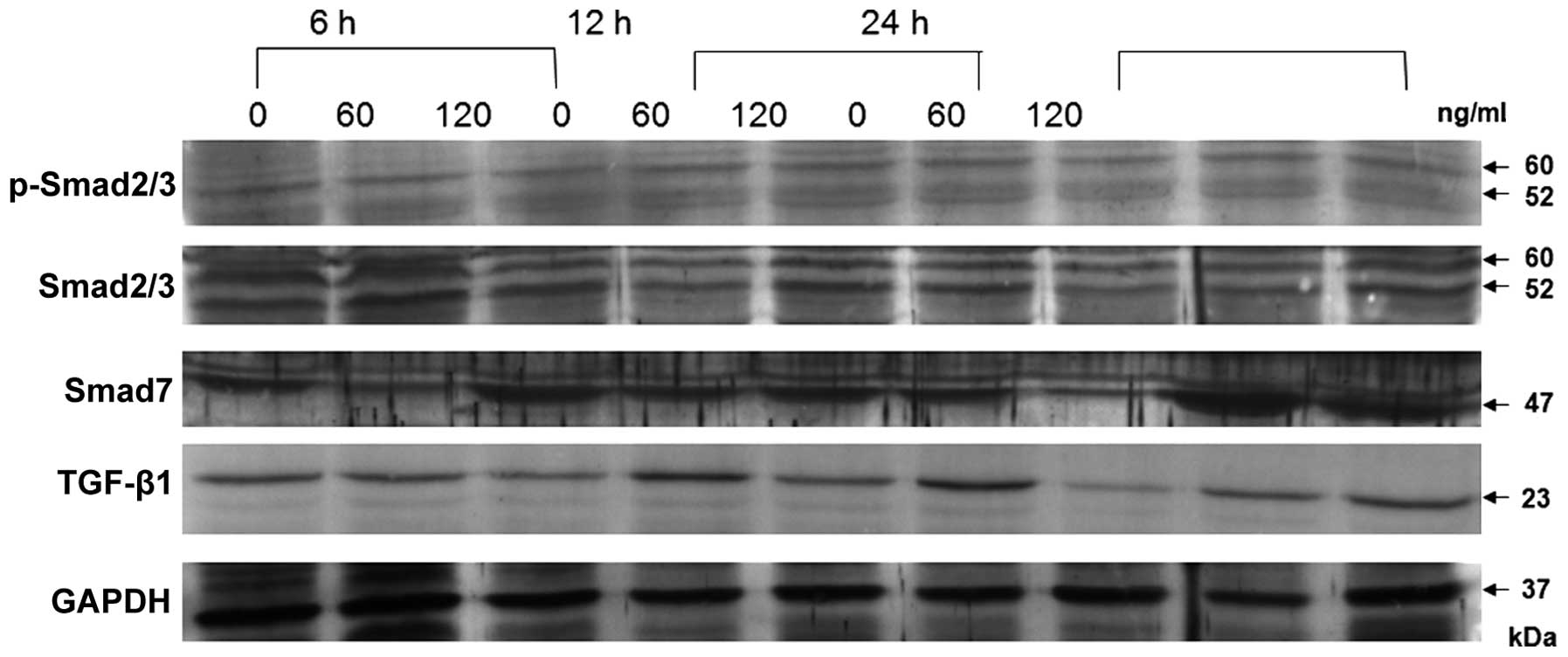
|
1
|
Li J, Chen J and Kirsner R:
Pathophysiology of acute wound healing. Clin Dermatol. 25:9–18.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Werner S and Grose R: Regulation of wound
healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev. 83:835–870.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS,
Brem H and Tomic-Canic M: Growth factors and cytokines in wound
healing. Wound Repair Regen. 16:585–601. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li J, Zhang YP and Kirsner RS:
Angiogenesis in wound repair: angiogenic growth factors and the
extracellular matrix. Microsc Res Tech. 60:107–114. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Itoh S, Itoh F, Goumans MJ and Ten Dijke
P: Signaling of transforming growth factor-beta family members
through Smad proteins. Eur J Biochem. 267:6954–6967. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ashcroft GS and Roberts AB: Loss of Smad3
modulates wound healing. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:125–131.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Derynck R, Zhang Y and Feng XH: Smads:
transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell. 95:737–740.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Massagué J: TGF-beta signal transduction.
Annu Rev Biochem. 67:753–791. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hayashi H, Abdollah S, Qiu Y, et al: The
MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGFbeta receptor and
functions as an antagonist of TGFbeta signaling. Cell.
89:1165–1173. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lyons RM, Gentry LE, Purchio AF and Moses
HL: Mechanism of activation of latent recombinant transforming
growth factor beta 1 by plasmin. J Cell Biol. 110:1361–1367. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miyazono K and Heldin CH: Role for
carbohydrate structures in TGF-beta 1 latency. Nature. 338:158–160.
1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Taipale J, Lohi J, Saarinen J, Kovanen PT
and Keski-Oja J: Human mast cell chymase and leukocyte elastase
release latent transforming growth factor-beta 1 from the
extracellular matrix of cultured human epithelial and endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 270:4689–4696. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okamoto Y, Takai S and Miyazaki M: Effect
of chymase-dependent transforming growth factor beta on peritoneal
adhesion formation in a rat model. Surg Today. 34:865–867. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Urata H, Kinoshita A, Misono KS, Bumpus FM
and Husain A: Identification of a highly specific chymase as the
major angiotensin II-forming enzyme in the human heart. J Biol
Chem. 265:22348–22357. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saarinen J, Kalkkinen N, Welgus HG and
Kovanen PT: Activation of human interstitial procollagenase through
direct cleavage of the Leu83-Thr84 bond by mast cell chymase. J
Biol Chem. 269:18134–18140. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vartio T, Seppä H and Vaheri A:
Susceptibility of soluble and matrix fibronectins to degradation by
tissue proteinases, mast cell chymase and cathepsin G. J Biol Chem.
256:471–477. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takai S and Miyazaki M: A novel
therapeutic strategy against vascular disorders with chymase
inhibitor. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 1:217–224. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Doggrell SA and Wanstall JC: Vascular
chymase: pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential of
inhibition. Cardiovasc Res. 61:653–662. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong X, Chen J, Zhang Y and Cen Y: Mast
cell chymase promotes cell proliferation and expression of certain
cytokines in a dose-dependent manner. Mol Med Rep. 5:1487–1490.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong X, Geng Z, Zhao Y, Chen J and Cen Y:
Involvement of mast cell chymase in burn wound healing in hamsters.
Exp Ther Med. 5:643–647. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nishikori Y, Kakizoe E, Kobayashi Y, et
al: Skin mast cell promotion of matrix remodeling in burn wound
healing in mice: relevance of chymase. Arch Dermatol Res.
290:553–560. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Massagué J: How cells read TGF-beta
signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:169–178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhao XY, Zhao LY, Zheng QS, et al: Chymase
induces profibrotic response via transforming growth
factor-beta1/Smad activation in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Mol Cell
Biochem. 310:159–166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Maruichi M, Takai S, Sugiyama T, et al:
Role of chymase on growth of cultured canine Tenon’s capsule
fibroblasts and scarring in a canine conjunctival flap model. Exp
Eye Res. 79:111–118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Algermissen B, Hermes B,
Feldmann-Boeddeker I, Bauer F and Henz BM: Mast cell chymase and
tryptase during tissue turnover: analysis on in vitro mitogenesis
of fibroblasts and keratinocytes and alterations in cutaneous
scars. Exp Dermatol. 8:193–198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takai S, Jin D, Sakaguchi M, et al: A
novel chymase inhibitor,
4-[1-([bis-(4-methyl-phenyl)-methyl]-carbamoyl)3-
(2-ethoxy-benzyl)-4-oxo-azetidine-2-yloxy]-benzoic acid (BCEAB),
suppressed cardiac fibrosis in cardiomyopathic hamsters. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 305:17–23. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanzaki T, Olofsson A, Morén A, et al:
TGF-beta 1 binding protein: a component of the large latent complex
of TGF-beta 1 with multiple repeat sequences. Cell. 61:1051–1061.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Simard E, Jin D, Takai S, et al:
Chymase-dependent conversion of Big endothelin-1 in the mouse in
vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 328:540–548. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rhett JM, Ghatnekar GS, Palatinus JA,
O’Quinn M, Yost MJ and Gourdie RG: Novel therapies for scar
reduction and regenerative healing of skin wounds. Trends
Biotechnol. 26:173–180. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Owens P, Han G, Li AG and Wang XJ: The
role of Smads in skin development. J Invest Dermatol. 128:783–790.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ponugoti B, Xu F, Zhang C, Tian C, Pacios
S and Graves DT: FOXO1 promotes wound healing through the
up-regulation of TGF-β1 and prevention of oxidative stress. J Cell
Biol. 203:327–343. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kajdaniuk D, Marek B, Borgiel-Marek H and
Kos-Kudła B: Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) in physiology
and pathology. Endokrynol Pol. 64:384–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Attisano L and Wrana JL: Signal
transduction by the TGF-beta superfamily. Science. 296:1646–1647.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Euler-Taimor G and Heger J: The complex
pattern of SMAD signaling in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc
Res. 69:15–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rodríguez-Vita J, Sánchez-López E, Esteban
V, Rupérez M, Egido J and Ruiz-Ortega M: Angiotensin II activates
the Smad pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells by a transforming
growth factor-beta-independent mechanism. Circulation.
111:2509–2517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Morén A, et al:
Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of TGF-beta
signalling. Nature. 389:631–635. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mori Y, Chen SJ and Varga J: Modulation of
endogenous Smad expression in normal skin fibroblasts by
transforming growth factor-beta. Exp Cell Res. 258:374–383. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|