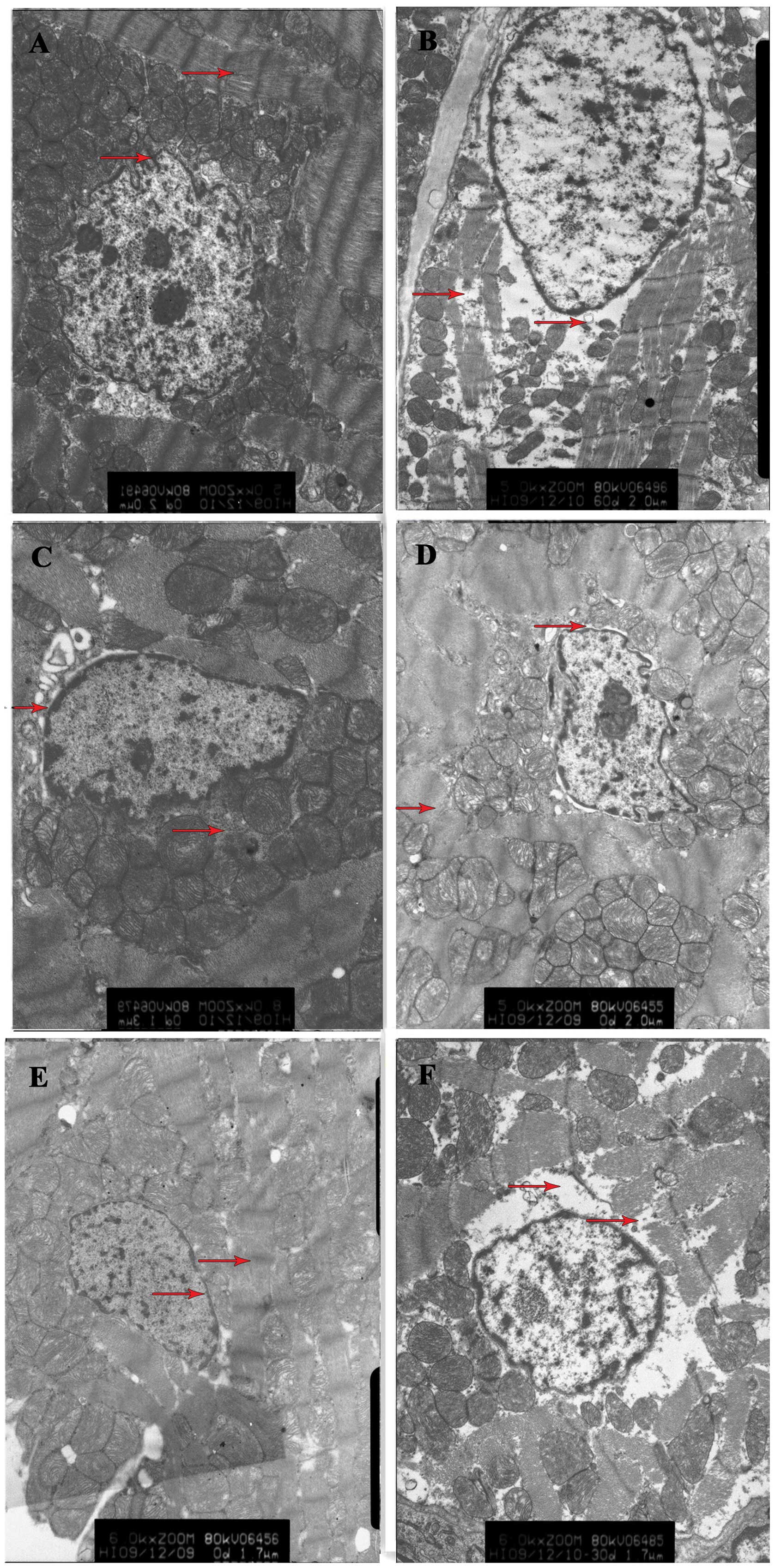
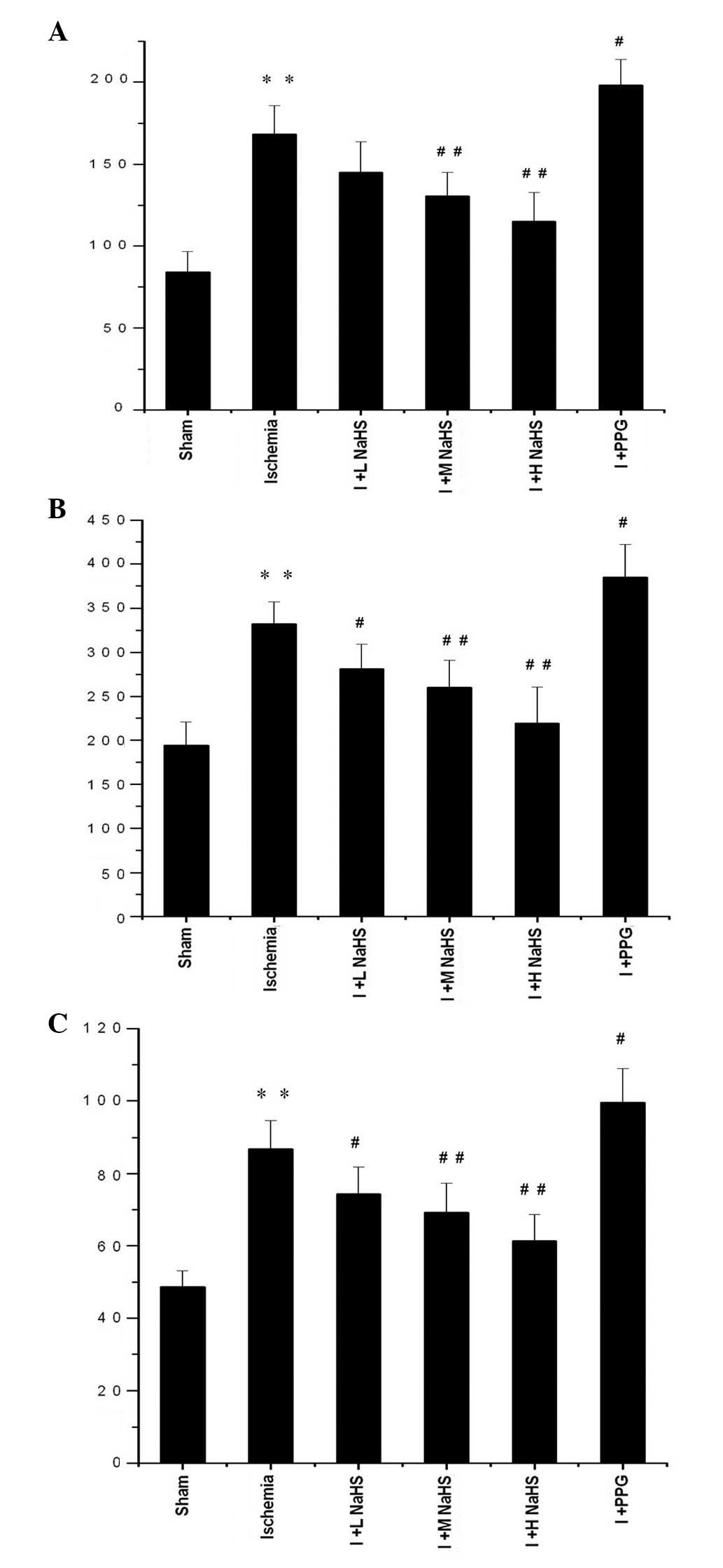
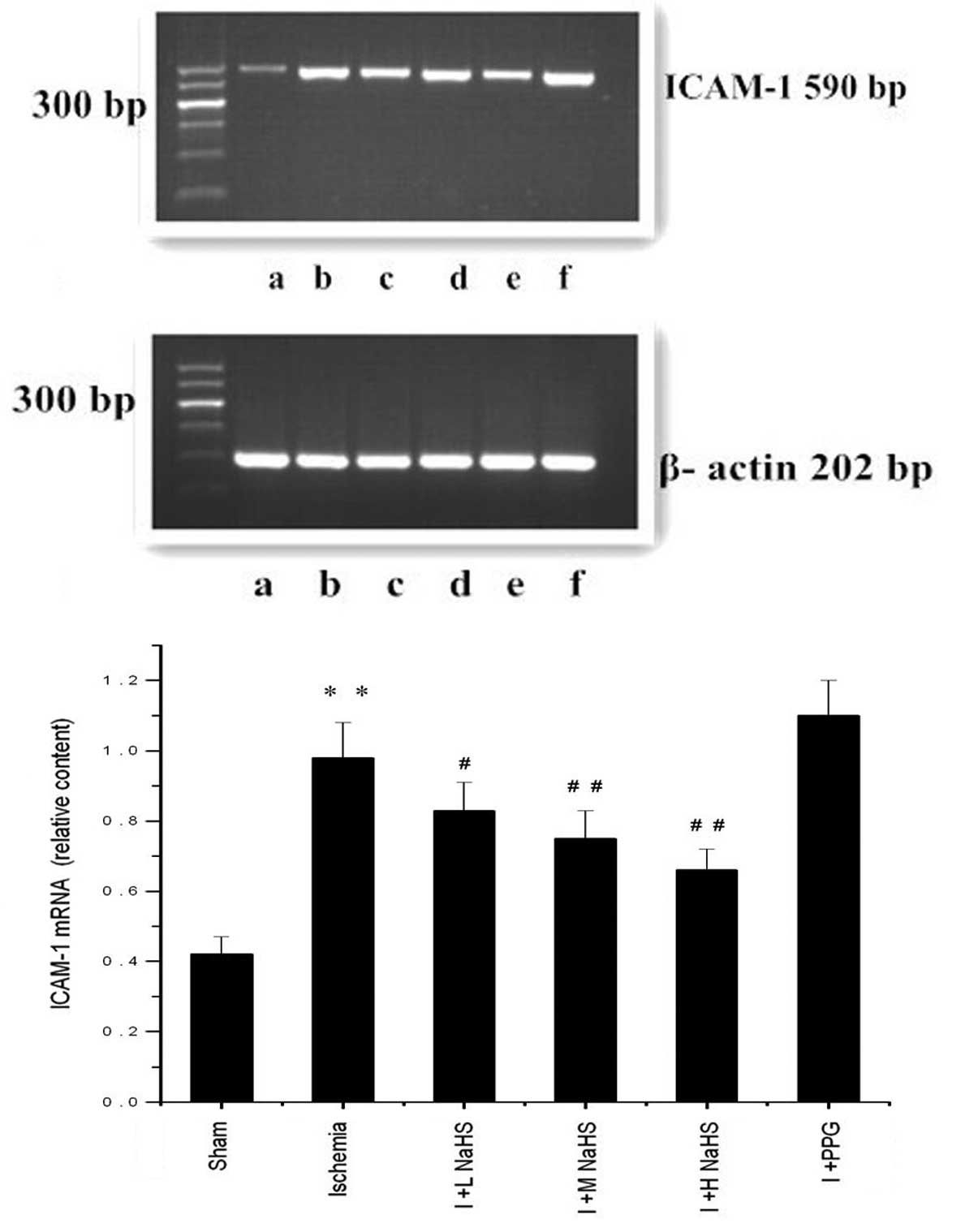
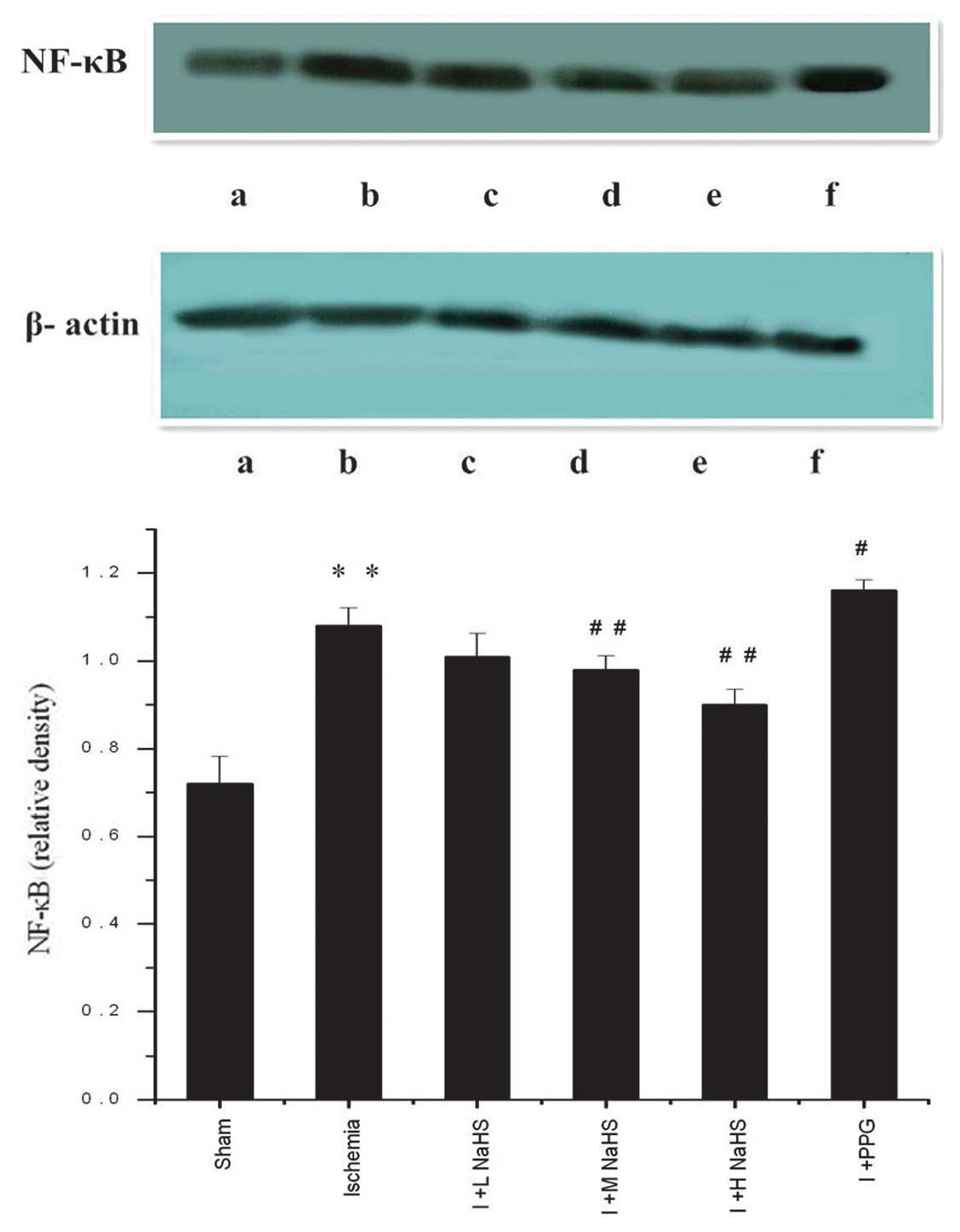
|
1
|
Chen X and Chen WZ: Cardiovascular
Pharmacology. 3rd Edition. People’s Medical Publishing House;
Beijing, China: pp. 4052002
|
|
2
|
Prior MG, Sharma AK, Yong S and Lopez A:
Concentration-time interactions in hydrogen sulphide toxicity in
rats. Can J Vet Res. 52:375–379. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reiffenstein RJ, Hulbert WC and Roth SH:
Toxicology of hydrogen sulfide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
32:109–134. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abe K and Kimura H: The possible role of
hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci.
16:1066–1071. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kimura H: Hydrogen sulfide induces cyclic
AMP and modulates the NMDA receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
267:129–133. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Szabó C: Hydrogen sulphide and its
therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:917–935. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang R: Two’s company, three’s a crowd:
can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J.
16:1792–1798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu X, Li T, Bi S, et al: Possible role of
hydrogen sulfide on the preservation of donor rat hearts.
Transplant Proc. 39:3024–3029. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li XH, Du JB and Tang CS: Impact of
hydrogen sulfide donor on pulmonary vascular structure and
vasoactive peptides in rats with pulmonary hypertension induced by
high pulmonary blood flow. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao.
28:159–163. 2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen YH, Yao WZ, Geng B, et al: Endogenous
hydrogen sulfide, in patients with COPD. Chest. 128:3205–3211.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y and Wang R: The
vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP)
channel opener. EMBO J. 20:6008–6016. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan H, Du J and Tang C: The possible role
of hydrogen sulfide on pathogenesis of spontaneous hypertension in
rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 313:22–27. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hongfang J, Bailin Cong, Bin Zhao, et al:
Effects of hydrogen sulfides on hypoxic pulmonary vascular
structural remodeling. Life Sci. 78:1299–1309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Geng B, Yang J, Qi Y, et al: H2S generated
by heart in rat and its effect on cardiac function. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 313:362–368. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang G, Sun X and Wang R: Hydrogen
sulfide-induced apoptosis of human aorta smooth muscle cells via
the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and caspase-3.
FASEB J. 18:1782–1784. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chunyu Z, Junbao D, Dingfang B, et al: The
regulatory effect of hydrogen sulfide on hypoxic pulmonary
hypertension in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 302:810–816.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johansen D, Ytrehus K and Baxter GF:
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) protects against regional
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury - evidenve for a role of K
ATP channels. Basic Res Cardiol. 101:53–60. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zanardo RC, Brancaleone V, Distrutti E, et
al: Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous modulator of
leukocyte-mediated inflammation. Faseb J. 20:2118–2120. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sivarajah A, Collino M, Yasin M, et al:
Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of hydrogen sulfide in
a rat model of regional myocardial I/R. Shock. 31:267–274. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mitchell TW, Savage JC and Gould DH:
High-performance liquid chromatography detection of sulfide in
tissues from sulfide-treated mice. J Appl Toxicol. 13:389–394.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang GD and Wang R: H(2)S and cellular
proliferation and opoptosis. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 59:133–140.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stipanuk MH and Beck PW: Characterization
of the enzymic capacity for cysteine desulphhydration in liver and
kidney of the rat. Biochem J. 206:267–277. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stipanuk MH: Sulfur amino acid metabolism:
pathways for production and removal of homocysteine and cysteine.
Annu Rev Nutr. 24:539–577. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kamoun P: Endogenous production of
hydrogen sulfide in mammals. Amino Acids. 26:243–254. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y and Wang R: The
vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP)
channel opener. EMBO J. 20:6008–6016. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eto K, Ogasawara M, Umemura K, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide is produced in response to neuronal excitation. J
Neurosci. 22:3386–3391. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hosoki R, Matsuki N and Kimura H: The
possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous smooth muscle
relaxant in synergy with nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
237:527–531. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang R: The gasotransmitter role of
hydrogen sulfide. Antioxid Redox Signal. 5:493–501. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu YZ, Wang ZJ, Ho P, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide and its possible roles in myocardial ischemia in
experimental rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 102:261–268. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Johansen D, Ytrehus K and Baxter GF:
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) protects again stregional
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury - Evidence for a role of K
ATP channels. Basic Res Cardiol. 101:53–60. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Łowicka E and Bełtowski J: Hydrogen
sulfide (H2S) - the third gas of interest for pharmacologists.
Pharmacol Rep. 59:4–24. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siebenlist U, Fronzoso G and Brown K:
Structure regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell
Biol. 10:405–455. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee JI and Burckart GJ: Nuclear factor
kappa B: important transcription factor and therapeutic target. J
Clin Pharmacol. 38:981–993. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Atreya I, Atreya R and Neurath MF:
NF-kappaB in inflammatory bowel disease. J Intern Med. 263:591–596.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Distrutti E, et
al: Inhibition of hydrogen sulfide generation contributes to
gastric injury caused by anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs.
Gastroenterology. 129:1210–1224. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meldrum DR: Tumor necrosis factor in the
heart. Am J Physiol. 274:R577–R595. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Otterbein LE, Bach FH, Alam J, et al:
Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Nat Med. 6:422–428. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Marino M, Scuderi F, Mazzarelli P, et al:
Constitutive and cytokine-induced expression of MHC and
intercellular adhesion molecule-l (ICAM-l) on human myoblasts. J
Neuroimmunol. 116:94–101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kupatt C, Habazettl H, Goedecke A, et al:
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha contributes to ischemia- and
reperfusion-induced endothelial activation in isolated hearts. Circ
Res. 84:392–400. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roivainen M, Vilk-Kajander M, Palosuo T,
et al: Infections, inflammation and the risk of coronary heart
disease. Circulation. 101:252–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hansen PR: Role of neutrophils in
myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation. 91:1872–1875.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vanden Berghe W, Vermeulen L, De Wilde G,
et al: Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and gene
regulation of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6. Biochem
Pharmacol. 60:1185–1195. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li C, Browder W and Kao RL: Early
activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB during ischemia in
perfused rat heart. Am J Physiol. 276:H543–H552. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|