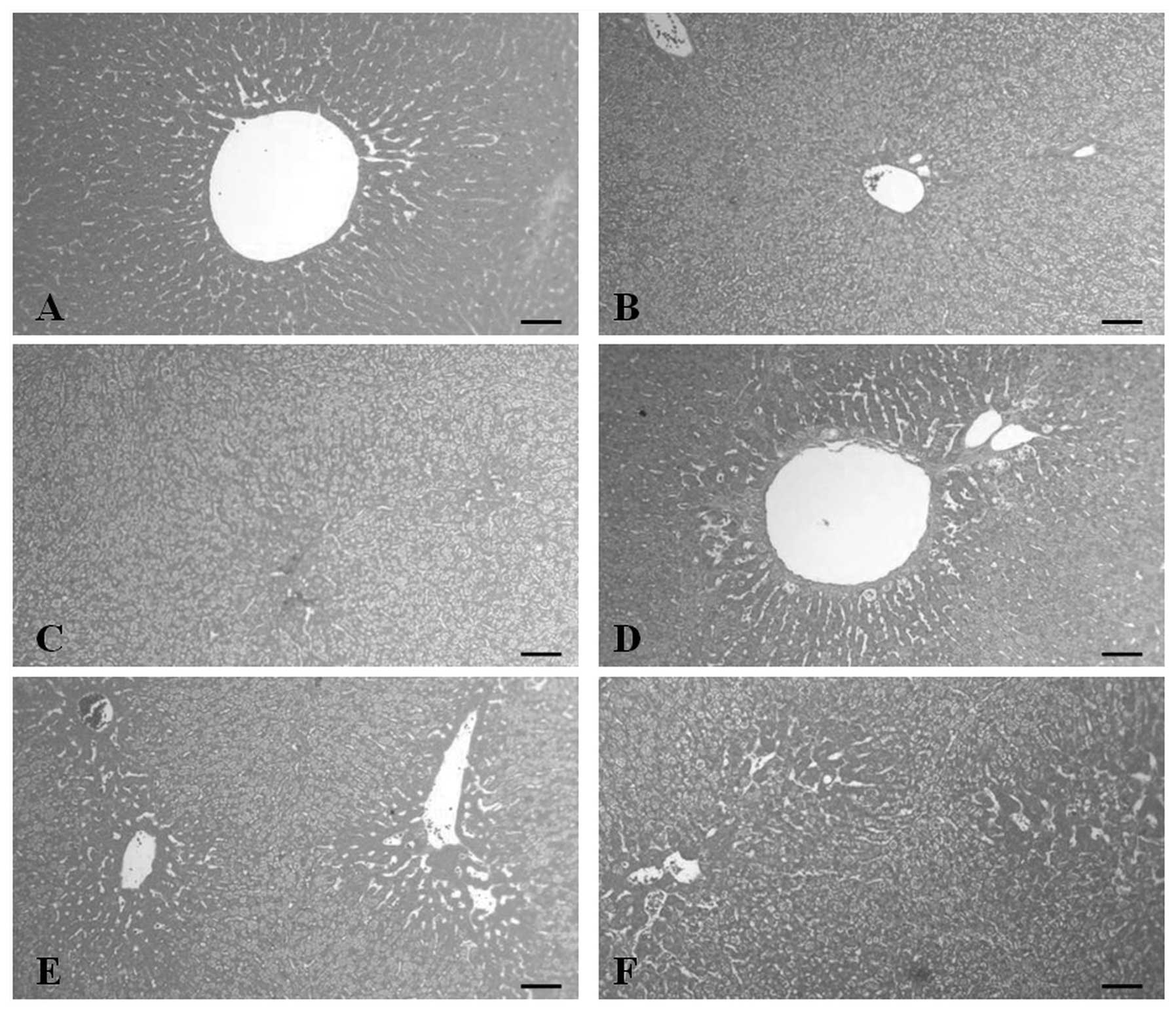
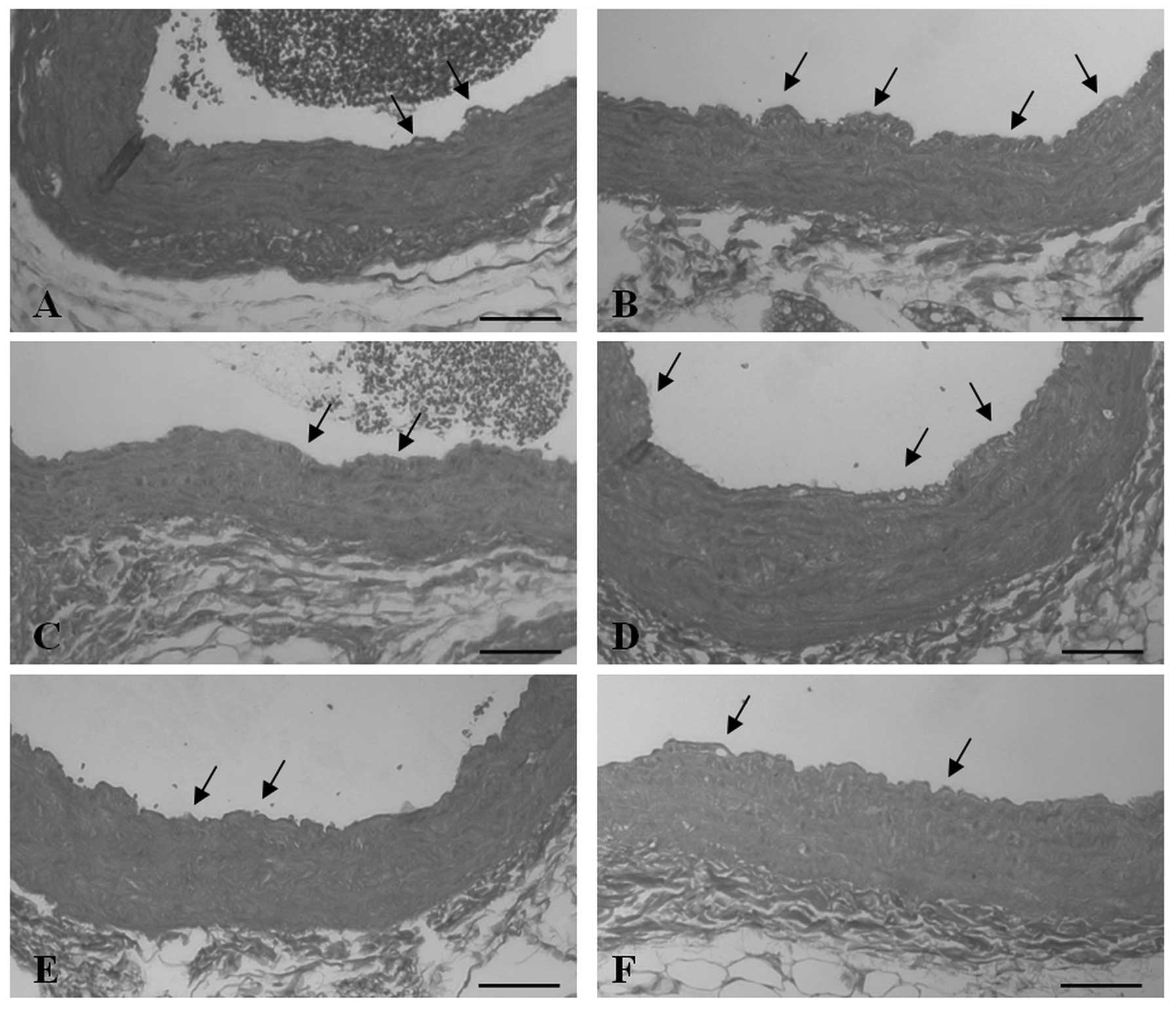
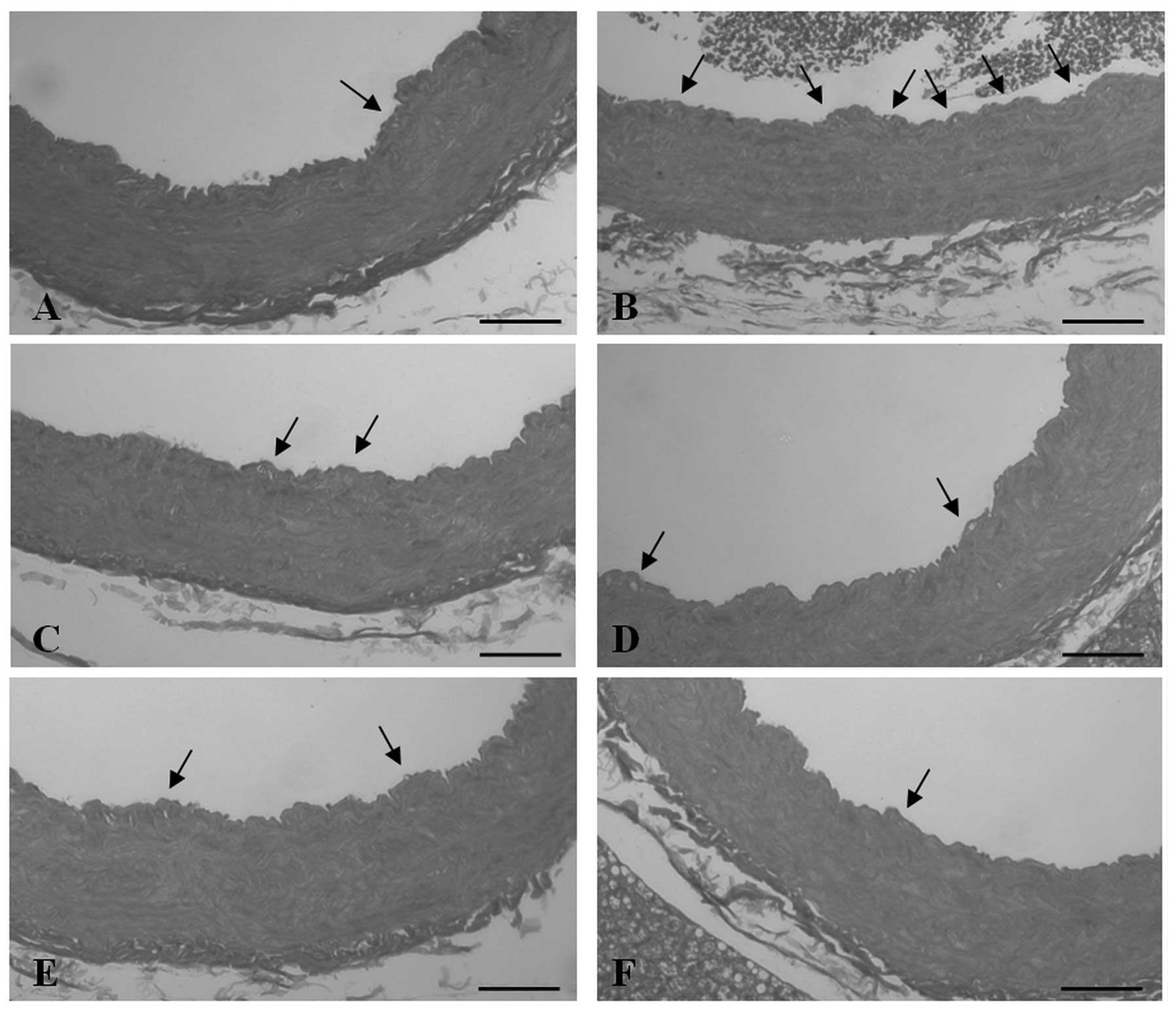
|
1
|
Grundy SM: Cholesterol and coronary heart
disease. A new era. JAMA. 256:2849–2858. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Neaton JD, Kuller LH, Wentworth D and
Borhani NO: Total and cardiovascular mortality in relation to
cigarette smoking, serum cholesterol concentration, and diastolic
blood pressure among black and white males followed up for five
years. Am Heart J. 108:759–769. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan BK, Tan CH and Pushparaj PN:
Anti-diabetic activity of the semi-purified fractions of Averrhoa
bilimbi in high fat diet fed-streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Life Sci. 76:2827–2839. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
el-Saadany SS, el-Massry RA, Labib SM and
Sitohy MZ: The biochemical role and hypocholesterolaemic potential
of the legume Cassia fistula in hypercholesterolaemic rats.
Nahrung. 35:807–815. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sima A, Stancu C, Constantinescu E,
Ologeanu L and Simionescu M: The hyperlipemic hamster - a model for
testing the anti-atherogenic effect of amlodipine. J Cell Mol Med.
5:153–162. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Stary HC: The sequence of cell and matrix
changes in atherosclerotic lesions of coronary arteries in the
first forty years of life. Eur Heart J. 11(Supple E): 3–19. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sima A, Bulla A and Simionescu N:
Experimental obstructive coronary atherosclerosis in the
hyperlipidemic hamster. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 22:1–16.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sullivan MP, Cerda JJ, Robbins FL, Burgin
CW and Beatty RJ: The gerbil, hamster, and guinea pig as rodent
models for hyperlipidemia. Lab Anim Sci. 43:575–578.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bishop RW: Structure of the hamster low
density lipoprotein receptor gene. J Lipid Res. 33:549–557.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vickers S, Duncan CA, Vyas KP, Kari PH,
Arison B, Prakash SR, Ramjit HG, Pitzenberger SM, Stokker G and
Duggan DE: In vitro and in vivo biotransformation of simvastatin,
an inhibitor of HMG CoA reductase. Drug Metab Dispos. 18:476–483.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Steinmetz EF, Buckley C, Shames ML, Ennis
TL, Vanvickle-Chavez SJ, Mao D, Goeddel LA, Hawkins CJ and Thompson
RW: Treatment with simvastatin suppresses the development of
experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms in normal and
hypercholesterolemic mice. Ann Surg. 241:92–101. 2005.
|
|
12
|
Czop JK: The role of beta-glucan receptors
on blood and tissue leukocytes in phagocytosis and metabolic
activation. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 5:286–296. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Estrada A, Yun CH, Van Kessel A, Li B,
Hauta S and Laarveld B: Immunomodulatory activities of oat
beta-glucan in vitro and in vivo. Microbiol Immunol. 41:991–998.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bell S, Goldman VM, Bistrian BR, Arnold
AH, Ostroff G and Forse RA: Effect of beta-glucan from oats and
yeast on serum lipids. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 39:189–202. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lia A, Hallmans G, Sandberg AS, Sundberg
B, Aman P and Andersson H: Oat beta-glucan increases bile acid
excretion and a fiber-rich barley fraction increases cholesterol
excretion in ileostomy subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 62:1245–1251.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Delaney B, Nicolosi RJ, Wilson TA, Carlson
T, Frazer S, Zheng GH, Hess R, Ostergren K, Haworth J and Knutson
N: Beta-glucan fractions from barley and oats are similarly
antiatherogenic in hypercholesterolemic Syrian golden hamsters. J
Nutr. 133:468–475. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wilson TA, Nicolosi RJ, Delaney B,
Chadwell K, Moolchandani V, Kotyla T, Ponduru S, Zheng GH, Hess R,
Knutson N, Curry L, Kolberg L, Goulson M and Ostergren K: Reduced
and high molecular weight barley beta-glucans decrease plasma total
and non-HDL-cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic Syrian golden
hamsters. J Nutr. 134:2617–2622. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pereira FE, Motta L and Cardoso AA:
Kupffer cell activation with BCG. Corynebacterium parvum or zymosan
protects against acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride
in rats. Arq Gastroenterol. 34:157–162. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kutina SN and Zubakhin AA: Liver
resistance to CCl (4)-induced injury after stimulation of
macrophages with various preparations. Bull Exp Biol Med.
129:524–526. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seo HP, Kim JM, Shin HD, Kim TK, Chang HJ,
Park BR and Lee JW: Production of β-1,3/1,6-glucan by Aureobasidium
pullulans SM-2001. Kor J Bitechnol Bioeng. 17:376–380. 2002.
|
|
21
|
Auger C, Caporiccio B, Landrault N,
Teissedre PL, Laurent C, Cros G, Besançon P and Rouanet JM: Red
wine phenolic compounds reduce plasma lipids and apolipoprotein B
and prevent early aortic atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic
golden Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus). J Nutr.
132:1207–1213. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim HG, Une M, Kuramoto T, Noshiro M and
Fujimura K: Hypocholesterolemic effect of bile acid sulfonate
analogs in hamsters. Biol Pharm Bull. 24:218–220. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang CY, Yang KM, Yang L, Miao ZX, Wang
YH and Zhu HB: A 1H NMR-based metabonomic investigation of
time-related metabolic trajectories of the plasma, urine and liver
extracts of hyperlipidemic hamsters. PLoS One. 8:e667862013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Wu C, Wu H, Sheng L, et al:
Anti-hyperlipidemic effects and potential mechanisms of action of
the caffeoylquinic acid-rich Pandanus tectorius fruit extract in
hamsters fed a high fat-diet. PLoS One. 8:e619222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao H, Long Y, Jiang X, Liu Z, Wang D,
Zhao Y, Li D and Sun BL: Beneficial effects of Yerba Mate tea (Ilex
paraguariensis) on hyperlipidemia in high-fat-fed hamsters. Exp
Gerontol. 48:572–578. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Naples M, Baker C, Lino M, Iqbal J,
Hussain MM and Adeli K: Ezetimibe ameliorates intestinal
chylomicron overproduction and improves glucose tolerance in a
diet-induced hamster model of insulin resistance. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302:G1043–G1052. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han LK, Zheng YN, Yoshikawa M, Okuda H and
Kimura Y: Anti-obesity effects of chikusetsusaponins isolated from
Panax japonicus rhizomes. BMC Complement Altern Med. 5:92005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Olsson B, Bohlooly-Y M, Fitzgerald SM,
Frick F, Ljungberg A, Ahrén B, Törnell J, Bergström G and Oscarsson
J: Bovine growth hormone transgenic mice are resistant to
diet-induced obesity but develop hyperphagia, dyslipidemia, and
diabetes on a high-fat diet. Endocrinology. 146:920–930. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yamashita J and Hayashi S: The effect of
dietary protein source on plasma cholesterol level and fecal
steroid excretion in obese mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).
36:545–558. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mukai M, Ozasa K, Hayashi K and Kawai K:
Various S-GOT/S-GPT ratios in nonviral liver disorders and related
physical conditions and life-style. Dig Dis Sci. 47:549–555. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hoyos M, Guerrero JM, Perez-Cano R, Olivan
J, Fabiani F, Garcia-Pergañeda A and Osuna C: Serum cholesterol and
lipid peroxidation are decreased by melatonin in diet-induced
hypercholesterolemic rats. J Pineal Res. 28:150–155. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lal JJ, Sreeranjit Kumar CV, Suresh MV,
Indira M and Vijayammal PL: Effect of in utero exposure of Toddy
(coconut palm wine) on liver function and lipid metabolism in rat
fetuses. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 52:209–219. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Blé-Castillo JL, Rodríguez-Hernández A,
Miranda-Zamora R, Juárez-Oropeza MA and Díaz-Zagoya JC: Arthrospira
maxima prevents the acute fatty liver induced by the administration
of simvastatin, ethanol and a hypercholesterolemic diet to mice.
Life Sci. 70:2665–2673. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Campo GM, Squadrito F, Ceccarelli S, et
al: Reduction of carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver injury by
IRFI 042, a novel dual vitamin E-like antioxidant. Free Radic Res.
34:379–393. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mansuy D, Sassi A, Dansette PM and Plat M:
A new potent inhibitor of lipid peroxidation in vitro and in vivo,
the hepatoprotective drug anisyldithiolthione. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 135:1015–1021. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Taylor SL and Tappel AL: Effect of dietary
antioxidants and phenobarbital pretreatment on microsomal lipid
peroxidation and activation by carbon tetrachloride. Life Sci.
19:1151–1160. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Krizková L, Duracková Z, Sandula J,
Slamenová D, Sasinková V, Sivonová M and Krajcovic J: Fungal
beta-(1–3)-D-glucan derivatives exhibit high antioxidative and
antimutagenic activity in vitro. Anticancer Res. 23:2751–2756.
2003.
|
|
38
|
Sener G, Toklu H, Ercan F and Erkanli G:
Protective effect of beta-glucan against oxidative organ injury in
a rat model of sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol. 5:1387–1396. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Forrester JS, Makkar R and Shah PK:
Increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in dyslipidemia by
cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibition: an update for
clinicians. Circulation. 111:1847–1854. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kamada T, Hata J, Kusunoki H, Ito M,
Tanaka S, Kawamura Y, Chayama K and Haruma K: Eradication of
Helicobacter pylori increases the incidence of hyperlipidaemia and
obesity in peptic ulcer patients. Dig Liver Dis. 37:39–43. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Milionis HJ, Kakafika AI, Tsouli SG,
Athyros VG, Bairaktari ET, Seferiadis KI and Elisaf MS: Effects of
statin treatment on uric acid homeostasis in patients with primary
hyperlipidemia. Am Heart J. 148:635–640. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng JW: Rosuvastatin in the management
of hyperlipidemia. Clin Ther. 26:1368–1387. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pirat B, Korkmaz ME, Eroǧlu S, Tayfun E,
Yildirir A, Uluçam M, Ozin B and Müderrisoǧlu H: The effects of
simvastatin combined with different antioxidant vitamin regimens on
serum lipid profile in patients with low HDL cholesterol levels.
Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 4:318–322. 2004.(In Turkish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zdrenghea D, Gligor E, Ossian V and Pop D:
The effect of simvastatin associated with ranitidine and alcohol
upon serum lipids. Rom J Intern Med. 42:143–148. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Morishita S, Saito T, Mishima Y, Mizutani
A, Hirai Y, Koyama S and Kawakami M: Strains and species
differences in experimental hyperlipidemia. Nihon Yakurigaku
Zasshi. 87:259–264. 1986.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ausman LM, Rong N and Nicolosi RJ:
Hypocholesterolemic effect of physically refined rice bran oil:
studies of cholesterol metabolism and early atherosclerosis in
hypercholesterolemic hamsters. J Nutr Biochem. 16:521–529. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Deepa PR and Varalakshmi P:
Atheroprotective effect of exogenous heparin-derivative treatment
on the aortic disturbances and lipoprotein oxidation in
hypercholesterolemic diet fed rats. Clin Chim Acta. 355:119–130.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Illman RJ and Topping DL: Effects of
dietary oat bran on faecal steroid excretion, plasma volatile fatty
acids and lipid synthesis in the rat. Nutr Res. 5:839–846. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Judd PA and Truswell AS: The effects of
rolled oats on blood lipids and fecal steroid excretion in man. Am
J Clin Nutr. 34:2061–2067. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rieckhoff D, Trautwein EA, Mälkki Y and
Ebersdobler HF: Effects of different cereal fibers on cholesterol
and bile acid metabolism in the Syrian golden hamster. Cereal Chem.
76:788–795. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Anderson JW, Story L, Sieling B, Chen WJ,
Petro MS and Story J: Hypocholesterolemic effects of oat-bran or
bean intake for hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr.
40:1146–1155. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kirby RW, Anderson JW, Sieling B, Rees ED,
Chen WJ, Miller RE and Kay RM: Oat-bran intake selectively lowers
serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations in
hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 34:824–829.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|