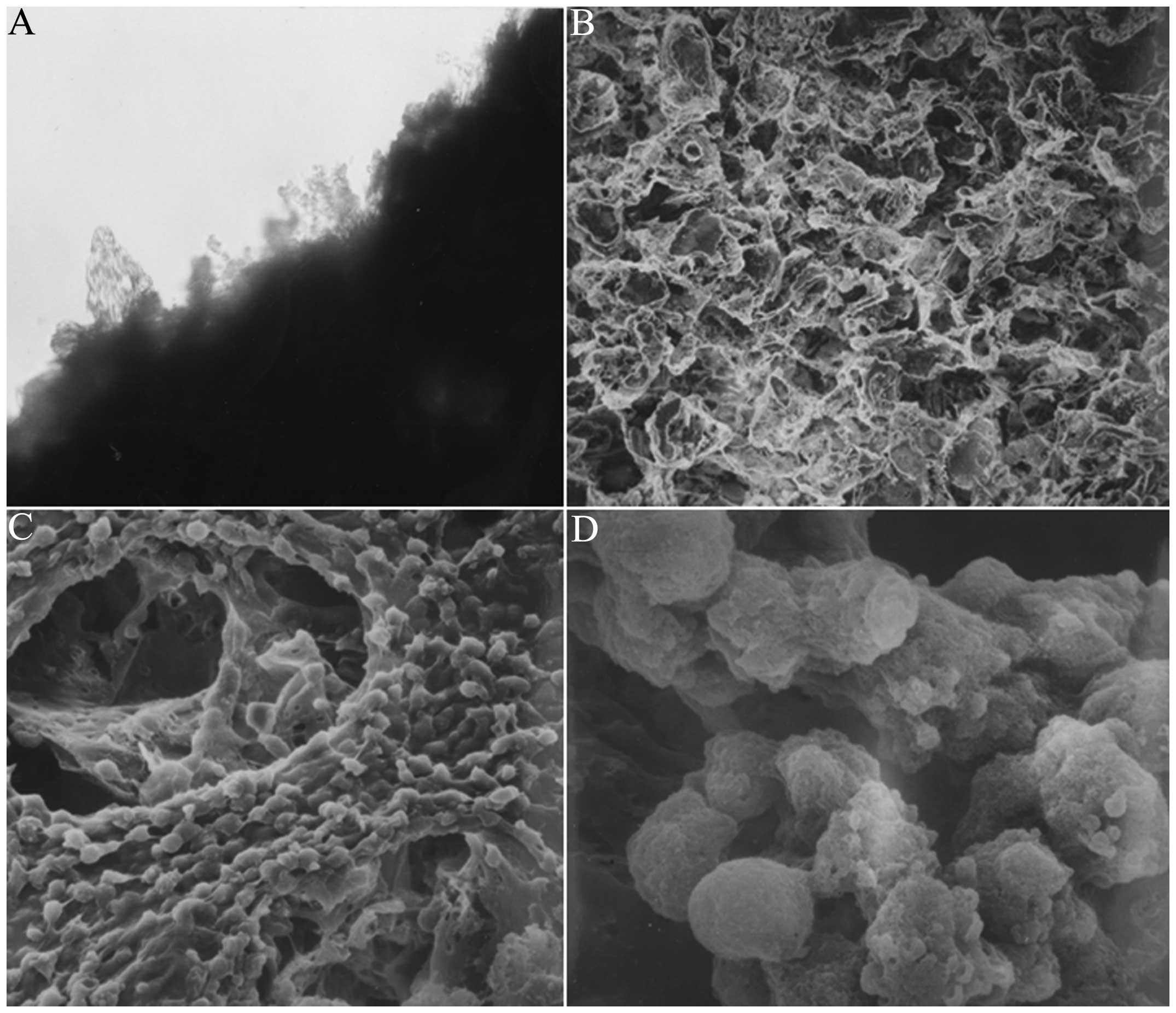
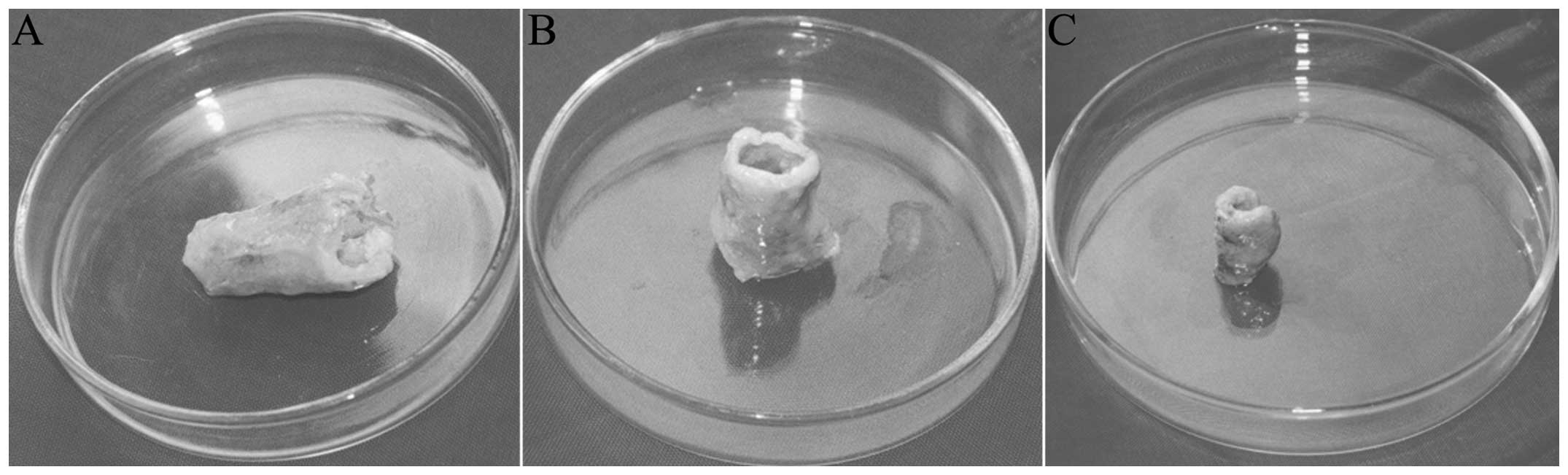
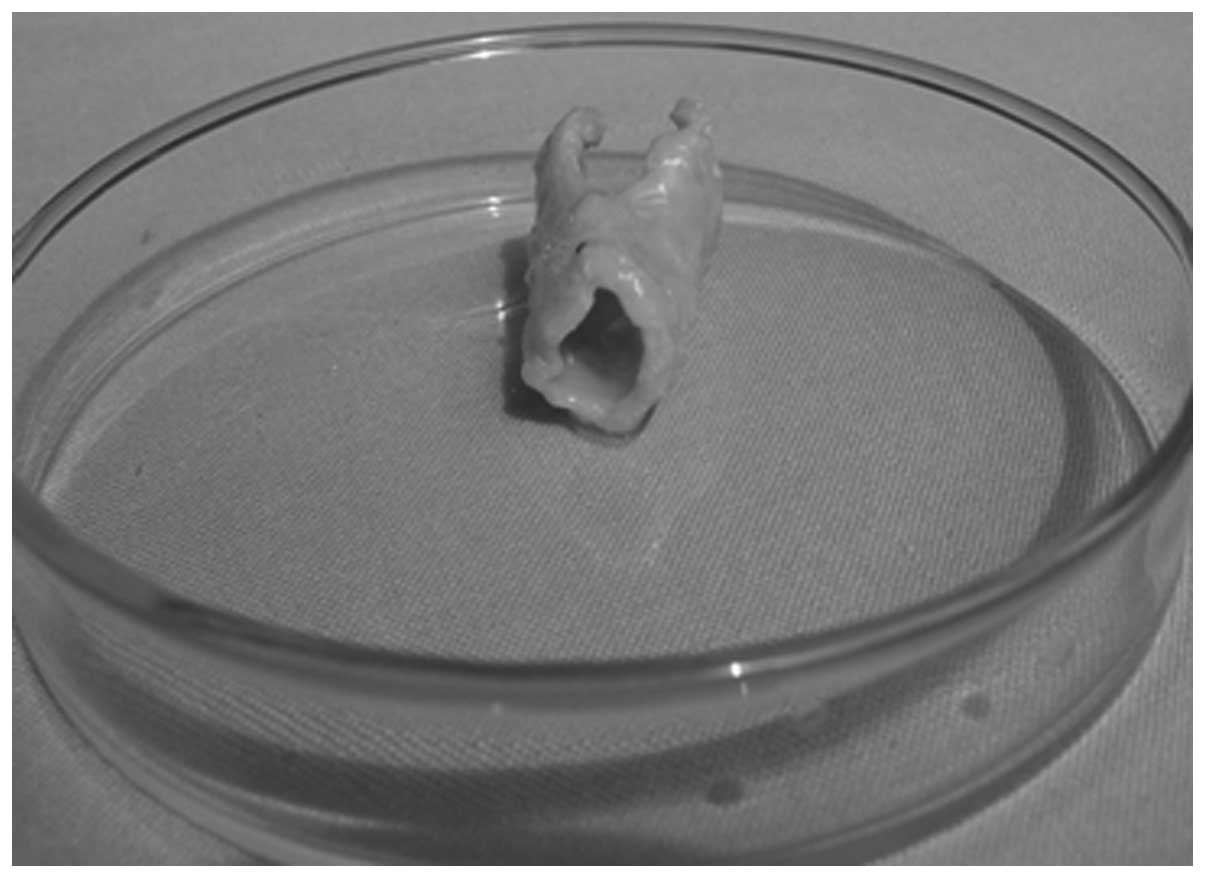
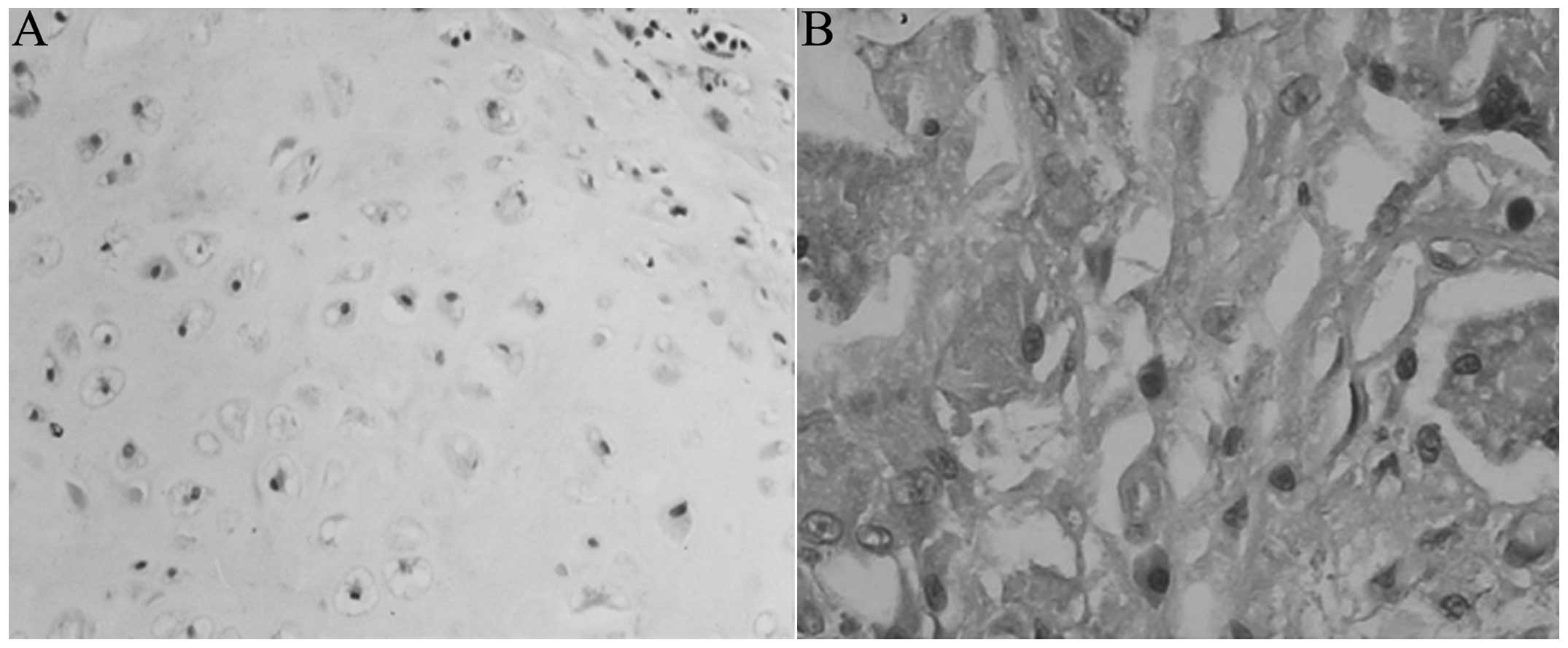
|
1
|
Sterodimas A and de Faria J: Human
auricular tissue engineering in an immunocompetent animal model.
Aesthet Surg J. 33:283–289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheng NC, Estes BT, Young TH and Guilak F:
Engineered cartilage using primary chondrocytes cultured in a
porous cartilage-derived matrix. Regen Med. 6:81–93. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Fishman JM, De Coppi P, Elliott MJ, Atala
A, Birchall MA and Macchiarini P: Airway tissue engineering. Expert
Opin Biol Ther. 11:1623–1635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fisher MB and Mauck RL: Tissue engineering
and regenerative medicine: recent innovations and the transition to
translation. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 19:1–13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Lu T, Li Y and Chen T: Techniques for
fabrication and construction of three-dimensional scaffolds for
tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 8:337–350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deng Y, Lin XS, Zheng Z, Deng JG, Chen JC,
Ma H and Chen GQ: Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyhexanoate)
promoted production of extracellular matrix of articular cartilage
chondrocytes in vitro. Biomaterials. 24:4273–4281. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Veleirinho B, Coelho DS, Dias PF,
Maraschin M, Ribeiro-do-Valle RM and Lopes-da-Silva JA: Nanofibrous
poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/chitosan scaffolds
for skin regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 51:343–350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mikos AG, Sarakinos G, Leite SM, Vacanti
JP and Langer R: Laminated three-dimensional biodegradable foams
for use in tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 14:323–330. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang R and Ma PX:
Poly(alpha-hydroxylacids)/hydroxyaptite porous composites for
bone-tissue engineering. I Preparation and morphology. J Biomed
Mater Res. 44:446–455. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gilpin DA, Weidenbecher MS and Dennis JE:
Scaffold-free tissue-engineered cartilage implants for
laryngotracheal reconstruction. Laryngoscope. 120:612–617. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shahin K and Doran PM: Improved seeding of
chondrocytes into polyglycolic acid scaffolds using semi-static and
alginate loading methods. Biotechnol Prog. 27:191–200. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
El Sayed K, Marzahn U, John T, et al:
PGA-associated heterotopic chondrocyte cocultures: implications of
nasoseptal and auricular chondrocytes in articular cartilage
repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 7:61–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chaim IA, Sabino MA, Mendt M, Müller AJ
and Ajami D: Evaluation of the potential of novel PCL-PPDX
biodegradable scaffolds as support materials for cartilage tissue
engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 6:272–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xue J, Feng B, Zheng R, et al: Engineering
ear-shaped cartilage using electrospun fibrous membranes of
gelatin/polycaprolactone. Biomaterials. 34:2624–2631. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vacanti CA and Upton J: Tissue-engineered
morphogenesis of cartilage and bone by means of cell
transplantation using synthetic biodegradable polymer matrices.
Clin Plast Surg. 21:445–462. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cohen SB, Meirisch CM, Wilson HA and
Diduch DR: The use of absorbable co-polymer pads with alginate and
cells for articular cartilage repair in rabbits. Biomaterials.
24:2653–2660. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baek CH and Ko YJ: Characteristics of
tissue-engineered cartilage on macroporous biodegradable PLGA
scaffold. Laryngoscope. 116:1829–1834. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhijun L and Wanming W: Latest progress in
biological scaffold materials for tissue engineered cartilage.
Zhongguo zu zhi gong cheng yan jiu. 11:3625–3628. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Asti A and Gioglio L: Natural and
synthetic biodegradable polymers: different scaffolds for cell
expansion and tissue formation. Int J Artif Organs. 37:187–205.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao K, Deng Y, Chun Chen J and Chen GQ:
Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) scaffolds with good mechanical
properties and biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 24:1041–1045. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ye C, Hu P, Ma MX, Xiang Y, Liu RG and
Shang XW: PHB/PHBHHX scaffolds and human adipose-derived stem cells
for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 30:4401–4406. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun AK, Li WT, Meng QY, Liu SB, Chen W and
Tang WW: Fabrication of larynx-shape tissue engineered cartilage by
means of filling together with wrapping with pedicle myofascial
flap. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 46:1019–1023.
2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Nomoto Y, Okano W, Imaizumi M, Tani A,
Nomoto M and Omori K: Bioengineered prosthesis with allogenic
heterotopic fibroblasts for cricoid regeneration. Laryngoscope.
122:805–809. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lange P, Fishman JM, Elliott MJ, De Coppi
P and Birchall MA: What can regenerative medicine offer for infants
with laryngotracheal agenesis? Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
145:544–550. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanemaru S, Hirano S, Umeda H, et al: A
tissue-engineering approach for stenosis of the trachea and/or
cricoid. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 563:79–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Glatz F, Neumeister M, Suchy H, Lyons S,
Damikas D and Mowlavi A: A tissue-engineering technique for
vascularized laryngotracheal reconstruction. Arch Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 129:201–206. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aslim EJ, Rasheed MZ, Lin F, Ong YS and
Tan BK: Use of the anterolateral thigh and vertical rectus
abdominis musculocutaneous flaps as utility flaps in reconstructing
large groin defects. Arch Plast Surg. 41:556–561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang SL, Wang YY, Chen WL and Zhang DM:
Use of extended vertical lower trapezius island myocutaneous flaps
to cover exposed reconstructive plates. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
72:209.e1–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhi L, Wenli W, Pengfei G, et al:
Laryngotracheal reconstruction with autogenous rib cartilage graft
for complex laryngotracheal stenosis and/or anterior neck defect.
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 271:317–322. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chanowski EJ, Haxer MJ and Chepeha DB:
Microvascular cricoid cartilage reconstruction with the
thoracodorsal artery scapular tip autogenous transplant.
Laryngoscope. 122:282–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao Y, Zhang W, Zhao J, Li Z and He S:
Reconstruction of soft tissue defects in oral and maxillofacial
regions after tumors surgery using cervical pedicle tissue flaps.
Zhogguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 19:780–783. 2005.
|