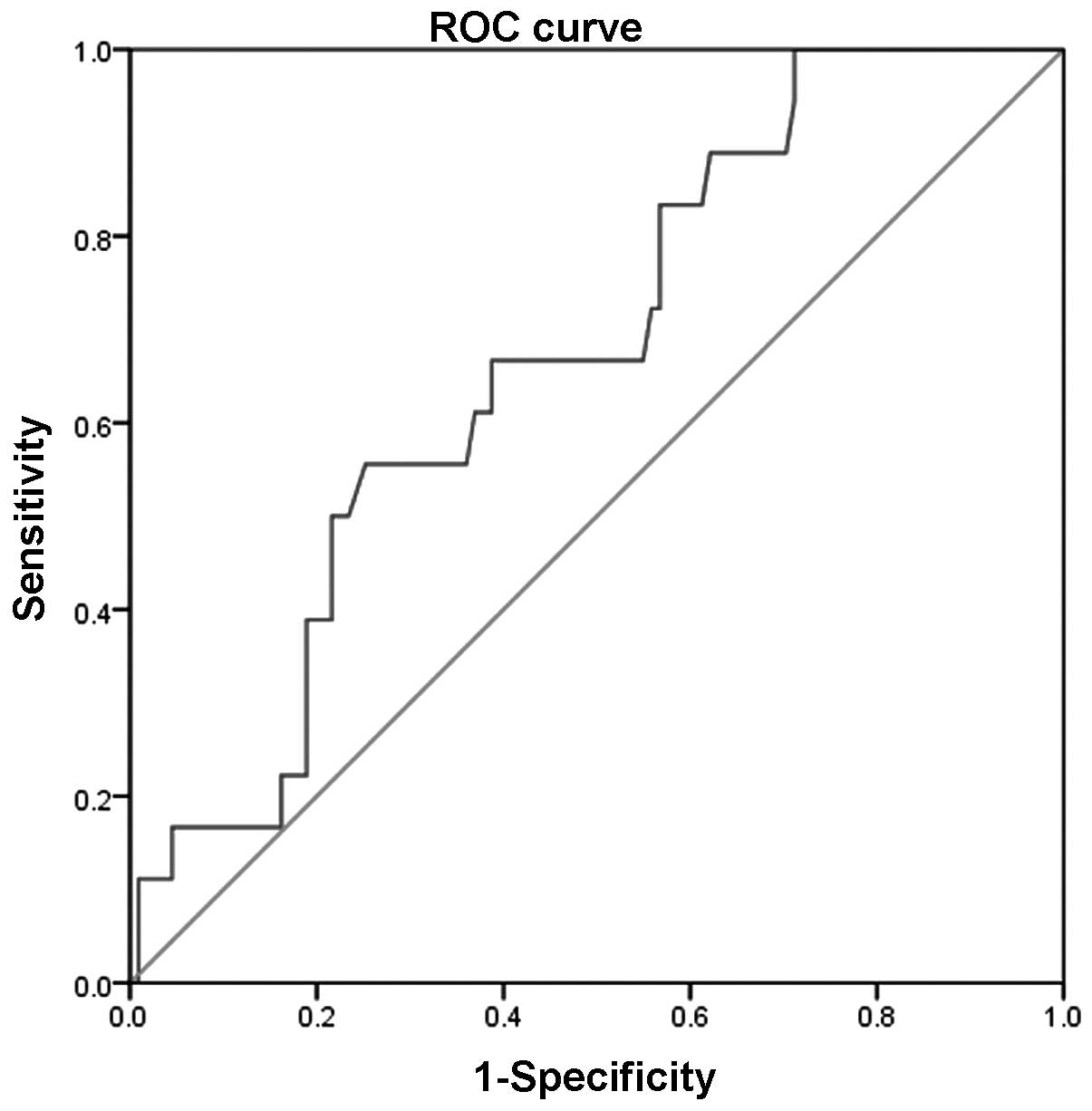
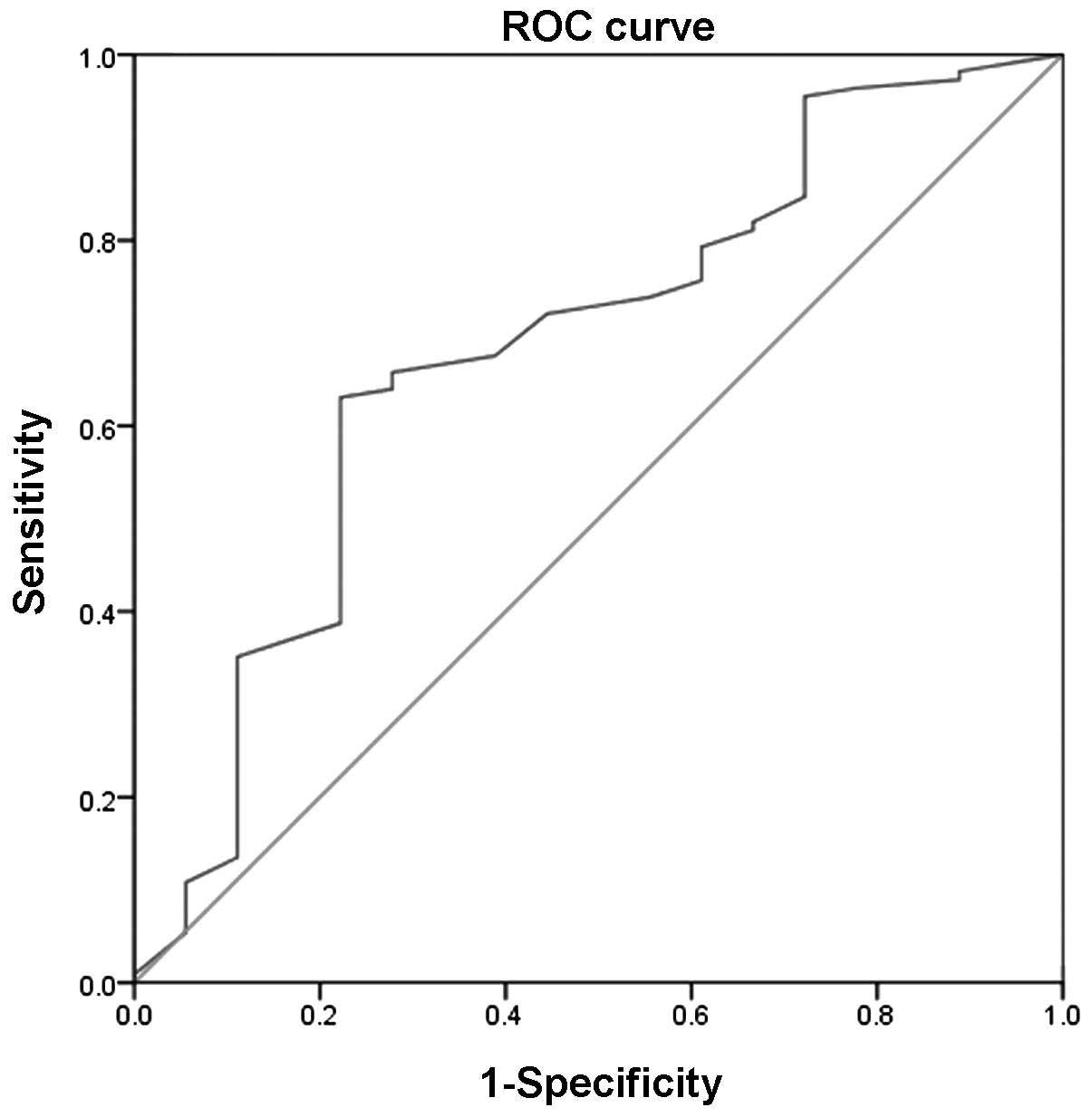
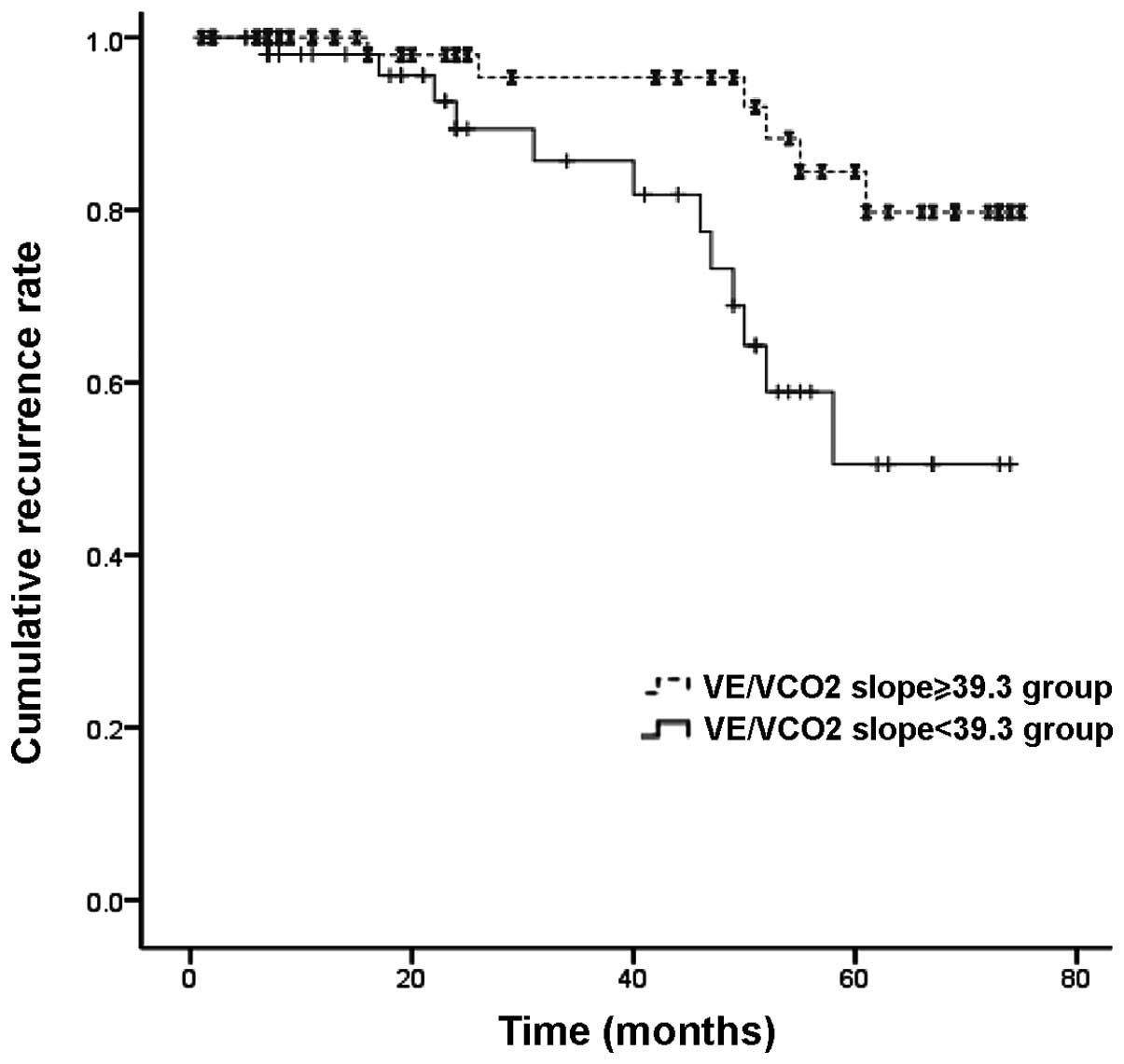
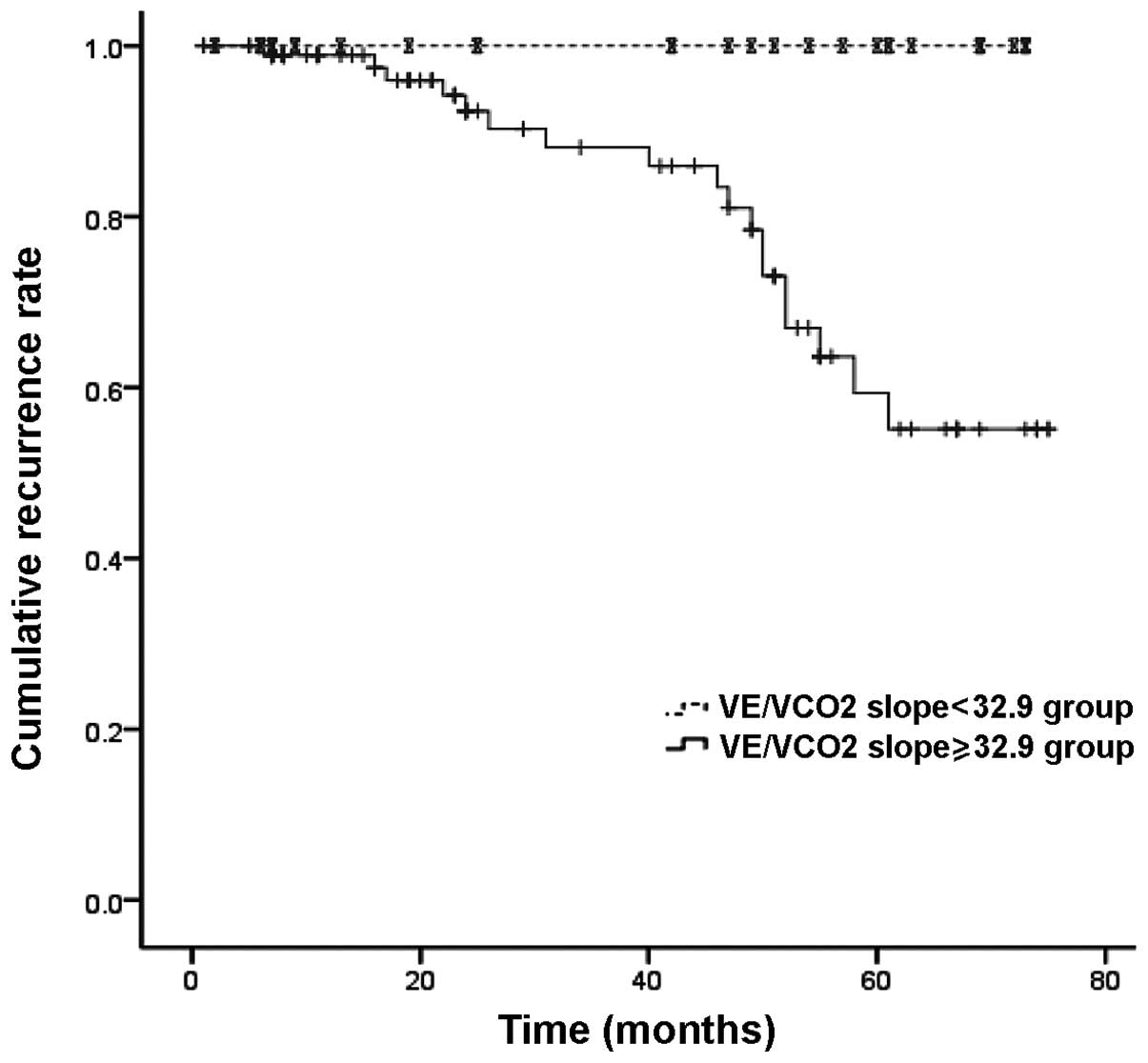
|
1
|
Johnson RL Jr: Gas exchange efficiency in
congestive heart failure. Circulation. 101:2774–2776. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ponikowski P, Chua TP, Anker SD, et al:
Peripheral chemoreceptor hypersensitivity: an ominous sign in
patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 104:544–549.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Metra M, Dei Cas L, Panina G and Visioli
O: Exercise hyperventilation chronic congestive heart failure, and
its relation to functional capacity and hemodynamics. Am J Cardiol.
70:622–628. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clark AL, Volterrani M, Swan JW and Coats
AJ: The increased ventilatory response to exercise in chronic heart
failure: relation to pulmonary pathology. Heart. 77:138–146. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cicoira M, Zanolla L, Franceschini L, et
al: Skeletal muscle mass independently predicts peak oxygen
consumption and ventilatory response during exercise in
non-cachectic patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 37:2080–2085. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arena R, Myers J, Abella J, Peberdy MA,
Bensimhon D, Chase P and Guazzi M: The ventilatory classification
system effectively predicts hospitalization in patients with heart
failure. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 28:195–198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Francis DP, Shamim W, Davies LC, Piepoli
MF, Ponikowski P, Anker SD and Coats AJ: Cardiopulmonary exercise
testing for prognosis in chronic heart failure: continuous and
independent prognostic value from VE/VCO(2) slope and peak VO(2).
Eur Heart J. 21:154–161. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arena R, Myers J, Aslam SS, Varughese EB
and Peberdy MA: Peak VO2 and VE/VCO2 slope in
patients with heart failure: a prognostic comparison. Am Heart J.
147:354–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Corrà U, Mezzani A, Bosimini E, Scapellato
F, Imparato A and Giaanuzzi P: Ventilatory response to exercise
improves risk stratification in patients with chronic heart failure
and intermediate functional capacity. Am Heart J. 143:418–426.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bard RL, Gillespie BW, Clarke NS, Egan TG
and Nicklas JM: Determining the best ventilatory efficiency measure
to predict mortality in patients with heart failure. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 25:589–595. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arena R, Guazzi M, Myers J, et al: The
prognostic utility of cardiopulmonary exercise testing stands the
test of time in patients with heart failure. J Cardiopulm Rehabil
Prev. 32:198–202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Poggio R, Arazi HC, Giorgi M and Miriuka
SG: Prediction of severe cardiovascular events by
VE/VCO2 slope versus peak VO2 in systolic
heart failure: a meta-analysis of the published literature. Am
Heart J. 160:1004–1014. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chinese Society of Cardiology of Chinese
Medical Association; Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of
Cardiology. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic
heart failure. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 35:1076–1095.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Radford MJ, Arnold JM, Bennett SJ, et al;
American College of Cardiology; American Heart Association Task
Force on Clinical Data Standards; American College of Chest
Physicians; International Society for Heart and Lung
Transplantation; Heart Failure Society of America. ACC/AHA key data
elements and definitions for measuring the clinical management and
outcomes of patients with chronic heart failure: a report of the
American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task
Force on Clinical Data Standards (Writing Committee to Develop
Heart Failure Clinical Data Standards): developed in collaboration
with the American College of Chest Physicians and the International
Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: endorsed by the Heart
Failure Society of America. Circulation. 112:1888–1916. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fisher JD: New York Heart Association
Classification. Arch Intern Med. 129:8361972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheitlin MD, Armstrong WF, Aurigemma GP,
et al; ACC; AHA; ASE. ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 Guideline Update for the
Clinical Application of Echocardiography: summary article. A report
of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association
Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASE Committee to Update
the 1997 Guidelines for the Clinical Application of
Echocardiography). J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 16:1091–1110.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lebeau R, Di Lorenzo M, Amyot R, et al: A
new tool for estimating left ventricular ejection fraction derived
from wall motion score index. Can J Cardiol. 19:397–404.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Devereux RB, Alonso DR, Lutas EM, Gottlieb
GJ, Campo E, Sachs I and Reichek N: Echocardiographic assessment of
left ventricular hypertrophy: comparison to necropsy findings. Am J
Cardiol. 57:450–458. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boone J, Koppo K and Bouckaert J: The VO2
response to submaximal ramp cycle exercise: Influence of ramp slope
and training status. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 161:291–297. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Borg G: Psychophysical bases of perceived
exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 14:377–381. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Beaver WL, Wasserman K and Whipp BJ: A new
method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 60:2020–2027. 1986.
|
|
22
|
Bard RL, Gillespie BW, Clarke NS, Egan TG
and Nicklas JM: Determining the best ventilatory efficiency measure
to predict mortality in patients with heart failure. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 25:589–595. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al: 2013
ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of
the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart
Association task force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol.
62:e147–e239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chinese Society of Cardiology of Chinese
Medical Association and Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of
Cardiology. Chinese guideline for diagnosis and treatment of heart
failure 2014. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 42:98–122. 2014.In
Chinese.
|
|
25
|
Corrà U, Giordano A, Mezzani A, et al:
Prognostic significance of peak oxygen consumption ≤ 10 ml/kg/min
in heart failure: context vs. criteria. Int J Cardiol.
168:3419–3423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
O’Neill JO, Young JB, Pothier CE and Lauer
MS: Peak oxygen consumption as a predictor of death in patients
with heart failure receiving β-blockers. Circulation.
111:2313–2318. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sarullo FM, Fazio G, Brusca I, et al:
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in patients with chronic heart
failure: prognostic comparison from peak VO2 and
VE/VCO2 slope. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 4:127–134. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arena R and Humphrey R: Comparison of
ventilatory expired gas parameters used to predict hospitalization
in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J. 143:427–432. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kleber FX, Vietzke G, Wernecke KD, et al:
Impairment of ventilatory efficiency in heart failure: prognostic
impact. Circulation. 101:2803–2809. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ponikowski P, Francis DP, Piepoli MF, et
al: Enhanced ventilatory response to exercise in patients with
chronic heart failure and preserved exercise tolerance: marker of
abnormal cardiorespiratory reflex control and predictor of poor
prognosis. Circulation. 103:967–972. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guazzi M, Arena R and Myers J: Comparison
of the prognostic value of cardiopulmonary exercise testing between
male and female patients with heart failure. Int J Cardiol.
113:395–400. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Francis DP, Shamim W, Davies LC, et al:
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing for prognosis in chronic heart
failure: continuous and independent prognostic value from VE/VCO(2)
slope and peak VO(2). Eur Heart J. 21:154–161. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Arena R, Myers J, Abella J and Peberdy MA:
Influence of heart failure etiology on the prognostic value of peak
oxygen consumption and minute ventilation/carbon dioxide production
slope. Chest. 128:2812–2817. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arena RA, Guazzi M, Myers J and Abella J:
The prognostic value of ventilatory efficiency with beta-blocker
therapy in heart failure. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 39:213–219. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|