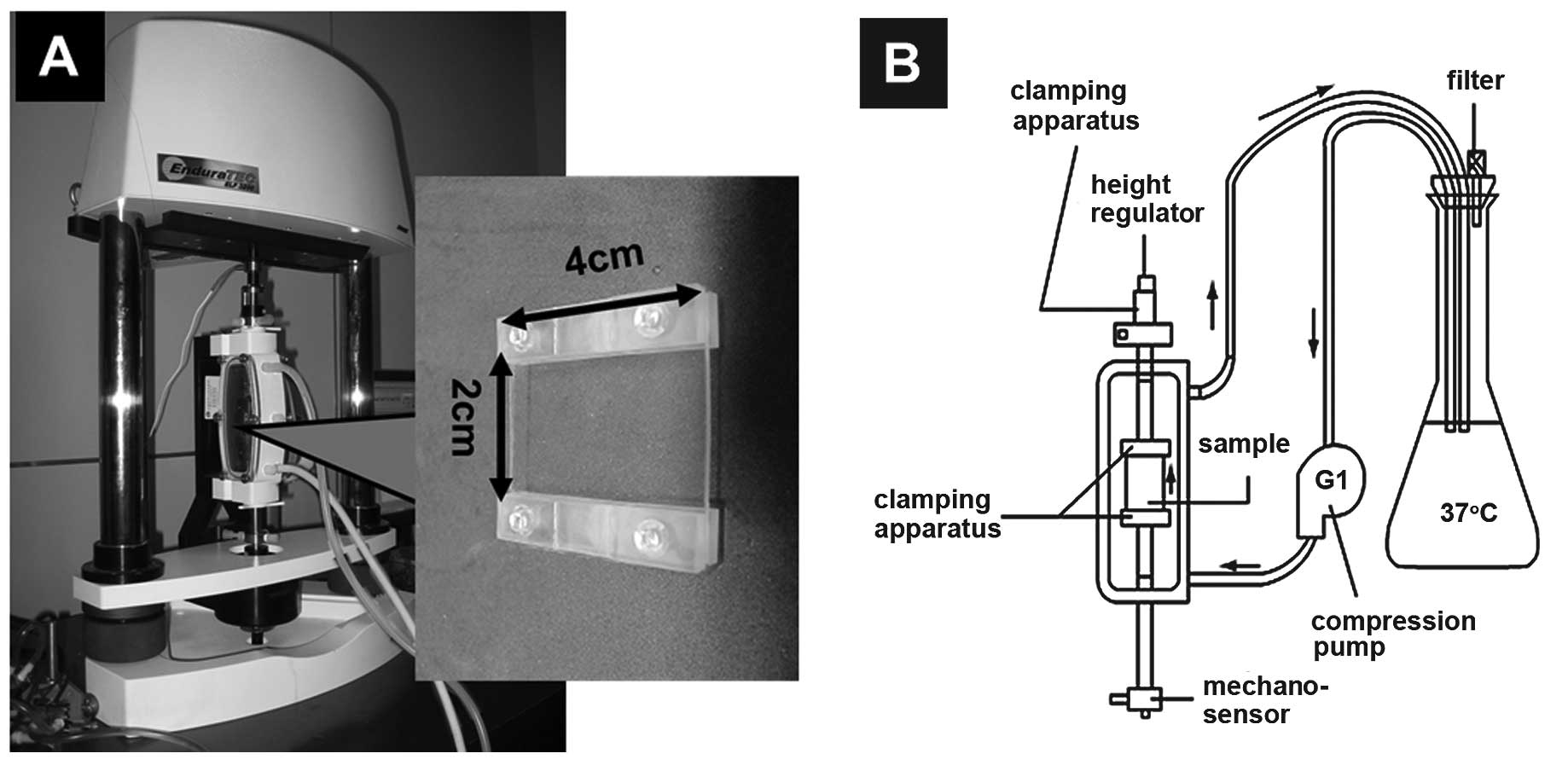
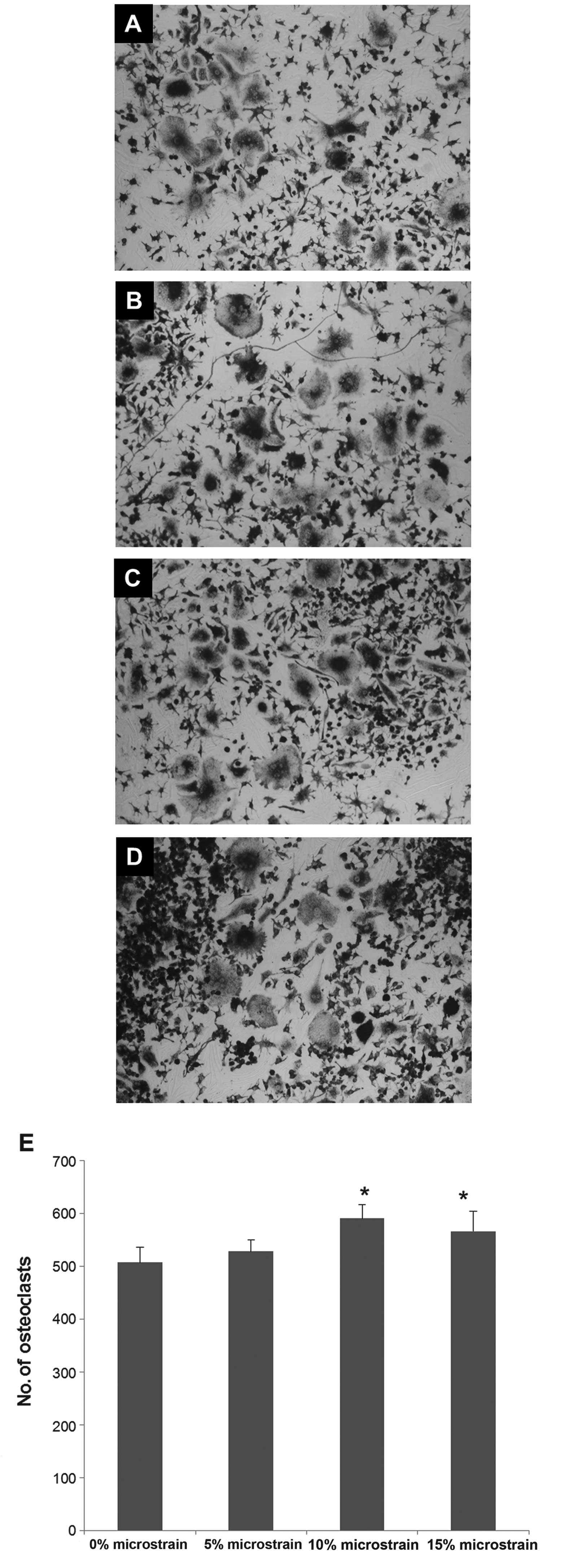
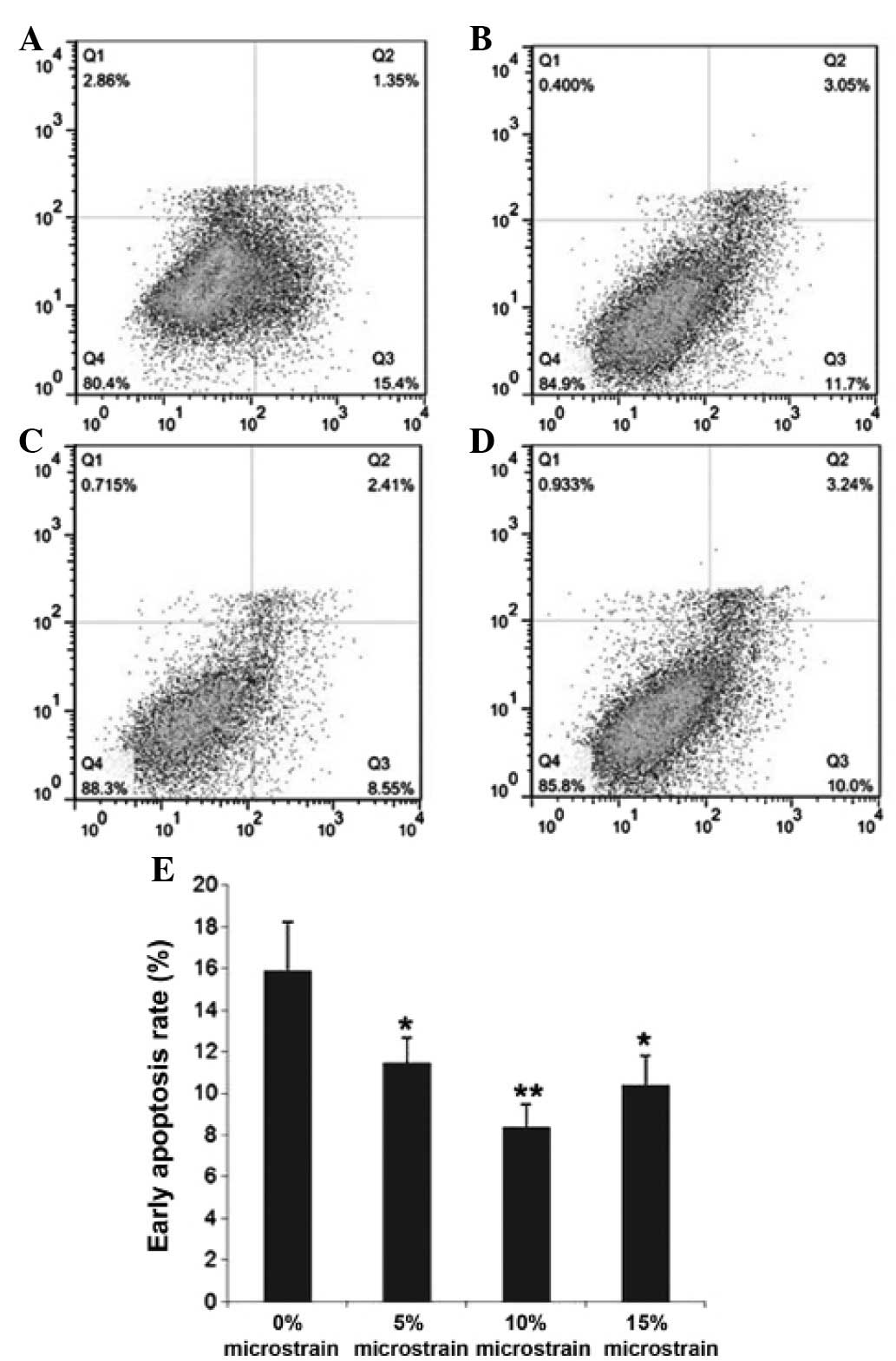
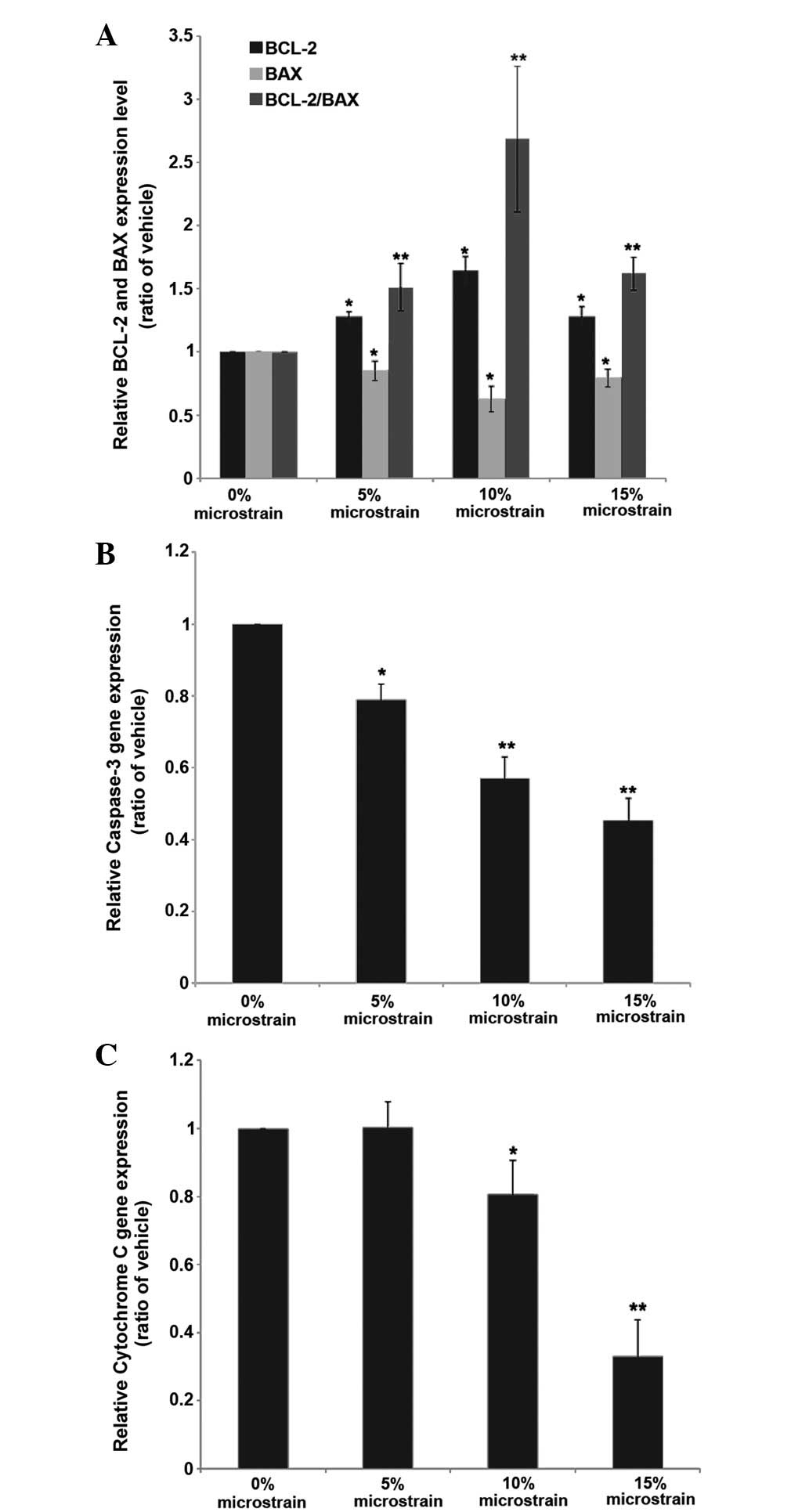
|
1
|
Nakahama K: Cellular communications in
bone homeostasis and repair. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:4001–4009. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu H and Li B: p53 control of bone
remodeling. J Cell Biochem. 111:529–534. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ehrlich PJ and Lanyon LE: Mechanical
strain and bone cell function: A review. Osteoporos Int.
13:688–700. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chow JW, Jagger CJ and Chambers TJ:
Reduction in dynamic indices of cancellous bone formation in rat
tail vertebrae after caudal neurectomy. Calcif Tissue Int.
59:117–120. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huiskes R, Ruimerman R, van Lenthe GH and
Janssen JD: Effects of mechanical forces on maintenance and
adaptation of form in trabecular bone. Nature. 405:704–706. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rubin CT and Lanyon LE: Kappa Delta Award
paper. Osteoregulatory nature of mechanical stimuli: Function as a
determinant for adaptive remodeling in bone. J Orthop Res.
5:300–310. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jee WS, Li XJ and Schaffler MB: Adaptation
of diaphyseal structure with aging and increased mechanical usage
in the adult rat: A histomorphometrical and biomechanical study.
Anat Rec. 230:332–338. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Turner CH, Akhter MP, Raab DM, Kimmel DB
and Recker RR: A noninvasive, in vivo model for studying strain
adaptive bone modeling. Bone. 12:73–79. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chambers TJ, Evans M, Gardner TN,
Turner-Smith A and Chow JW: Induction of bone formation in rat tail
vertebrae by mechanical loading. Bone Miner. 20:167–178. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Forwood MR and Turner CH: Skeletal
adaptations to mechanical usage: Results from tibial loading
studies in rats. Bone. 17(4 Suppl): 197S–205S. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mosley JR, March BM, Lynch J and Lanyon
LE: Strain magnitude related changes in whole bone architecture in
growing rats. Bone. 20:191–198. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cowin SC, Moss-Salentijn L and Moss ML:
Candidates for the mechanosensory system in bone. J Biomech Eng.
113:191–197. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weinbaum S, Cowin SC and Zeng Y: A model
for the excitation of osteocytes by mechanical loading-induced bone
fluid shear stresses. J Biomech. 27:339–360. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kaspar D, Seidl W, Neidlinger-Wilke C, et
al: Proliferation of human-derived osteoblast-like cells depends on
the cycle number and frequency of uniaxial strain. J Biomech.
35:873–880. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaspar D, Seidl W, Neidlinger-Wilke C, et
al: Dynamic cell stretching increases human osteoblast
proliferation and CICP synthesis but decreases osteocalcin
synthesis and alkaline phosphatase activity. J Biomech. 33:45–51.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Neidlinger-Wilke C, Wilke HJ and Claes L:
Cyclic stretching of human osteoblasts affects proliferation and
metabolism: A new experimental method and its application. J Orthop
Res. 12:70–78. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen YJ, Huang CH, Lee IC, et al: Effects
of cyclic mechanical stretching on the mRNA expression of
tendon/ligament-related and osteoblast-specific genes in human
mesenchymal stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 49:7–14. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hara F, Fukuda K, Ueno M, et al: Pertussis
toxin-sensitive G proteins as mediators of stretch-induced decrease
in nitric-oxide release of osteoblast-like cells. J Orthop Res.
17:593–597. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Searby ND, Steele CR and Globus RK:
Influence of increased mechanical loading by hypergravity on the
microtubule cytoskeleton and prostaglandin E2 release in primary
osteoblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 289:C148–C158. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanno T, Takahashi T, Tsujisawa T, et al:
Mechanical stress-mediated Runx2 activation is dependent on
Ras/ERK1/2 MAPK signaling in osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem.
101:1266–1277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Quinn JM and Gillespie MT: Modulation of
osteoclast formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 328:739–745.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suzuki N, Yoshimura Y, Deyama Y, et al:
Mechanical stress directly suppresses osteoclast differentiation in
RAW264. 7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 21:291–296. 2008.
|
|
24
|
Kurata K, Uemura T, Nemoto A, et al:
Mechanical strain effect on bone-resorbing activity and messenger
RNA expressions of marker enzymes in isolated osteoclast culture. J
Bone Miner Res. 16:722–730. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weinstein RS and Manolagas SC: Apoptosis
and osteoporosis. Am J Med. 108:153–164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abe K, Yoshimura Y, Deyama Y, et al:
Effects of bisphosphonates on osteoclastogenesis in RAW264. 7
cells. Int J Mol Med. 29:1007–1015. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Mdel M Arriero, Ramis JM, Perelló J and
Monjo M: Inositol hexakisphosphate inhibits osteoclastogenesis on
RAW 264.7 cells and human primary osteoclasts. PLoS One.
7:e431872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Osdoby P, Martini MC and Caplan AI:
Isolated osteoclasts and their presumed progenitor cells, the
monocyte, in culture. J Exp Zool. 224:331–344. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zallone A Zambonin, Teti A and Primavera
MV: Isolated osteoclasts in primary culture: First observations on
structure and survival in culture media. Anat Embryol (Berl).
165:405–413. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tezuka K, Tezuka Y, Maejima A, et al:
Molecular cloning of a possible cysteine proteinase predominantly
expressed in osteoclasts. J Biol Chem. 269:1106–1109.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Akatsu T, et al:
The bone marrow-derived stromal cell lines MC3T3-G2/PA6 and ST2
support osteoclast-like cell differentiation in cocultures with
mouse spleen cells. Endocrinology. 125:1805–1813. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Collin-Osdoby P, Oursler MJ, Webber D and
Osdoby P: Osteoclast-specific monoclonal antibodies coupled to
magnetic beads provide a rapid and efficient method of purifying
avian osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 6:1353–1365. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Quinn JM, Neale S, Fujikawa Y, et al:
Human osteoclast formation from blood monocytes, peritoneal
macrophages, and bone marrow cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 62:527–531.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duncan RL and Turner CH:
Mechanotransduction and the functional response of bone to
mechanical strain. Calcif Tissue Int. 57:344–358. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Skerry TM and Suva LJ: Investigation of
the regulation of bone mass by mechanical loading: From
quantitative cytochemistry to gene array. Cell Biochem Funct.
21:223–229. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Adams JM and Cory S: Bcl-2-regulated
apoptosis: Mechanism and therapeutic potential. Curr Opin Immunol.
19:488–496. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yin XM: Bid, a BH3-only multi-functional
molecule, is at the cross road of life and death. Gene. 369:7–19.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, et
al: Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular
addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell.
9:351–365. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kuwana T and Newmeyer DD: Bcl-2-family
proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 15:691–699. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hellebrand EE and Varbiro G: Development
of mitochondrial permeability transition inhibitory agents: A novel
drug target. Drug Discov Ther. 4:54–61. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jilka RL, Noble B and Weinstein RS:
Osteocyte apoptosis. Bone. 54:264–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Timmer JC and Salvesen GS: Caspase
substrates. Cell Death Differ. 14:66–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dai C, Zhang B, Liu X, et al:
Pyrimethamine sensitizes pituitary adenomas cells to temozolomide
through cathepsin B-dependent and caspase-dependent apoptotic
pathways. Int J Cancer. 133:1982–1993. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cryns V and Yuan J: Proteases to die for.
Genes Dev. 12:1551–1570. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|