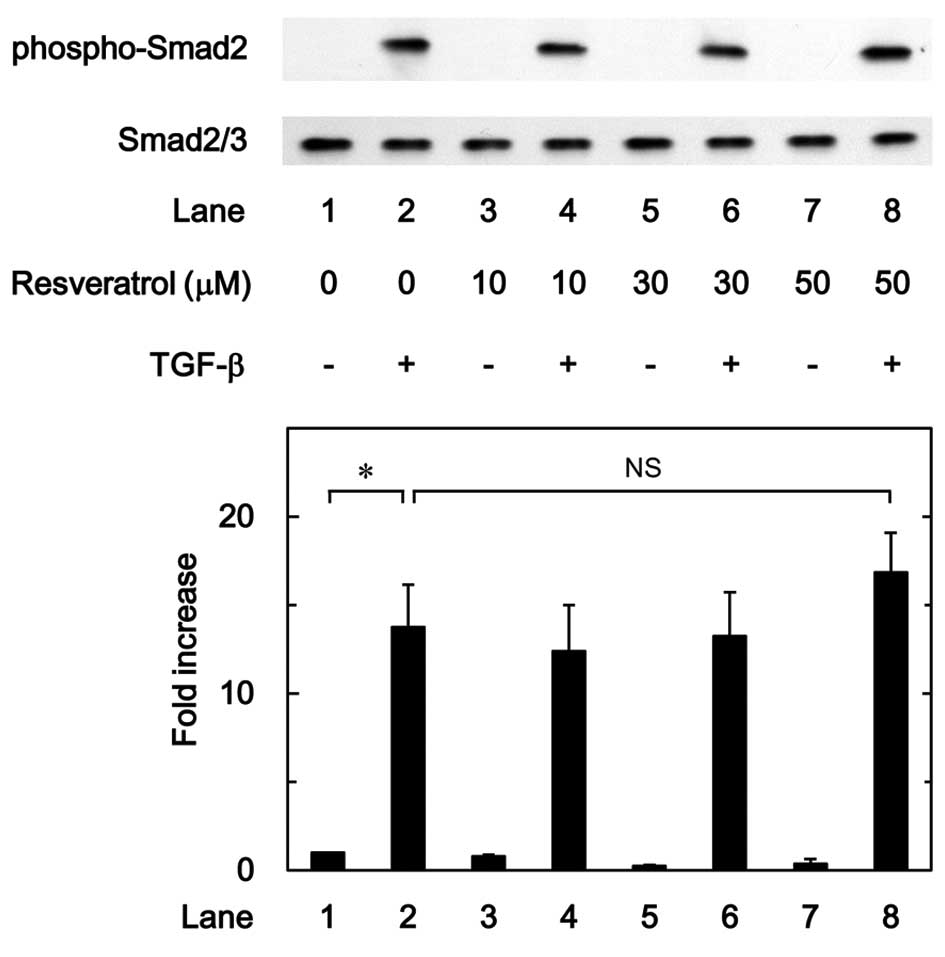
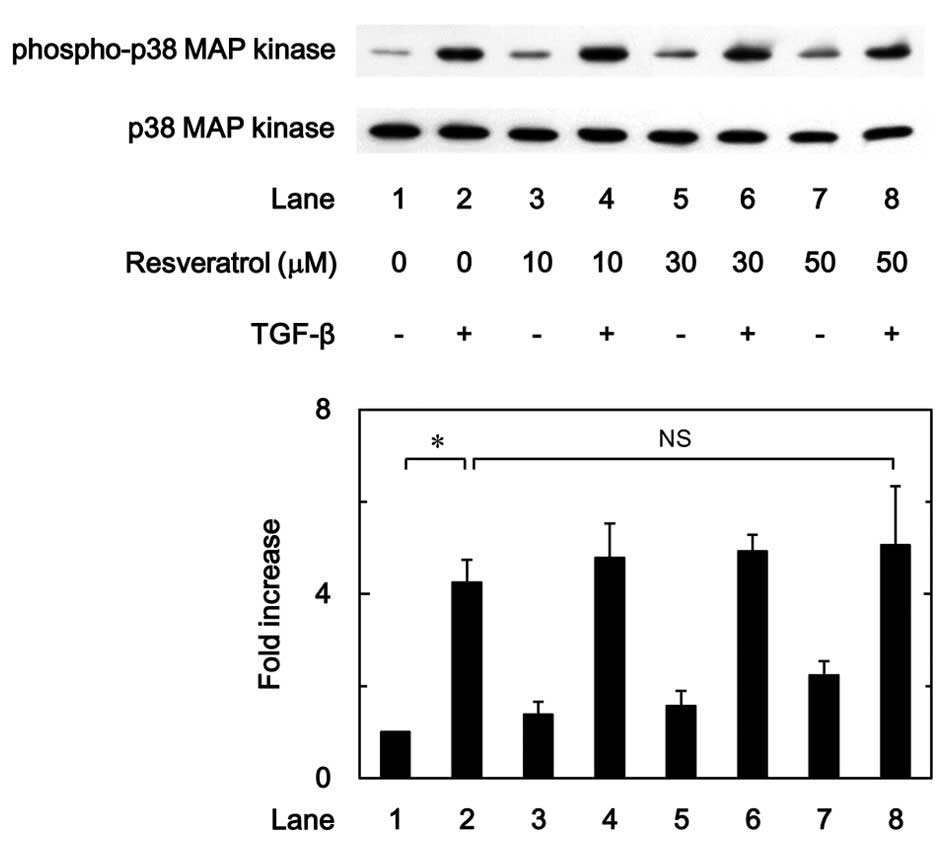
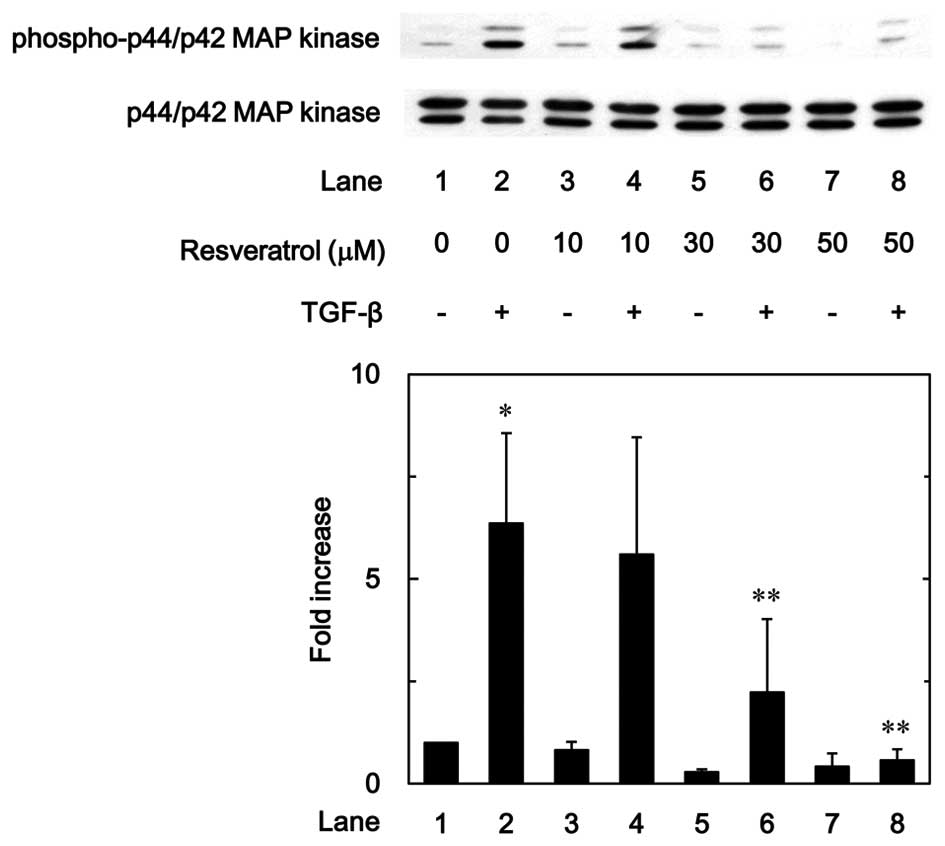
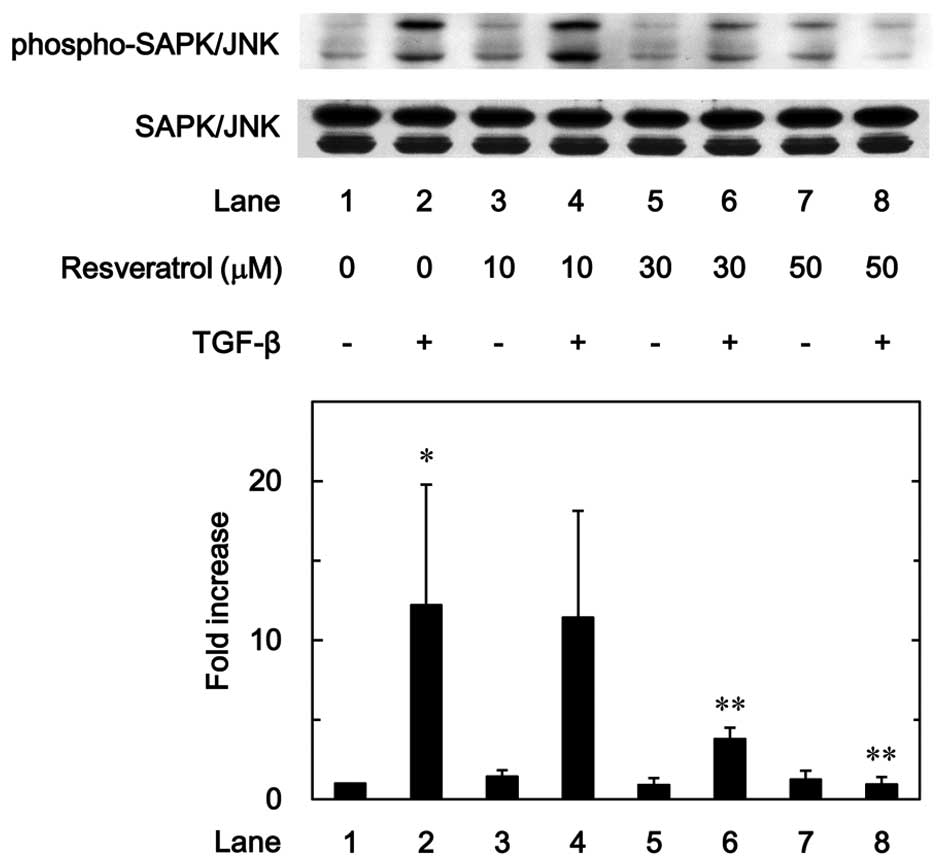
|
1
|
Kular J, Tickner J, Chim SM and Xu J: An
overview of the regulation of bone remodelling at the cellular
level. Clin Biochem. 45:863–873. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, Kuek V, Guo
B, Zhang G, Rosen V, Erber W and Xu J: Angiogenic factors in bone
local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:297–310. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parfitt AM: Targeted and nontargeted bone
remodeling: Relationship to basic multicellular unit origination
and progression. Bone. 30:5–7. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: The regulation
of TGFbeta signal transduction. Development. 136:3699–3714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang Y, Wu X, Lei W, Pang L, Wan C, Shi Z,
Zhao L, Nagy TR, Peng X, Hu J, et al: TGF-beta1-induced migration
of bone mesenchymal stem cells couples bone resorption with
formation. Nat Med. 15:757–765. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karsenty G and Wagner EF: Reaching a
genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev
Cell. 2:389–406. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhen G and Cao X: Targeting TGFβ signaling
in subchondral bone and articular cartilage homeostasis. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 35:227–236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Clarkin CE and Gerstenfeld LC: VEGF and
bone cell signalling: An essential vessel for communication? Cell
Biochem Funct. 31:1–11. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tokuda H, Hatakeyama D, Akamatsu S, Tanabe
K, Yoshida M, Shibata T and Kozawa O: Involvement of MAP kinases in
TGF-beta-stimulated vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in
osteoblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 415:117–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kanno Y, Ishisaki A, Yoshida M, Tokuda H,
Numata O and Kozawa O: SAPK/JNK plays a role in transforming growth
factor-beta-induced VEGF synthesis in osteoblasts. Horm Metab Res.
37:140–145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Blander G and Guarente L: The Sir2 family
of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:417–435. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koo SH and Montminy M: In vino veritas: A
tale of two sirt1s? Cell. 127:1091–1093. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Renaud S and de Lorgeril M: Wine, alcohol,
platelets, and the French paradox for coronary heart disease.
Lancet. 339:1523–1526. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kubo JT, Stefanick ML, Robbins J,
Wactawski-Wende J, Cullen MR, Freiberg M and Desai M: Preference
for wine is associated with lower hip fracture incidence in
post-menopausal women. BMC Womens Health. 13:362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kondo A, Otsuka T, Kuroyanagi G, Yamamoto
N, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Mizutani J, Kozawa O and Tokuda H:
Resveratrol inhibits BMP-4-stimulated VEGF synthesis in
osteoblasts: Suppression of S6 kinase. Int J Mol Med. 33:1013–1018.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuroyanagi G, Tokuda H,
Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kondo A, Mizutani J, Kozawa O and Otsuka T:
Resveratrol suppresses prostaglandin F(2α)-induced osteoprotegerin
synthesis in osteoblasts: Inhibition of the MAP kinase signaling.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 542:39–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuroyanagi G, Mizutani J, Kondo A,
Yamamoto N, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Otsuka T, Kozawa O and Tokuda
H: Suppression by resveratrol of prostaglandin D2-stimulated
osteoprotegerin synthesis in osteoblasts. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 91:73–80. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sudo H, Kodama HA, Amagai Y, Yamamoto S
and Kasai S: In vitro differentiation and calcification in a new
clonal osteogenic cell line derived from newborn mouse calvaria. J
Cell Biol. 96:191–198. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kozawa O, Tokuda H, Miwa M, Kotoyori J and
Oiso Y: Cross-talk regulation between cyclic AMP production and
phosphoinositide hydrolysis induced by prostaglandin E2
in osteoblast-like cells. Exp Cell Res. 198:130–134. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simpson DA, Feeney S, Boyle C and Stitt
AW: Retinal VEGF mRNA measured by SYBR green I fluorescence: A
versatile approach to quantitative PCR. Mol Vis. 6:178–183.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kato K, Ito H, Hasegawa K, Inaguma Y,
Kozawa O and Asano T: Modulation of the stress-induced synthesis of
hsp27 and alpha B-crystallin by cyclic AMP in C6 rat glioma cells.
J Neurochem. 66:946–950. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Milne JC, Lambert PD, Schenk S, et al:
Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the
treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nature. 450:712–716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo X and Wang XF: Signaling cross-talk
between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 19:71–88. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Howitz KT, Bitterman KJ, Cohen HY, et al:
Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces
cerevisiae lifespan. Nature. 425:191–196. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, et al:
Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie
diet. Nature. 444:337–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Non-Smad
TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci. 118:3573–3584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|