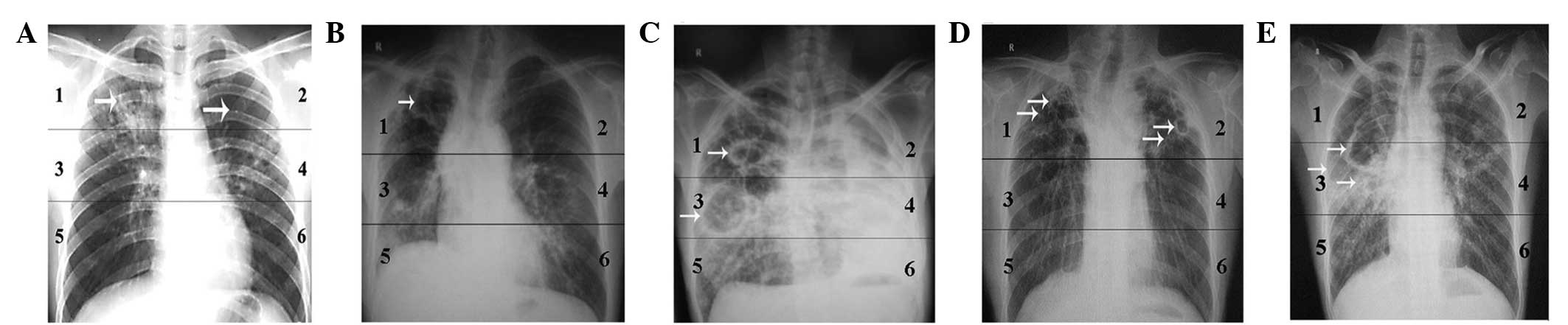
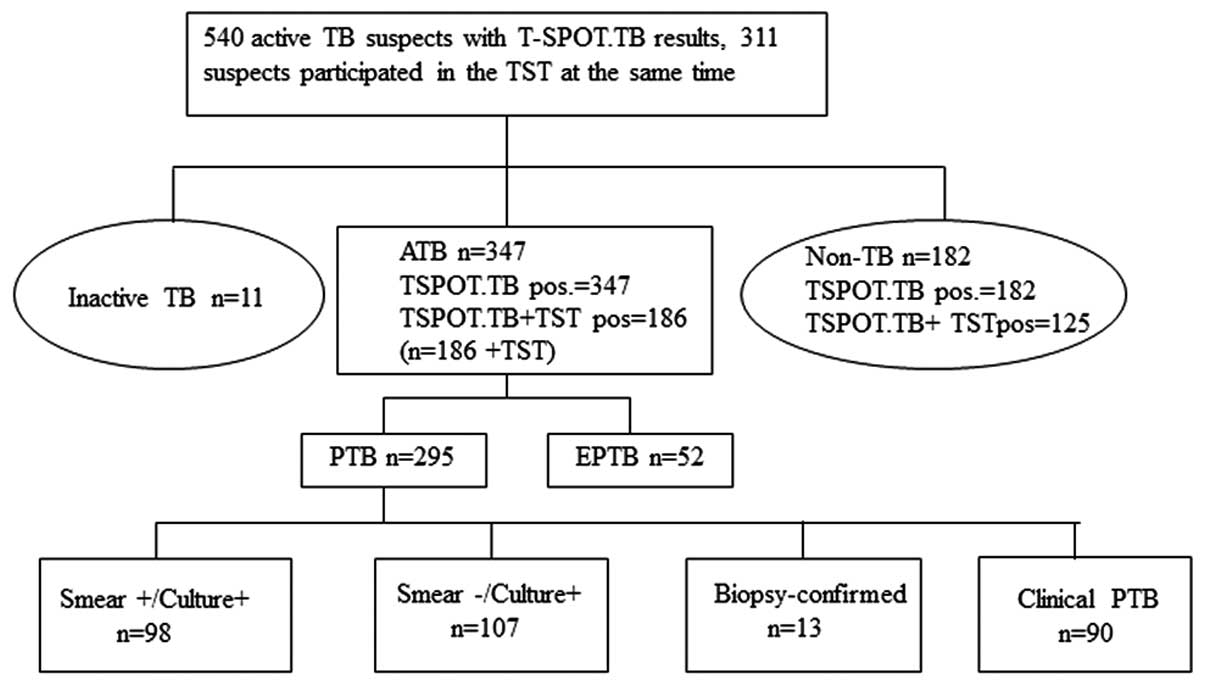
|
1
|
Moyle PM and Toth I: Modern subunit
vaccines: Development, components and research opportunities.
ChemMedChem. 8:360–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brodie D and Schluger NW: The diagnosis of
tuberculosis. Clin Chest Med. 26:247–271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Richeldi L: An update on the diagnosis of
tuberculosis infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 174:736–742.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang W, Shao L, Zhang Y, et al:
High-sensitive and rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection by IFN-gamma release assay among HIV-infected individuals
in BCG-vaccinated area. BMC Immunol. 10:312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Diel R, Loddenkemper R and Nienhaus A:
Evidence-based comparison of commercial interferon-gamma release
assays for detecting active TB: A metaanalysis. Chest. 137:952–968.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lalvani A and Pareek M: Interferon gamma
release assays: Principles and practice. Enferm Infecc Microbiol
Clin. 28:245–252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ewer K, Deeks J, Alvarez L, et al:
Comparison of T-cell-based assay with tuberculin skin test for
diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a school
tuberculosis outbreak. Lancet. 361:1168–1173. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Andersen P, Munk ME, Pollock JM and
Doherty TM: Specific immune-based diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Lancet. 356:1099–1104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang CH, Chan PC, Liao ST, et al: Strategy
to better select HIV-infected individuals for latent TB treatment
in BCG-vaccinated population. PLoS One. 8:e730692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu Y, Zhao X, Wang W, et al: Diagnostic
performance of interferon-gamma releasing assay in HIV-infected
patients in China. PLoS One. 8:e709572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singanayagam A, Manalan K, Sridhar S, et
al: Evaluation of screening methods for identification of patients
with chronic rheumatological disease requiring tuberculosis
chemoprophylaxis prior to commencement of TNF-α antagonist therapy.
Thorax. 68:955–961. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dai Y, Feng Y, Xu R, Xu W, Lu W and Wang
J: Evaluation of interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis
of tuberculosis: An updated meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Microbiol
Infect Dis. 31:3127–3137. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan L, Chen Z, Hao XH, Hu ZY and Xiao HP:
Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of extrapulmonary
tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. FEMS Immunol
Med Microbiol. 65:456–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng Y, Diao N, Shao L, et al:
Interferon-gamma release assay performance in pulmonary and
extrapulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS One. 7:e326522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Domínguez J, De Souza-Galvão M,
Ruiz-Manzano J, et al: T-cell responses to the Mycobacterium
tuberculosis-specific antigens in active tuberculosis patients at
the beginning, during and after antituberculosis treatment. Diagn
Microbiol Infect Dis. 63:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bosshard V, Roux-Lombard P, Perneger T, et
al: Do results of the T-SPOT.TB interferon-gamma release assay
change after treatment of tuberculosis? Respir Med. 103:30–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ribeiro S, Dooley K, Hackman J, et al:
T-SPOT.TB responses during treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. BMC
Infect Dis. 9:232009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chee CB, KhinMar KW, Gan SH, et al:
Tuberculosis treatment effect on T-cell interferon-gamma responses
to Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens. Eur Respir J.
36:355–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cho OH, Park KH, Kim SM, et al: Diagnostic
performance of T-SPOT.TB for extrapulmonary tuberculosis according
to the site of infection. J Infect. 63:362–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liao CH, Chou CH, Lai CC, et al:
Diagnostic performance of an enzyme-linked immunospot assay for
interferon-gamma in extrapulmonary tuberculosis varies between
different sites of disease. J Infect. 59:402–408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
World Health Organization (WHO), . The
global plan to stop TB 2011–2015. Geneva: WHO; 2010
|