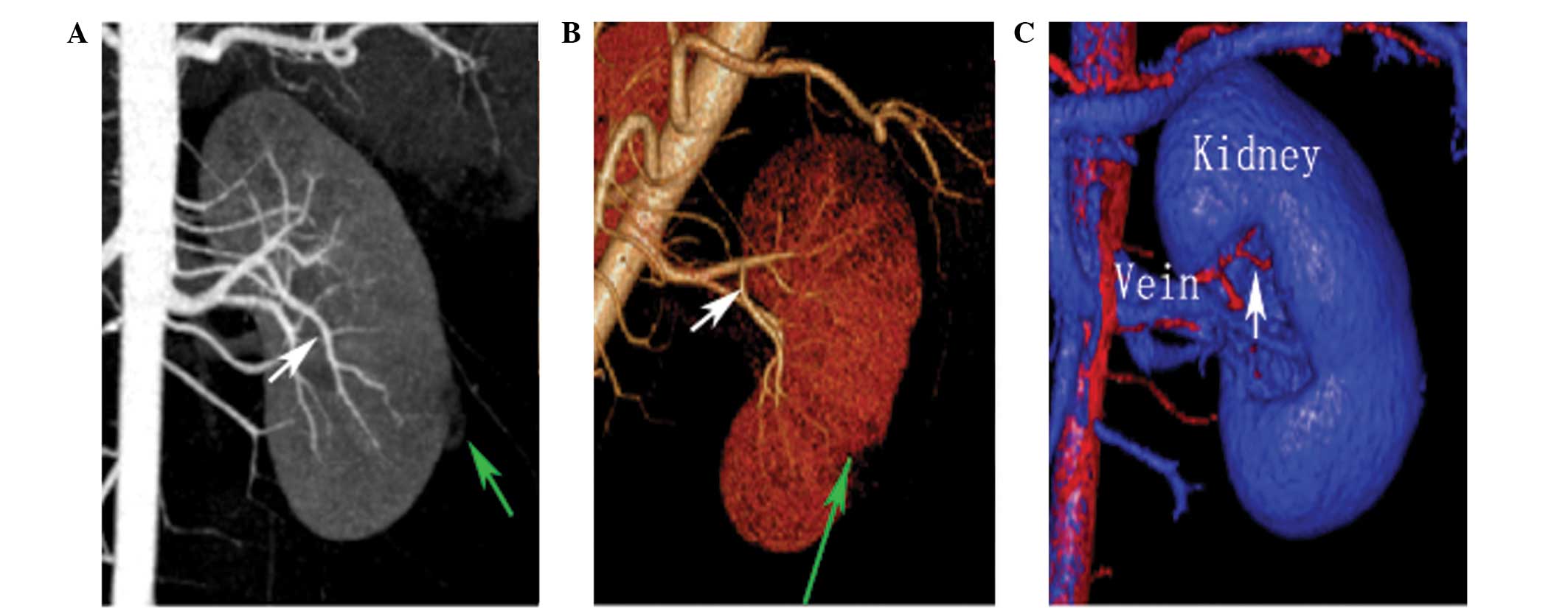
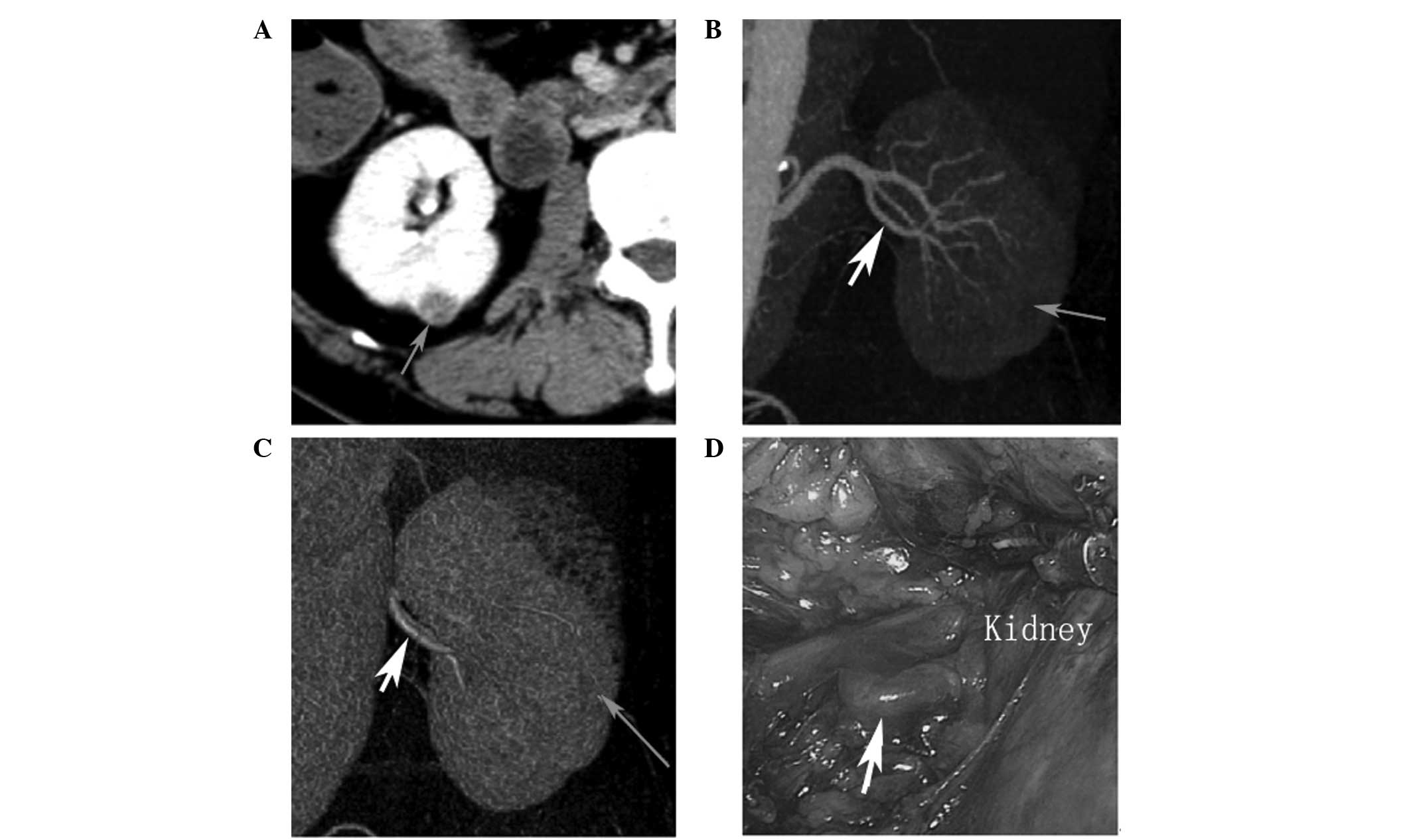
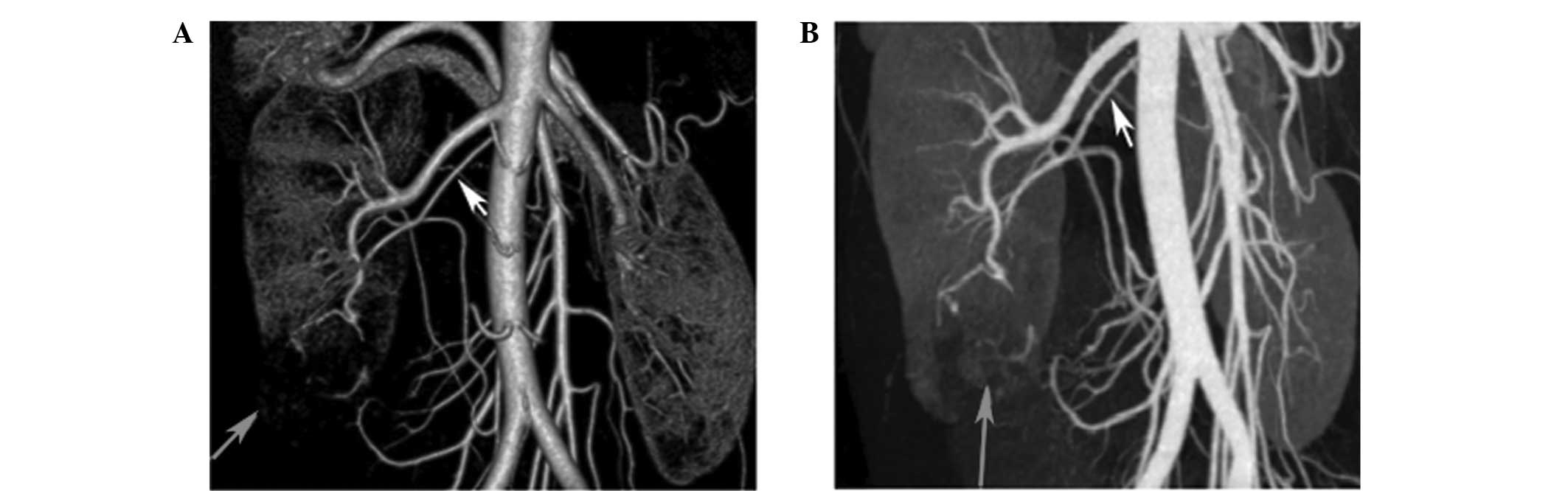
|
1
|
Van Poppel H, Da Pozzo L, Albrecht W, et
al: A prospective, randomised EORTC intergroup phase 3 study
comparing the oncologic outcome of elective nephron-sparing surgery
and radical nephrectomy for low-stage renal cell carcinoma. Eur
Urol. 59:543–552. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gill IS, Eisenberg MS, Aron M, Berger A,
Ukimura O, et al: Zero ischemia partial nephrectomy: Novel
laparoscopic and robotic technique. Eur Urol. 59:128–134. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gill IS, Kavoussi LR, Lane BR, et al:
Comparison of 1,800 laparoscopic and open partial nephrectomies for
single renal tumors. J Urol. 178:41–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shao P, Qin C, Yin C, Meng X, Ju X, Li J,
Lv Q, Zhang W and Xu Z: Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy with
segmental renal artery clamping: Technique and clinical outcomes.
Eur Urol. 59:849–855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi JD, Park JW, Choi JY, Kim HS, Jeong
BC, Jeon SS, Lee HM, Choi HY and Seo SI: Renal damage caused by
warm ischaemia during laparoscopic and robot-assisted partial
nephrectomy: An assessment using Tc 99m-DTPA glomerular filtration
rate. Eur Urol. 58:900–905. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peyronnet B, Baumert H, Mathieu R, et al:
Early unclamping technique during robot-assisted laparoscopic
partial nephrectomy can minimise warm ischaemia without increasing
morbidity. BJU Int. 114:741–747. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsi RS, Macleod LC, Gore JL, Wright JL and
Harper JD: Comparison of selective parenchymal clamping to hilar
clamping during robotic-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.
Urology. 83:339–344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang WY, Sung DJ, Park BJ, et al:
Perihilar branching patterns of renal artery and extrarenal length
of arterial branches and tumour-feeding arteries on multidetector
CT angiography. Br J Radiol. 86:201203872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rastogi N, Sahani DV, Blake MA, Ko DC and
Mueller PR: Evaluation of living renal donors: Accuracy of
three-dimensional 16-section CT. Radiology. 240:136–144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gill IS, Desai MM, Kaouk JH, et al:
Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for renal tumor: Duplicating open
surgical techniques. J Urol. 167:469–7; discussion 475–476. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Porpiglia F, Fiori C, Bertolo R, Morra I,
Russo R, Piccoli G, Angusti T and Podio V: Long-term functional
evaluation of the treated kidney in a prospective series of
patients who underwent laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for small
renal tumors. Eur Urol. 62:130–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Porpiglia F, Fiori C, Bertolo R, et al:
The effects of warm ischaemia time on renal function after
laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in patients with normal
contralateral kidney. World J Urol. 30:257–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thompson RH, Lane BR, Lohse CM, et al:
Every minute counts when the renal hilum is clamped during partial
nephrectomy. Eur Urol. 58:340–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Türkvatan A, Ozdemir M, Cumhur T and Olçer
T: Multidetector CT angiography of renal vasculature: Normal
anatomy and variants. Eur Radiol. 19:236–244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Raman SS, Pojchamarnwiputh S, Muangsomboon
K, Schulam PG, Gritsch HA and Lu DS: Utility of 16-MDCT angiography
for comprehensive preoperative vascular evaluation of laparoscopic
renal donors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 186:1630–1638. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pozniak MA, Balison DJ, Lee FT Jr,
Tambeaux RH, Uehling DT and Moon TD: CT angiography of potential
renal transplant donors. Radiographics. 18:565–587. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uflacker R: Abdominal aorta and
branchesAtlas of Vascular Anatomy: An Angiographic Approach. 2nd.
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 111–222.
2006
|
|
18
|
Satyapal KS, Haffejee AA, Singh B,
Ramsaroop L, Robbs JV and Kalideen JM: Additional renal arteries:
Incidence and morphometry. Surg Radiol Anat. 23:33–38. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nohara T, Fujita H, Yamamoto K, Kitagawa
Y, Gabata T and Namiki M: Modified anatrophic partial nephrectomy
with selective renal segmental artery clamping to preserve renal
function: A preliminary report. Int J Urol. 15:961–966. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weld KJ, Bhayani SB, Belani J, Ames CD,
Hruby G and Landman J: Extrarenal vascular anatomy of kidney:
Assessment of variations and their relevance to partial
nephrectomy. Urology. 66:985–989. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|