Spandidos Publications style
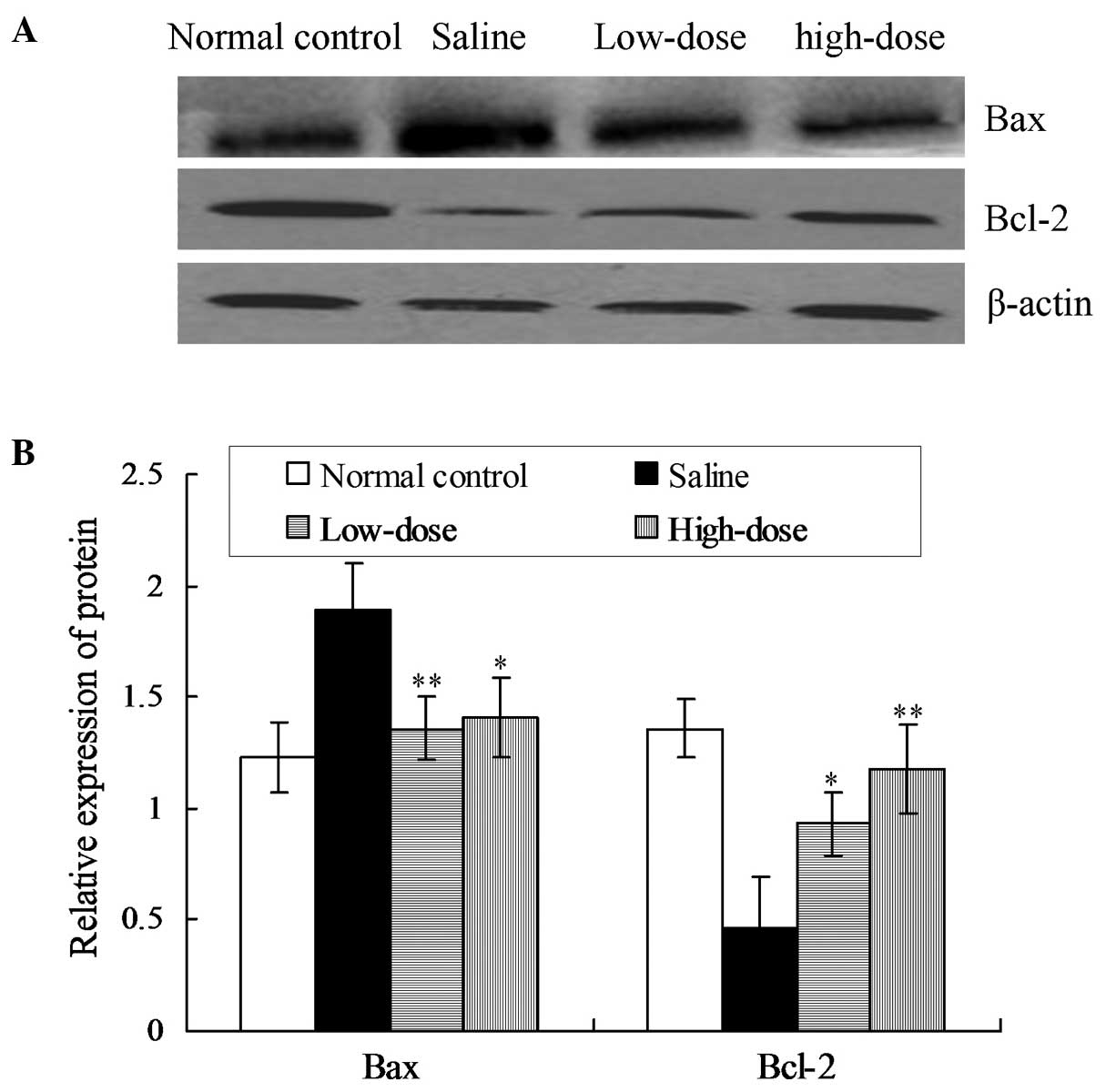
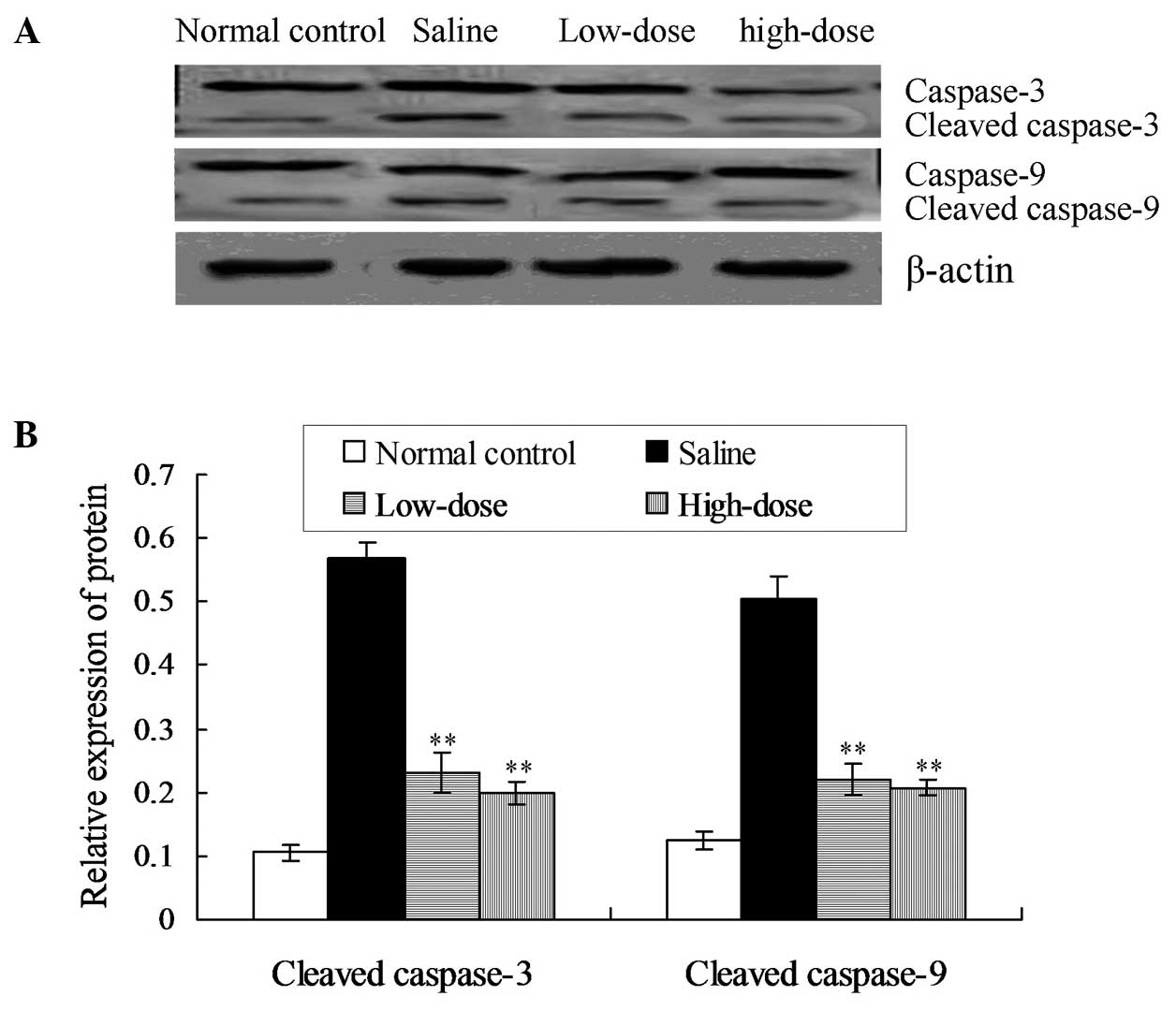
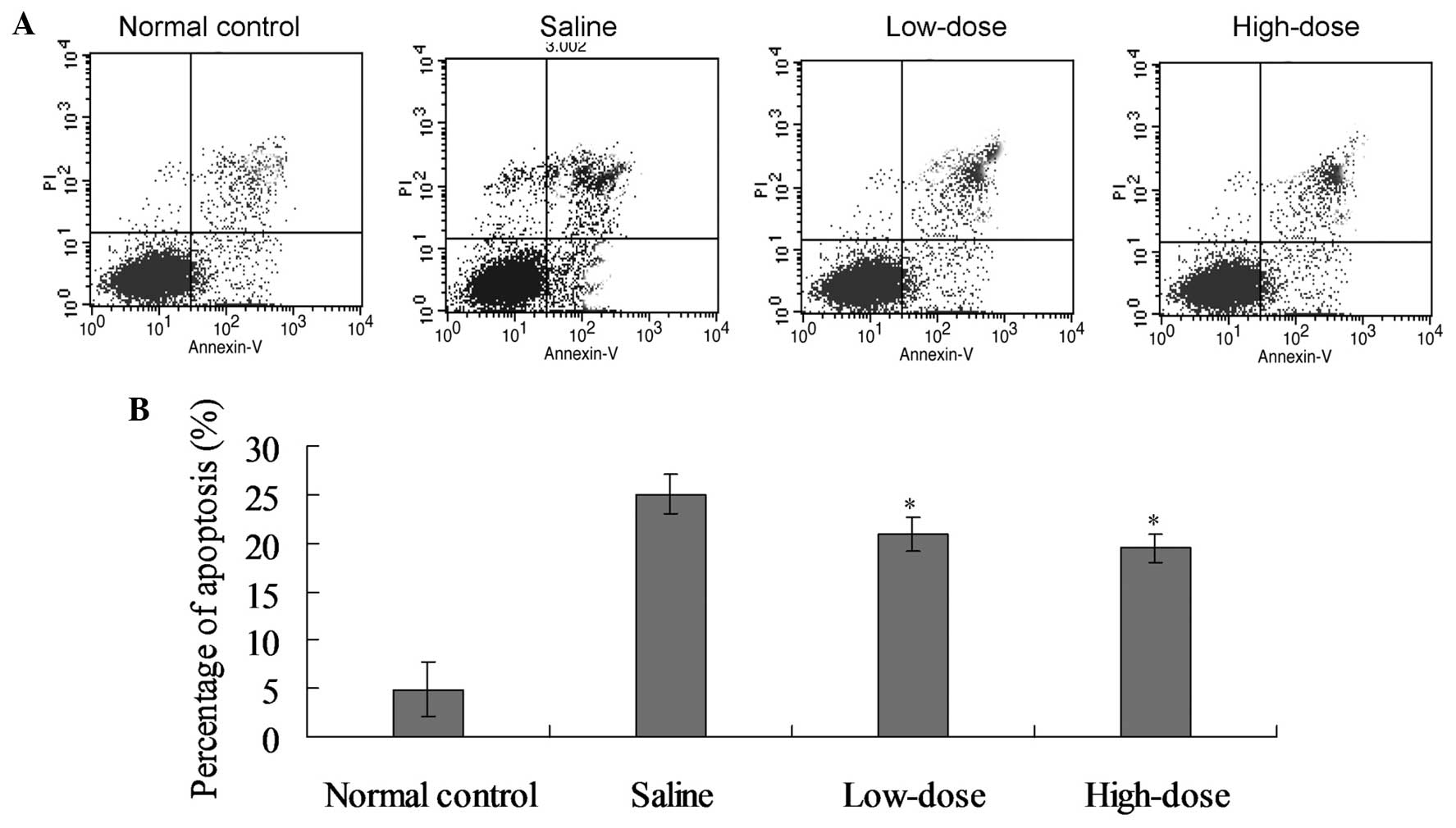
Shi L, Teng H, Zhu M, Li C, Huang K, Chen B, Dai Y and Wang J: Paeoniflorin inhibits nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by regulating the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspase-9 in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration Retraction in /10.3892/etm.2025.12907. Exp Ther Med 10: 257-262, 2015.
APA
Shi, L., Teng, H., Zhu, M., Li, C., Huang, K., Chen, B. ... Wang, J. (2015). Paeoniflorin inhibits nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by regulating the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspase-9 in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration Retraction in /10.3892/etm.2025.12907. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 10, 257-262. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2501
MLA
Shi, L., Teng, H., Zhu, M., Li, C., Huang, K., Chen, B., Dai, Y., Wang, J."Paeoniflorin inhibits nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by regulating the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspase-9 in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration Retraction in /10.3892/etm.2025.12907". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 10.1 (2015): 257-262.
Chicago
Shi, L., Teng, H., Zhu, M., Li, C., Huang, K., Chen, B., Dai, Y., Wang, J."Paeoniflorin inhibits nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by regulating the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspase-9 in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration Retraction in /10.3892/etm.2025.12907". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 10, no. 1 (2015): 257-262. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2501