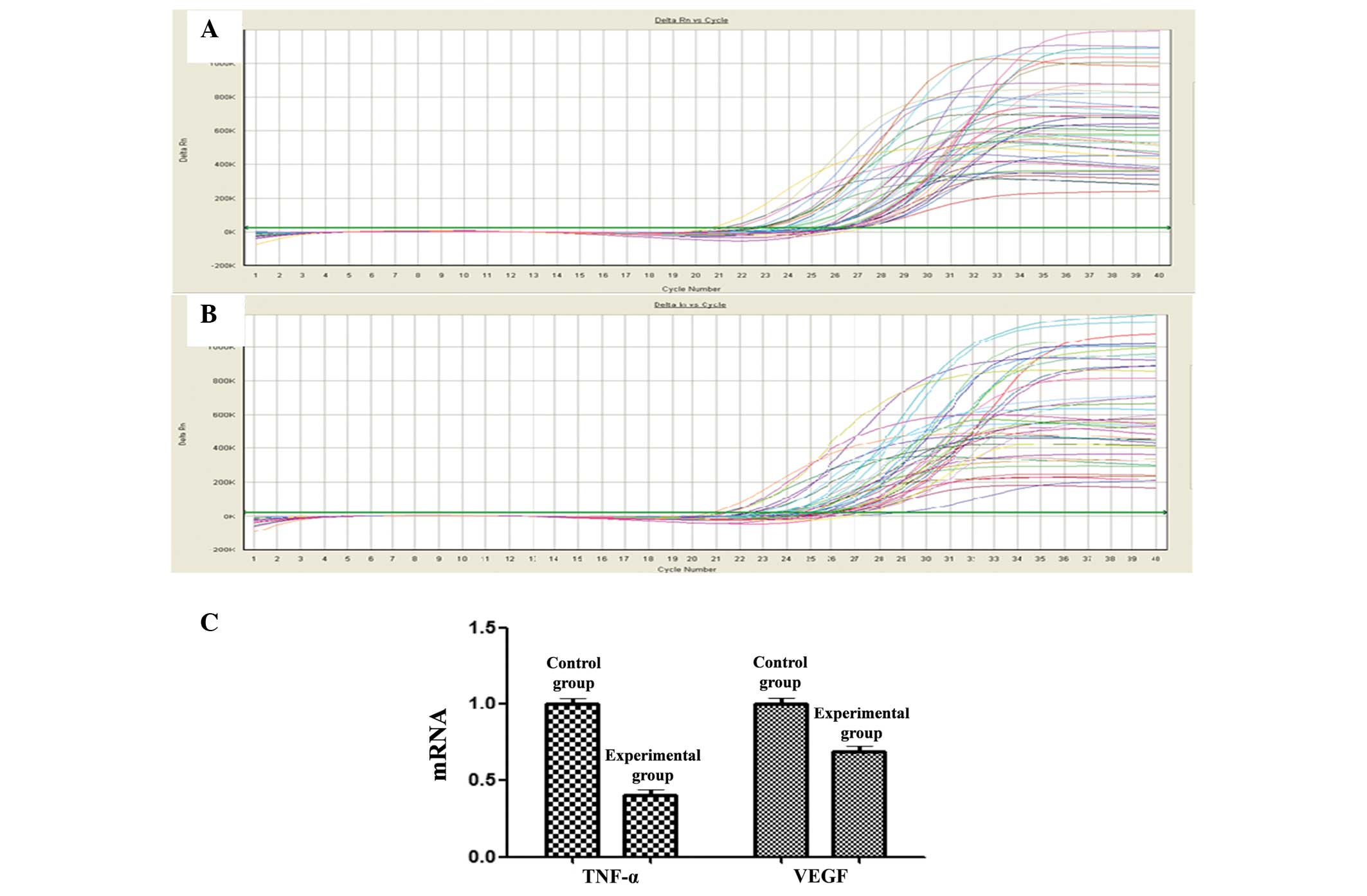
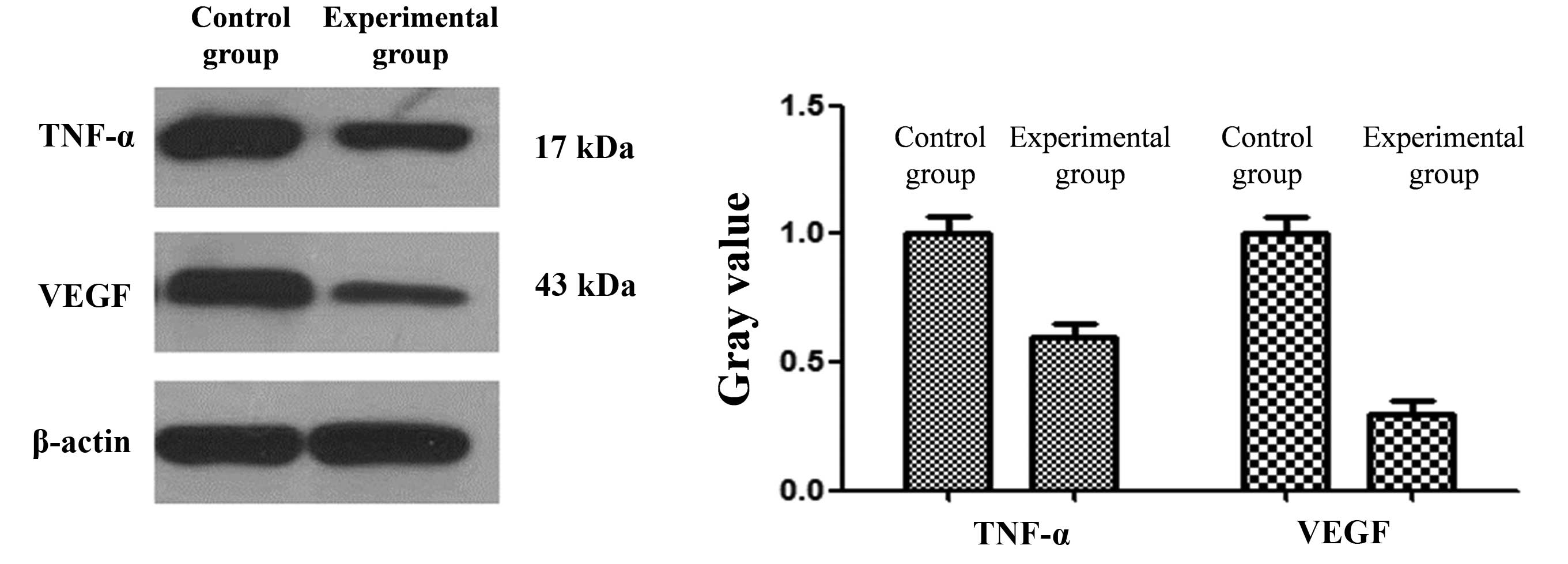
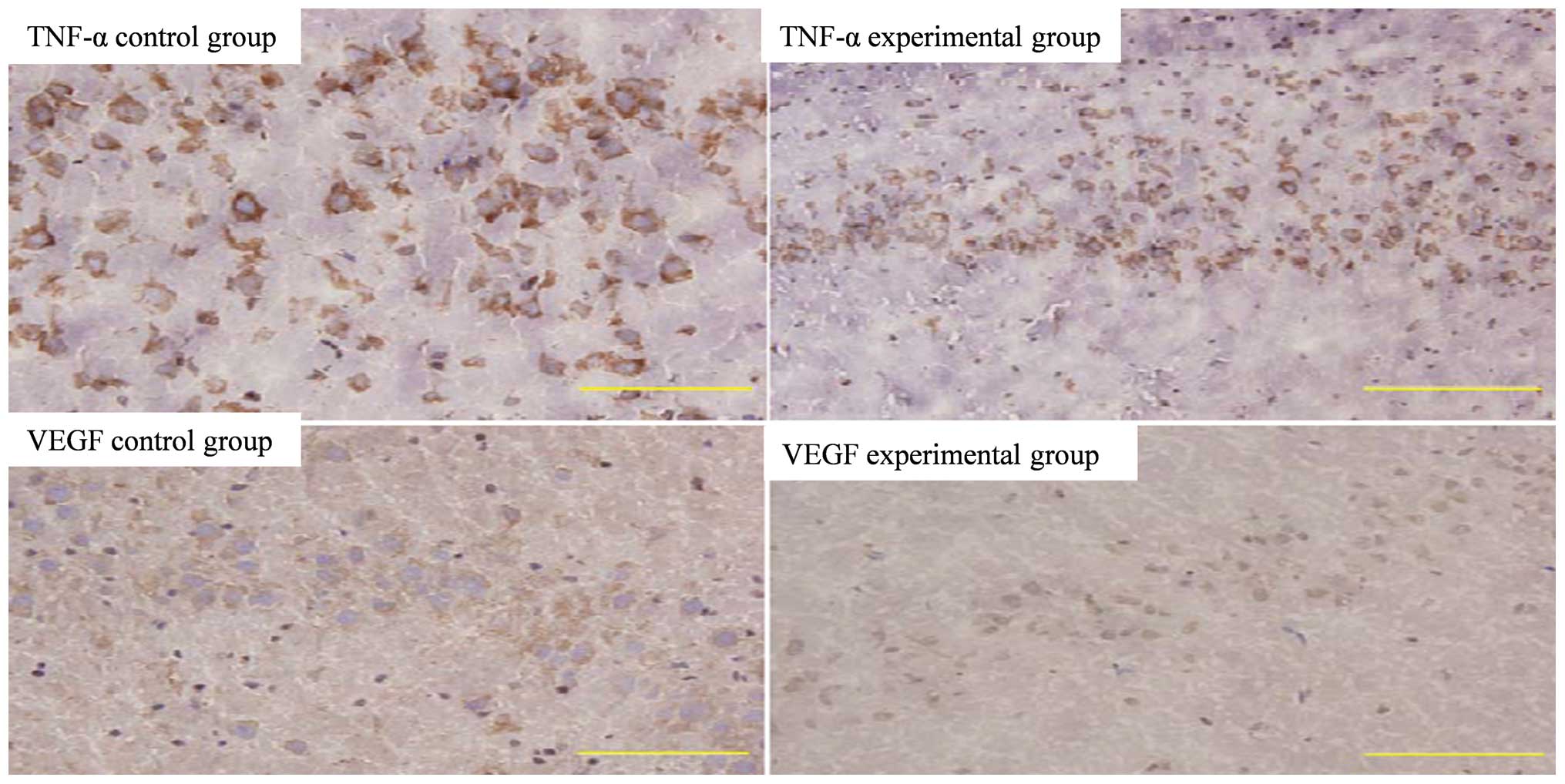
|
1
|
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R,
Koretz D, Merikangas KR, Rush AJ, Walters EE and Wang PS: National
Comorbidity Survey Replication: The epidemiology of major
depressive disorder: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey
Replication (NCS-R). JAMA. 289:3095–3105. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wray NR, Pergadia ML, Blackwood DH,
Penninx BW, Gordon SD, Nyholt DR, et al: Genome-wide association
study of major depressive disorder: New results, meta-analysis, and
lessons learned. Mol Psychiatry. 17:36–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McEwen BS: Plasticity of the hippocampus:
Adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Ann NY Acad Sci.
933:265–277. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Diniz BS, Teixeira AL, Machado-Vieira R,
Talib LL, Gattaz WF and Forlenza OV: Reduced serum nerve growth
factor in patients with late-life depression. Am J Geriatr
Psychiatry. 21:493–496. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Streeter CC, Gerbarg PL, Saper RB, Ciraulo
DA and Brown RP: Effects of yoga on the autonomic nervous system,
gamma-aminobutyric-acid, and allostasis in epilepsy, depression,
and post-traumatic stress disorder. Med Hypotheses. 78:571–579.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao J, Wang J, Kuang L, Chen J, Ai M, Wang
W, Chen X, Lv Z and Wang H: Plasma level of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor and the related analysis in depressive patients
with suicide attempt. Zhong Guo Shen Jing Jing Shen Bing Za Zhi.
39:597–601. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Smeeding SJ, Bradshaw DH, Kumpfer K,
Trevithick S and Stoddard GJ: Outcome evaluation of the Veterans
Affairs Salt Lake City Integrative Health Clinic for chronic pain
and stress-related depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress
disorder. J Altern Complement Med. 16:823–835. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dean B, Tawadros N, Scarr E and Gibbons
AS: Regionally-specific changes in levels of tumour necrosis factor
in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex obtained postmortem from
subjects with major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord.
120:245–248. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fournier NM and Duman RS: Role of vascular
endothelial growth factor in adult hippocampal neurogenesis:
Implications for the pathophysiology and treatment of depression.
Behav Brain Res. 227:440–449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu B, Xu C, Wu X, Liu F, Du Y, Sun J, Tao
J and Dong J: Icariin exerts an antidepressant effect in an
unpredictable chronic mild stress model of depression in rats and
is associated with the regulation of hippocampal neuroinflammation.
Neuroscience. 294:193–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Balkwill F: TNF-alpha in promotion and
progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:409–416. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kunz M, Ceresér KM, Goi PD, Fries GR,
Teixeira AL, Fernandes BS, Belmonte-de-Abreu PS, Kauer-Sant'Anna M,
Kapczinski F and Gama CS: Serum levels of IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α in
patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: Differences in
pro-and anti-inflammatory balance. Rev Bras Psiquiat. 33:268–274.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pezoa-Jares RE, Alvarez-Sekely AM,
Lopez-Bago AL, Vasquez-Medina JA, Cruz-Fuentes CS and
Lascurain-Ledesma R: 1395 - Quality of life and TNF-α levels in
Mexican patients with tuberculosis and major depressive disorder.
Eur Psychiatry. 28:12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rapisarda A and Melillo G: Role of the
VEGF/VEGFR axis in cancer biology and therapy. Adv Cancer Res.
114:237–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Perera TD, Coplan JD, Lisanby SH, Lipira
CM, Arif M, Carpio C, Spitzer G, Santarelli L, Scharf B, Hen R,
Rosoklija G, Sackeim HA and Dwork AJ: Antidepressant-induced
neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult nonhuman primates. J
Neurosci. 27:4894–4901. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun ST and Zhao HQ: Relationship of VEGF
and depression. Guo Ji Jing Sheng Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2:83–85.
2013.
|
|
17
|
Chauvet S, Burk K and Mann F: Navigation
rules for vessels and neurons: cooperative signaling between VEGF
and neural guidance cues. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:1685–1703. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kiuchi T, Lee H and Mikami T: Regular
exercise cures depression-like behavior via VEGF-Flk-1 signaling in
chronically stressed mice. Neuroscience. 207:208–217. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song G, Ouyang G, Mao Y, Ming Y, Bao S and
Hu T: Osteopontin promotes gastric cancer metastasis by augmenting
cell survival and invasion through Akt-mediated HIF-1alpha
up-regulation and MMP9 activation. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1706–1718.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Frank E, Prien RF, Jarrett RB, Keller MB,
Kupfer DJ, Lavori PW, Rush AJ and Weissman MM: Conceptualization
and rationale for consensus definitions of terms in major
depressive disorder: Remission, recovery, relapse, and recurrence.
Arch Gen Psychiatry. 48:851–855. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Willner P, Towell A, Sampson D,
Sophokleous S and Muscat R: Reduction of sucrose preference by
chronic unpredictable mild stress and its restoration by a
tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 93:358–364.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barr AM, Brotto LA and Phillips AG:
Chronic corticosterone enhances the rewarding effect of
hypothalamic self-stimulation in rats. Brain Res. 875:196–201.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matthews K, Forbes N and Reid IC: Sucrose
consumption as an hedonic measure following chronic unpredictable
mild stress. Physiol Behav. 57:241–248. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anisman H and Matheson K: Stress,
depression, and anhedonia: Caveats concerning animal models.
Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 29:525–546. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
D'Aquila PS, Peana AT, Carboni V and Serra
G: Exploratory behaviour and grooming after repeated restraint and
chronic mild stress: Effect of desipramine. Eur J Pharmacol.
399:43–47. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Redrobe JP, Dumont Y, Fournier A, Baker GB
and Quirion R: Role of serotonin (5-HT) in the antidepressant-like
properties of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in the mouse forced swim test.
Peptides. 26:1394–1400. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cryan JF, Valentino RJ and Lucki I:
Assessing substrates underlying the behavioral effects of
antidepressants using the modified rat forced swimming test.
Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 29:547–569. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Wei, Liu Jia, Bai Jiayuan, Gu Changqin,
Zhang Wanpo, Cheng Guofu and Hu Xueying: Recent progress of tumor
necrosis factor-α. Dong Wu Yi Xue Fa Zhan. 31:108–111. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Tian XS, Hu N, Song L, Sun ZX and Cheng W:
Effects of Suanzaoren decoction on expression of TNF-α, IL-1β and
c-fos in hippocampus of depression rats model. Zhong Guo Yao Xue
Bao. 2:44–46. 2013.
|
|
30
|
Zhao SH, Kong JH, Yang CJ, Lin YH and Wang
LZ: Effect of duloxetine on the levels of cytokines in patients
with first-episode depression. Zhong Guo Xing Wei Yi Xue Yu Nao Ke
Xue. 21:158–160. 2012.
|
|
31
|
Fischer R and Maier O: Interrelation of
oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease:
role of TNF. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:6108132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Warner-Schmidt JL and Duman RS: VEGF is an
essential mediator of the neurogenic and behavioral actions of
antidepressants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:4647–4652. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nowacka MM and Obuchowicz E: Vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its role in the central
nervous system: A new element in the neurotrophic hypothesis of
antidepressant drug action. Neuropeptides. 46:1–10. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu X: The effect of Tiandan capsule on
VEGF, inflammatory cytokines and NSE of the patients with acute
cerebral infarction. Xi Nan Jun Za Zhi She. 13:24–26. 2011.
|
|
35
|
Qian XD, Luo CX and Zhu DY: Recent
progress in neural stem cells transplantation. Zhong Guo Xi Bao
Sheng Wu Xue Xue Bao. 34:212–217. 2012.
|
|
36
|
Alfonso J, Frasch AC and Flugge G: Chronic
stress, depression and antidepressants: Effects on gene
transcription in the hippocampus. Rev Neuroscience. 16:43–56. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|