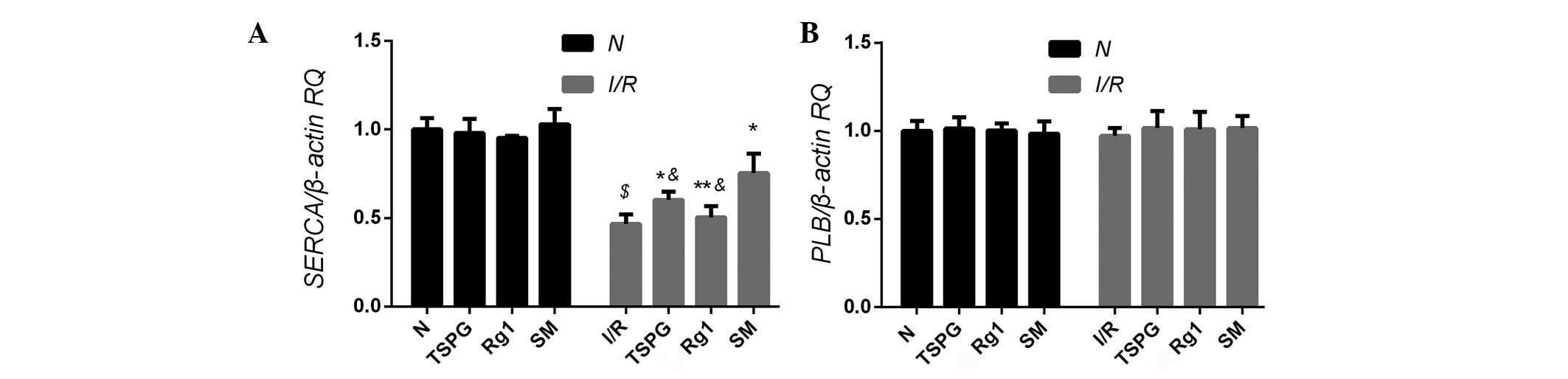
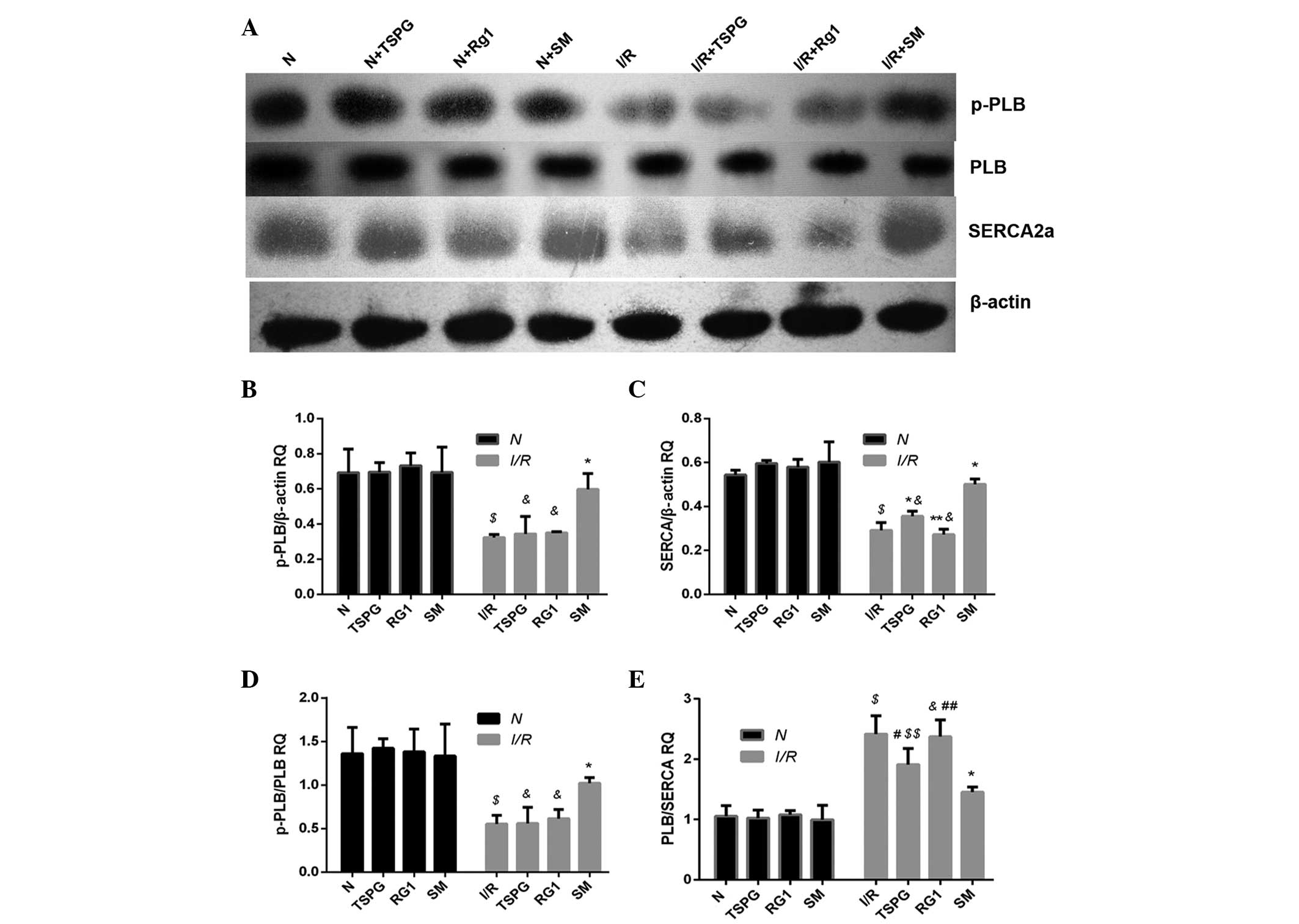
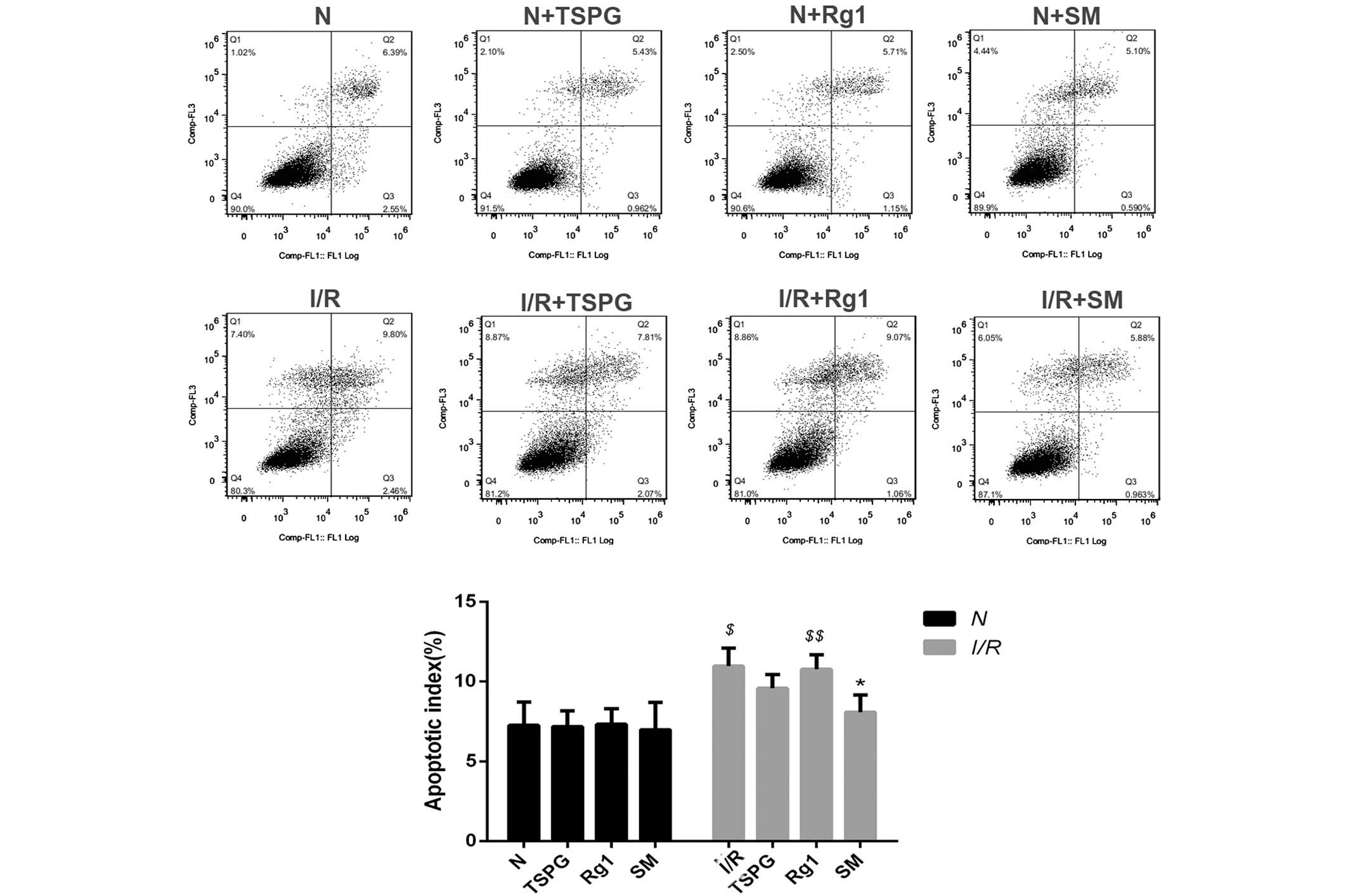
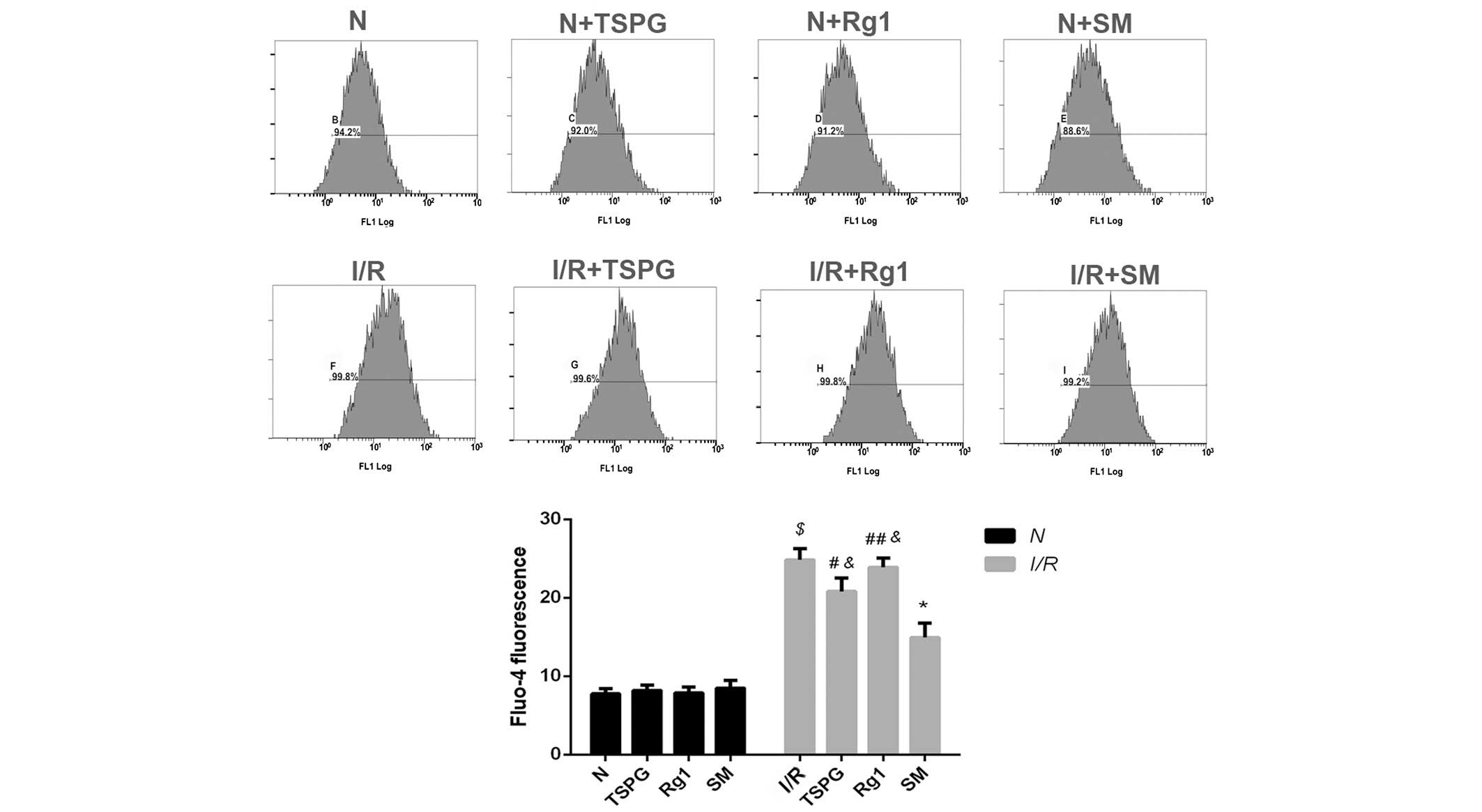
|
1
|
World Health Oganization, . Fact Sheet No.
310: The top 10 causes of death. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/Accessed.
November 19–2014.
|
|
2
|
Braunwald E: Heart failure. JACC Heart
Fail. 1:1–20. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marks AR: Cardiac intracellular calcium
release channels: Role in heart failure. Circ Res. 87:8–11. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ramón de Berrazueta J: The role of calcium
in the regulation of normal vascular tone and in arterial
hypertension. Rev Esp Cardiol. (52 Suppl):3:25–33. 1999.(In
Spanish).
|
|
5
|
Spinale FG, de Gasparo M, Whitebread S,
Hebbar L, Clair MJ, Melton DM, Krombach RS, Mukherjee R, Iannini JP
and O SJ: Modulation of the renin-angiotensin pathway through
enzyme inhibition and specific receptor blockade in pacing-induced
heart failure: I. Effects on left ventricular performance and
neurohormonal systems. Circulation. 96:2385–2396. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kranias EG and Hajjar RJ: Modulation of
cardiac contractility by the phospholamban/SERCA2a regulatome. Circ
Res. 110:1646–1660. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun Y, Hu S, Wang L, Hu Y and Zhou J:
Comparison of low and high doses of carvedilol on restoration of
cardiac function and calcium-handling proteins in rat failing
heart. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 32:553–560. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun Y, Hu S, Wang L, Hu Y and Zhou J:
Changes of calcium handling protein after acute myocardial
infarction in rats and effect of carvedilol. Zhong Guo Bing Li
Sheng Li Za Zhi. 21:1085–1089. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Changyu Qin and Zhizhen Qin: Zheng Yin Mai
Zhi. First edition. Shanghai wei sheng chu ban she; Shanghai:
1958
|
|
10
|
Hou YZ, Mao JY, Wang XL, Liu CX and Zhang
C: Shenmai injection in heart failure patients: A systematic review
and Meta-analysis. Zhong Guo Xun Zheng Yi Xue Za Zhhi She.
10:939–945. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Zhang L, Wang BH, Hu J and Shang HC:
Shenmai injection for children with viral myocarditis: A systematic
review. Zhong Guo Xun Zheng Yi Xue Za Zhi She. 10:700–706.
2010.
|
|
12
|
Li KJ: Shenmai injection for acute
ischemic stroke: A systematic review of randomized controlled
trial. Zhong Yi Yao Xue Bao. 34:4–7. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Liu JG: Systematic review on Shenmai
Injection treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy. Zhong Cheng Yao.
34:1456–1461. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Hu J, Zhang W, Xie YM, Wang LX, Nie XL and
Zhang YL: Meta-analysis of Shenmai injection treatment for acute
myocardial infarction. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi She.
37:2760–2767. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Gong W and Hu Z: Clinical application of
Shenmai injection. Yi Yao Dao Bao. 19:181–183. 2000.(In
Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Hu J, Xiao L, Zhang Y, Zhao W,
Zheng W and Shang H: Adverse drug reactions of Shenmai injection: A
systematic review. J Evid-Based Med. 3:177–182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bai CX, Takahashi K, Masumiya H,
Sawanobori T and Furukawa T: Nitric oxide-dependent modulation of
the delayed rectifier K+ current and the L-type
Ca2+ current by ginsenoside Re, an ingredient of
Panax ginseng, in guinea-pig cardiomyocytes. Br J Pharmacol.
142:567–575. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scott GI, Colligan PB, Ren BH and Ren J:
Ginsenosides Rb1 and Re decrease cardiac contraction in adult rat
ventricular myocytes: Role of nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol.
134:1159–1165. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bai CX, Sunami A, Namiki T, Sawanobori T
and Furukawa T: Electrophysiological effects of ginseng and
ginsenoside Re in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol.
476:35–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Z, Li Z and Liu X: Effect of
ginsenoside Re on cardiomyocyte apoptosis and expression of
Bcl-2/Bax gene after ischemia and reperfusion in rats. J Huazhong
Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 22:305–309. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
He L, Sun S and Fan J: Effect of Shenmai
injection on neurocyte apoptosis and change of cytoplasmic calcium.
Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 21:605–607. 2001.(In
Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Hou M and Ao D: Study on the mechanism of
ginsenosides against ischemia-reperfusion injury of myocardium.
Zhong Guo Xiong Xin Xue Guan Wai Ke Lin Chuang Za Zhi. 7:256–9.
2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Cui X, Pan L, Li Z, Ji C and Du K:
Electron microscopic observation and Ca2+ analysis on
protective effect of ginsenoside from fruit on myocardium of
hemorrhagic shock in dogs. Bai Qiu En Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
24:452–454. 1998.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Zhao X, Li Z, Cao Y, Geng Q, An L and Tang
H: (2001) The influence of ginsenosides on intracellular free
calcium concentration during hypoxia in guinea pigs. J Chin Med
Univ. 30:431–434. 2001.
|
|
25
|
He Q, Sun J, Wang Q, Wang W and He B:
Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 against oxygen-glucose
deprivation in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Chin Med Assoc.
77:142–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu D, Wu L, Li CR, Wang XW, Ma YJ, Zhong
ZY, Zhao HB, Cui J, Xun SF, Huang XL, et al: Ginsenoside Rg1
protects rat cardiomyocyte from hypoxia/reoxygenation oxidative
injury via antioxidant and intracellular calcium homeostasis. J
Cell Biochem. 108:117–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Simpson P and Savion S: Differentiation of
rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating
nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure and
chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 50:101–116. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stamm C, Friehs I, Cowan DB, CaoDanh H,
Choi YH, Duebener LF, McGowan FX and del Nido PJ: Dopamine
treatment of postischemic contractile dysfunction rapidly induces
calcium-dependent pro-apoptotic signaling. Circulation.
106:I290–I298. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cao S, Nie L, Wang G and Lin R: Study on
ginsenosides contents of Shenmai injection and its intermediates by
UPLC. Yao Wu Fen Xi Za Zhi. 7:1264–68. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Chen Y, Hao R and Huang Q: Shenmai
injection protects rat cardiomyocytes from angiotensin II-induced
apoptosis in vitro. Zhong Guo Bing Li Sheng Li Za Zhi. 9:76–80.
2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Hao R, Lou J, Zhang Y, Zheng H and Huang
Q: The effect of Shenmai injection on cardiac myocyte apoptosis
after hypoxia. Zhong Guo Bing Li Sheng Li Za Zhi. 4:660–663.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Koss KL, Ponniah S, Jones WK, Grupp IL and
Kranias EG: Differential phospholamban gene expression in murine
cardiac compartments. Molecular and physiological analyses. Circ
Res. 77:342–353. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ito K, Yan X, Feng X, Manning WJ, Dillmann
WH and Lorell BH: Transgenic expression of sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca(2+) ATPase modifies the transition from hypertrophy to early
heart failure. Circ Res. 89:422–429. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schmidt U, del Monte F, Miyamoto MI,
Matsui T, Gwathmey JK, Rosenzweig A and Hajjar RJ: Restoration of
diastolic function in senescent rat hearts through adenoviral gene
transfer of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase. Circulation.
101:790–796. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Plank DM, Yatani A, Ritsu H, Witt S,
Glascock B, Lalli MJ, Periasamy M, Fiset C, Benkusky N, Valdivia HH
and Sussman MA: Calcium dynamics in the failing heart: Restoration
by beta-adrenergic receptor blockade. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 285:H305–H315. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|