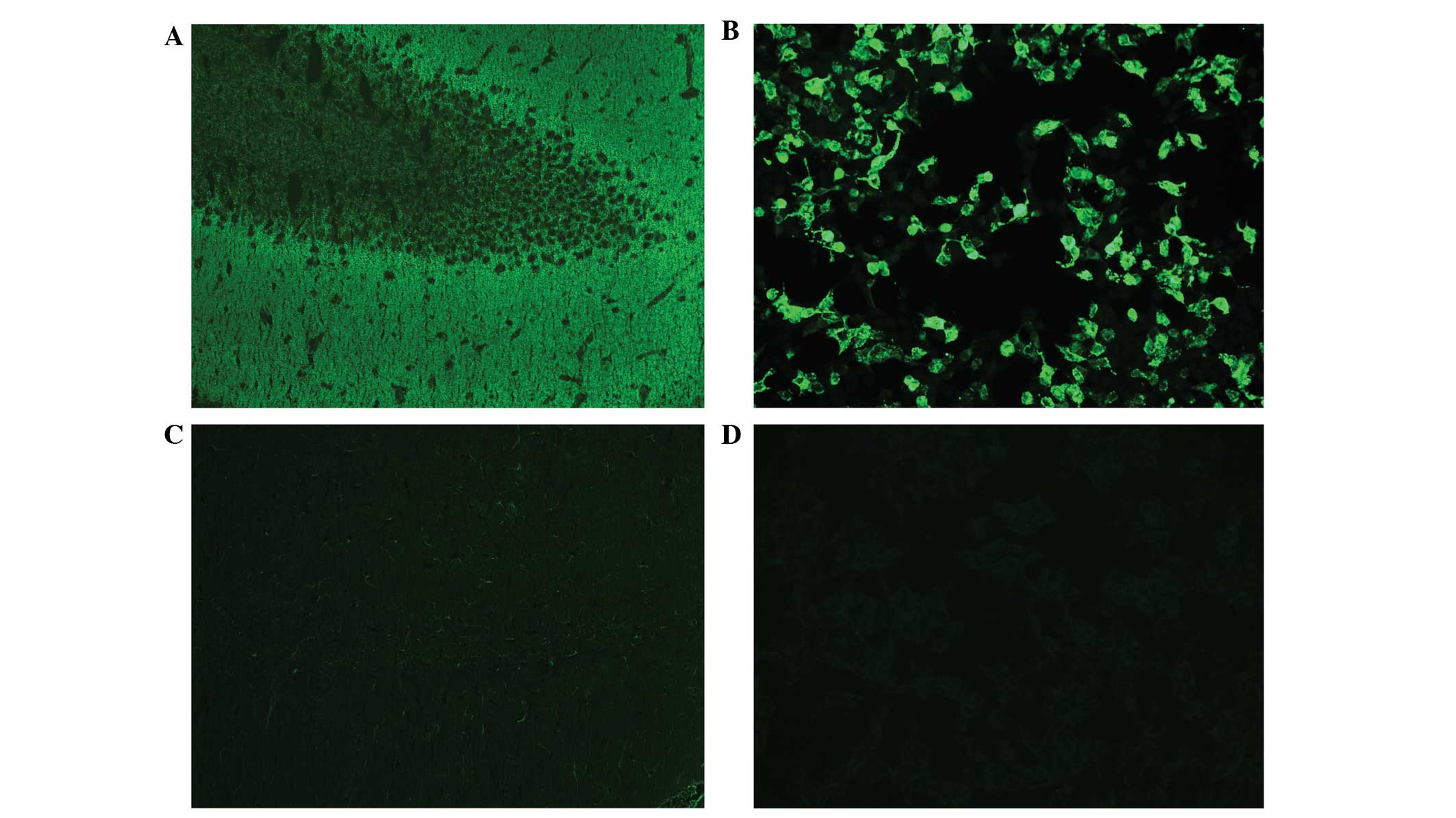
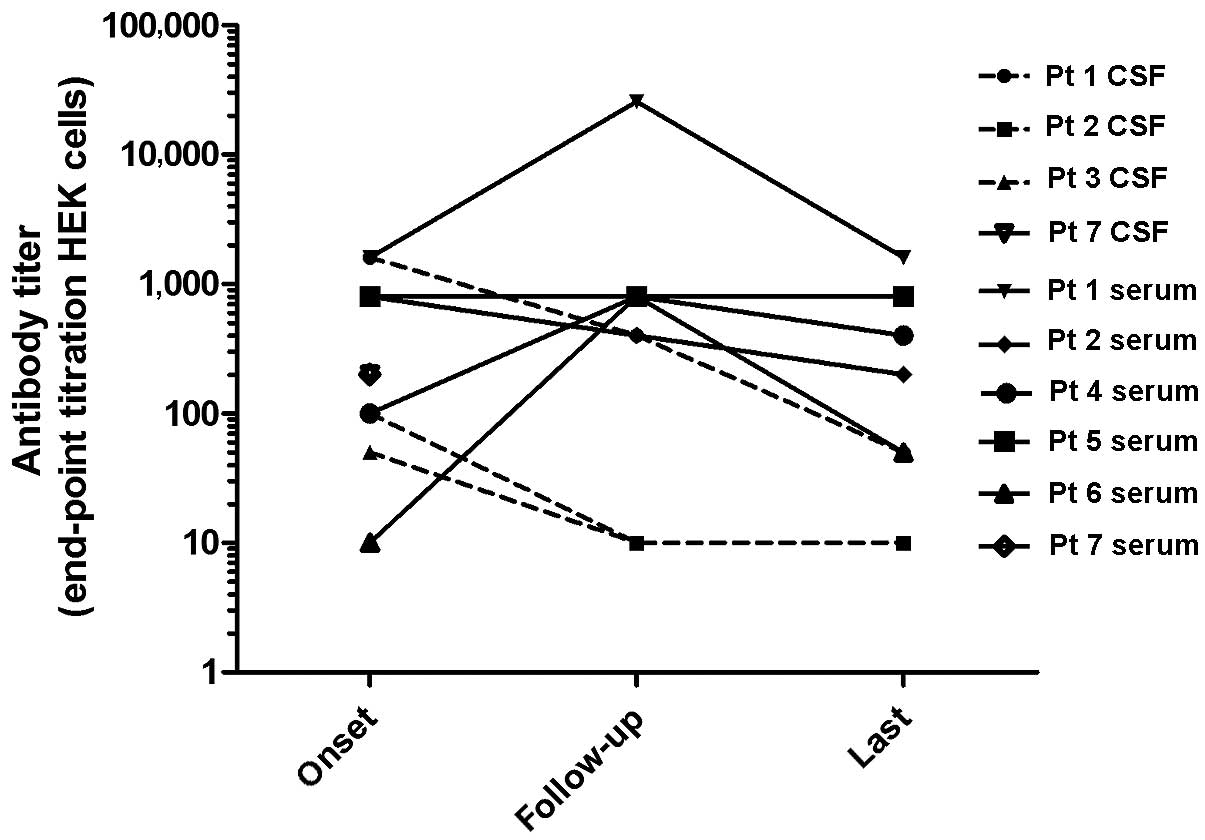
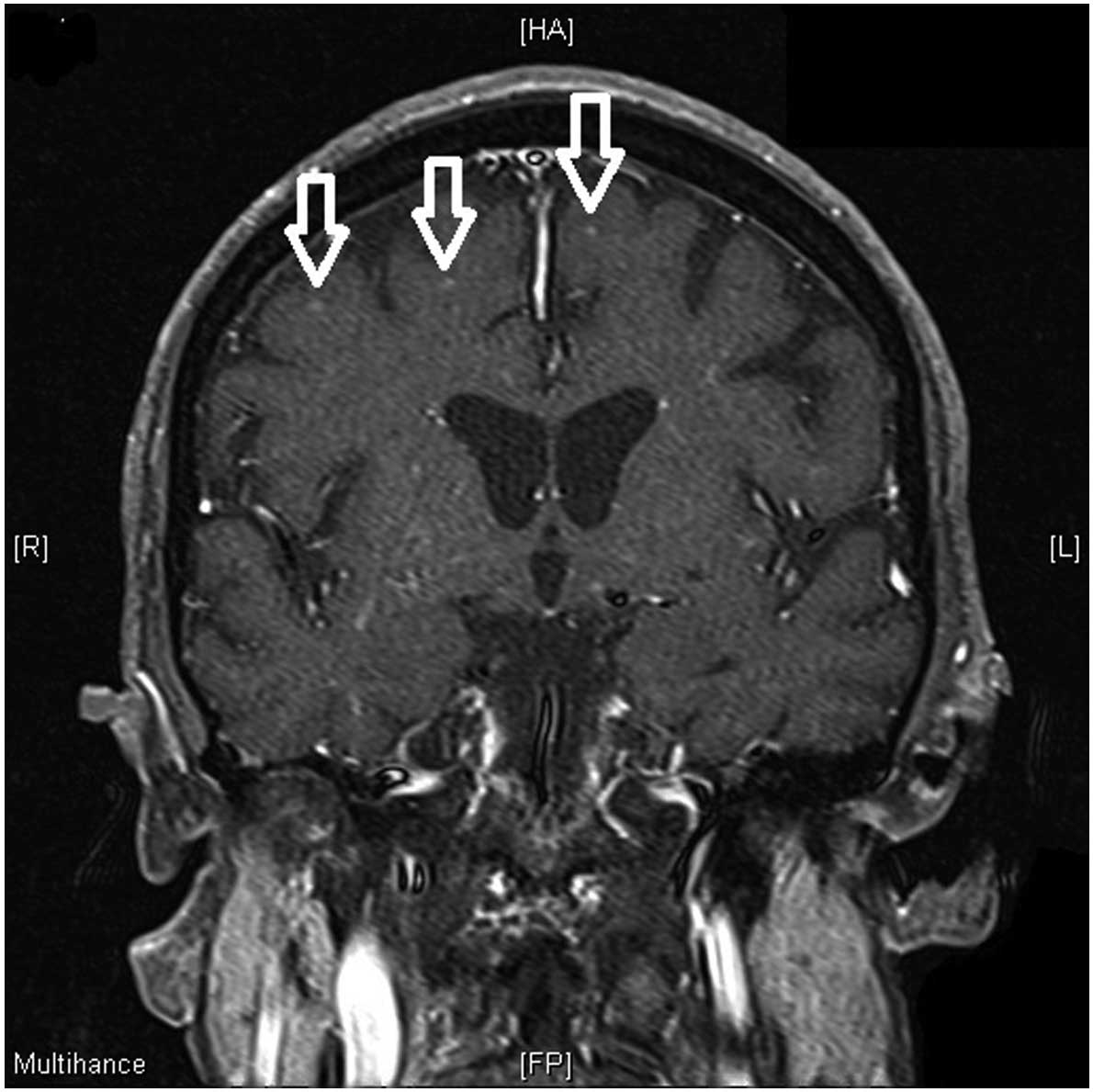
|
1
|
Brierley JB, Corsellis JAN, Hierons R and
Nevin S: Subacute encephalitis of later adult life. Mainly
affecting the limbic areas. Brain. 83:357–368. 1960. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Graus F, Saiz A and Dalmau J: Antibodies
and neuronal autoimmune disorders of the CNS. J Neurol.
257:509–517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Graus F, Illa I, Agusti M, Ribalta T,
Cruz-Sanchez F and Juarez C: Effect of intraventricular injection
of an anti-Purkinje cell antibody (anti-Yo) in a guinea pig model.
J Neurol Sci. 106:82–87. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bien CG, Vincent A, Barnett MH, Becker AJ,
Blümcke I, Graus F, Jellinger KA, Reuss DE, Ribalta T, Schlegel J,
et al: Immunopathology of autoantibody-associated encephalitides:
Clues for pathogenesis. Brain. 135:1622–1638. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giometto B, Grisold W, Vitaliani R, Graus
F, Honnorat J and Bertolini G: PNS Euronetwork: Paraneoplastic
neurologic syndrome in the PNS Euronetwork database: A European
study from 20 centers. Arch Neurol. 67:330–335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ances BM, Vitaliani R, Taylor RA,
Liebeskind DS, Voloschin A, Houghton DJ, Galetta SL, Dichter M,
Alavi A, Rosenfeld MR and Dalmau J: Treatment-responsive limbic
encephalitis identified by neuropil antibodies: MRI and PET
correlates. Brain. 128:1764–1777. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bataller L, Kleopa KA, Wu GF, Rossi JE,
Rosenfeld MR and Dalmau J: Autoimmune limbic encephalitis in 39
patients: Immunophenotypes and outcomes. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 78:381–385. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dalmau J, Tuzün E, Wu HY, Masjuan J, Rossi
JE, Voloschin A, Baehring JM, Shimazaki H, Koide R, King D, et al:
Paraneoplastic anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis
associated with ovarian teratoma. Ann Neurol. 61:25–36. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gold M, Pul R, Bach JP, Stangel M and
Dodel R: Pathogenic and physiological autoantibodies in the central
nervous system. Immunol Rev. 248:68–86. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dalmau J, Lancaster E, Martinez-Hernandez
E, Rosenfeld MR and Balice-Gordon R: Clinical experience and
laboratory investigations in patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis.
Lancet Neurol. 10:63–74. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Titulaer MJ, McCracken L, Gabilondo I,
Armangué T, Glaser C, Iizuka T, Honig LS, Benseler SM, Kawachi I,
Martinez-Hernandez E, et al: Treatment and prognostic factors for
long-term outcome in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis:
An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 12:157–165. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dalmau J, Gleichman AJ, Hughes EG, Rossi
JE, Peng X, Lai M, Dessain SK, Rosenfeld MR, Balice-Gordon R, Lynch
DR, et al: Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: Case series and
analysis of the effects of antibodies. Lancet Neurol. 7:1091–1098.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pruss H, Finke C, Höltje M, Hofmann J,
Klingbeil C, Probst C, Borowski K, Ahnert-Hilger G, Harms L, Schwab
JM, et al: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies in herpes
simplex encephalitis. Ann Neurol. 72:902–911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lancaster E, Lai M, Peng X, Hughes E,
Constantinescu R, Raizer J, Friedman D, Skeen MB, Grisold W, Kimura
A, et al: Antibodies to the GABA (B) receptor in limbic
encephalitis with seizures: Case series and characterisation of the
antigen. Lancet Neurol. 9:67–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lai M, Hughes EG, Peng X, Zhou L,
Gleichman AJ, Shu H, Matà S, Kremens D, Vitaliani R, Geschwind MD,
et al: AMPA receptor antibodies in limbic encephalitis alter
synaptic receptor location. Ann Neurol. 65:424–434. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wong SH, Saunders MD, Larner AJ, Das K and
Hart IK: An effective immunotherapy regimen for VGKC
antibody-positive limbic encephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 81:1167–1169. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kleopa KA, Elman LB, Lang B, Vincent A and
Scherer SS: Neuromyotonia and limbic encephalitis sera target
mature Shaker-type K+ channels: Subunit specificity
correlates with clinical manifestations. Brain. 129:1570–1584.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Paoletti P, Bellone C and Zhou Q: NMDA
receptor subunit diversity: Impact on receptor properties, synaptic
plasticity and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:383–400. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Traynelis SF, Wollmuth LP, McBain CJ,
Menniti FS, Vance KM, Ogden KK, Hansen KB, Yuan H, Myers SJ and
Dingledine R: Glutamate receptor ion channels: Structure,
regulation and function. Pharmacol Rev. 62:405–496. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dzamba D, Honsa P and Anderova M: NMDA
Receptors in glial cells: Pending questions. Curr Neuropharmacol.
11:250–262. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee MC, Ting KK, Adams S, Brew BJ, Chung R
and Guillemin GJ: Characterisation of the expression of NMDA
receptors in human astrocytes. PLoS One. 5:e141232010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Verkhratsky A and Kirchhoff F:
Glutamate-mediated neuronal-glial transmission. J Anat.
210:651–660. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Verkhratsky A and Kirchhoff F: NMDA
Receptors in glia. Neuroscientist. 13:28–37. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boeck AL, Logemann F, Krauß T, Hussein K,
Bültmann E, Trebst C and Stangel M: Ovarectomy despite negative
imaging in anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: Effective even late.
Case Rep Neurol Med. 2013:8431922013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wegner F, Wilke F, Raab P, Tayeb SB, Boeck
AL, Haense C, Trebst C, Voss E, Schrader C, Logemann F, et al:
Anti-leucine rich glioma inactivated 1 protein and
anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis show distinct
patterns of brain glucose metabolism in
18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission
tomography. BMC Neurol. 14:1362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gresa Arribas, Titulaer MJ, Torrents A,
Aguilar E, McCracken L, Leypoldt F, Gleichman AJ, Balice-Gordon R,
Rosenfeld MR, Lynch D, et al: Antibody titres at diagnosis and
during follow-up of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: A
retrospective study. Lancet Neurol. 13:167–177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Irani SR, Bera K, Waters P, Zuliani L,
Maxwell S, Zandi MS, Friese MA, Galea I, Kullmann DM, Beeson D, et
al: N-methyl-D-aspartate antibody encephalitis: Temporal
progression of clinical and paraclinical observations in a
predominantly non-paraneoplastic disorder of both sexes. Brain.
133:1655–1667. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Day GS, High SM, Cot B and Tang-Wai DF:
Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: Case report and literature review
of an under-recognized condition. J Gen Intern Med. 26:811–816.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gable MS, Gavali S, Radner A, Tilley DH,
Lee B, Dyner L, Collins A, Dengel A, Dalmau J and Glaser CA:
Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: Report of ten cases and comparison
with viral encephalitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.
28:1421–1429. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Titulaer MJ, Hoftberger R, Iizuka T,
Leypoldt F, McCracken L, Cellucci T, Benson LA, Shu H, Irioka T,
Hirano M, et al: Overlapping demyelinating syndromes and
anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Ann Neurol:.
75:411–428. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Whitacre CC: Sex differences in autoimmune
disease. Nat Immunol. 2:777–780. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Manto M, Dalmau J, Didelot A, Rogemond V
and Honnorat J: Afferent facilitation of corticomotor responses is
increased by IgGs of patients with NMDA-receptor antibodies. J
Neurol. 258:27–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kleinig TJ, Thompson PD, Matar W, Duggins
A, Kimber TE, Morris JG, Kneebone CS and Blumbergs PC: The
distinctive movement disorder of ovarian teratoma-associated
encephalitis. Mov Disord. 23:1256–1261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hammer C, Zerche M, Schneider A, Begemann
M, Nave KA and Ehrenreich H: Apolipoprotein E4 carrier status plus
circulating anti-NMDAR1 autoantibodies: Association with
schizoaffective disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 19:1054–1056. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dutschmann M, Morschel M, Rybak IA and
Dick TE: Learning to breathe: Control of the inspiratory-expiratory
phase transition shifts from sensory- to central-dominated during
postnatal development in rats. J Physiol. 587:4931–4948. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Henson MA, Roberts AC, Pérez-Otaño I and
Philpot BD: Influence of the NR3A subunit on NMDA receptor
functions. Prog Neurobiol. 91:23–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burzomato V, Frugier G, Pérez-Otano I,
Kittler JT and Attwell D: The receptor subunits generating NMDA
receptor mediated currents in oligodendrocytes. J Physiol.
588:3403–3414. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Krebs C, Fernandes HB, Sheldon C, Raymond
LA and Baimbridge KG: Functional NMDA receptor subtype 2B is
expressed in astrocytes after ischemia in vivo and anoxia
in vitro. J Neurosci. 23:3364–3372. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Irani SR, Alexander S, Waters P, Kleopa
KA, Pettingill P, Zuliani L, Peles E, Buckley C, Lang B and Vincent
A: Antibodies to Kv1 potassium channel-complex proteins
leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1 protein and contactin-associated
protein-2 in limbic encephalitis, Morvan's syndrome and acquired
neuromyotonia. Brain. 133:2734–2748. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Skripuletz T, Schwenkenbecher P, Pars K,
Stoll M, Conzen J, Bolat S, Pul R, Vonberg RP, Sedlacek L, Wurster
U, et al: Importance of follow-up cerebrospinal fluid analysis in
cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. Dis Markers. 2014:1625762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen B, Wang Y, Geng Y, Huang Y, Guo S and
Mao X: Marked improvement of anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
encephalitis by large-dose methylprednisolone and plasmapheresis
therapy combined with F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission
tomography imaging: A case report. Exp Ther Med. 8:1167–1169.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dahm L, Ott C, Steiner J, Stepniak B,
Teegen B, Saschenbrecker S, Hammer C, Borowski K, Begemann M, Lemke
S, et al: Seroprevalence of autoantibodies against brain antigens
in health and disease. Ann Neurol. 76:82–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hammer C, Stepniak B, Schneider A, Papiol
S, Tantra M, Begemann M, Sirén AL, Pardo LA, Sperling S, Mohd
Jofrry S, et al: Neuropsychiatric disease relevance of circulating
anti-NMDA receptor autoantibodies depends on blood-brain barrier
integrity. Mol Psychiatry. 19:1143–1149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pruss H, Hültje M, Maier N, Gomez A,
Buchert R, Harms L, Ahnert-Hilger G, Schmitz D, Terborg C, Kopp U,
et al: IgA NMDA receptor antibodies are markers of synaptic
immunity in slow cognitive impairment. Neurology. 78:1743–1753.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|