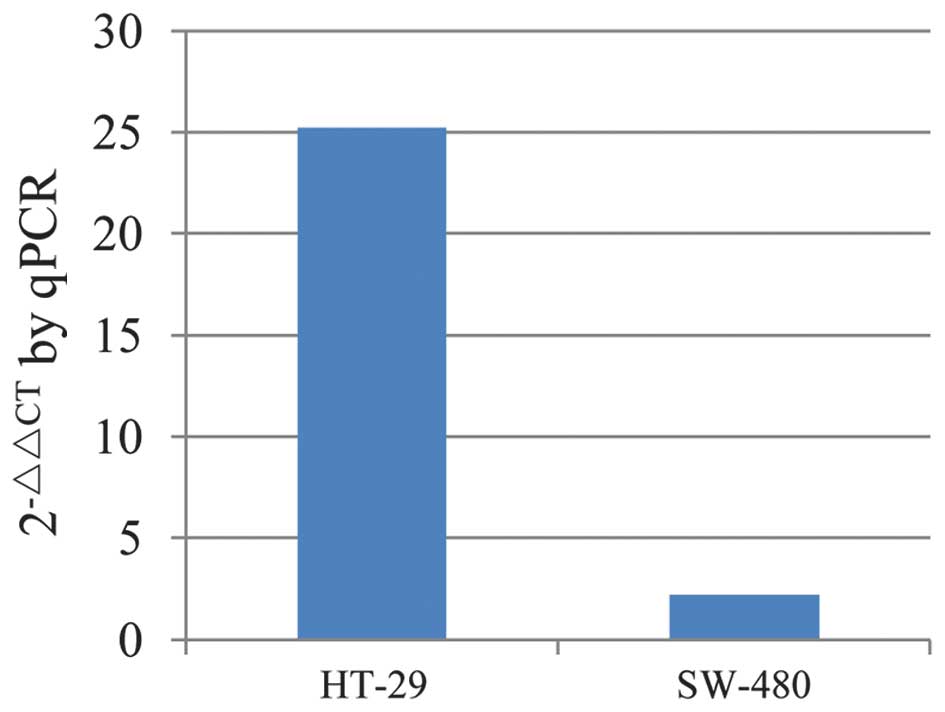
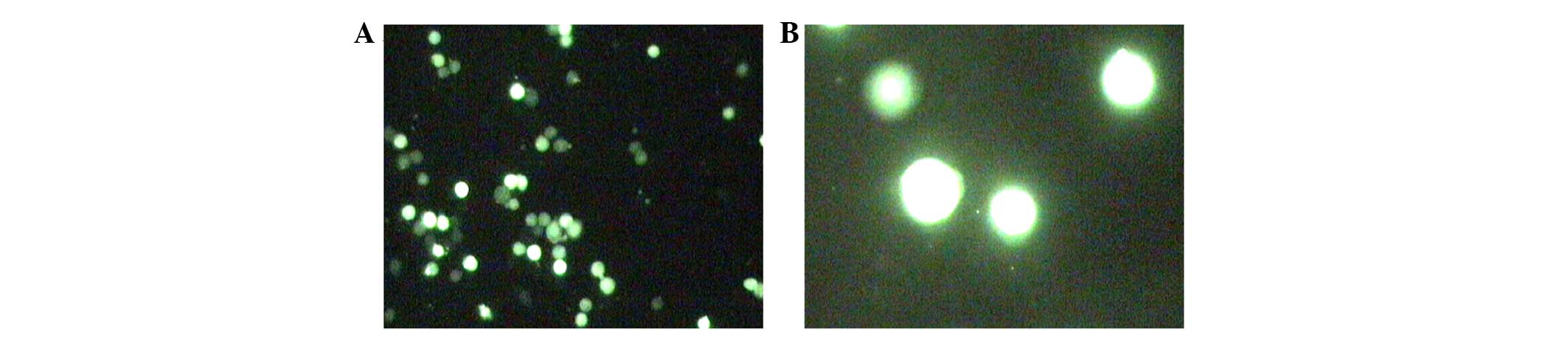
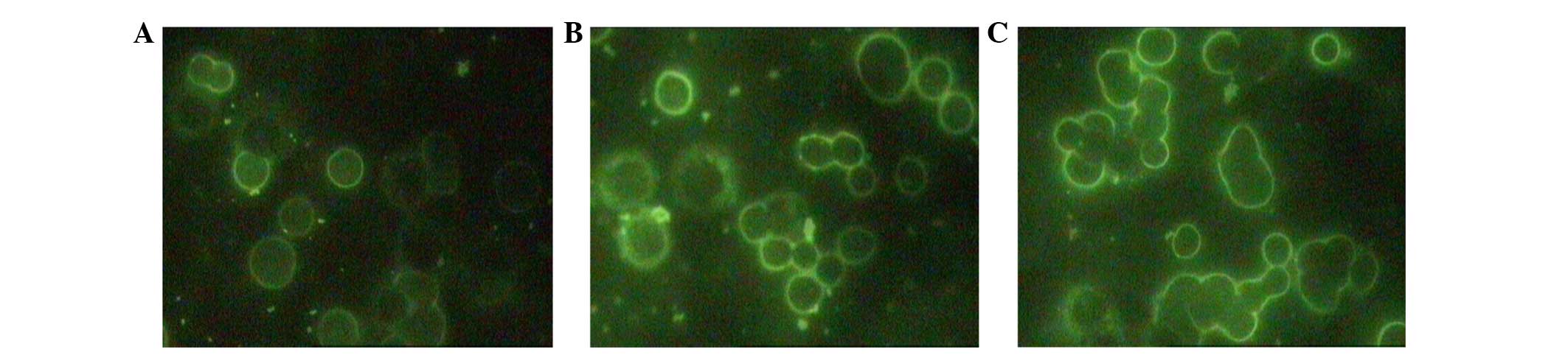
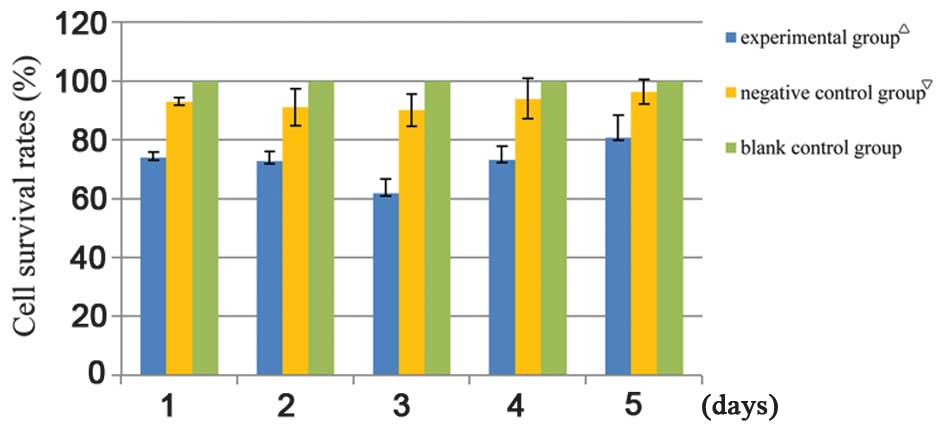
|
1
|
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, Melikian A,
Berahovich R, Miao Z, Penfold ME, Sunshine MJ, Littman DR, Kuo CJ,
et al: A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in
cell survival, cell adhesion and tumor development. J Exp Med.
203:2201–2213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hartmann TN, Grabovsky V, Pasvolsky R,
Shulman Z, Buss EC, Spiegel A, Nagler A, Lapidot T, Thelen M and
Alon R: A crosstalk between intracellular CXCR7 and CXCR4 involved
in rapid CXCL12-triggered integrin activation but not in
chemokine-triggered motility of human T lymphocytes and CD34+
cells. J Leukoc Biol. 84:1130–1140. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levoye A, Balabanian K, Baleux F,
Bachelerie F and Lagane B: CXCR7 heterodimerizes with CXCR4 and
regulates CXCL12-mediated G protein signaling. Blood.
113:6085–6093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Heinrich EL, Lee W, Lu J, Lowy AM and Kim
J: Chemokine CXCL12 activates dual CXCR4 and CXCR7-mediated
signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer cells. J Transl Med.
10:682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Odemis V, Boosmann K, Heinen A, Küry P and
Engele J: CXCR7 is an active component of SDF-1 signalling in
astrocytes and Schwann cells. J Cell Sci. 123:1081–1088. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Infantino S, Moepps B and Thelen M:
Expression and regulation of the orphan receptor RDC1 and its
putative ligand in human dendritic and B cells. J Immunol.
176:2197–2207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miao Z, Luker KE, Summers BC, Berahovich
R, Bhojani MS, Rehemtulla A, Kleer CG, Essner JJ, Nasevicius A,
Luker GD, et al: CXCR7 (RDC1) promotes breast and lung tumor growth
in vivo and is expressed on tumor-associated vasculature. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:15735–15740. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Li G, Stanco A, Long JE, Crawford
D, Potter GB, Pleasure SJ, Behrens T and Rubenstein JL: CXCR4 and
CXCR7 have distinct functions in regulating interneuron migration.
Neuron. 69:61–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zabel BA, Lewén S, Berahovich RD, Jaén JC
and Schall TJ: The novel chemokine receptor CXCR7 regulates
trans-endothelial migration of cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:732011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang HX, Chen DJ, Hu G, Cheng W and Yang
KY: The effect of lentiviral vector of shRNA on CXCR7 expression in
human colon cancer. Zhong Hua Pu Tong Wai Ke Za Zhi. 18:156–161.
2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D,
Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, et al:
Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 410:50–56. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J and Struyf
S: The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer
Lett. 267:226–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hao M, Zheng J, Hou K and Wang J, Chen X,
Lu X, Bo J, Xu C, Shen K and Wang J: Role of chemokine receptor
CXCR7 in bladder cancer progression. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:204–214.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yates TJ, Knapp J, Gosalbez M, Lokeshwar
SD, Gomez CS, Benitez A, Ekwenna OO, Young EE, Manoharan M and
Lokeshwar VB: C-X-C chemokine receptor 7: A functionally associated
molecular marker for bladder cancer. Cancer. 119:61–71. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schrevel M, Karim R, ter Haar NT, van der
Burg SH, Trimbos JB, Fleuren GJ, Gorter A and Jordanova ES: CXCR7
expression is associated with disease-free and disease-specific
survival in cervical cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 106:1520–1525.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Shiozawa Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Jung
Y, Pienta KJ, Mehra R, Loberg R and Taichman RS: The role of
CXCR7/RDC1 as a chemokine receptor for CXCL12/SDF-1 in prostate
cancer. J Biol Chem. 283:4283–4294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng K, Li HY, Su XL, Wang XY, Tian T, Li
F and Ren GS: Chemokine receptor CXCR7 regulates the invasion,
angiogenesis and tumor growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Décaillot FM, Kazmi MA, Lin Y, Ray-Saha S,
Sakmar TP and Sachdev P: CXCR7/CXCR4 heterodimer constitutively
recruits beta-arrestin to enhance cell migration. J Biol Chem.
286:32188–32197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi YH, Burdick MD, Strieter BA, Mehrad B
and Strieter RM: CXCR4, but not CXCR7, discriminates metastatic
behavior in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res.
12:38–47. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu L, Zhao X, Zhu X, Zhong Z, Xu R, Wang
Z, Cao J and Hou Y: Decreased expression of miR-430 promotes the
development of bladder cancer via the upregulation of CXCR7. Mol
Med Rep. 8:140–146. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hawkins OE and Richmond A: The dynamic
yin-yang interaction of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in breast cancer
metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 14:1032012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Berahovich RD, Penfold ME and Schall TJ:
Nonspecific CXCR7 antibodies. Immunol Lett. 133:112–114. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh RK and Lokeshwar BL: The
IL-8-regulated chemokine receptor CXCR7 stimulates EGFR signaling
to promote prostate cancer growth. Cancer Res. 71:3268–3277. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|