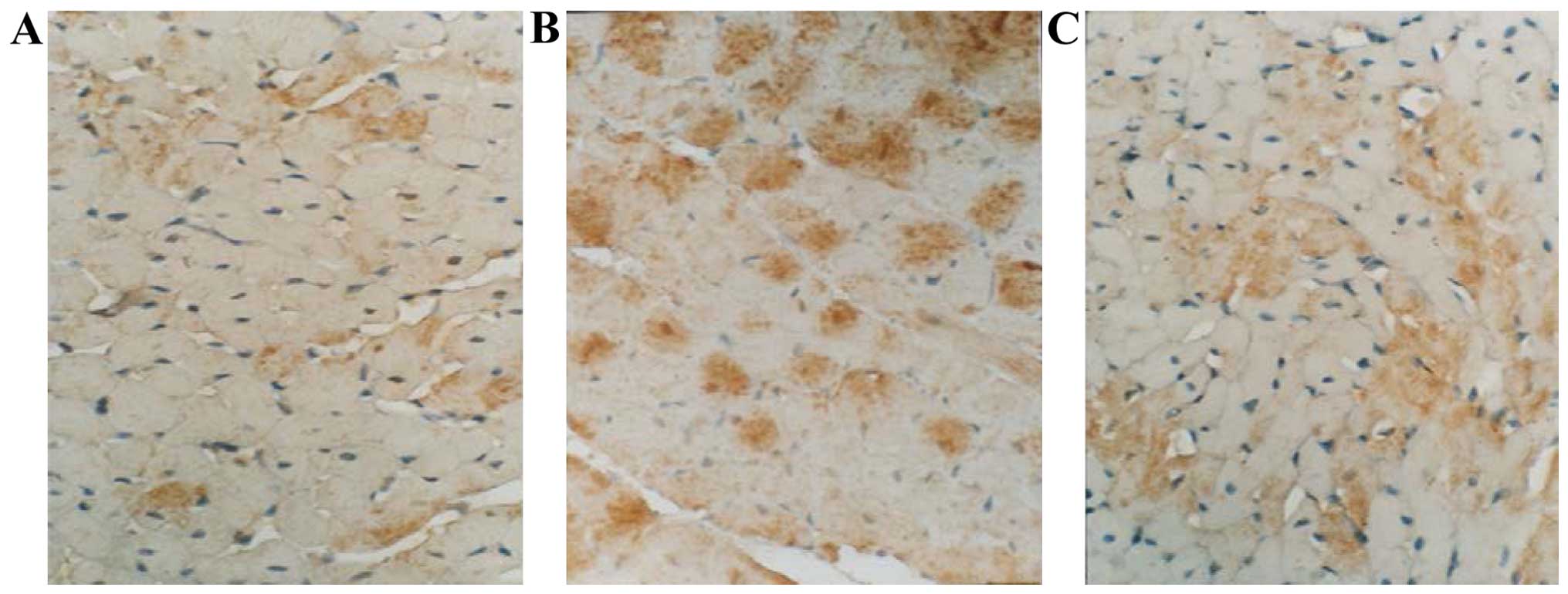
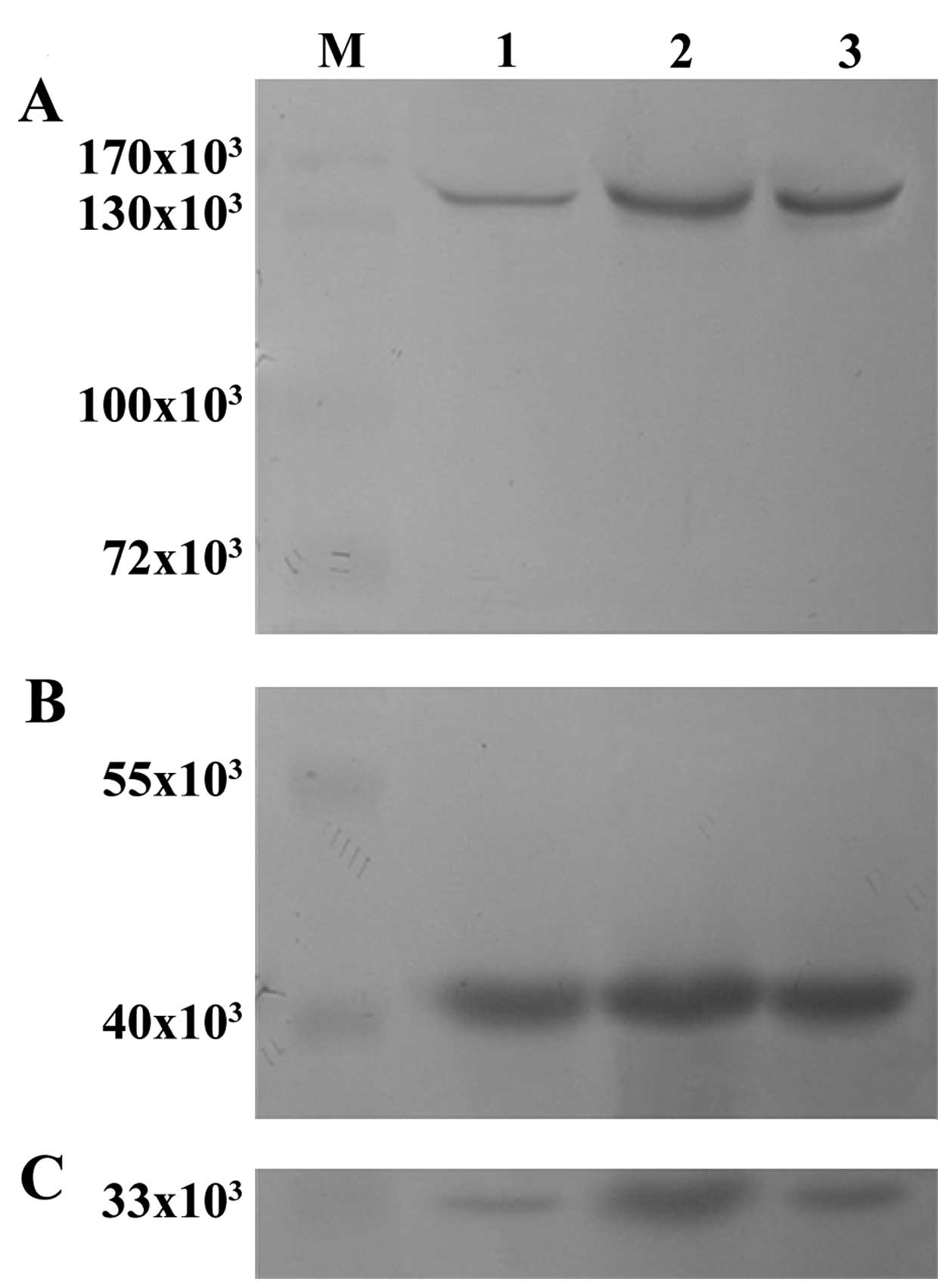
|
1
|
Shah AM and Mann DL: In search of new
therapeutic targets and strategies for heart failure: Recent
advances in basic science. Lancet. 378:704–712. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu YZ, Zhu YC, Wang ZJ, Lu Q, Lee HS and
Unger T: Time-dependent apoptotic development and pro-apoptotic
genes expression in rat heart after myocardial infarction. Jpn J
Pharmacol. 86:355–358. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Savateev AV and Savateeva-Liubimova TN:
Apoptosis-universal mechanisms of cell death and survival in
ischemia and reperfusion: Ways to pharmacological control. Eksp
Klin Farmakol. 73:44–49. 2010.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abbate A, Bussani R, Amin MS, Vetrovec GW
and Baldi A: Acute myocardial infarction and heart failure: Role of
apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:1834–1840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gladden JD, Ahmed MI, Litovsky SH, Schiros
CG, Lloyd SG, Gupta H, Denney TS Jr, Darley-Usmar V, McGiffin DC
and Dell'Italia LJ: Oxidative stress and myocardial remodeling in
chronic mitral regurgitation. Am J Med Sci. 342:114–119. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Doehner W and Landmesser U: Xanthine
oxidase and uric acid in cardiovascular disease: Clinical impact
and therapeutic options. Semin Nephrol. 31:433–440. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mellin V, Isabelle M, Oudot A,
Vergely-Vandriesse C, Monteil C, Di Meglio B, Henry JP, Dautreaux
B, Rochette L, Thuillez C, et al: Transient reduction in myocardial
free oxygen radical levels is involved in the improved cardiac
function and structure after long-term allopurinol treatment
initiated in established chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J.
26:1544–1550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang LP, Zhao Y, Yu HS, Liu YX, Xiong CQ,
Tan DW, Jia JM, Wang HT, Tian SY and Ma BP: Identification of
chemical constituents in qiliqiangxin capsule by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS(E).
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 46:1231–1236. 2011.[In Chinese]. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu W, Chen J, Xu T, Tian W, Li Y, Zhang Z
and Li W: Qiliqiangxin improves cardiac function in spontaneously
hypertensive rats through the inhibition of cardiac chymase. Am J
Hypertens. 25:250–260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao H, Song Y, Li Y, Liao YH and Chen J:
Qiliqiangxin regulates the balance between tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and interleukin-10 and improves cardiac function in
rats with myocardial infarction. Cell Immunol. 260:51–55. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen L, Han JZ, Li C, Yue SJ, Liu Y, Qin
XQ, Liu HJ and Luo ZQ: Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on
glutamate-induced lung injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:392–397.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu DH, Bao YM, Wei CL and An LJ: Studies
of chemical constituents and their antioxidant activities from
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge. Biomed Environ Sci. 18:297–301.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Chen R, Shang Y, Jiao B and Huang
C: Superoxide radicals scavenging and xanthine oxidase inhibitory
activity of magnesium lithospermate B from Salvia miltiorrhiza. J
Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 24:663–668. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karmazyn M, Moey M and Gan XT: Therapeutic
potential of ginseng in the management of cardiovascular disorders.
Drugs. 71:1989–2008. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen R, Shao H, Lin S, Zhang JJ and Xu KQ:
Treatment with Astragalus membranaceus produces antioxidative
effects and attenuates intestinal mucosa injury induced by
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Am J Chin Med. 39:879–887.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Konstam MA, Kramer DG, Patel AR, Maron MS
and Udelson JE: Left ventricular remodeling in heart failure:
Current concepts in clinical significance and assessment. JACC
Cardiovasc Imaging. 4:98–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gajarsa JJ and Kloner RA: Left ventricular
remodeling in the post-infarction heart: A review of cellular,
molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic modalities. Heart Fail Rev.
16:13–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Finkel T: Signal transduction by reactive
oxygen species. J Cell Biol. 194:7–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abbate A, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Bussani R,
Dobrina A, Camilot D, Feroce F, Rossiello R, Baldi F, Silvestri F,
Biasucci LM, et al: Increased myocardial apoptosis in patients with
unfavorable left ventricular remodeling and early symptomatic
post-infarction heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 41:753–760. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sam F, Sawyer DB, Chang DL, Eberli FR,
Ngoy S, Jain M, Amin J, Apstein CS and Colucci WS: Progressive left
ventricular remodeling and apoptosis late after myocardial
infarction in mouse heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
279:H422–H428. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee P, Sata M, Lefer DJ, Factor SM, Walsh
K and Kitsis RN: Fas pathway is a critical mediator of cardiac
myocyte death and MI during ischemia-reperfusion in vivo. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 284:H456–H463. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Foo RS, Mani K and Kitsis RN: Death begets
failure in the heart. J Clin Invest. 115:565–571. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schwarz K, Simonis G, Yu X, Wiedemann S
and Strasser RH: Apoptosis at a distance: Remote activation of
caspase-3 occurs early after myocardial infarction. Mol Cell
Biochem. 281:45–54. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Holly TA, Drincic A, Byun Y, Nakamura S,
Harris K, Klocke FJ and Cryns VL: Caspase inhibition reduces
myocyte cell death induced by myocardial ischemia and reperfusion
in vivo. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 31:1709–1715. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saitoh T, Nakajima T, Takahashi T and
Kawahara K: Changes in cardiovascular function on treatment of
inhibitors of apoptotic signal transduction pathways in left
ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc
Pathol. 15:130–138. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsieh MH and Nguyen HT: Molecular
mechanism of apoptosis induced by mechanical forces. Int Rev Cytol.
245:45–90. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin JS, Chan CY, Yang C, Wang YH, Chiou HY
and Su YC: Zhi-fuzi, a cardiotonic Chinese herb, a new medical
treatment choice for portal hypertension? Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
232:557–564. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shah AM and Channon KM: Free radicals and
redox signalling in cardiovascular disease. Heart. 90:486–487.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Murdoch CE, Zhang M, Cave AC and Shah AM:
NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signalling in cardiac hypertrophy,
remodelling and failure. Cardiovasc Res. 71:208–215. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oktyabrsky ON and Smirnova GV: Redox
regulation of cellular functions. Biochemistry (Mosc). 72:132–145.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li PF, Dietz R and von Harsdorf R: p53
regulates mitochondrial membrane potential through reactive oxygen
species and induces cytochrome c-independent apoptosis blocked by
Bcl-2. EMBO J. 18:6027–6036. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McCubrey JA, Lahair MM and Franklin RA:
Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of the MAP kinase
signaling pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:1775–1789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kinugawa S, Tsutsui H, Hayashidani S, Ide
T, Suematsu N, Satoh S, Utsumi H and Takeshita A: Treatment with
dimethylthiourea prevents left ventricular remodeling and failure
after experimental myocardial infarction in mice: Role of oxidative
stress. Circ Res. 87:392–398. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matsushima S, Ide T, Yamato M, Matsusaka
H, Hattori F, Ikeuchi M, Kubota T, Sunagawa K, Hasegawa Y, Kurihara
T, et al: Overexpression of mitochondrial peroxiredoxin-3 prevents
left ventricular remodeling and failure after myocardial infarction
in mice. Circulation. 113:1779–1786. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shiomi T, Tsutsui H, Matsusaka H, Murakami
K, Hayashidani S, Ikeuchi M, Wen J, Kubota T, Utsumi H and
Takeshita A: Overexpression of glutathione peroxidase prevents left
ventricular remodeling and failure after myocardial infarction in
mice. Circulation. 109:544–549. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Verheij M, Bose R, Lin XH, Yao B, Jarvis
WD, Grant S, Birrer MJ, Szabo E, Zon LI, Kyriakis JM, et al:
Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in
stress-induced apoptosis. Nature. 380:75–79. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nagai H, Noguchi T, Takeda K and Ichijo H:
Pathophysiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase signaling pathways. J
Biochem Mol Biol. 40:1–6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|