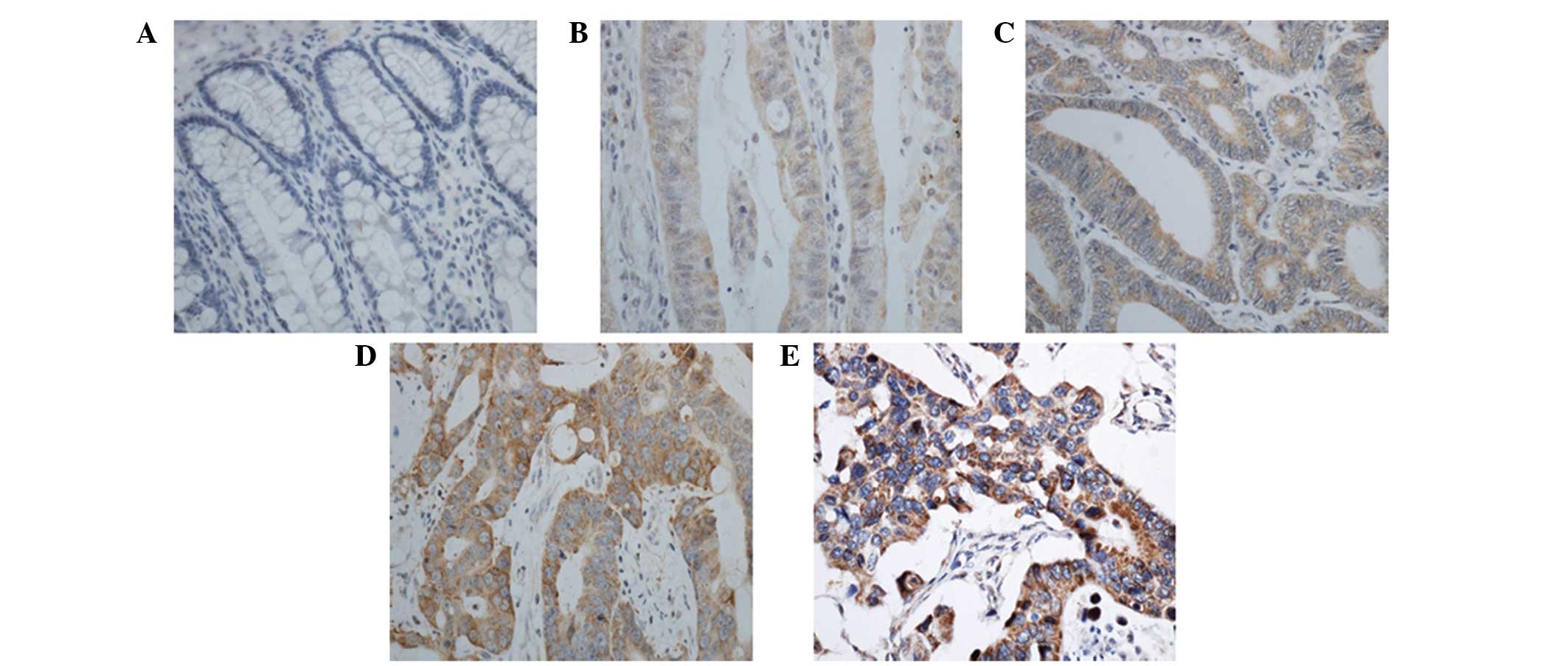
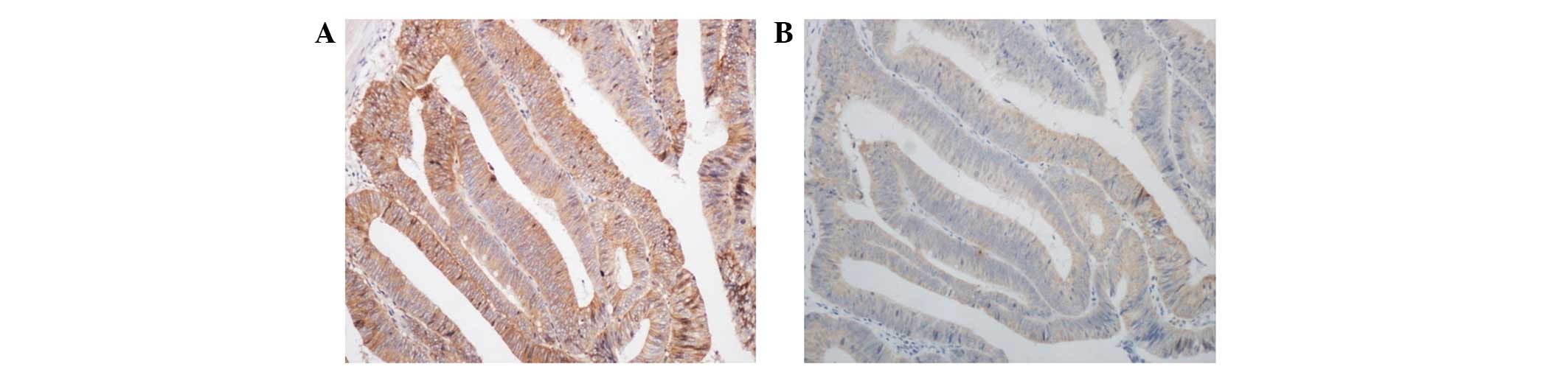
|
1
|
Cui C, Zhang M, Tian L, Jiang W, Zeng Z
and Li L: Survival implications of pretreatment pelvic CT in rectal
cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and surgery.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:12801–12809. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maffione AM, Chondrogiannis S, Capirci C,
Galeotti F, Fornasiero A, Crepaldi G, Grassetto G, Rampin L,
Marzola MC and Rubello D: Early prediction of response by (18)F-FDG
PET/CT during preoperative therapy in locally advanced rectal
cancer, A systematic review. Eur J Surg Oncol. 40:1186–1194. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Probst CP, Becerra AZ, Aquina CT, Tejani
MA, Hensley BJ, González MG, Noyes K, Monson JR and Fleming FJ:
Watch and wait? - Elevated pretreatment CEA is associated with
decreased pathological complete response in rectal cancer. J
Gastrointest Surg Nov. 6:2015.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
4
|
Strizzi L, Hardy KM, Margaryan V, Hillman
DW, Seftor EA, Chen B, Geiger XJ, Thompson EA, Lingle WL, et al:
Potential for the embryonic morphogen Nodal as a prognostic and
predictive biomarker in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
14:R752012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Murata K, Nunomura W, Takakuwa Y and Cherr
GN: Two different unique cardiac isoforms of protein 4.1R in
zebrafish, Danio rerio, and insights into their cardiac
functions as related to their unique structures. Dev Growth Differ.
52:591–602. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Clucas J and Valderrama F: ERM proteins in
cancer progression. J Cell Sci. 127:267–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fiévet B, Louvard D and Arpin M: ERM
proteins in epithelial cell organization and functions. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1773:653–660. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tepass U: FERM proteins in animal
morphogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 19:357–367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bennett V and Baines AJ: Spectrin and
ankyrin-based pathways: Metazoan inventions for integrating cells
into tissues. Physiol Rev. 81:1353–1392. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu H, Zhang Y, Ye L and Jiang WG: The FERM
family proteins in cancer invasion and metastasis. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 16:1536–1550. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goldie SJ, Mulder KW, Tan DW, Lyons SK,
Sims AH and Watt FM: FRMD4A upregulation in human squamous cell
carcinoma promotes tumor growth and metastasis and is associated
with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 72:3424–3436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Johnson C, Drgon T, Liu QR, Zhang PW,
Walther D, Li CY, Anthony JC, Ding Y, Eaton WW and Uhl GR: Genome
wide association for substance dependence, Convergent results from
epidemiologic and research volunteer samples. BMC Med Genet.
9:1132008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoon D, Kim YJ, Cui WY, Van der Vaart A,
Cho YS, Lee JY, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Li MD and Park T: Large-scale
genome-wide association study of Asian population reveals genetic
factors in FRMD4A and other loci influencing smoking initiation and
nicotine dependence. Hum Genet. 131:1009–1021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ikenouchi J and Umeda M: FRMD4A regulates
epithelial polarity by connecting Arf6 activation with the PAR
complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:748–753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng XH, Zhao JJ, Jia B, Pan J, Chen J,
Qiu XL, Han JS and Chu HX: The influence of inactive FRMD4A gene on
the biological behavior of human tongue cancer CAL-27 cell. Shi
Yong Yi Xue Za Zhi. 10:99–103. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Heerboth S, Housman G, Leary M, Longacre
M, Byler S, Lapinska K, Willbanks A and Sarkar S: EMT and tumor
metastasis. Clin Transl Med. 4:62015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Steinestel K, Eder S and Schrader AJ: andS
teinestel J: Clinical significance of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Clin Transl Med. 3:172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hirano M, Hashimoto S, Yonemura S, Sabe H
and Aizawa S: EPB41L5 functions to post-transcriptionally regulate
cadherin and integrin during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J
Cell Biol. 182:1217–1230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Radovanović Z, Radovanović D, Breberina M,
Petrović T, Golubović A and Bokorov B: The value of endorectal
ultrasonography in rectal cancer staging. Med Pregl. 61:557–561.
2008.(In Serbian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|