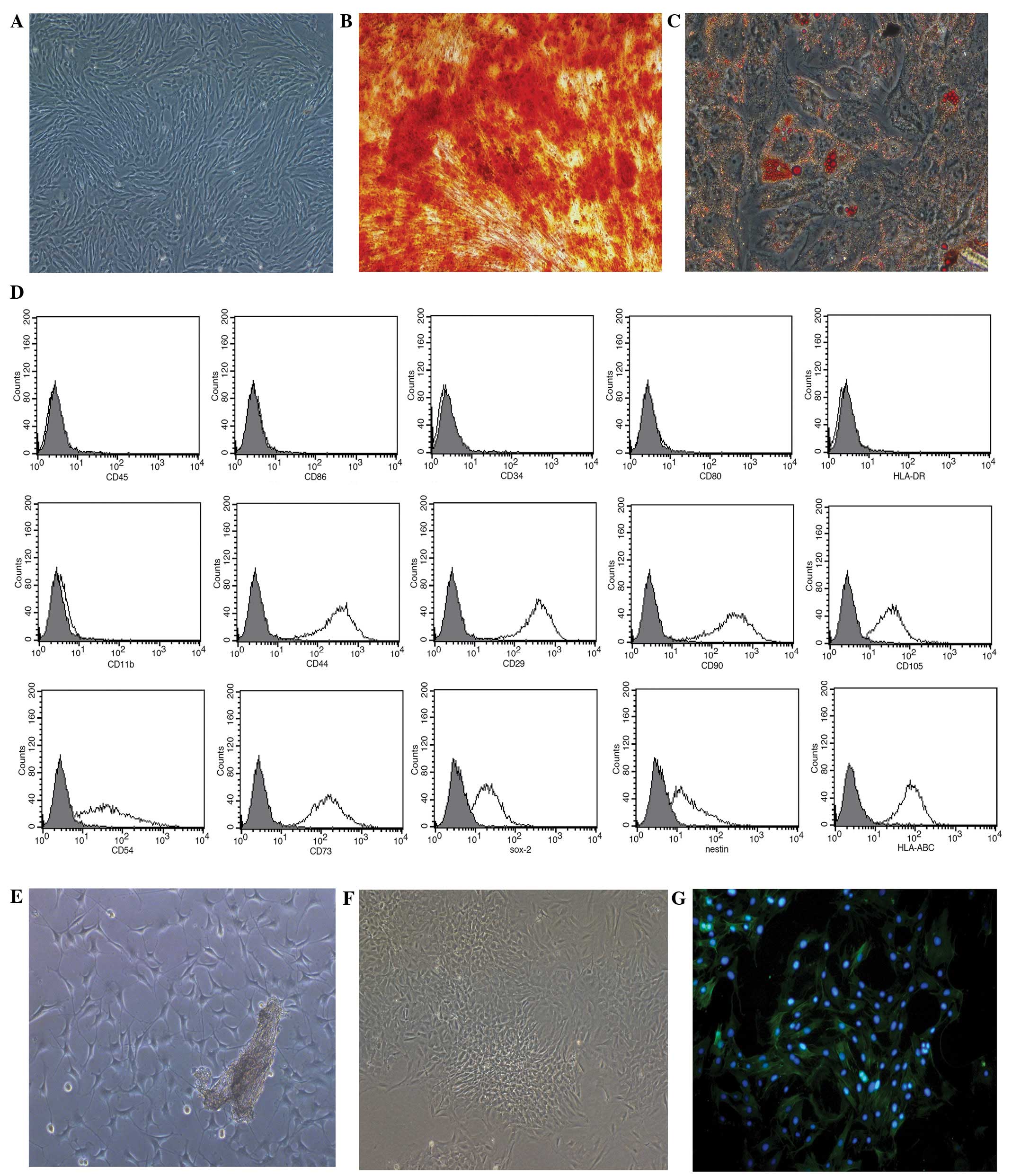
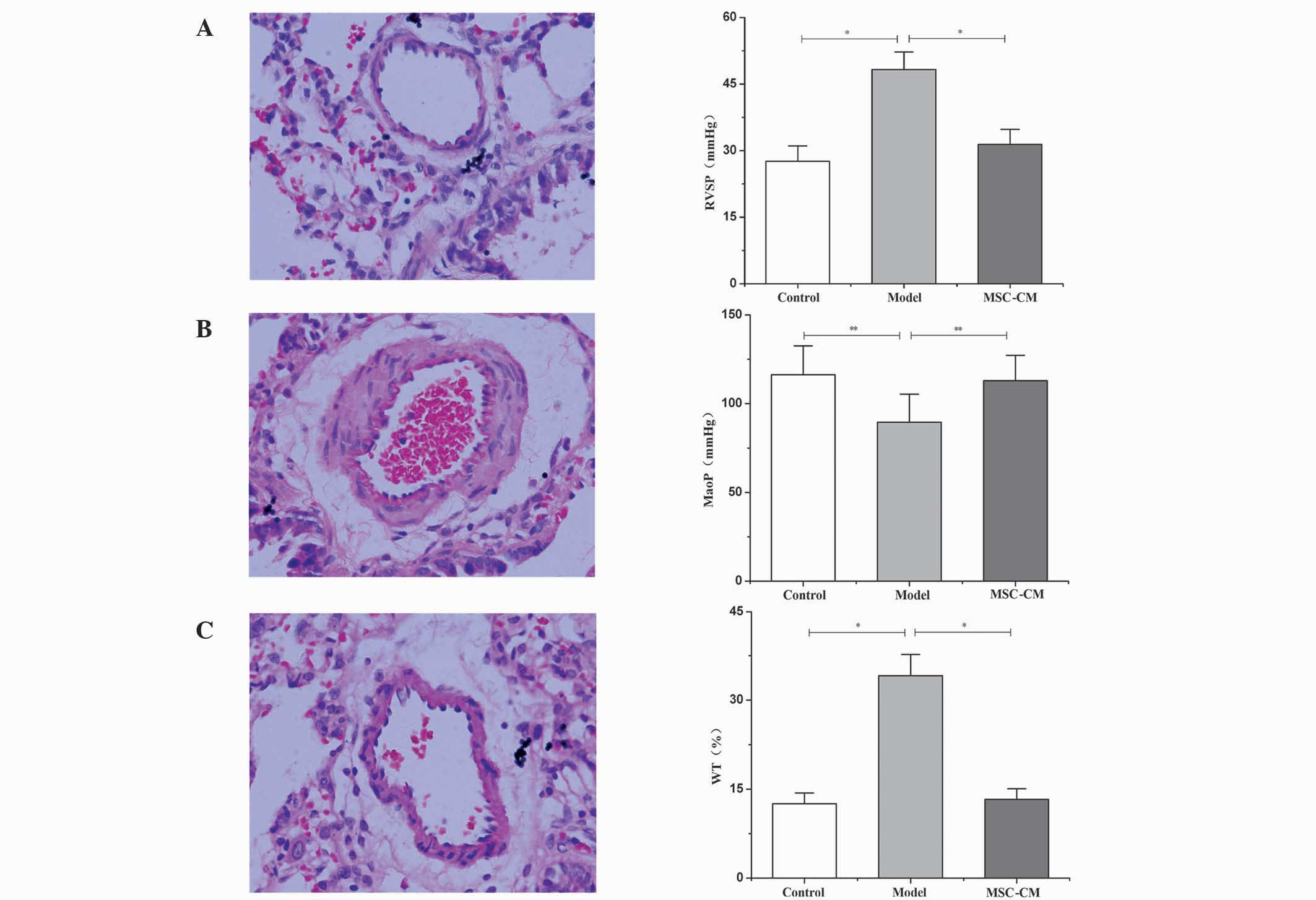
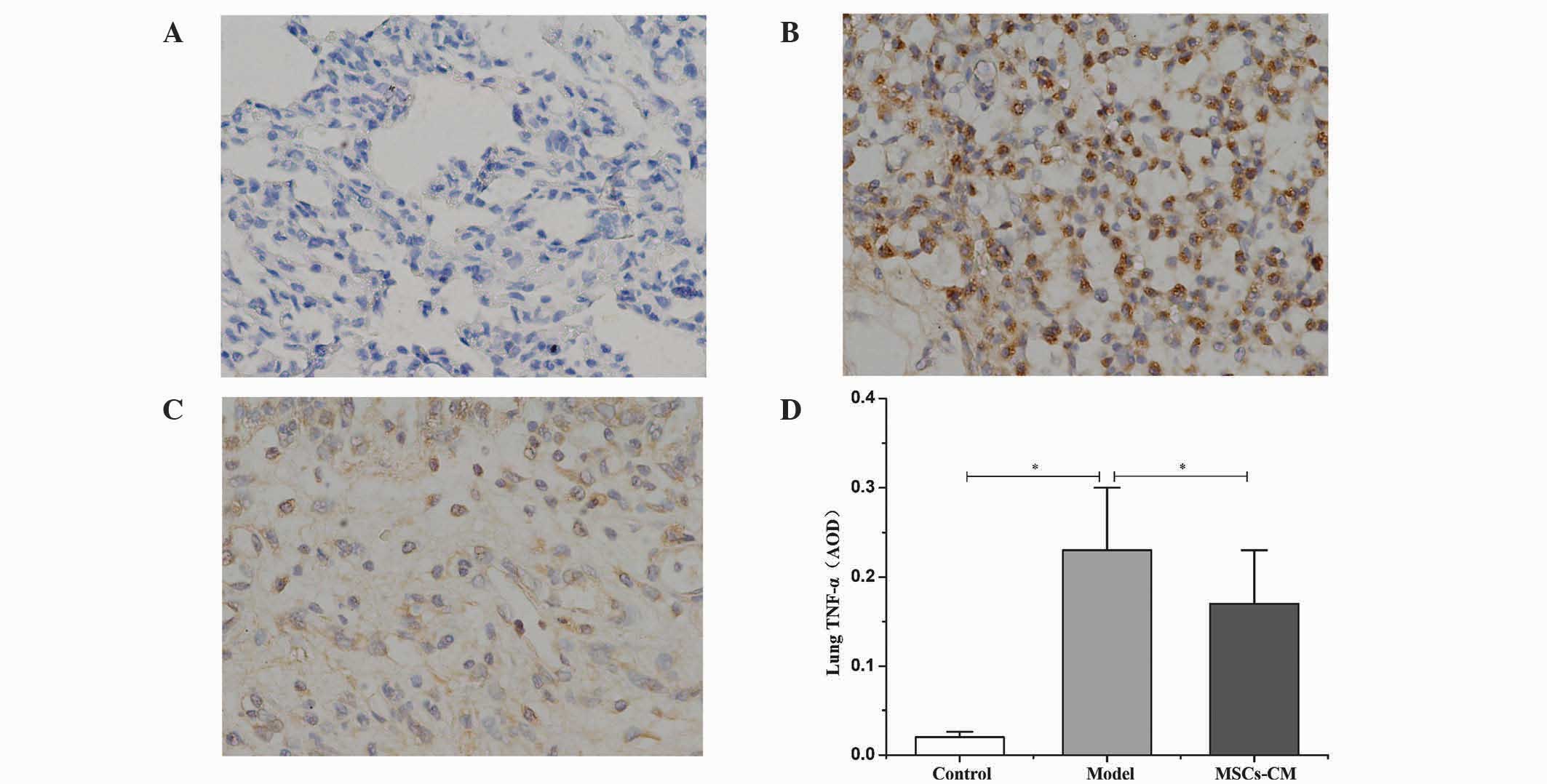
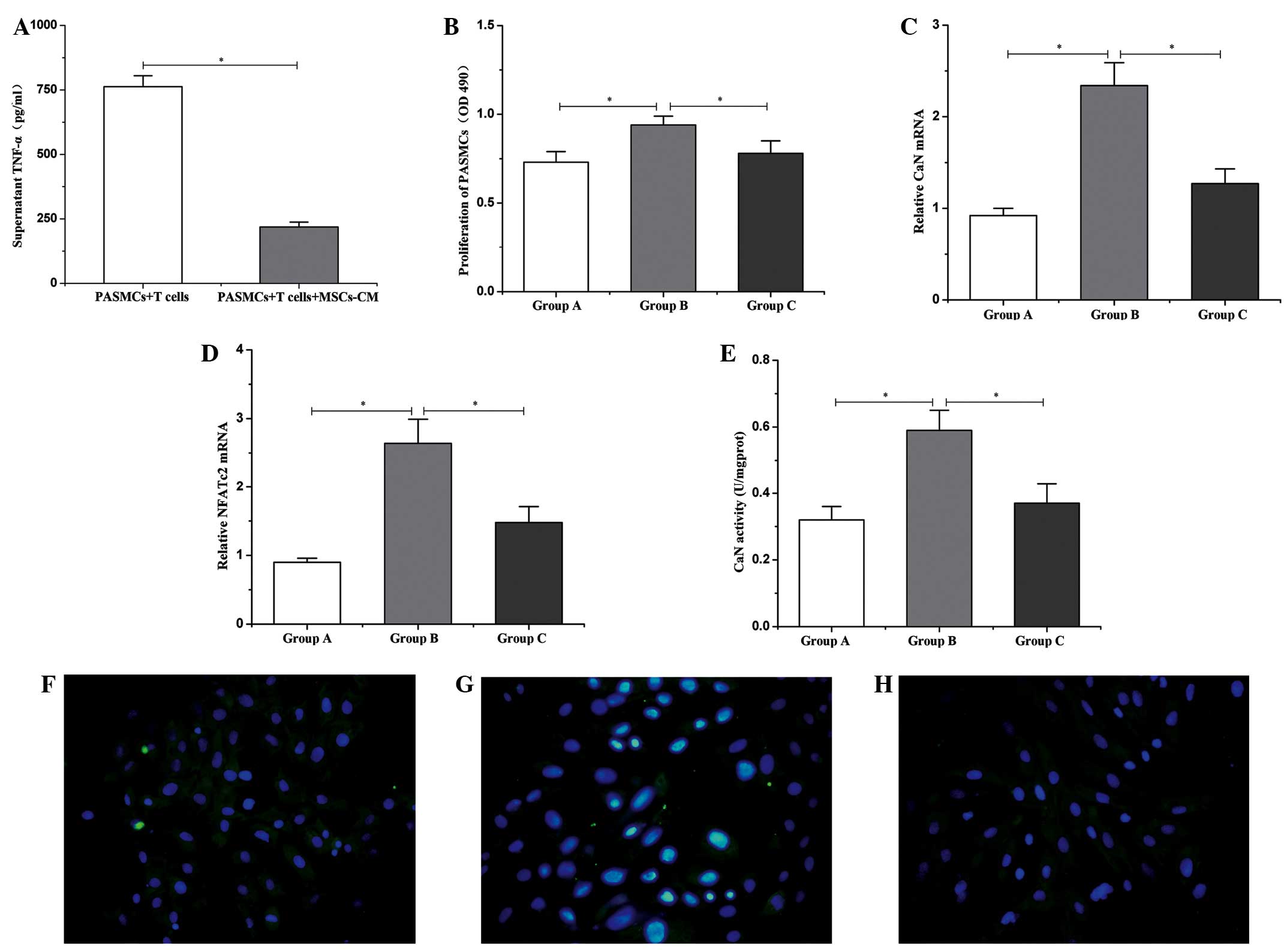
|
1
|
Bazan IS and Fares WH: Pulmonary
hypertension: Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Ther Clin Risk
Manag. 11:1221–1233. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tonelli AR: Pulmonary hypertension
survival effects and treatment options in cystic fibrosis. Curr
Opin Pulm Med. 19:652–661. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tonelli AR, Fernandez-Bussy S, Lodhi S,
Akindipe OA, Carrie RD, Hamilton K, Mubarak K and Baz MA:
Prevalence of pulmonary hypertension in end-stage cystic fibrosis
and correlation with survival. J Heart Lung Transplant. 29:865–872.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hayes D Jr, Higgins RS, Kirkby S, McCoy
KS, Wehr AM, Lehman AM and Whitson BA: Impact of pulmonary
hypertension on survival in patients with cystic fibrosis
undergoing lung transplantation, An analysis of the UNOS registry.
J Cyst Fibros. 13:416–423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pinto RF: HiguchiM de L and Aiello VD:
Decreased numbers of T-lymphocytes and predominance of recently
recruited macrophages in the walls of peripheral pulmonary arteries
from 26 patients with pulmonary hypertension secondary to
congenital cardiac shunts. Cardiovasc Pathol. 13:268–275. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Perros F, Dorfmüller P, Montani D, Hammad
H, Waelput W, Girerd B, Raymond N, Mercier O, Mussot S,
Cohen-Kaminsky S, et al: Pulmonary lymphoid neogenesis in
idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 185:311–321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heath D and Edwards JE: The pathology of
hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease; a description of six
grades of structural changes in the pulmonary arteries with special
reference to congenital cardiac septal defects. Circulation.
18:533–547. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soon E, Holmes AM, Treacy CM, Doughty NJ,
Southgate L, Machado RD, Trembath RC, Jennings S, Barker L, Nicklin
P, et al: Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines predict
survival in idiopathic and familial pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Circulation. 122:920–927. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Frid MG, Brunetti JA, Burke DL, Carpenter
TC, Davie NJ, Reeves JT and Roedersheimer MT: vanR ooijen N and
Stenmark KR: Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling requires
recruitment of circulating mesenchymal precursors of a
monocyte/macrophage lineage. Am J Pathol. 168:659–669. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rowlands DJ, Islam MN, Das SR, Huertas A,
Quadri SK, Horiuchi K, Inamdar N, Emin MT, Lindert J, Ten VS, et
al: Activation of TNFR1 ectodomain shedding by mitochondrial
Ca2+ determines the severity of inflammation in mouse
lung microvessels. J Clin Invest. 121:1986–1999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Said SI, Hamidi SA and Gonzalez Bosc L:
Asthma and pulmonary arterial, hypertension. Do they share a key
mechanism of pathogenesis? Eur Respir J. 35:730–734. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bonnet S, Rochefort G, Sutendra G, Archer
SL, Haromy A, Webster L, Hashimoto K, Bonnet SN and Michelakis ED:
The nuclear factor of activated T cells in pulmonary arterial
hypertension can be therapeutically targeted. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:11418–11423. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Frutos S, Spangler R, Alò D and Bosc
LV: NFATc3 mediates chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial
remodeling with alpha-actin up-regulation. J Biol Chem.
282:15081–15089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang ZX, Han ZB, Ji YR, Wang YW, Liang L,
Chi Y, Yang SG, Li LN, Luo WF, Li JP, et al: CD106 identifies a
subpopulation of mesenchymal stem cells with unique
immunomodulatory properties. PLoS One. 8:e593542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aslam M, Baveja R, Liang OD,
Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Lee C, Mitsialis SA and Kourembanas S: Bone
marrow stromal cells attenuate lung injury in a murine model of
neonatal chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
180:1122–1130. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu LL, Liu YJ, Yang SG, Zhao QJ, Wang X,
Gong W, Han ZB, Xu ZS, Lu YX, Liu D, et al: Isolation and
characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials.
Haematologica. 91:1017–1026. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsuda Y, Hoshikawa Y, Ameshima S, Suzuki
S, Okada Y, Tabata T, Sugawara T, Matsumura Y and Kondo T: Effects
of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands on
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Nihon Kokyuki
Gakkai Zasshi. 43:283–288. 2005.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu JF, DU ZD, Chen Z, Han ZC and He ZX:
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor attenuates
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension by upregulating
endothelial progenitor cells via the nitric oxide system. Exp Ther
Med. 6:1402–1408. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maruyama H, Watanabe S, Kimura T, Liang J,
Nagasawa T, Onodera M, Aonuma K and Yamaguchi I: Granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor prevents progression of
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Circ
J. 71:138–143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Woodrum DT, Ford JW, Cho BS, Hannawa KK,
Stanley JC, Henke PK and Upchurch GR Jr: Differential effect of
17-beta-estradiol on smooth muscle cell and aortic explant MMP2. J
Surg Res. 155:48–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ahmad S, Choudhry MA, Shankar R and Sayeed
MM: Transforming growth factor-beta negatively modulates T-cell
responses in sepsis. FEBS Lett. 402:213–218. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu JF, Han ZB, Han ZC and He ZX:
Mesenchymal stem cells suppress CaN/NFAT expression in the
pulmonary arteries of rats with pulmonary hypertension. Exp Ther
Med. 10:1657–1664. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tuder RM, Marecki JC, Richter A,
Fijalkowska I and Flores S: Pathology of pulmonary hypertension.
Clin Chest Med. 28:23–42. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weiss DJ, Bertoncello I, Borok Z, Kim C,
Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Reynolds S, Rojas M, Stripp B, Warburton D
and Prockop DJ: Stem cells and cell therapies in lung biology and
lung diseases. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 8:223–72. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, Gaupp D,
Baddoo M, Kaminski N and Phinney DG: Mesenchymal stem cell
engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure
and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hansmann G, Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Aslam M,
Vitali SH, Martin T, Mitsialis SA and Kourembanas S: Mesenchymal
stem cell-mediated reversal of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and
associated pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2:170–81. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jun D, Garat C, West J, Thorn N, Chow K,
Cleaver T, Sullivan T, Torchia EC, Childs C, Shade T, et al: The
pathology of bleomycin-induced fibrosis is associated with loss of
resident lung mesenchymal stem cells that regulate effector T cell
proliferation. Stem Cells. 29:725–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan MG, Xiong Y and Chen F: NFAT gene
family in inflammation and cancer. Curr Mol Med. 13:543–554. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kudryavtseva O, Aalkjaer C and Matchkov
VV: Vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype is defined by
Ca2+-dependent transcription factors. FEBS J.
280:5488–5499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koulmann N, Novel-Chaté V, Peinnequin A,
Chapot R, Serrurier B, Simler N, Richard H, Ventura-Clapier R and
Bigard X: Cyclosporin A inhibits hypoxia-induced pulmonary
hypertension and right ventricle hypertrophy. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 174:699–705. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|