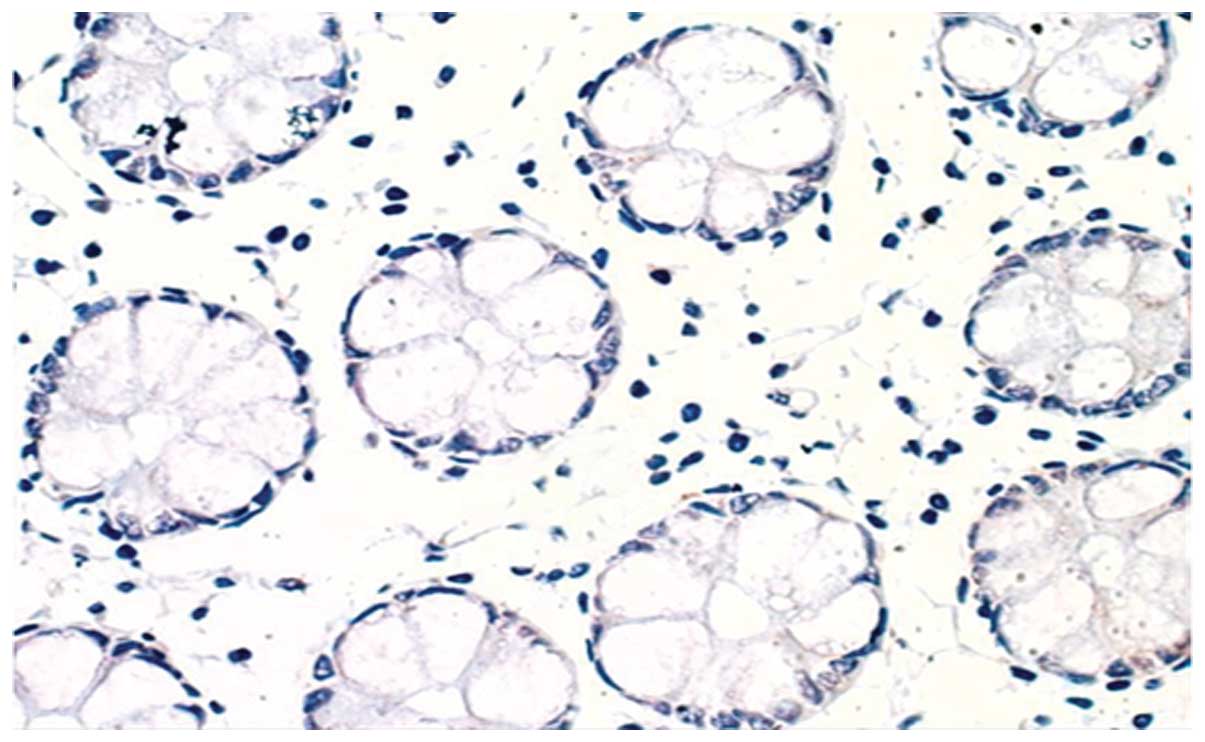
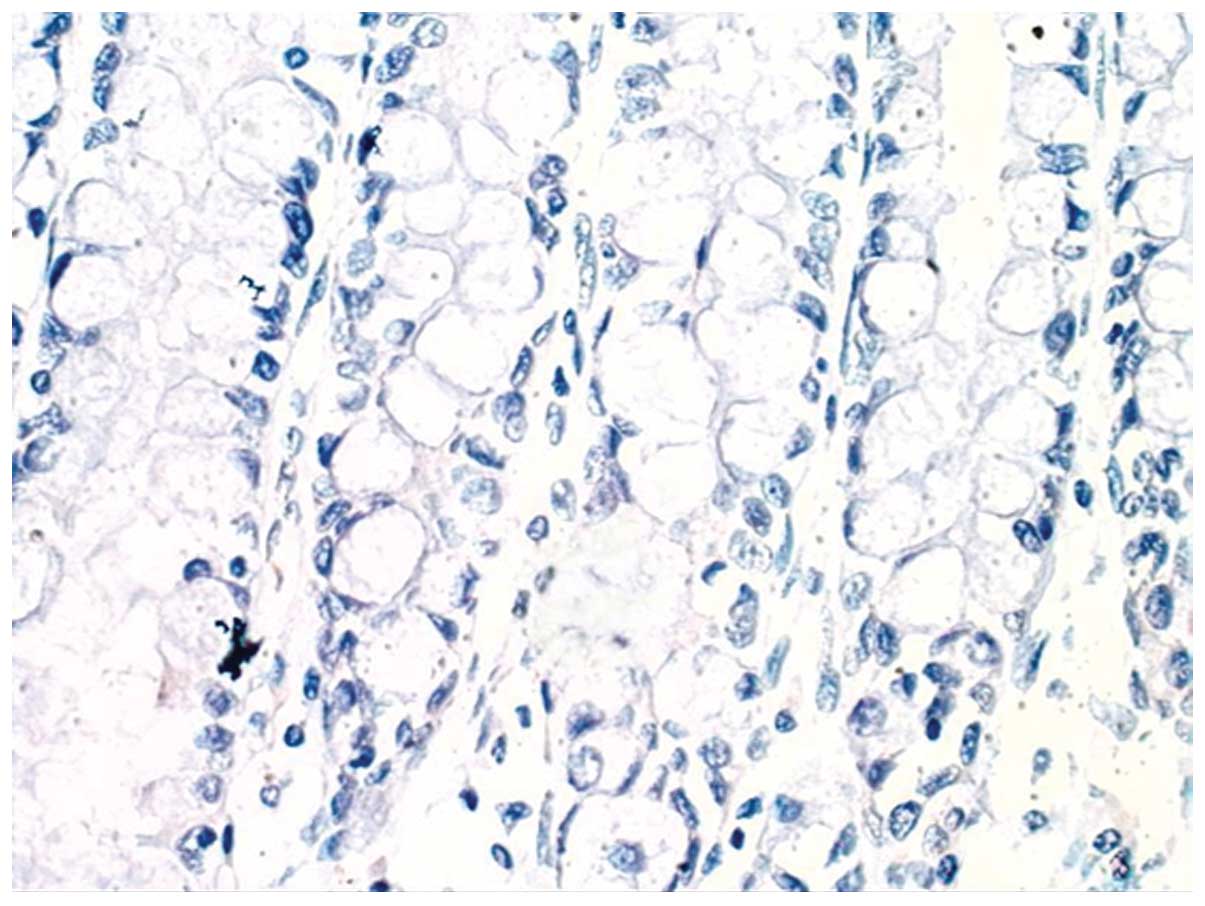
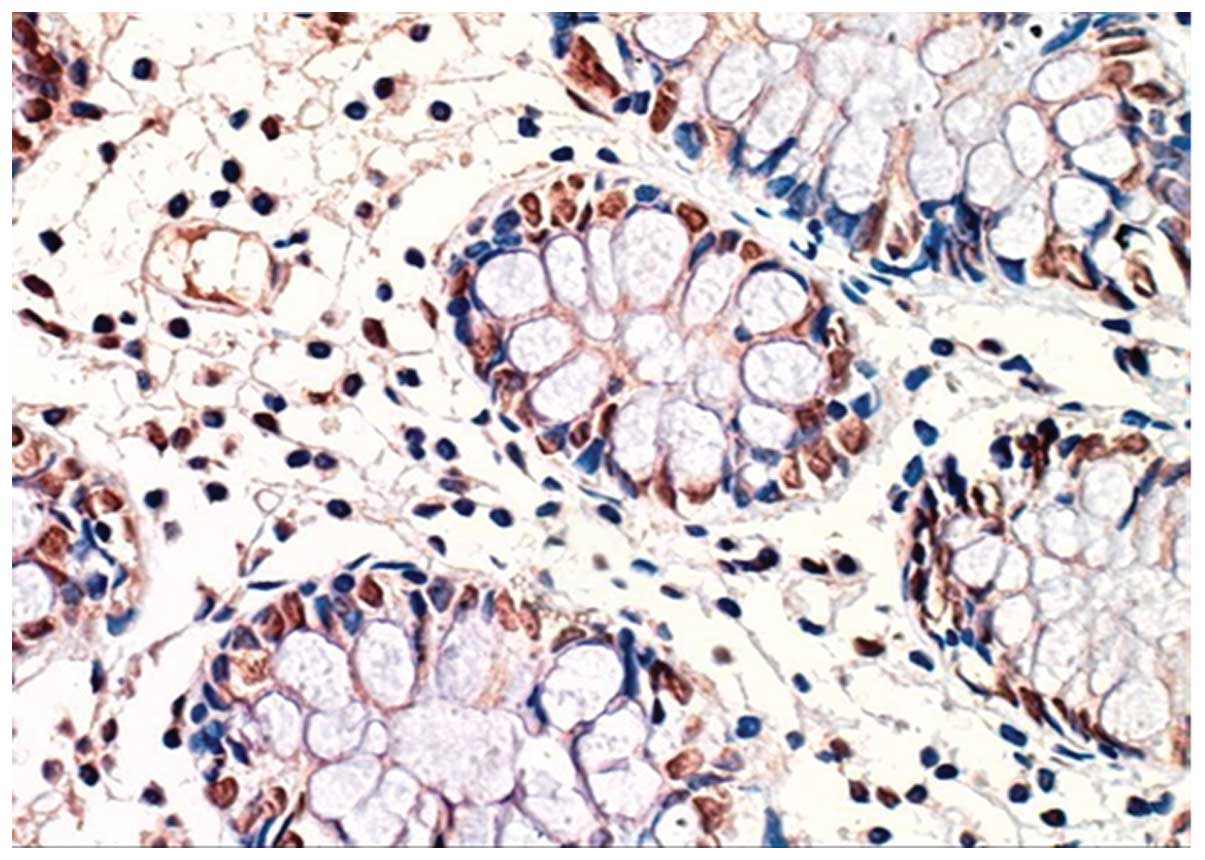
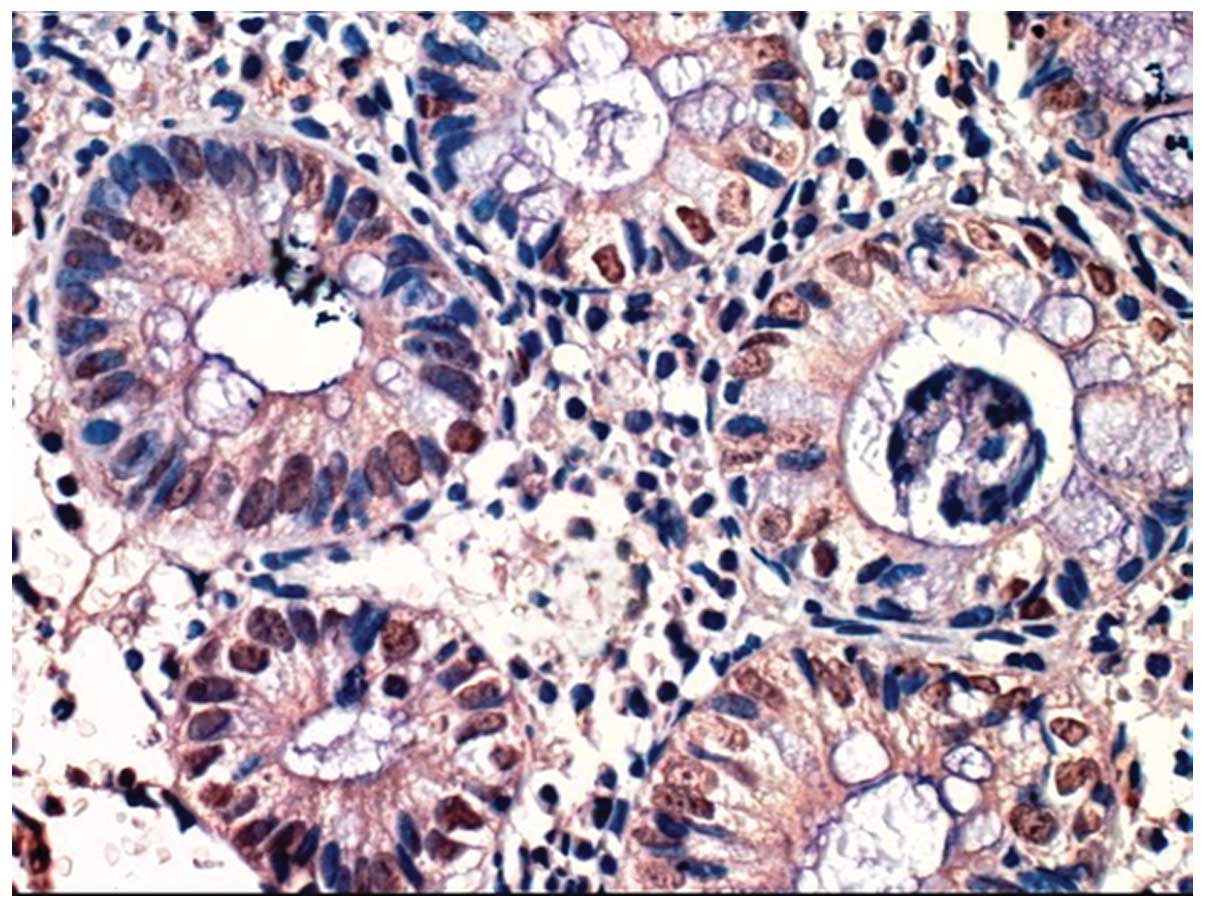
|
1
|
Diamanti A, Knafelz D, Panetta F, De
Angelis P, Candusso M, Bracci F, Papadatou B, Francalanci P, Monti
L and Torre G: Thalidomide as rescue therapy for acute severe
ulcerative colitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:1690–1693.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu D, Xia SL, Shao XX, Yu LQ, Lin XX, Guo
M, Lin XQ and Jiang Y: Association of ulcerative colitis with
TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) gene polymorphisms
and plasma soluble TRAIL levels in Chinese Han population. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:467–476. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong WG, Liu SP, Yu BP, Wu DF, Luo HS and
Yu JP: Ameliorative effects of sodium ferulate on experimental
colitis and their mechanisms in rats. World J Gastroenterol.
9:2533–2538. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pica R, Cassieri C, Pronio AM, Zippi M,
Avallone EV, Montesani C, Occhigrossi G and Paoluzi P: Quality of
life in ulcerative colitis patients treated medically versus
patients undergoing surgery. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:693–698.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bai R, Zhao AQ, Zhao ZQ, Liu WL and Jian
DM: MicroRNA-195 induced apoptosis in hypoxic chondrocytes by
targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 19:545–551. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei H, Li F, Fu P and Liu X: Effects of
the silencing of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha on metastasis of
pancreatic cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:436–446.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang M, Gao X, Bai SJ, Ye XM and Zhang J:
Effect of pioglitazone on expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
and vascular endothelial growth factor in ischemic hindlimb of
diabetic rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:1307–1314.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Semenza GL and Wang GL: A nuclear factor
induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human
erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional
activation. Mol Cell Bio. 12:5447–5454. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Maxwell PH, Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ:
Activation of the HIF pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
11:293–299. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thornton RD, Lane P, Borghaei Re, et al:
Interleukin 1 induceshypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human gingival
and synovialfibroblasts. Biochem J. 350:307–312. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Albina JE, Mastrofrancesco B, Vessella JA,
et al: HIF-1 expression in healing wounds: HIF-1alpha induction in
primary inflammatory cells by TNF-alpha. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
281:1971–1977. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Ouyang Q, Hu PJ, Qian JM, Zheng JJ and Hu
RW: Consensus on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in
China in 2007. J Dig Dis. 8:545–561. 2007.
|
|
13
|
Urgesi R, Zampaletta C, Masini A, Pelecca
G, Pastorelli A, De Lorenzo A and Faggiani R: Spontaneous right
ventricular thrombus in a patient with active ulcerative colitis
and protein C deficiency: a review with a case report. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 14:455–463. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Federico A, Tuccillo C, Grossi E, Abbiati
R, Garbagna N, Romano M, Tiso A, del Blanco CV and Loguercio C: The
effect of a new symbiotic formulation on plasma levels and
peripheral blood mononuclear cell expression of some
pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with ulcerative colitis: a
pilot study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 13:285–293. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blanco MI, Becerra M, González-Siso MI and
Cerdán ME: Functional characterization of KlHEM13, a hypoxic gene
of Kluyveromyces lactis. Can J Microbiol. 51:241–249. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Le QT, Denko NC and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxic
gene expression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 23:293–310.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sanges M, Valente G, Rea M, Della Gatta R,
De Franchis G, Sollazzo R and D'Arienzo A: Probiotics in
spondyloarthropathy associated with ulcerative colitis: a pilot
study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 13:233–234. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schmidt C, Lautenschläger C, Petzold B,
Sakr Y, Marx G and Stallmach A: Confocal laser endomicroscopy
reliably detects sepsis-related and treatment-associated changes in
intestinal mucosal microcirculation. Br J Anaesth. 111:996–1003.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Harrois A, Baudry N, Huet O, Kato H, Lohez
M, Ziol M, Duranteau J and Vicaut E: Synergistic deleterious effect
of hypoxemia and hypovolemia on microcirculation in intestinal
villi. Crit Care Med. 41:e376–e384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lehmann Ch, Abdo I, Kern H, Maddison L,
Pavlovic D, Sharawi N, Starkopf J, Hall R, Johnson P, Williams L,
et al: MiDAS (Microcirculation Diagnostics and Applied Studies)
group: Clinical evaluation of the intestinal microcirculation using
sidestream dark field imaging - recommendations of a round table
meeting. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 57:137–146. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yeh YC, Sun WZ, Ko WJ, Chan WS, Fan SZ,
Tsai JC and Lin TY: Dexmedetomidine prevents alterations of
intestinal microcirculation that are induced by surgical stress and
pain in a novel rat model. Anesth Analg. 115:46–53. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Armuzzi A, De Pascalis B, Lupascu A,
Fedeli P, Leo D, Mentella MC, Vincenti F, Melina D, Gasbarrini G,
Pola P, et al: Infliximab in the treatment of steroid-dependent
ulcerative colitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 8:231–233.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Maltezos E,
Papazoglou D, Simopoulos C, Gatter KC, Harris AL and Koukourakis
MI: Hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha and 2alpha overexpression in
inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Pathol. 56:209–213. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jeong HJ, Chung HS, Lee BR, Kim SJ, Yoo
SJ, Hong SH and Kim HM: Expression of proinflammatory cytokines via
HIF-1alpha and NF-kappaB activation on desferrioxamine-stimulated
HMC-1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 306:805–811. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu CM, Dong WG, Yu BP, et al: Expression
of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and inflammation-induced enzyme in
inflammatory bowel disease. J Clinical Gastroente. 17:103–105.
2005.
|
|
26
|
Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Förster
I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, Haase VH, Jaenisch R, Corr M, Nizet V,
et al: HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated
inflammation. Cell. 112:645–657. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu F, Liu H, Xu L, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α perpetuates synovial fibroblast
interactions with T cells and B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur
J Immunol. November 25–2015.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1002/eji.201545784. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang X, Liu J, Wan L, et al: Up-regulated
expressions of HIF-1α, VEGF and CD34 promote synovial angiogenesis
in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 31:1053–1056. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee SH, Lee SH, Kim CH, et al: Increased
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia
inducible factor-1α in lung tissue of patients with chronic
bronchitis. Clin Biochem. 47:552–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tao H, Luo W, Pei H, Zhu S, Zhang M, Chen
B, He J, Zhang M and Zhou R: Expression and significance of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in patients withchronic obstructive
pulmonary disease and smokers with normal lung function. Xi Bao Yu
Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 30:852–855. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu JB, Ding JQ and Wang L:
Immunohistochemical study of dental pulp inflammation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. J Clin Stomatol. 19:77–78. 2003.
|
|
32
|
Hellwig-Bürgel T, Rutkowski K, Metzen E,
Fandrey J and Jelkmann W: Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha stimulate DNA binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1.
Blood. 94:1561–1567. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang BL and Wang XR: Regulation of hypoxia
inducible factor-1α by the inflammatory mediators. Int J Pathol
Clin Med. 90:1673–2588. 2008.
|
|
34
|
Ngo DT, Farb MG, Kikuchi R, Karki S,
Tiwari S, Bigornia SJ, Bates DO, LaValley MP, Hamburg NM, Vita JA,
et al: Antiangiogenic actions of vascular endothelial growth
factor-A165b, an inhibitory isoform of vascular endothelial growth
factor-A, in human obesity. Circulation. 130:1072–1080. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cătană CS, Neagoe Berindan I, Cozma V,
Magdaş C, Tăbăran F and Dumitraşcu DL: Contribution of the
IL-17/IL-23 axis to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease.
World J Gastroenterol. 21:5823–5830. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Avallone EV, Pica R, Cassieri C, Zippi M,
Paoluzi P and Vernia P: Azathioprine treatment in inflammatory
bowel disease patients: type and time of onset of side effects. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:165–170. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|