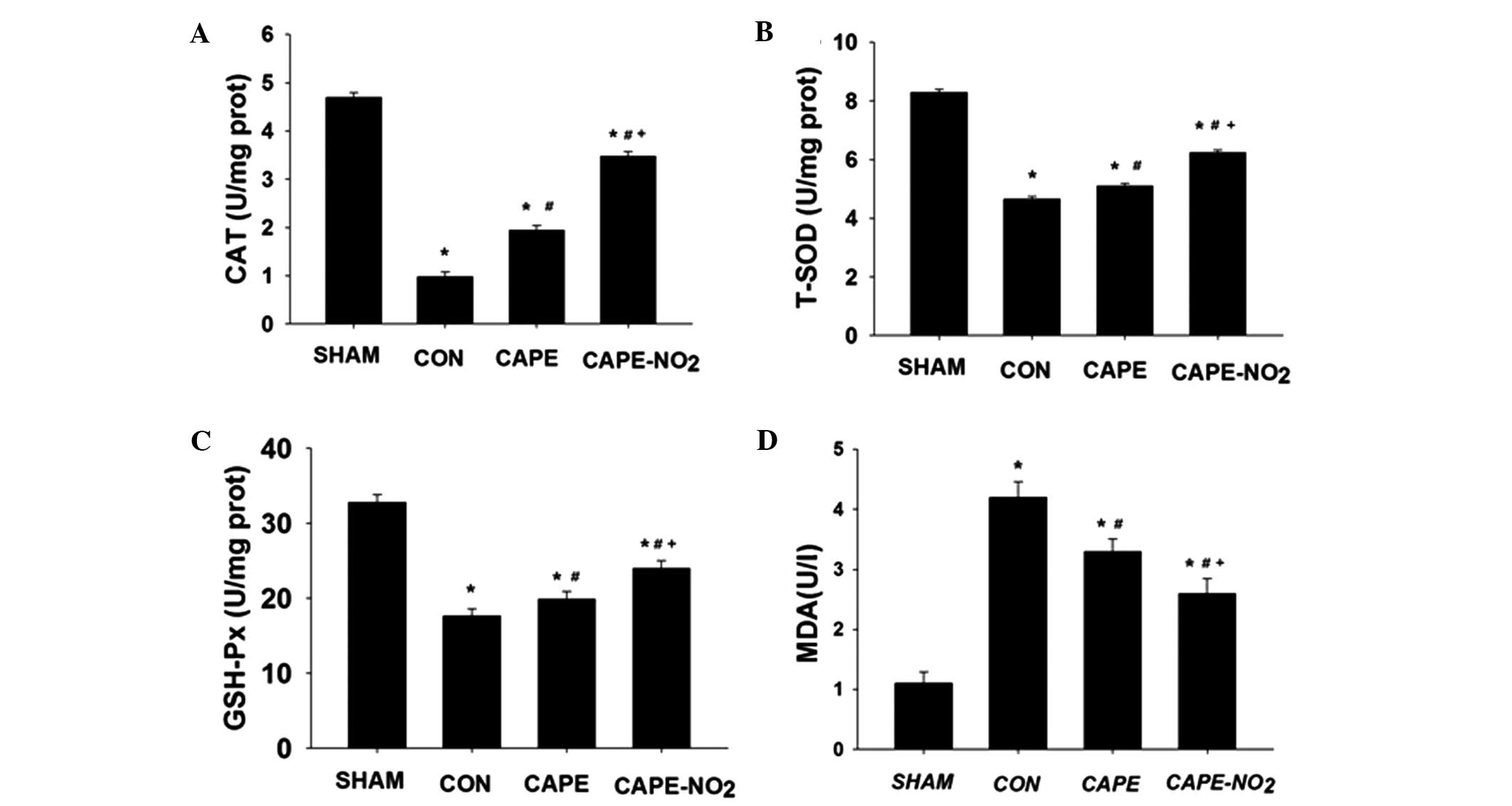
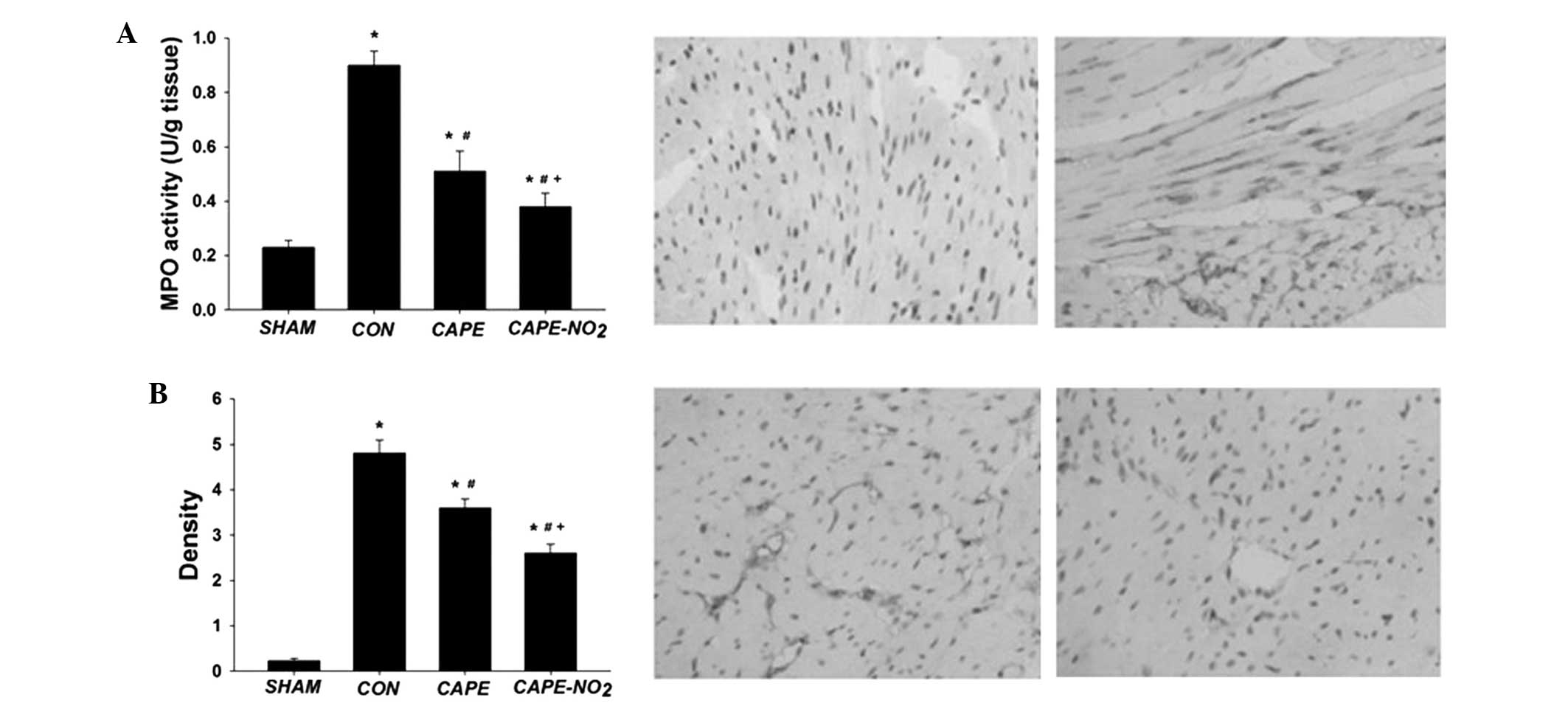
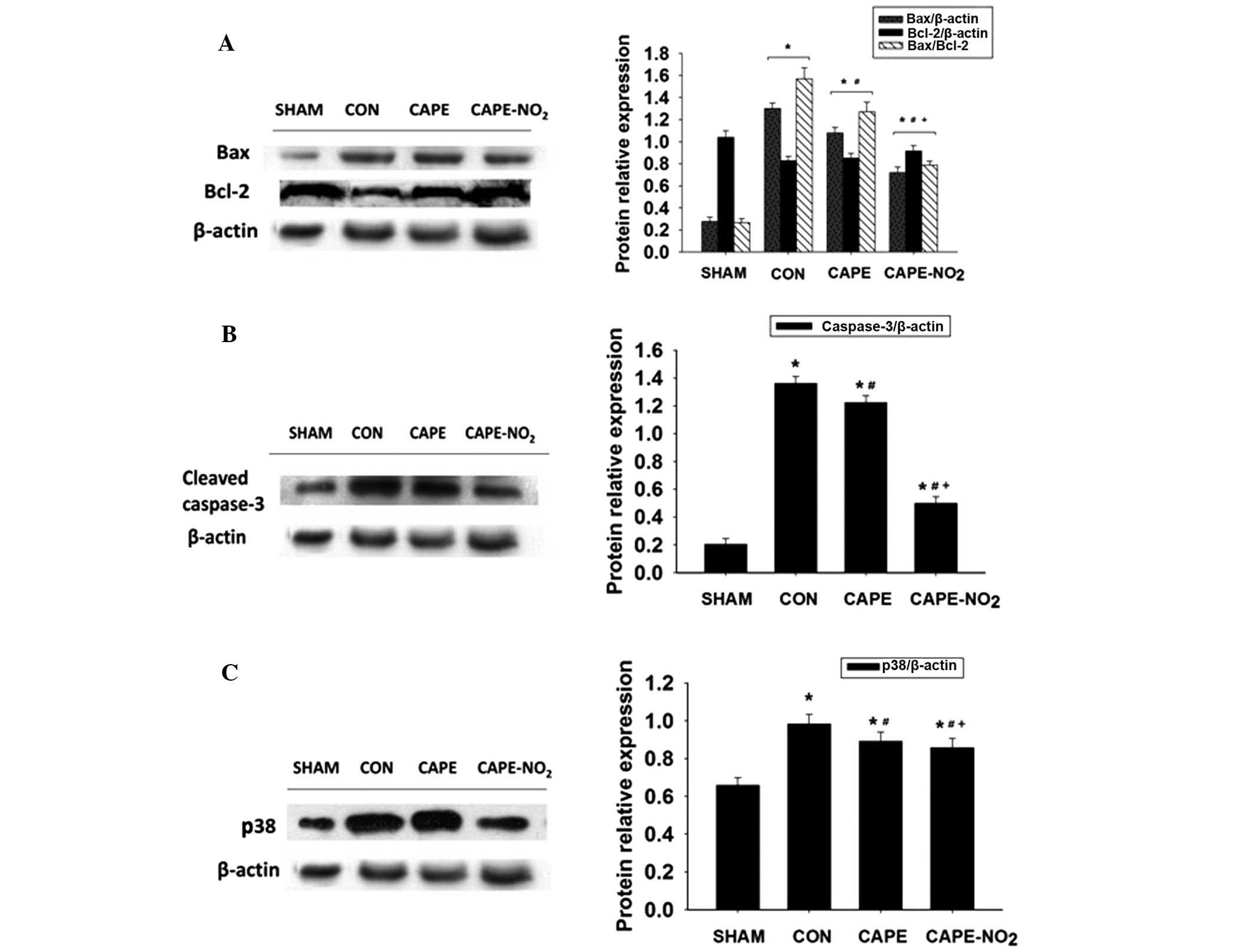
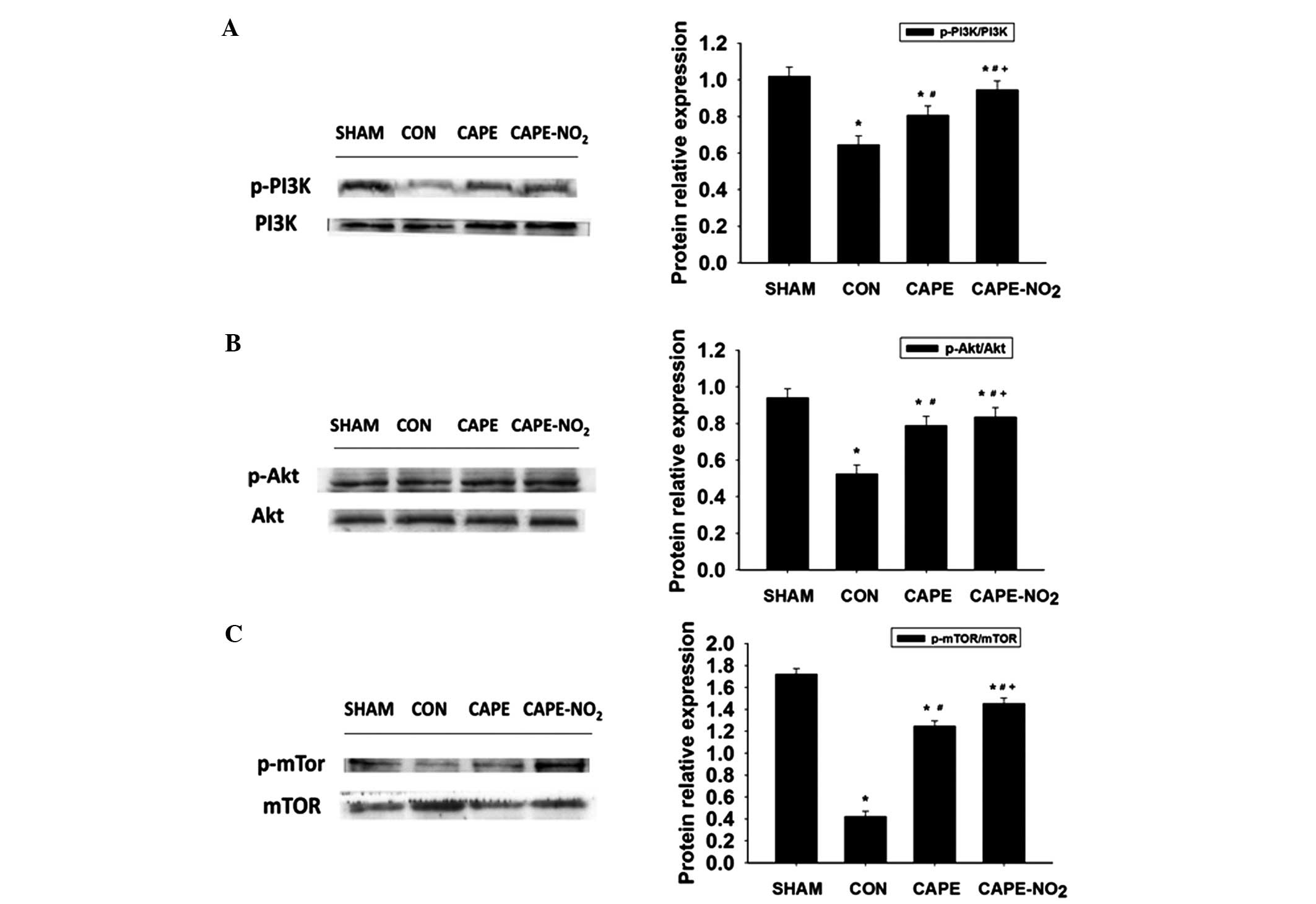
|
1
|
Parlakpinar H, Sahna E, Acet A, Mizrak B
and Polat A: Protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester
(CAPE) on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion-induced apoptotic cell
death. Toxicology. 209:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu H, Guo X, Chu Y and Lu S: Heart
protective effects and mechanism of quercetin preconditioning on
anti-myocardial ischemia reperfusion (IR) injuries in rats. Gene.
545:149–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei B, Li WW, Ji J, Hu QH and Ji H: The
cardioprotective effect of sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate and the
optimizing of therapeutic time window in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Atherosclerosis. 235:318–327.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yin Y, Guan Y, Duan J, Wei G, Zhu Y, Quan
W, Guo C, Zhou D, Wang Y, Xi M and Wen A: Cardioprotective effect
of Danshensu against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and
inhibits apoptosis of H9c2 cardiomyocytes via Akt and ERK1/2
phosphorylation. Eur J Pharmacol. 699:219–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quan W, Wu B, Bai Y, Zhang X, Yin J, Xi M,
Guan Y, Shao Q, Chen Y, Wu Q and Wen A: Magnesium lithospermate B
improves myocardial function and prevents simulated
ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes apoptosis
through Akt-dependent pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 151:714–721. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Forbes-Hernández TY, Giampieri F,
Gasparrini M, Mazzoni L, Quiles JL, Alvarez-Suarez JM and Battino
M: The effects of bioactive compounds from plant foods on
mitochondrial function: A focus on apoptotic mechanisms. Food Chem
Toxicol. 68:154–182. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou K, Li X, Du Q, Li D, Hu M, Yang X,
Jiang Q and Li Z: A CAPE analogue as novel antiplatelet agent
efficiently inhibits collagen-induced platelet aggregation.
Pharmazie. 69:615–620. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu TL, Li D, Du Q, Li C, Xiaohua L and Li
Z: Novel caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) analogues as
immunoregulatory agents: Synthesis and SAR study. Lat Am J Pharm.
32:329–334. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Parlakpinar H, Ozer MK and Acet A: Effects
of captopril and angiotensin II receptor blockers (AT1, AT2) on
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion induced infarct size. Cytokine.
56:688–694. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Galang N, Sasaki H and Maulik N: Apoptotic
cell death during ischemia/reperfusion and its attenuation by
antioxidant therapy. Toxicology. 148:111–118. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harrison D, Griendling KK, Landmesser U,
Hornig B and Drexler H: Role of oxidative stress in
atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 91:7A–11A. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang WL, Zhang SM, Tang XX and Liu HZ:
Protective roles of cornuside in acute myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury in rats. Phytomedicine. 18:266–271. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Campo GM, Avenoso A, Campo S, Nastasi G,
Traina P, D'Ascola A, Rugolo CA and Calatroni A: The antioxidant
activity of chondroitin-4-sulphate, in carbon tetrachloride-induced
acute hepatitis in mice, involves NF-kappaB and caspase activation.
Br J Pharmacol. 155:945–956. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koh PO: Ferulic acid prevents the cerebral
ischemic injury-induced decrease of Akt and Bad phosphorylation.
Neurosci Lett. 507:156–160. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu M, Feng J, Lucchinetti E, Fischer G,
Xu L, Pedrazzini T, Schaub MC and Zaugg M: Ischemic
postconditioning protects remodeled myocardium via the PI3K-PKB/Akt
reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res.
72:152–162. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhan JK, Wang YJ, Wang Y, Wang S, Tan P,
Huang W and Liu YS: The mammalian target of rapamycin signalling
pathway is involved in osteoblastic differentiation of vascular
smooth muscle cells. Can J Cardiol. 30:568–575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Chen Y, Wu Y, Ha T and Li C: The
cardioprotection induced by lipopolysaccharide involves
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and high mobility group box 1
pathways. J Biomed Res. 24:324–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen M, Li B, Zhao X, Zuo H, He X, Li Z,
Liu X and Chen L: Effect of diallyl trisulfide derivatives on the
induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Mol
Cell Biochem. 363:75–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morkuniene R, Arandarcikaite O and
Borutaite V: Estradiol prevents release of cytochrome c from
mitochondria and inhibits ischemia-induced apoptosis in perfused
heart. Exp Gerontol. 41:704–708. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|