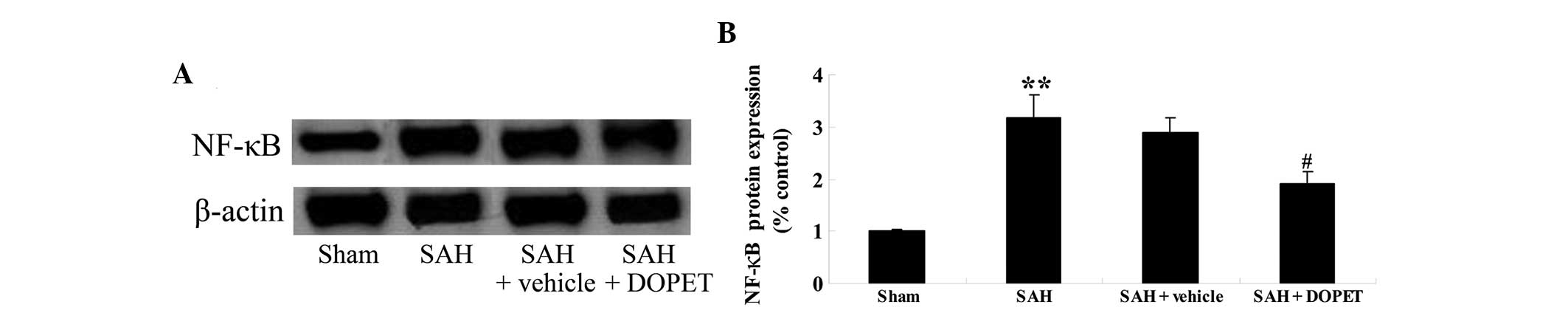
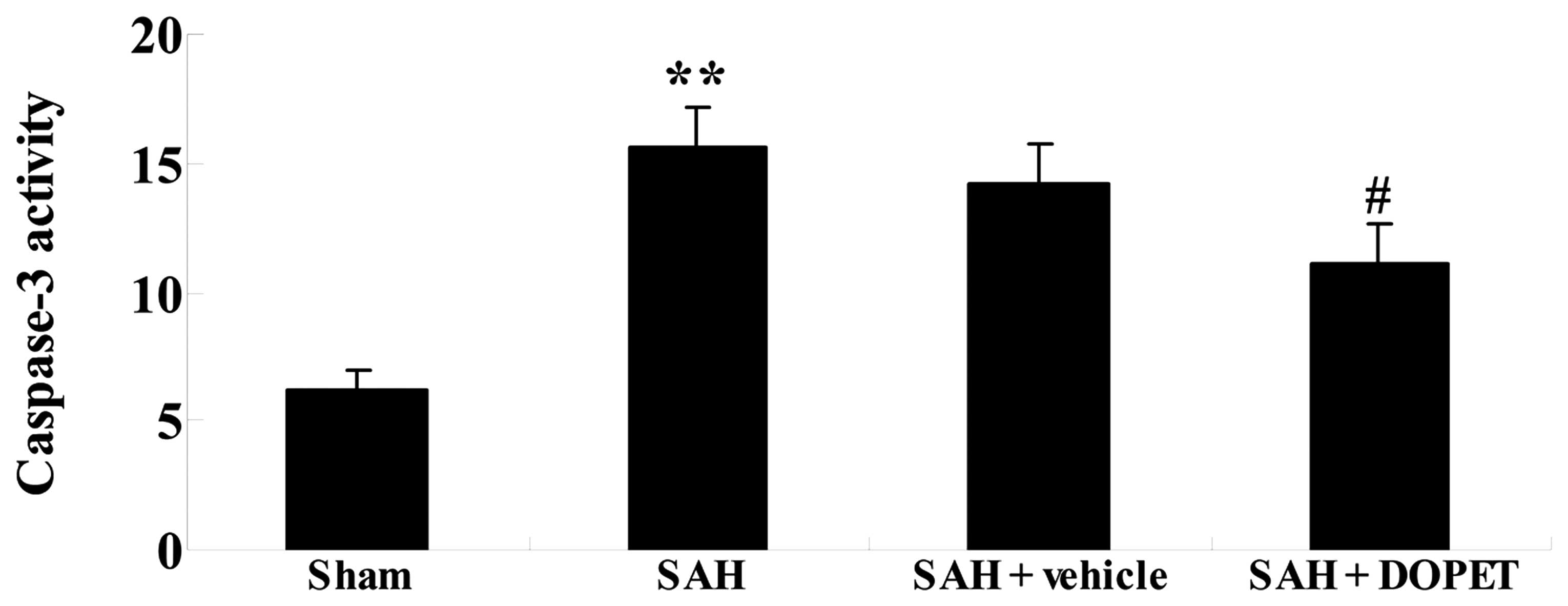
|
1
|
Bremond-Gignac D, Nezzar H, Bianchi PE,
Messaoud R, Lazreg S, Voinea L, Speeg-Schatz C, Hartani D, Kaercher
T, Kocyla-Karczmarewicz B, et al: AZI Study Group: Efficacy and
safety of azithromycin 1.5% eye drops in paediatric population with
purulent bacterial conjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 98:739–745.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bederson JB, Connolly ES Jr, Batjer HH,
Dacey RG, Dion JE, Diringer MN, Duldner JE Jr, Harbaugh RE, Patel
AB and Rosenwasser RH: American Heart Association: Guidelines for
the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A statement
for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the
Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 40:994–1025.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dorhout Mees SM, Algra A, Vandertop WP,
van Kooten F, Kuijsten HA, Boiten J, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Al-Shahi
Salman R, Lavados PM, Rinkel GJ and van den Bergh WM: MASH-2 Study
Group: Magnesium for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (MASH-2):
A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 380:44–49. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
He Y, Qu QC, Wang BX, DU FY and Guo ZH:
FOS protein expression and role of the vagus nerve in the rat
medullary visceral zone in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exp Ther Med. 5:223–228.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sehba FA, Hou J, Pluta RM and Zhang JH:
The importance of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Prog Neurobiol. 97:14–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dai Y, Zhang W, Zhou X and Shi J:
Activation of the protein kinase B (Akt) reduces Nur77-induced
apoptosis during early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage in rat. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 45:615–622. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu L, Xie K, Chen H, Dong X, Li Y and Yu
Y, Wang G and Yu Y: Inhalation of hydrogen gas attenuates brain
injury in mice with cecal ligation and puncture via inhibiting
neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis. Brain
Res. 1589:78–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang T, Su J, Wang K, Zhu T and Li X:
Ursolic acid reduces oxidative stress to alleviate early brain
injury following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosci
Lett. 579:12–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang XS, Zhang X, Zhou ML, Zhou XM, Li N,
Li W, Cong ZX, Sun Q, Zhuang Z, Wang CX and Shi JX: Amelioration of
oxidative stress and protection against early brain injury by
astaxanthin after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J
Neurosurg. 121:42–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Attoub S, De Wever O, Bruyneel E, Mareel M
and Gespach C: The transforming functions of PI3-kinase-gamma are
linked to disruption of intercellular adhesion and promotion of
cancer cell invasion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1138:204–213. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hasegawa Y, Suzuki H, Altay O and Zhang
JH: Preservation of tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) signaling
by sodium orthovanadate attenuates early brain injury after
subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke. 42:477–483. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hong Y, Shao A, Wang J, Chen S, Wu H,
McBride DW, Wu Q, Sun X and Zhang J: Neuroprotective effect of
hydrogen-rich saline against neurologic damage and apoptosis in
early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage: possible role
of the Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathway. PLoS One. 9:e962122014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dumont AS, Dumont RJ, Chow MM, Lin CL,
Calisaneller T, Ley KF, Kassell NF and Lee KS: Cerebral vasospasm
after subarachnoid hemorrhage: Putative role of inflammation.
Neurosurgery. 53:123–133. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dinh Tran YR, Jomaa A, Callebert J,
Reynier-Rebuffel AM, Tedgui A, Savarit A and Sercombe R:
Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in rabbit basilar artery
endothelial cells after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery.
48:626–633. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang CX, Xie GB, Zhou CH, Zhang XS, Li T,
Xu JG, Li N, Ding K, Hang CH, Shi JX and Zhou ML: Baincalein
alleviates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage in rats: Possible involvement of TLR4/NF-κB-mediated
inflammatory pathway. Brain Res. 1594:245–255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng D, Wang W, Dong Y, Wu L, Huang J, Ma
Y, Zhang Z, Wu S, Gao G and Qin H: Ceftriaxone alleviates early
brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by increasing excitatory
amino acid transporter 2 expression via the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB
signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 268:21–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo X, Shen L, Tong Y, Zhang J, Wu G, He
Q, Yu S, Ye X, Zou L, Zhang Z and Lian XY: Antitumor activity of
caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester and its pharmacokinetic
and metabolic properties. Phytomedicine. 20:904–912. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo C, Li Y, Wang H, Cui Y, Feng Z, Li H,
Li Y, Wang Y, Wurtz K, Weber P, et al: Hydroxytyrosol promotes
superoxide production and defects in autophagy leading to
anti-proliferation and apoptosis on human prostate cancer cells.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:625–639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Definition of Pain Distress and Reporting
Requirements for Laboratory Animals: Proceedings of the Workshop.
National Academy of Sciences (Washington DC). June 22–2000.
|
|
20
|
Ristagno G, Fumagalli F,
Porretta-Serapiglia C, Orrù A, Cassina C, Pesaresi M, Masson S,
Villanova L, Merendino A, Villanova A, et al: Hydroxytyrosol
attenuates peripheral neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetes
in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 60:5859–5865. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bederson JB, Germano IM and Guarino L:
Cortical blood flow and cerebral perfusion pressure in a new
noncraniotomy model of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke.
26:1086–1091. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Altay O, Suzuki H, Hasegawa Y, Caner B,
Krafft PR, Fujii M, Tang J and Zhang JH: Isoflurane attenuates
blood-brain barrier disruption in ipsilateral hemisphere after
subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Stroke. 43:2513–2516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhuang Z, Zhao X, Wu Y, Huang R, Zhu L,
Zhang Y and Shi J: The anti-apoptotic effect of PI3K-Akt signaling
pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Ann Clin Lab Sci.
41:364–372. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gu C, Wang Y, Li J, Chen J, Yan F, Wu C
and Chen G: Rosiglitazone attenuates early brain injury after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Brain Res.
1624:199–207. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee CI, Chou AK, Lin CC, Chou CH, Loh JK,
Lieu AS, Wang CJ, Huang CY, Howng SL and Hong YR: Immune and
inflammatory gene signature in rat cerebrum in subarachnoid
hemorrhage with microarray analysis. Mol Med Rep. 5:118–125.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schaffer S, Podstawa M, Visioli F, Bogani
P, Müller WE and Eckert GP: Hydroxytyrosol-rich olive mill
wastewater extract protects brain cells in vitro and ex vivo. J
Agric Food Chem. 55:5043–5049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cabrerizo S, De La Cruz JP,
López-Villodres JA, Muñoz-Marín J, Guerrero A, Reyes JJ, Labajos MT
and González-Correa JA: Role of the inhibition of oxidative stress
and inflammatory mediators in the neuroprotective effects of
hydroxytyrosol in rat brain slices subjected to hypoxia
reoxygenation. J Nutr Biochem. 24:2152–2157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ayer RE and Zhang JH: Oxidative stress in
subarachnoid haemorrhage: Significance in acute brain injury and
vasospasm. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 104:33–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sehba FA, Pluta RM and Zhang JH:
Metamorphosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage research: From delayed
vasospasm to early brain injury. Mol Neurobiol. 43:27–40. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng A, Li H, Cao K, Xu J, Zou X, Li Y,
Chen C, Liu J and Feng Z: Maternal hydroxytyrosol administration
improves neurogenesis and cognitive function in prenatally stressed
offspring. J Nutr Biochem. 26:190–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Granados-Principal S, El-Azem N, Pamplona
R, Ramirez-Tortosa C, Pulido-Moran M, Vera-Ramirez L, Quiles JL,
Sanchez-Rovira P, Naudí A, Portero-Otin M, et al: Hydroxytyrosol
ameliorates oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats with breast cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 90:25–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim GY, Park SY, Jo A, Kim M, Leem SH, Jun
WJ, Shim SI, Lee SC and Chung JW: Erratum to: Gecko proteins induce
the apoptosis of bladder cancer 5637 cells by inhibiting Akt and
activating the intrinsic caspase cascade. BMB Rep.
48:6422015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Incani A, Deiana M, Corona G, Vafeiadou K,
Vauzour D, Dessì MA and Spencer JP: Involvement of ERK, Akt and JNK
signalling in H2O2-induced cell injury and
protection by hydroxytyrosol and its metabolite homovanillic
alcohol. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:788–796. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Martín MA, Ramos S, Granado-Serrano AB,
Rodríguez-Ramiro I, Trujillo M, Bravo L and Goya L: Hydroxytyrosol
induces antioxidant/detoxificant enzymes and Nrf2 translocation via
extracellular regulated kinases and
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathways in HepG2
cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:956–966. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shih HC, Lin CL, Lee TY, Lee WS and Hsu C:
17beta-Estradiol inhibits subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced inducible
nitric oxide synthase gene expression by interfering with the
nuclear factor kappa B transactivation. Stroke. 37:3025–3031. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pang L, Zhang N, Dong N, Wang DW, Xu DH,
Zhang P and Meng XW: Erythropoietin protects rat brain injury from
carbon monoxide poisoning by inhibiting toll-like receptor
4/NF-kappa B-dependent inflammatory responses. Inflammation. Oct
31–2015.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma CX, Yin WN, Cai BW, Wu J, Wang JY, He
M, Sun H, Ding JL and You C: Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear
factor-kappa B signaling detected in brain after early subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Chin Med J (Engl). 122:1575–1581. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang X, Cao J, Jiang L and Zhong L:
Suppressive effects of hydroxytyrosol on oxidative stress and
nuclear Factor-kappaB activation in THP-1 cells. Biol Pharm Bull.
32:578–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Anter J, Tasset I, Demyda-Peyrás S,
Ranchal I, Moreno-Millán M, Romero-Jimenez M, Muntané J, de Castro
Luque MD, Muñoz-Serrano A and Alonso-Moraga Á: Evaluation of
potential antigenotoxic, cytotoxic and proapoptotic effects of the
olive oil by-product “alperujo,” hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol and
verbascoside. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 772:25–33.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|