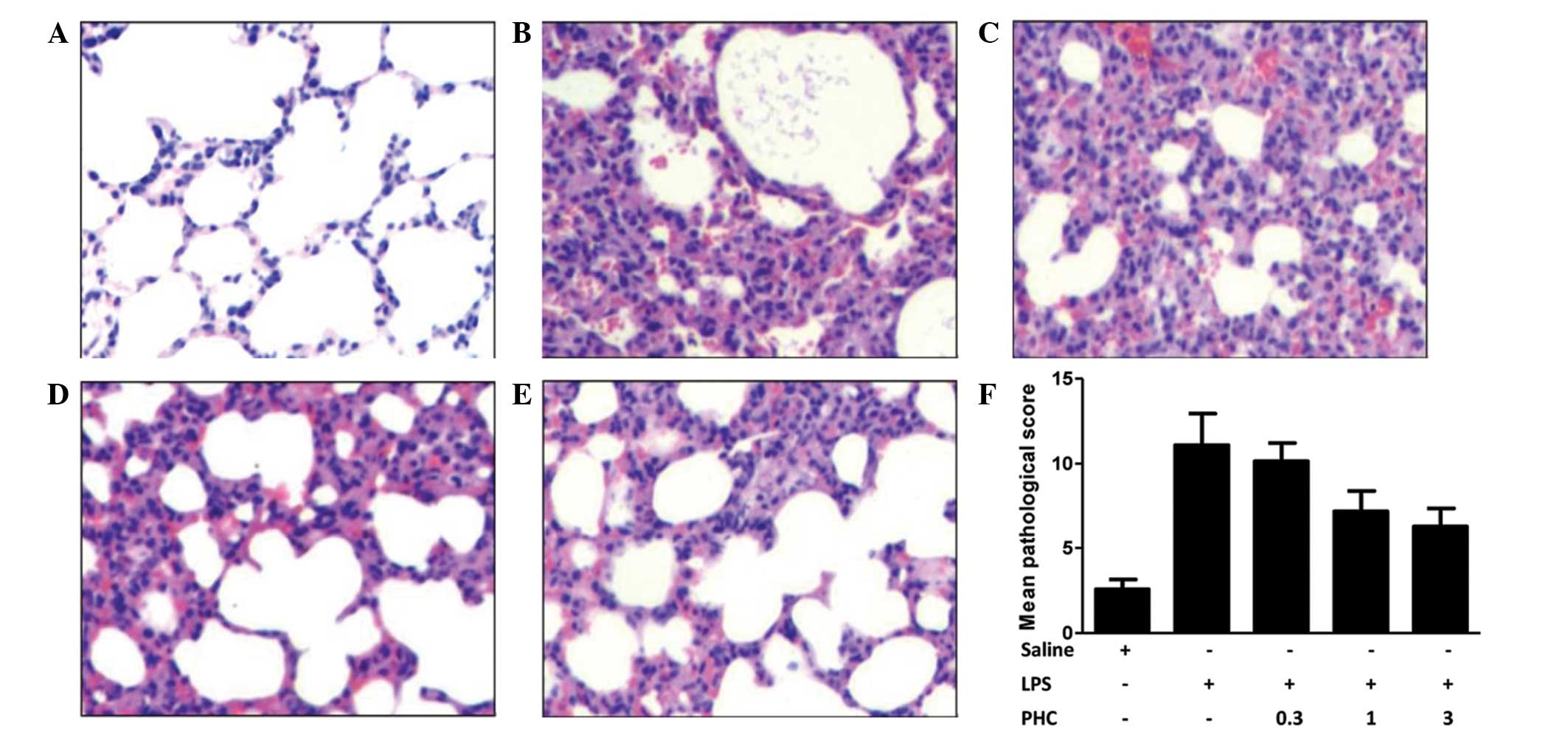
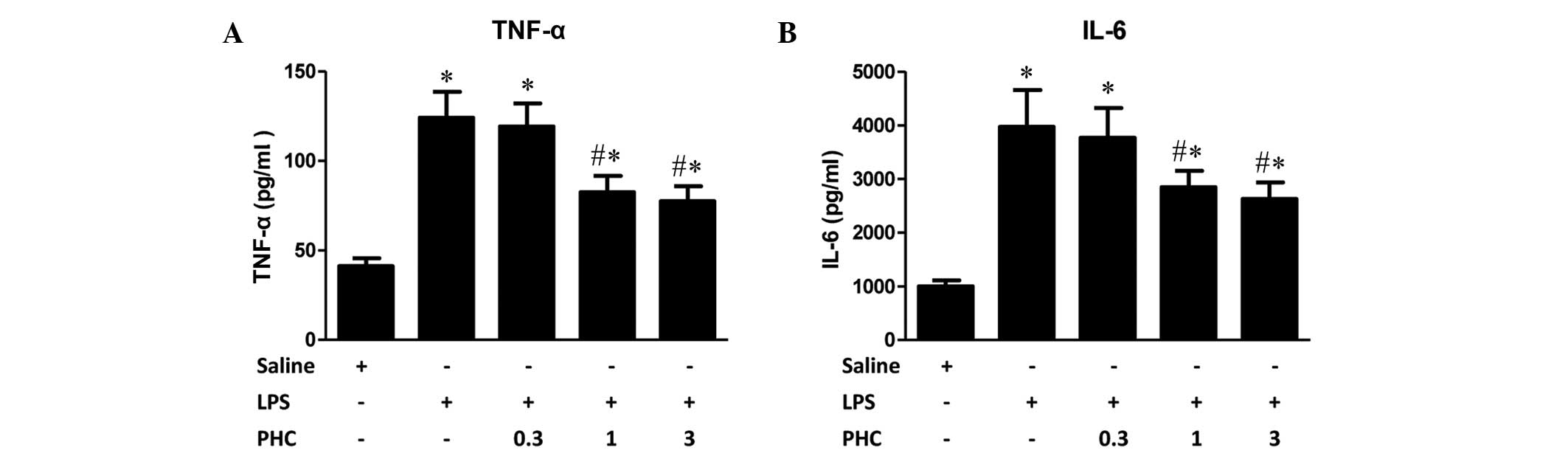
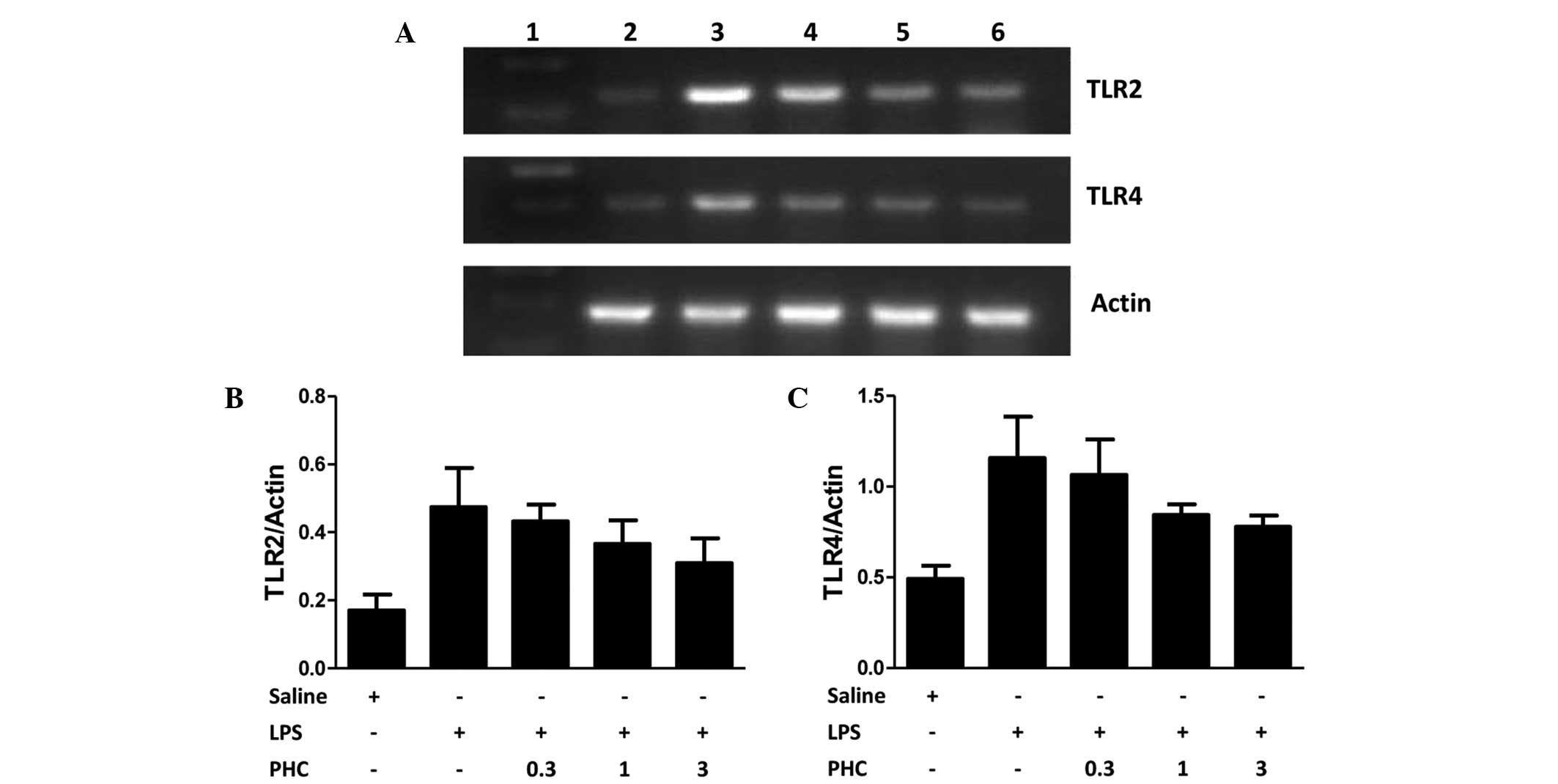
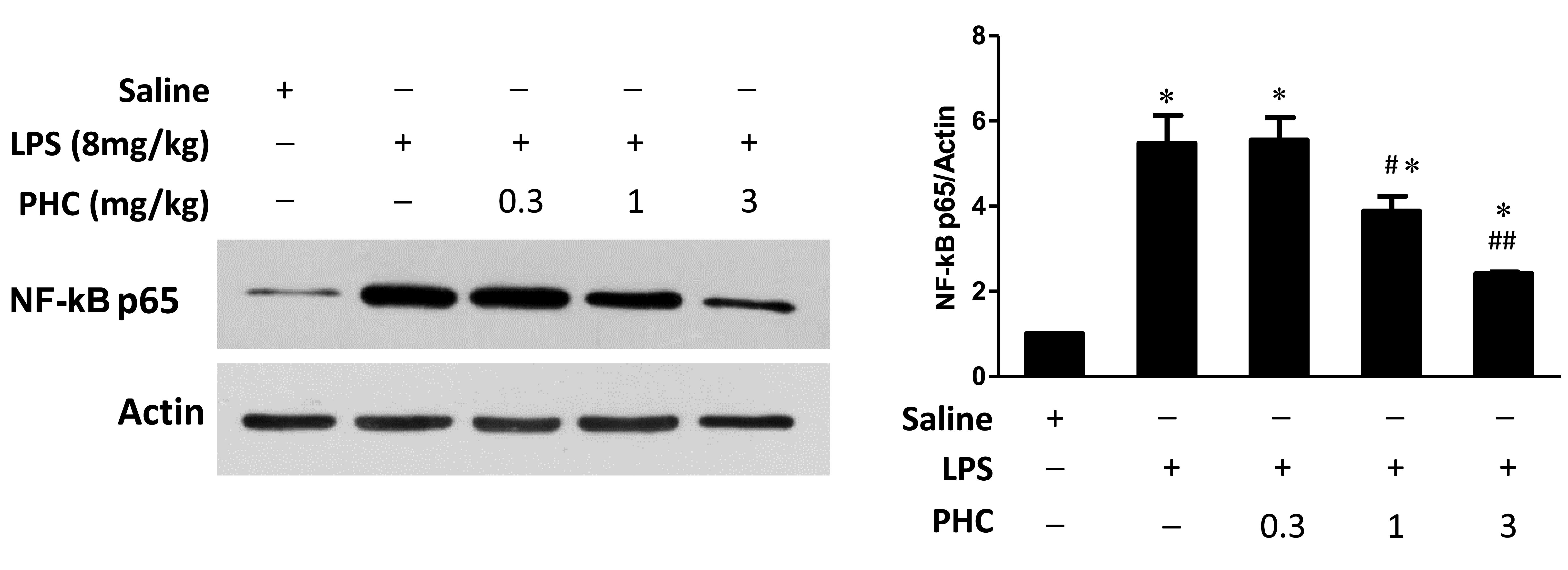
|
1
|
Luh SP and Chiang CH: Acute lung
injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS): The
mechanism, present strategies and future perspectives of therapies.
J Zhejiang Uni Sci B. 8:60–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chen H, Zhang L, Jin Z, Jin E, Fujiwara M,
Ghazizadeh M, Asoh S, Ohta S and Kawanami O: Anti-apoptotic PTD-FNK
protein suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in
rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 83:377–384. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu YY, Li LF, Yang CT, Lu KH, Huang CC,
Kao KC and Chiou SH: Suppressing NF-κB and NKRF pathways by induced
pluripotent stem cell therapy in mice with ventilator-induced lung
injury. PLoS One. 8:e667602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lucas R, Verin AD, Black SM and Catravas
JD: Regulators of endothelial and epithelial barrier integrity and
function in acute lung injury. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1763–1772.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Andonegui G, Bonder CS, Green F, Mullaly
SC, Zbytnuik L, Raharjo E and Kubes P: Endothelium-derived
Toll-like receptor-4 is the key molecule in LPS-induced neutrophil
sequestration into lungs. J Clin Invest. 111:1011–1020. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Andonegui G, Goyert SM and Kubes P:
Lipopolysaccharide-induced leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions:
A role for CD14 versus toll-like receptor 4 within microvessels. J
Immunol. 169:2111–2119. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ayala A, Chung CS, Lomas JL, Song GY,
Doughty LA, Gregory SH, Cioffi WG, LeBlanc BW, Reichner J, Simms HH
and Grutkoski PS: Shock-induced neutrophil mediated priming for
acute lung injury in mice: Divergent effects of TLR-4 and
TLR-4/FasL deficiency. Am J Pathol. 161:2283–2294. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Basu S and Fenton MJ: Toll-like receptors:
Function and roles in lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 286:L887–L892. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takeda K, Kaisho T and Akira S: Toll-like
receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 21:335–376. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hirschfeld M, Weis JJ, Toshchakov V,
Salkowski CA, Cody MJ, Ward DC, Qureshi N, Michalek SM and Vogel
SN: Signaling by toll-like receptor 2 and 4 agonists results in
differential gene expression in murine macrophages. Infect Immun.
69:1477–1482. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takaoka Y, Goto S, Nakano T, Tseng HP,
Yang SM, Kawamoto S, Ono K and Chen CL: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase (GAPDH) prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced,
sepsis-related severe acute lung injury in mice. Sci Rep.
4:52042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Perros F, Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: TLR4
signalling in pulmonary stromal cells is critical for inflammation
and immunity in the airways. Respir Res. 12:1252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiu RJ, Hammerschmidt DE, Coppo PA and
Jacob HS: Anisodamine inhibits thromboxane synthesis, granulocyte
aggregation and platelet aggregation. A possible mechanism for its
efficacy in bacteremic shock. JAMA. 247:1458–1460. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Chen Q, Liu S, Huang Y, Liu L, Wu
X, Chen G, Jin J, Teng G and Qiu H: Effects of recruitment
maneuvers with PEEP on lung volume distribution in canine models of
direct and indirect lung injury. Mol Biol Rep. 41:1325–1333. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Disse B: Antimuscarinic treatment for lung
diseases from research to clinical practice. Life Sci.
68:2557–2564. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang Z, Wang C, Tao J, Xiong J, Wan C and
Zhou F: Effect of early hemofiltration on pro- and
anti-inflammatory responses and multiple organ failure in severe
acute pancreatitis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci.
24:456–459. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng S, Ge Y, Yang J, Duan M and Xu J:
Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on lung inflammatory
response in septic rats. Zhong Hua Ma Zui Xue Za Zhi Bian Ji Bu.
28:63–67. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Huang C, He J, Chen Y, Zhang Y and Chen C:
Penehyclidine hydrochloride inhibits the LPS-induced inflammatory
response in microglia. J Surg Res. 188:260–267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lei L, Wang Y, Jia B, Zhan J and Wang C:
Protective effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on lung injury in
mice with sepsis and its mechanism. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu
Yi Xue. 19:623–625. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li BQ, Sun HC, Nie SN, Shao DB, Liu HM and
Qian XM: Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on patients with
acute lung injury and its mechanisms. Chin J Traumatol. 13:329–335.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Smith KM, Mrozek JD, Simonton SC, Bing DR,
Meyers PA, Connett JE and Mammel MC: Prolonged partial liquid
ventilation using conventional high-frequency ventilatory
techniques: Gas exchange and lung pathology in animal model of
respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 25:1888–1897. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rojas M, Woods CR, Mora AL, Xu J and
Brigham KL: Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice:structural,
functional, and biochemical responses. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 288:L333–L341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Petersen AM and Pedersen BK: The
anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J Appl Physiol. 98:1154–1162.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oeckinghaus A and Ghosh S: The NF-κB
family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 1:a0000342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aikawa N, Ishizaka A, Hirasawa H,
Shimazaki S, Yamamoto Y, Sugimoto H, Shinozaki M, Taenaka N, Endo
S, Ikeda T and Kawasaki Y: Reevaluation of the efficacy and safety
of the neutrophil elastase inhibitor, Sivelestat, for the treatment
of acute lung injury associated with systemic inflammatory response
syndroma phase IV study. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 24:549–554. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Haddad JJ: Nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B
blockade attenuates but does not abrogate LPS-mediated interleukin
(IL)-1 beta biosynthesis in alveolar epithelial cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 293:252–257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ben-Addi A, Mambole-Dema A, Brender C,
Martin SR, Janzen J, Kjaer S, Smerdon SJ and Ley SC: IκB
kinase-induced interaction of TPL-2 kinase with 14-3-3 is essential
for Toll-like receptor activation of ERK-1 and −2 MAP kinases. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E2394–E2403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chow JC, Young DW, Golenbock DT, Christ WJ
and Gusovsky F: Toll-like receptor-4 mediates
lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J Biol Chem.
274:10689–10692. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Erridge C, Kennedy S, Spickett CM and Webb
DJ: Oxidized phospholipid inhibition of toll-like receptor (TLR)
signaling is restricted to TLR2 and TLR4: Roles for CD14,
LPS-binding protein and MD2 as targets for specificity of
inhibition. J Biol Chem. 283:24748–24759. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shimazu RA, Kashi S, Ogata H, Nagai Y,
Fukudome K, Miyake K and Kimoto M: MD-2, a molecule that confer
1ipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4. J Exp
Med. 189:1777–1782. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Akira S: Toll-like receptor signaling. J
Biol Chem. 278:38105–38108. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brikos C, Wait R, Begum S, O'Neill LA and
Saklatvala J: Mass spectrometric analysis of the endogenous type I
interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor signaling complex formed after IL-1
binding identifies IL-1RAcP, MyD88 and IRAK-4 as the stable
components. Mol Cell Proteomics. 6:1551–1559. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kopp EB and Medzhitov R: The Toll-receptor
family and control innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 11:13–18.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Y, Wang Y, Yamakuchi M, Isowaki S,
Nagata E, Kanmura Y, Kitajima I and Maruyama I: Upregulation of
toll-like receptor 2 gene expression in macrophage response to
peptidoglycan and high concentration of lipopolysaccharide is
involved in NF-κB activation. Infect Immun. 69:2788–2796. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Musikacharoen T, Matsuguchi T, Kikuchi T
and Yoshikai Y: NF-kappa B and STAT5 play important roles in the
regulation of mouse Toll-like receptor 2 gene expression. J
Immunol. 166:4516–4524. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chow JC, Young DW, Golenbock DT, Christ WJ
and Gusovsky F: Toll-like receptor-4 mediates
lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J Biol Chem.
274:10689–10692. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gilmore TD: Introduction to NF-kappaB:
Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene. 25:6680–6684. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|