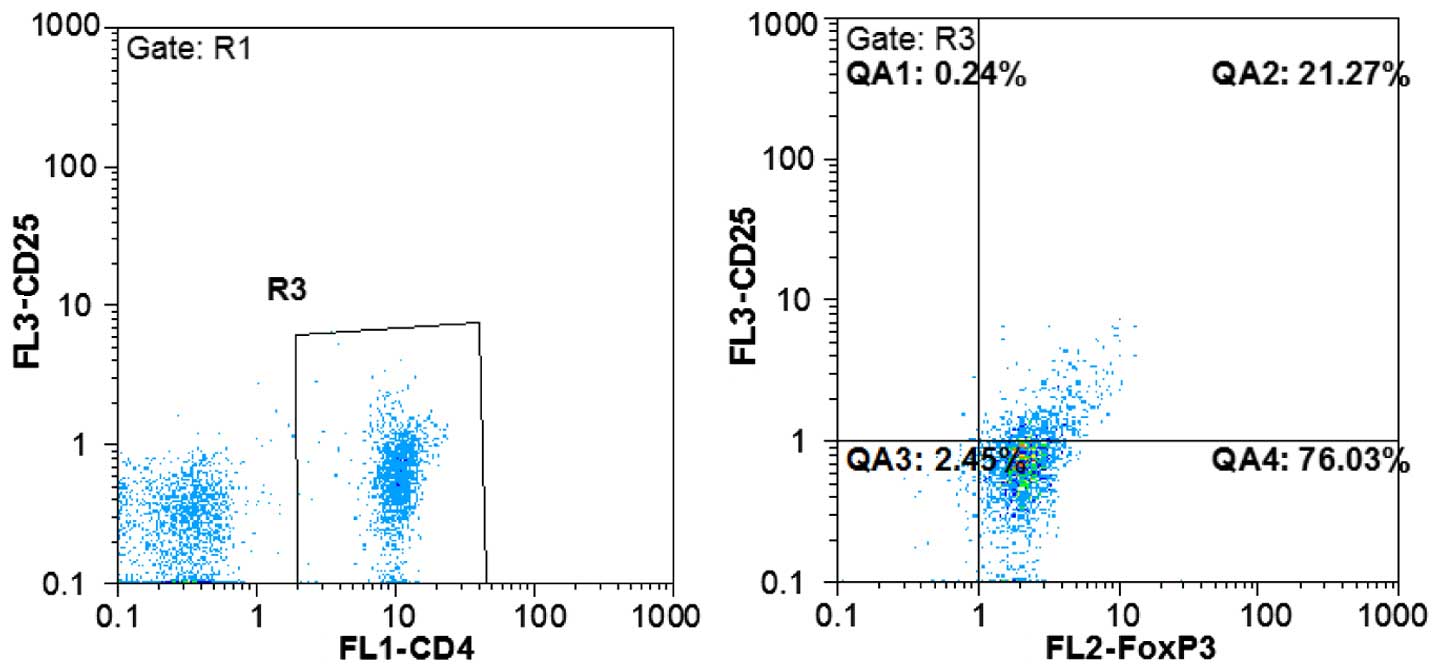
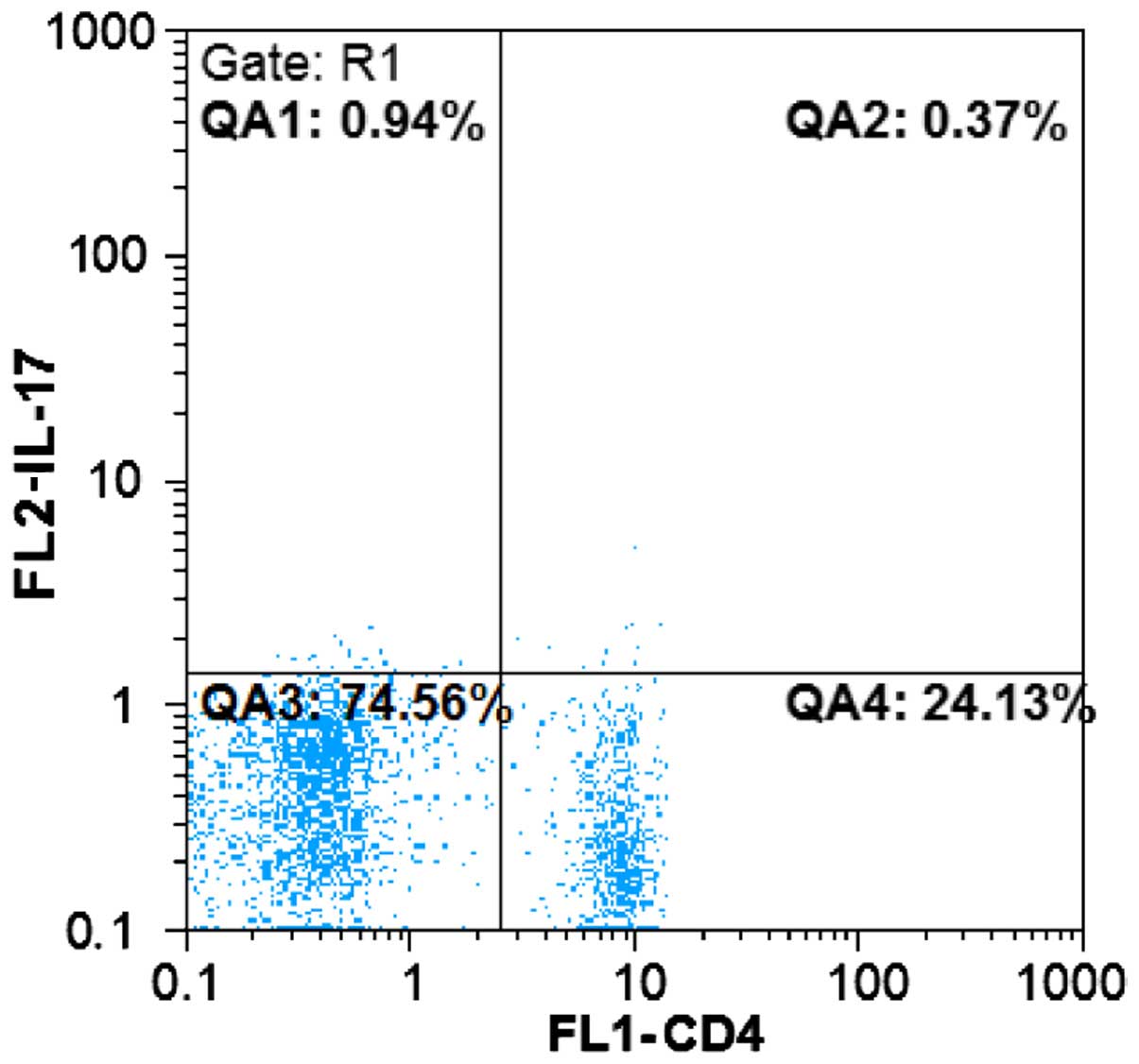
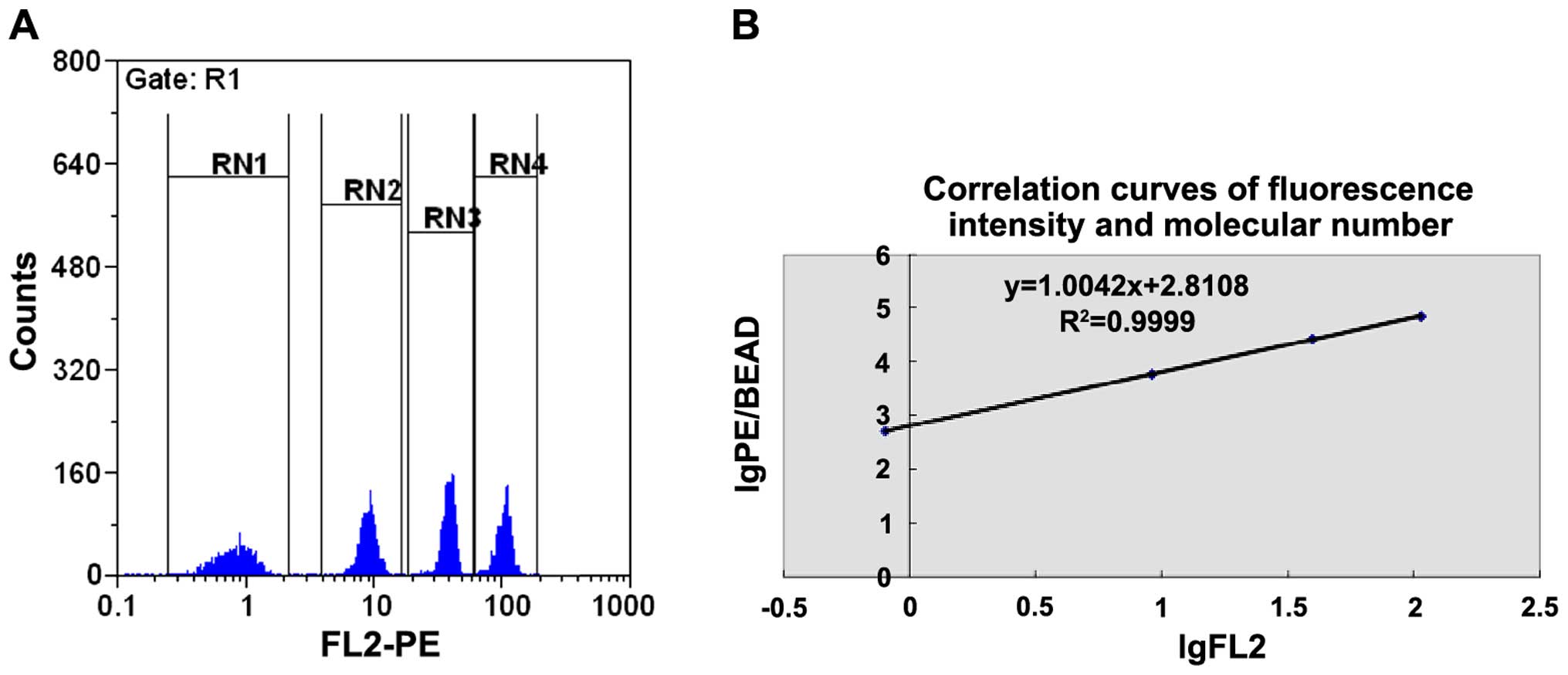
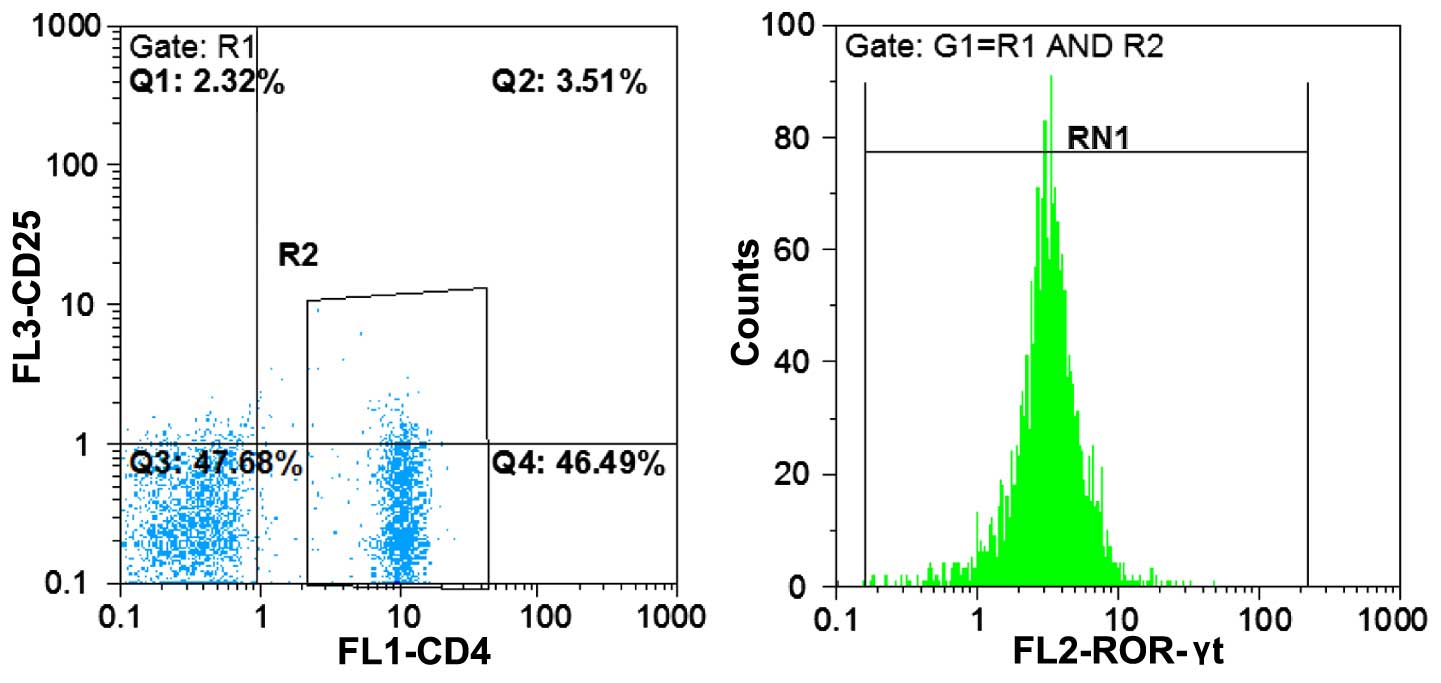
|
1
|
Dejung S, Rampini SS and Battegay E:
[Syphilis: Diagnosis andtreatment monitoring]. Praxis (Bern 1994).
100:1445–1448; quiz 1449–1450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leader BT, Godornes C, VanVoorhis WC and
Lukehart SA: CD4+ lymphocytes and gamma interferon
predominate in local immune responses in early experimental
syphilis. Infect Immun. 75:3021–3026. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li K, Wang C, Lu H, Gu X, Guan Z and Zhou
P: Regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid
of syphilis patients with and without neurological involvement.
PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 7:e25282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu A, Han H, Zhao H, Hu J, Jiang C, Xie F
and Wang F: Increased frequencies of Th17 and Th22 cells in the
peripheral blood of patients with secondary syphilis. FEMS Immunol
Med Microbiol. 66:299–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eisenstein EM and Williams CB: The
T(reg)/Th17 cell balance: A new paradigm for autoimmunity. Pediatr
Res. 65:26R–31R. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou L, Lopes JE, Chong MM, Ivanov II, Min
R, Victora GD, Shen Y, Du J, Rubtsov YP, Rudensky AY, et al:
TGF-beta-induced Foxp3 inhibits T(H)17 cell differentiation by
antagonizing RORgammat function. Nature. 453:236–240. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T,
Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL and Kuchroo VK: Reciprocal
developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector
TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 441:235–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Serada S, Fujimoto M, Mihara M, Koike N,
Ohsugi Y, Nomura S, Yoshida H, Nishikawa T, Terabe F, Ohkawara T,
et al: IL-6 blockade inhibits the induction of myelin
antigen-specific Th17 cells and Th1 cells in experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:9041–9046. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cho ML, Kang JW, Moon YM, Nam HJ, Jhun JY,
Heo SB, Jin HT, Min SY, Ju JH, Park KS, et al: STAT3 and NF-kappaB
signal pathway is required for IL-23-mediated IL-17 production in
spontaneous arthritis animal model IL-1 receptor
antagonist-deficient mice. J Immunol. 176:5652–5661. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laurence A, Tato CM, Davidson TS, Kanno Y,
Chen Z, Yao Z, Blank RB, Meylan F, Siegel R, Hennighausen L, et al:
Interleukin-2 signaling via STAT5 constrains T helper 17 cell
generation. Immunity. 26:371–381. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elias KM, Laurence A, Davidson TS,
Stephens G, Kanno Y, Shevach EM and O'Shea JJ: Retinoic acid
inhibits Th17 polarization and enhances FoxP3 expression through a
Stat-3/Stat-5 independent signaling pathway. Blood. 111:1013–1020.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shinohara ML, Kim JH, Garcia VA and Cantor
H: Engagement of the type I interferon receptor on dendritic cells
inhibits T helper 17 cell development: Role of intracellular
osteopontin. Immunity. 29:68–78. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Quintana FJ, Basso AS, Iglesias AH, Korn
T, Farez MF, Bettelli E, Caccamo M, Oukka M and Weiner HL: Control
of T(reg) and T(H)17 cell differentiation by the aryl hydrocarbon
receptor. Nature. 453:65–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Wang LN, Zuo YG, Liu YX, Liu XR, Lei
Y and Zheng HY: [Clinical analysis and study of immunological
function in syphilis patients with seroresistance]. Zhonghua Yi Xue
Za Zhi. 89:813–816. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Podwinska J, Lusiak M, Zaba R and Bowszyc
J: The pattern and level of cytokines secreted by Th1 and Th2
lymphocytes of syphilitic patients correlate to the progression of
the disease. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 28:1–14. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|