Introduction
The discovery of penicillin was crucial to the cure
of syphilis. However, the increase of syphilitic sero-resistance in
recent years has led to the cure of syphilis facing new challenges.
Early-stage syphilis patients undergoing regular treatment and
whose serum rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test titer is not negatively
conversed within 2 years indicate a condition of sero-resistance
(with elimination of neurosyphilis) (1). Once sero-resistance occurs, an increase
in the dose of penicillin and prolonging the course of treatment
cannot usually make serum converse negatively. Due to the 35%
recurrence rate of patients with sero-resistance (1), together with the influence of social
factors, this phenomenon has become an important clinical and
social issue.
Although various theories concerning the formative
cause of sero-resistance have been posited, the exact pathogenesis
remains unknown. In previously conducted clinical studies on
immunologic changes to patients with primary syphilis, secondary
syphilis, latent syphilis, as well as patients with sero-resistance
syphilis (2–4), it was identified that in various
immunological indicators, CD4+CD25+
regulatory T (Treg) cells showed more specific changes in patients
with sero-resistance and whose proportion of
CD4+CD25+ Treg cells was obviously higher
than those in other syphilitic groups (3). It has been suggested that Treg cells
may play an important role in the process of sero-resistance
formation.
The newly identified Treg cells and T helper 17
(Th17) cells have triggered endless relative research. A balance of
the two cell types has especially drawn the attention of scholars
in recent years. Previous findings showed that the abnormality of
Treg/Th17 cellular balance is associated with numerous diseases
(5). Thus, whether there is any
abnormality of Treg/Th17 cellular balance in syphilitic patients
with sero-resistance and whether the change of Treg cells
identified earlier the result of this change in balance, remains to
be considered. The aim of the study was to examine the proportion
and correlation of Treg and Th17 cells in syphilic patients with
sero-resistance.
Materials and methods
Study participants
A total of 49 subjects were enrolled in the study
and divided into two groups. The experimental group consisted of 26
sero-resistant syphilitic patients, 16 males and 10 females, aged
between 25 and 59 years (mean age, 31.8±8.2 years). The normal
control group comprised 23 non-syphilitic healthy donors, 14 males
and 9 females, aged between 21 and 40 (mean age, 27.6±5.7 years).
The 26 subjects with syphilis were outpatients of The First
People's Hospital of Xuzhou. Criteria used for patients with
sero-resistance were: Patients diagnosed with syphilis, following
regular treatment, whose RPR test did not turn negative after
continuous follow up of 2 years (reinfection, neurosyphilis and HIV
infection were eliminated). The distribution of RPR titers in
patients were as follows: 8 cases of 1:1, 7 cases of 1:2, 6 cases
of 1:4, 4 cases of 1:8, 1 case of 1:16. The stage of syphilis
following the initial treatment was: 1 case of primary syphilis, 4
cases of secondary syphilis, and 21 cases of latent syphilis.
The experimental protocol of the present study was
approved by the Hospital's Ethics Committee. Participants in the
two groups provided written informed consent.
Equipment
Flow cytometry (PAS model; Sysmex Partec GmbH,
Gorlitz, Germany) was applied to determine the proportion of Treg
and Th17 cells.
Antibodies and reagents
Fluorescently-labeled mouse anti-human monoclonal
antibody: Anti-CD4-FITC (host/isotype: mouse IgG1, cat. no.
11-0049, clone: RPA-T4, concentration: 5 µl/test);
anti-CD25-PerCP-Cy5.5 (host/isotype: mouse IgG1, cat. no.: 12-0259,
clone: BC96, concentration: 5 µl/test); anti- Foxp3-PE
(host/isotype: rat IgG2a, catalog no.: 12-4776, clone: PCH101,
concentration: 5 µl/test); anti-ROR-t-PE (host/isotype: rat IgG2a,
cat. no.: 12-6988, clone: AFKJS-9, concentration: 0.2 mg/ml);
anti-IL-17-PE (host/isotype: mouse IgG1, cat. no.: 12-7178, clone:
eBio64CAP17, concentration: 5 µl/test) and homotypic control
antibody with a corresponding fluorescent label were purchased from
eBioscience company (San Diego, CA, USA). A QuantiBRITE PE flow
quantification kit was purchased from BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA,
USA). Foxp3 fixation/permeabilization concentrate and diluent was
purchased from eBioscience Company. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
(PMA), Ionomycin and Brefeldin A (BFA), were purchased from Enzo
Life Sciences, Inc. (Farmingdale, NY, USA). RPMI-1640 was purchased
from Sigma Company (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Specimen preparation
Density gradient centrifugation was used to isolate
peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from a 5 ml sample of
peripheral blood (with heparin added as an anticoagulant),
RPMI-1640 was then used at a concentration of 6×106/ml
to perform resuspension as a standby.
Due to the relatively low concentration of the
interleukin (IL)-17 molecule in cells, PBMCs were cultured in
vitro prior to detection of the targeted molecules. The cell
suspension (500 µl) with a corresponding amount of PMA, ionomycin
and BFA were added at the working concentrations of 25 ng/ml, 1
µg/ml, and 10 µg/ml, respectively. The cells were then incubated
for 4 h at 37°C, 5% CO2, as a standby.
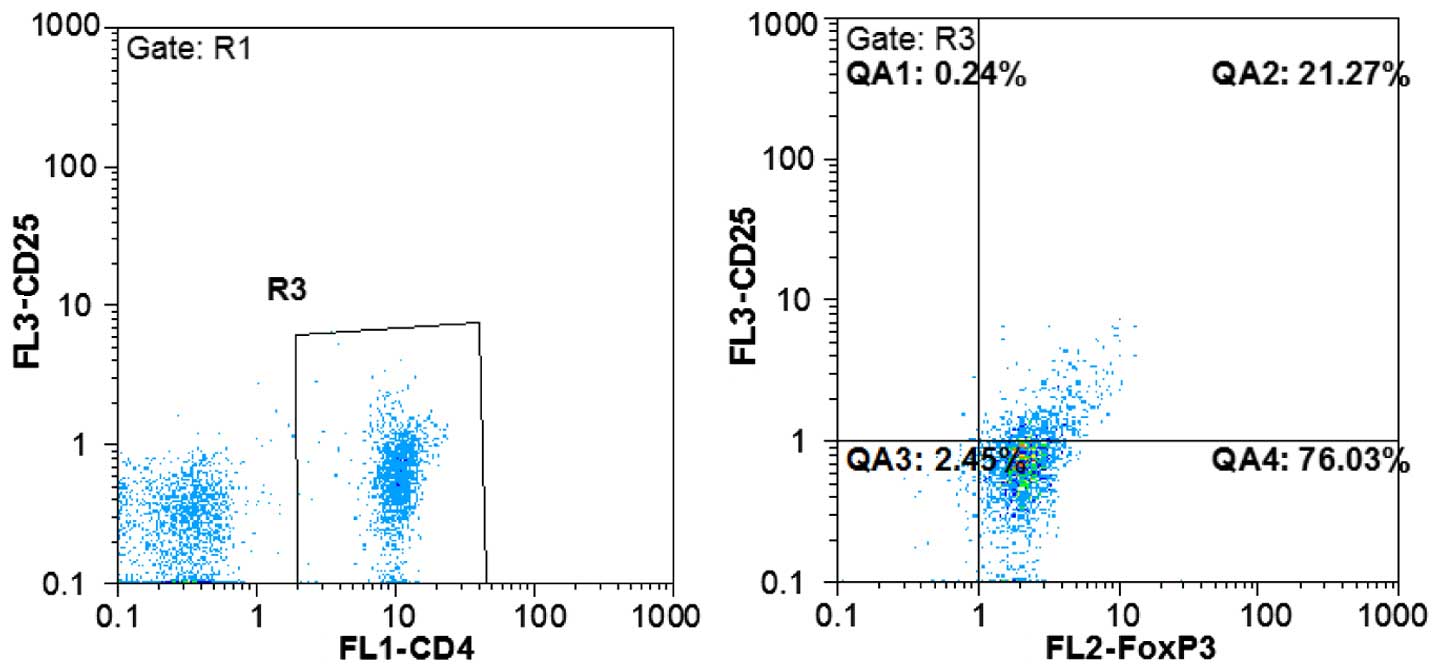
Detection of the proportion of Treg
cells
Fluorescently-labeled antibodies were used to detect
Foxp3 molecules in CD4 and CD25 antigens located at the surface of
Treg cells. To this end, uncultured PBMC suspension was added into
four test tubes, and in three of these, a corresponding homotypic
control antibody was added as a negative control. Anti-CD4-FITC and
anti-CD25-PerCP-Cy5.5 antibodies were added into the test tubes and
incubated for 20 min, at 4°C, in the dark. The fix/perm reagent was
added according to product protocol instruction, followed by 30 min
of incubation at 4°C. Following permeabilization, anti-Foxp3-PE
antibody was added, and the cell suspension was incubated for 20
min at 4°C, in the dark. After washing the sample, the
phosphate-buffered saline suspension was subjected to flow
cytometric analysis to determine the proportion of
CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cells in
CD4+ cells (Fig. 1).
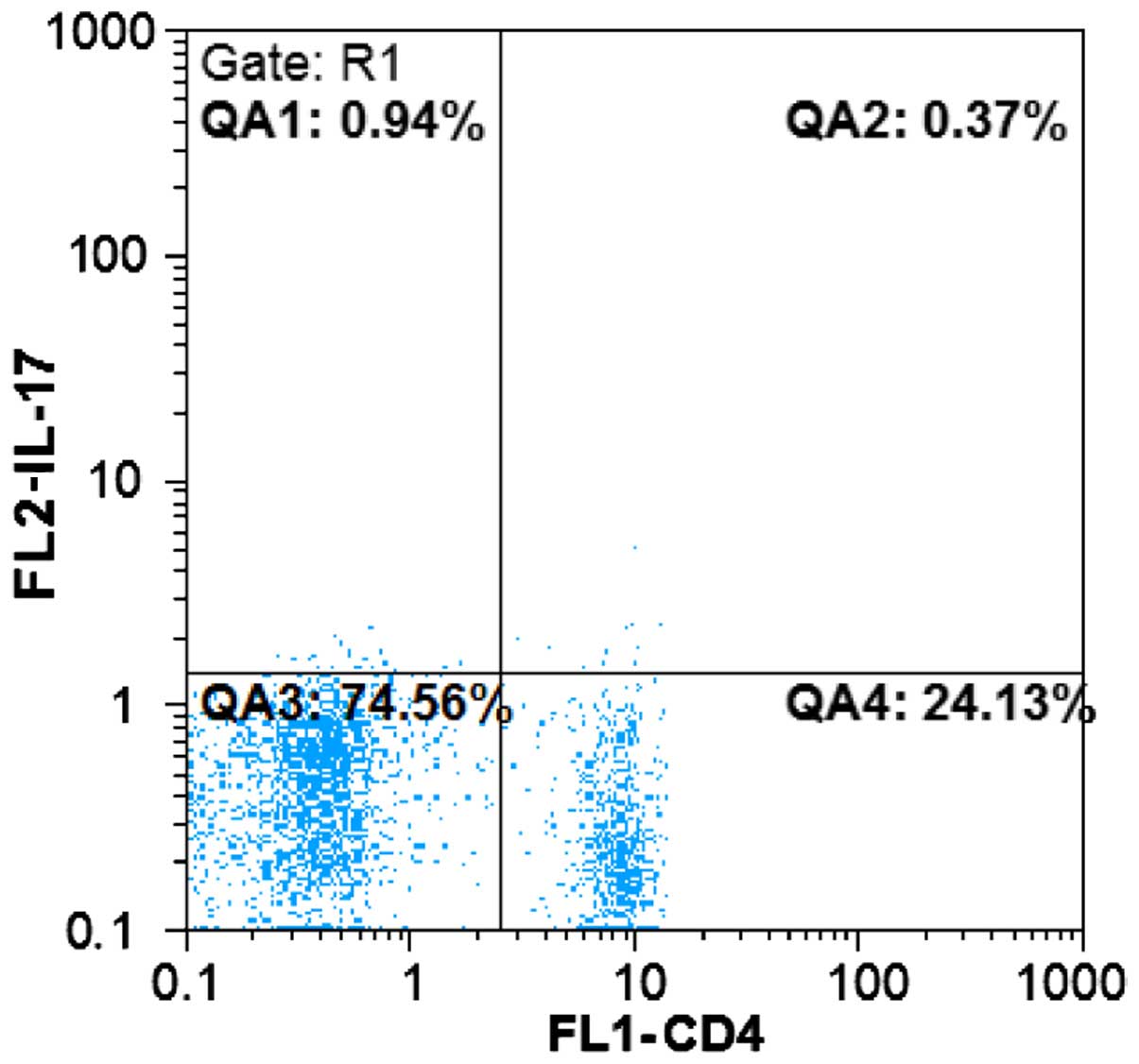
Detection for the proportion of Th17
cells
Cultured PBMC suspension was processed in accordance
with the flow cytometric testing mentioned earlier, with the cell
surface labeled by anti-CD4-FITC antibody. PE-labeled monoclonal
IL-17 antibody was added to detect intracellular molecules. The
cell suspension was washed and subjected to flow cytometric
analysis to determine the proportion of
CD4+IL-17+ cells in CD4+ cells
(Fig. 2).
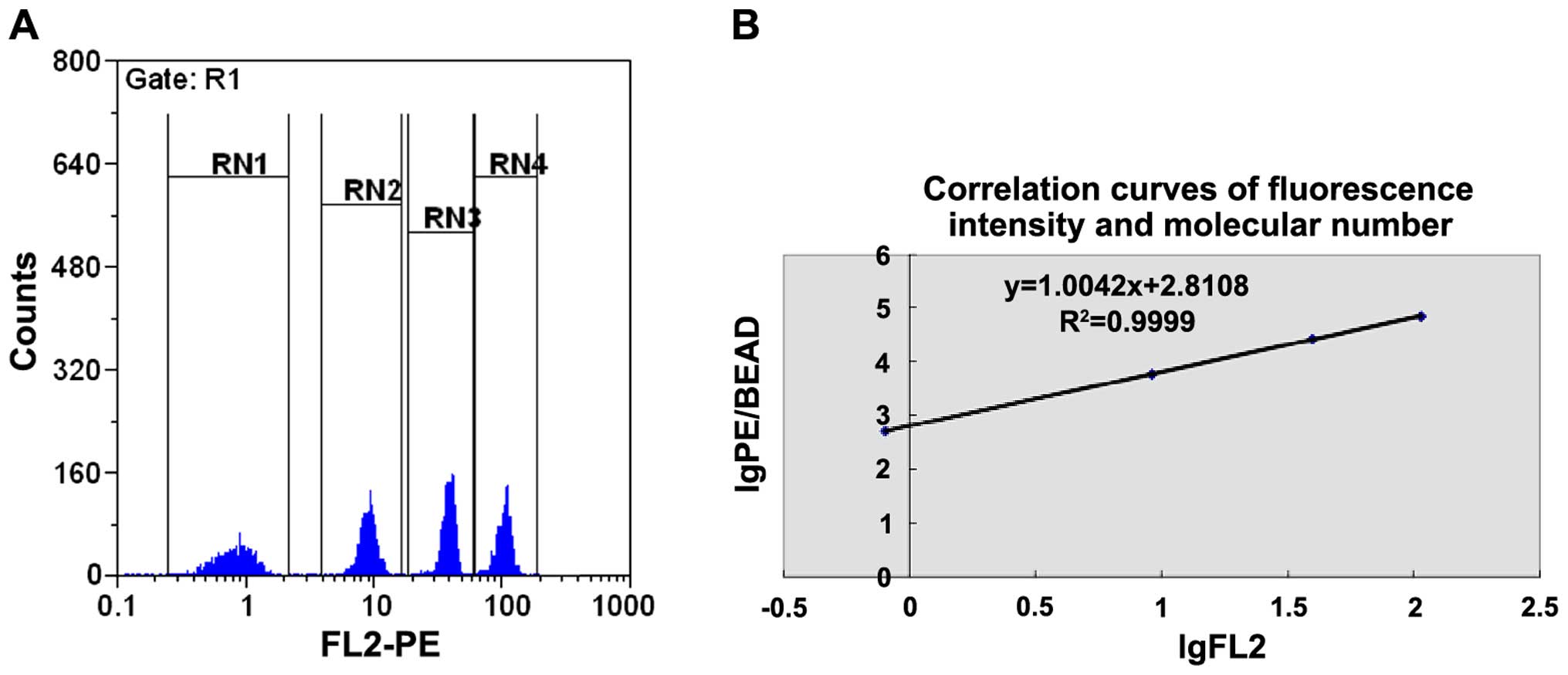
Quantitative flow cytometry for Foxp3
and ROR-γt cell molecules
The QuantiBRITE PE flow quantitative kit was used
under the same flow cytometric conditions as were applied to the
samples. The operational procedures were in accordance with the
protocol specifications. Quantitative microballoon coated with PE
molecules of different concentrations was mixed and detected using
flow cytometry. The geometric mean of the fluorescent intensities
(GFMI) of the microballoon in each group was obtained. The GFMI and
the number of coated PE molecules of different microballoon groups
were taken to logarithm to obtain the regression equation (Fig. 3).
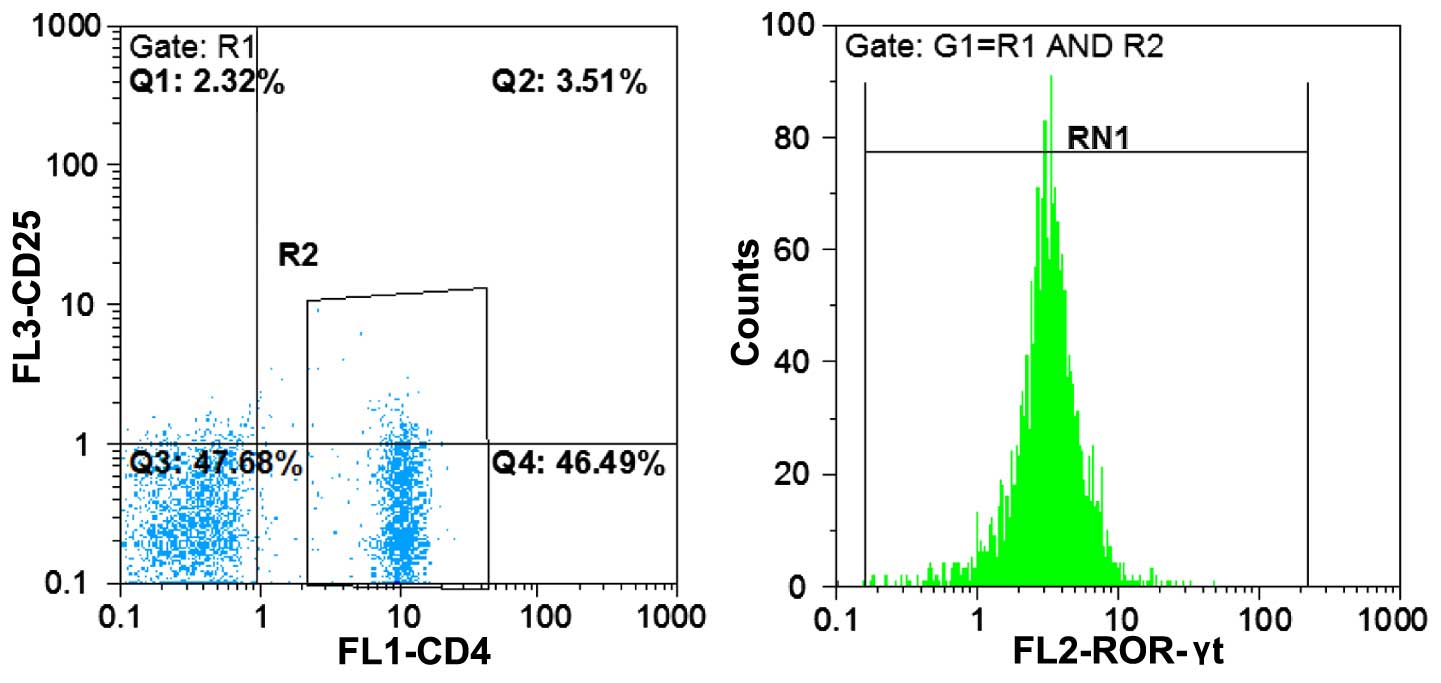
Uncultured PBMC cell suspension, performed using
flow cytometry, was initially labeled using CD4-FITC antibody on
cell surface. PE-labeled monoclonal antibodies were subsequently
used to detect the intracellular molecules of Foxp3 and ROR-γt.
(Fig. 4).
The measured GMFI values of related molecules in
single cells underwent the regression equation to identify the
corresponding expression quantity of targeted molecules.
A correlation analysis was conducted on the
expression data of FoxP3 and ROR-γt molecules in CD4+ T
cells.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 11.0 statistical software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago,
IL, USA) was used in our data analysis. Since the numerical data
did not meet normal distribution, non-parametric tests including
the Mann-Whitney U test for data analysis and the Spearman rank
test for correlation analysis were employed. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Dection of the proportion of Treg and
Th17 cells
Results of the present study detected the proportion
of Treg and Th17 cells in peripheral blood of enrolled
participants, and determined the quantitative expression of
relevant specific transcription factors (Foxp3 and ROR-γt) using
flow cytometry (Figs. 1–4). The results showed that the proportion
of Treg cells in peripheral blood withdrawn from syphilitic
patients with sero-resistance was significantly higher than that of
the normal control group (p<0.01), and that the proportion of
Th17 cells was significantly lower than that of the normal control
group (p<0.01). Additionally, the expression of transcription
factor Foxp3 in CD4+ T cells from syphilitic patients
with sero-resistance was higher than that in the normal control
group, while the expression of ROR-γt was lower in comparison to
the normal control (p<0.05).
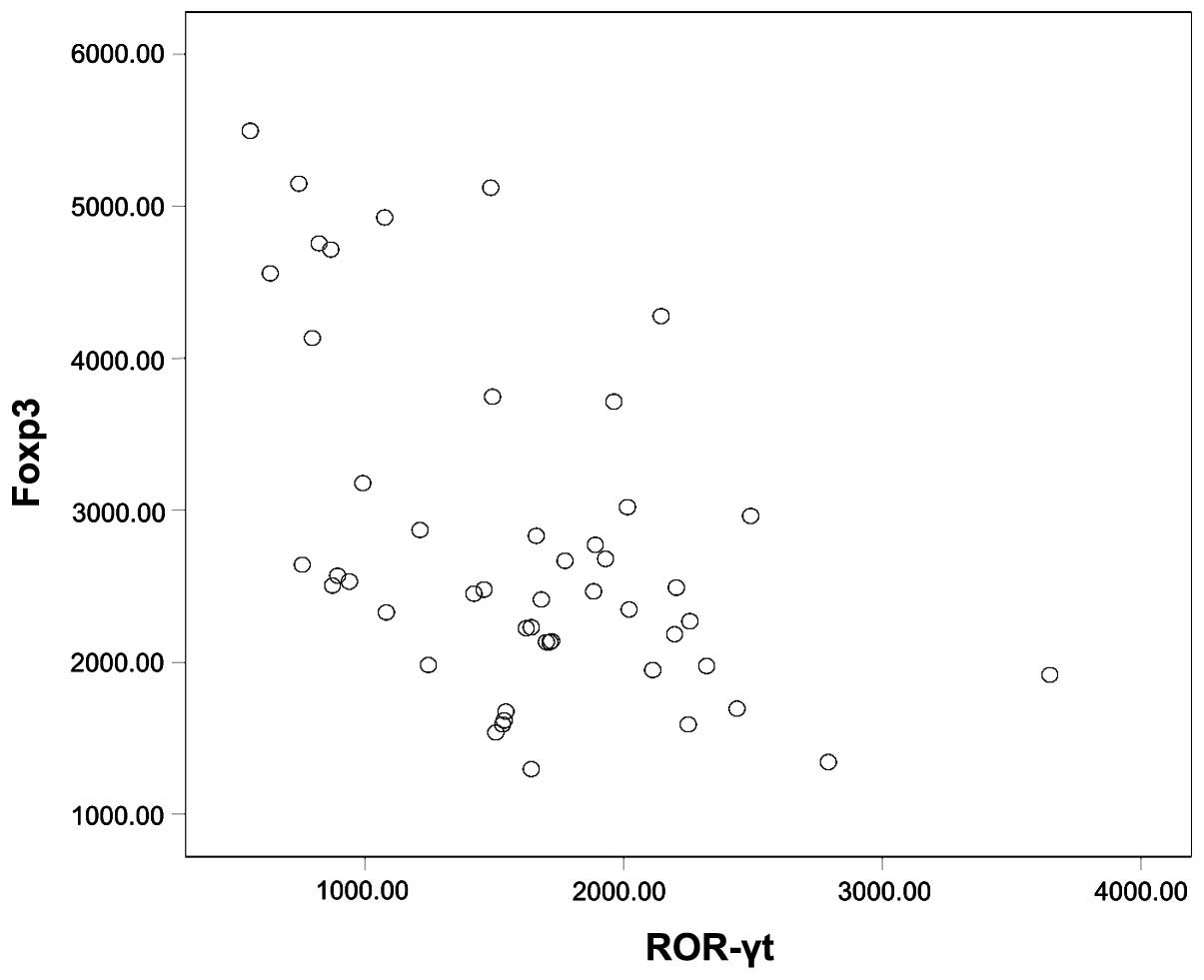
Scattering correlation of the
expression between Foxp3 and ROR-γt
Correlation of the expression of Foxp3 and ROR-γt in
peripheral blood CD4+ T cells had a negative correlation
when the samples were taken together (r=−0.481, P<0.01, Fig. 5).
Discussion
Treg and Th17 cells are dependent Th cell subsets
that are different from Th1 and Th2 cells. Treg cells have
immunosuppressive characteristics and may express the specific
transcription factor Foxp3 (5). Th17
may evoke an inflammatory response through the secretion of IL-17,
whose specific transcription factor is ROR-γt. Previous findings
have shown that the two play an important role in the occurrence
and development of infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases and
tumors (5). Notably, these two
functionally antagonistic cells are derived from the same naïve
CD4+ T cells under the influence of the same
transforming growth factor (TGF)-β cell factor (5). TGF-β, when exiting alone, can evoke
naïve CD4+ T cells to express Foxp3. Since Foxp3
restrains the function of ROR-γt, it promotes the differentiation
of Treg cell and restrains the generation of Th17 cells (6). However, Bettelli et al (7) demonstrated that it has been the
combined action of TGF-β and IL-6 may be counter-productive,
promoting the differentiation of Th17 cells (7).
Based on these findings, it has been hypothesized
(5) that there is a balance between
Treg/Th17 cells in the human body, and that the occurrence of
certain diseases may be caused by the imbalance of Treg/Th17 cells
in the process of naïve CD4+ T cell differentiation.
This hypothesis replenished the former Th1/Th2 balanced model, and
provided a new theoretical basis for some phenomena that could not
be explained by the Th1/Th2 model. It was assumed that, by
adjusting the balance between Treg and Th17, new treatment
strategies could be developed to resume the immune homeostasis. In
recent years, some investigators have attempted to examine this
method in vitro, using animal models and even in human
subjects with autoimmune diseases, as well as various
proinflammatory cytokine antagonists such as IL-6 and IL-1
antagonists (8,9), IL-2 (10), retinoic acid (11), interferon (12), and environmental toxins (13), with a certain degree of efficacy,
some of which showed promising results.
The results of the current study showed that the
proportion of Treg cells and the expression of Foxp3 in peripheral
blood lymphocytes from syphilitic patients with sero-resistance
were higher than those from the normal control group, while the
proportion of Th17 cells and the expression of ROR-γt were all
lower than those of the normal control group. The differences were
statistically significant. At the same time, when samples from all
the subjects were taken into consideration, the expression of Foxp3
was negatively correlated with the expression of ROR-γt in
CD4+ T lymphocytes. Based on the present experimental
results and the aforementioned Treg/Th17 balance theory, we suggest
that Treg and Th17 cells were antagonistic with each other in order
to maintain a dynamic equilibrium. Such an equilibrium in
syphilitic patients with sero-resistance may offset Treg cells,
promoting the differentiation of initial CD4+ T cells to
Treg cells and restraining the occurrence of Th17 cells, thus
leading to cell immunosuppression. In clinical treatment, although
a full dose of antibiotics was used, internal treponema pallidums
were, due to the cellular immunosuppression of the patients, not
cleaned thoroughly, which may stimulate the body to generate
antibodies resulting in the development of sero-resistance. This
may partly explain the reason for the high recurrence in patients,
though the underlying cause for this phenomenon remains to be
elucidated. However, whether these patients are congenitally
susceptible, or whether it is the long dormant treponema pallidums
that lead to the abnormality of the immune system remains to be
determined. While some studies indicated a higher proportion of
latent syphilis leading to sero-resistance (14), additional studies are required to
address these issues.
The antibiotic treatment of syphilis is beneficial
only with a normally working immune system of the body (15). The results showed the presence of
abnormality of the immunological state in syphilitic patients with
sero-resistance. This finding suggests that in addition to the
primary antibiotics treatment, we should also pay close attention
to patients' immunological state in the future clinical management
of syphilis, which may lead to the formulation of individualized
immunological intervention treatments.
In conclusion, the peripheral blood of syphilitic
patients with sero-resistance may have abnormalities in the
Treg/Th17 cellular balance, and these abnormalities may be
associated with the development of this phenomenon. Potential
treatments aiming to adjust the balance between Treg/Th17 may be
useful for sero-resistance in syphilitic patients.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China (project no. 30700718) and Social
Development Project of Science and Technology of Xuzhou City
(project no. XF10C057).
References
|
1
|
Dejung S, Rampini SS and Battegay E:
[Syphilis: Diagnosis andtreatment monitoring]. Praxis (Bern 1994).
100:1445–1448; quiz 1449–1450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leader BT, Godornes C, VanVoorhis WC and
Lukehart SA: CD4+ lymphocytes and gamma interferon
predominate in local immune responses in early experimental
syphilis. Infect Immun. 75:3021–3026. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li K, Wang C, Lu H, Gu X, Guan Z and Zhou
P: Regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid
of syphilis patients with and without neurological involvement.
PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 7:e25282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu A, Han H, Zhao H, Hu J, Jiang C, Xie F
and Wang F: Increased frequencies of Th17 and Th22 cells in the
peripheral blood of patients with secondary syphilis. FEMS Immunol
Med Microbiol. 66:299–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eisenstein EM and Williams CB: The
T(reg)/Th17 cell balance: A new paradigm for autoimmunity. Pediatr
Res. 65:26R–31R. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou L, Lopes JE, Chong MM, Ivanov II, Min
R, Victora GD, Shen Y, Du J, Rubtsov YP, Rudensky AY, et al:
TGF-beta-induced Foxp3 inhibits T(H)17 cell differentiation by
antagonizing RORgammat function. Nature. 453:236–240. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T,
Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL and Kuchroo VK: Reciprocal
developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector
TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 441:235–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Serada S, Fujimoto M, Mihara M, Koike N,
Ohsugi Y, Nomura S, Yoshida H, Nishikawa T, Terabe F, Ohkawara T,
et al: IL-6 blockade inhibits the induction of myelin
antigen-specific Th17 cells and Th1 cells in experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:9041–9046. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cho ML, Kang JW, Moon YM, Nam HJ, Jhun JY,
Heo SB, Jin HT, Min SY, Ju JH, Park KS, et al: STAT3 and NF-kappaB
signal pathway is required for IL-23-mediated IL-17 production in
spontaneous arthritis animal model IL-1 receptor
antagonist-deficient mice. J Immunol. 176:5652–5661. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laurence A, Tato CM, Davidson TS, Kanno Y,
Chen Z, Yao Z, Blank RB, Meylan F, Siegel R, Hennighausen L, et al:
Interleukin-2 signaling via STAT5 constrains T helper 17 cell
generation. Immunity. 26:371–381. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elias KM, Laurence A, Davidson TS,
Stephens G, Kanno Y, Shevach EM and O'Shea JJ: Retinoic acid
inhibits Th17 polarization and enhances FoxP3 expression through a
Stat-3/Stat-5 independent signaling pathway. Blood. 111:1013–1020.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shinohara ML, Kim JH, Garcia VA and Cantor
H: Engagement of the type I interferon receptor on dendritic cells
inhibits T helper 17 cell development: Role of intracellular
osteopontin. Immunity. 29:68–78. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Quintana FJ, Basso AS, Iglesias AH, Korn
T, Farez MF, Bettelli E, Caccamo M, Oukka M and Weiner HL: Control
of T(reg) and T(H)17 cell differentiation by the aryl hydrocarbon
receptor. Nature. 453:65–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Wang LN, Zuo YG, Liu YX, Liu XR, Lei
Y and Zheng HY: [Clinical analysis and study of immunological
function in syphilis patients with seroresistance]. Zhonghua Yi Xue
Za Zhi. 89:813–816. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Podwinska J, Lusiak M, Zaba R and Bowszyc
J: The pattern and level of cytokines secreted by Th1 and Th2
lymphocytes of syphilitic patients correlate to the progression of
the disease. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 28:1–14. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|