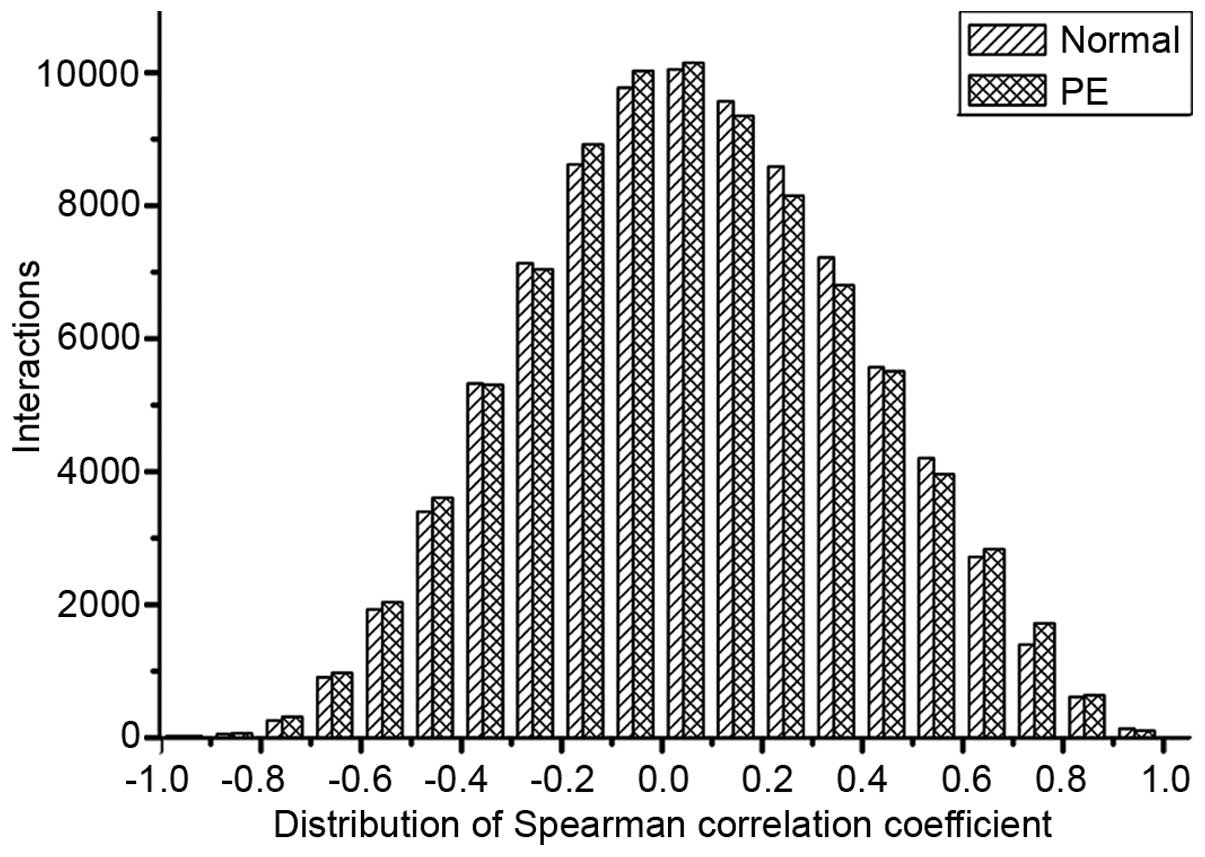
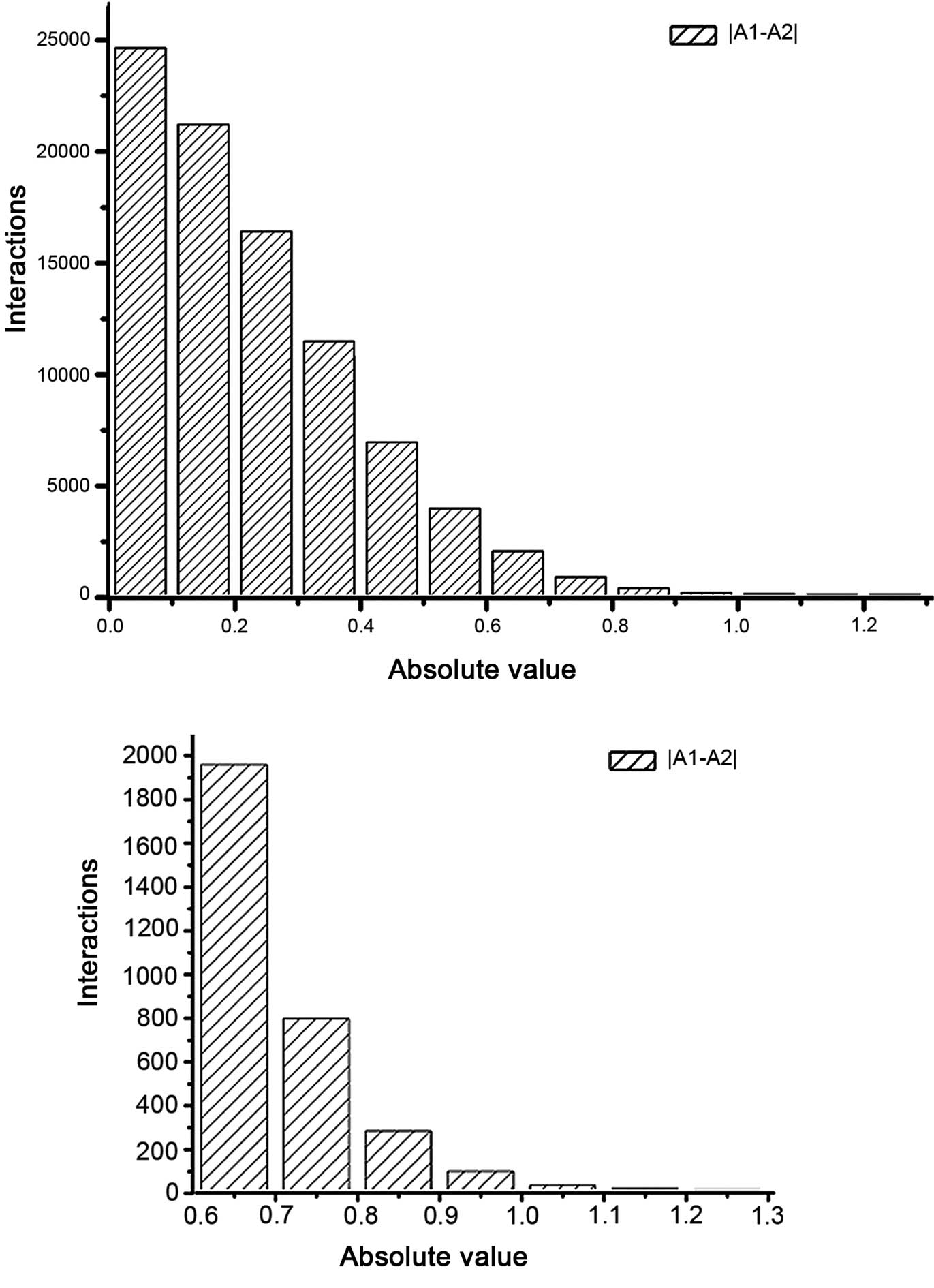
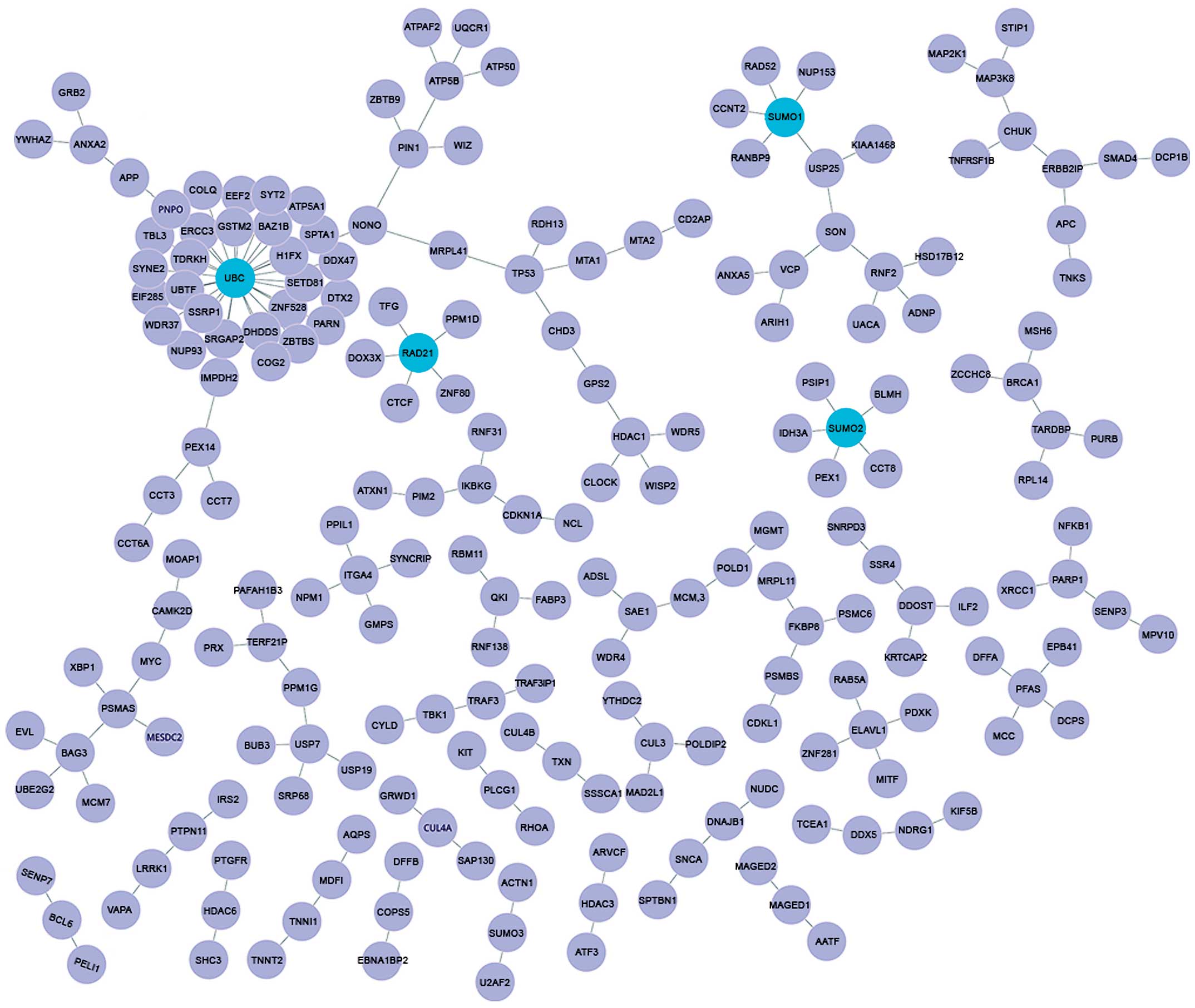
|
1
|
Eiland E, Nzerue C and Faulkner M:
Preeclampsia 2012. J Pregnancy. 2012:5865782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al-Jameil N, Aziz Khan F, Fareed Khan M
and Tabassum H: A brief overview of preeclampsia. J Clin Med Res.
6:1–7. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
American College of Obstetricians
Gynecologists. Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy:
Hypertension in pregnancy. Report of the American college of
obstetricians and gynecologists' task force on hypertension in
pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 122:1122–1131. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
World Health Organization: WHO
recommendations for prevention and treatment of preeclampsia and
eclampsia. World Health Organization. Geneva: 2011.
|
|
5
|
GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators: Global, regional and national age-sex specifi c
all-cause and cause-specifi c mortality for 240 causes of death,
1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease
Study 2013. The Lancet. 385:117–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yong HE, Melton PE, Johnson MP, Freed KA,
Kalionis B, Murthi P, Brennecke SP, Keogh RJ and Moses EK: [81-OR]:
Genome-wide transcriptome directed pathway analysis of maternal
preeclampsia susceptibility genes. Pregnancy Hypertens. 5:43–44.
2015.
|
|
7
|
Munaut C, Lorquet S, Pequeux C, Coulon C,
Le Goarant J, Chantraine F, Noël A, Goffin F, Tsatsaris V, Subtil D
and Foidart JM: Differential expression of VEGFR-2 and its soluble
form in preeclampsia. PloS One. 7:e334752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tripathi R, Rath G, Jain A and Salhan S:
Soluble and membranous vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-1 in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia. Ann Anat.
190:477–489. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sundrani DP, Reddy US, Joshi AA, Mehendale
SS, Chavan-Gautam PM, Hardikar AA, Chandak GR and Joshi SR:
Differential placental methylation and expression of VEGF, FLT-1
and KDR genes in human term and preterm preeclampsia. Clin
Epigenetics. 5:62013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Long W, Shi Z, Fan S, Liu L, Lu Y, Guo X,
Rong C, Cui X and Ding H: Association of maternal KIR and fetal
HLA-C genes with the risk of preeclampsia in Chinese Han
population. Placenta. 36:433–437. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun CJ, Zhang L and Zhang WY: Gene
expression profiling of maternal blood in early onset severe
preeclampsia: Identification of novel biomarkers. J Perinat Med.
37:609–616. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakanishi T, Oka T and Akagi T: Recent
advances in DNA microarrays. Acta Med Okayama. 55:319–328.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Herse F, Dechend R, Harsem NK, Wallukat G,
Janke J, Qadri F, Hering L, Muller DN, Luft FC and Staff AC:
Dysregulation of the circulating and tissue-based renin-angiotensin
system in preeclampsia. Hypertension. 49:604–611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Textoris J, Ivorra D, Ben Amara A,
Sabatier F, Ménard JP, Heckenroth H, Bretelle F and Mege JL:
Evaluation of current and new biomarkers in severe preeclampsia: A
microarray approach reveals the VSIG4 gene as a potential blood
biomarker. PloS One. 8:e826382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun SY, Liu ZP, Zeng T, Wang Y and Chen L:
Spatio-temporal analysis of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on
differential expression networks. Sci Rep. 3:22682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pepper SD, Saunders EK, Edwards LE, Wilson
C and Miller CJ: The utility of MAS5 expression summary and
detection call algorithms. BMC Bioinformatics. 8:2732007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taminau J, Meganck S, Lazar C, Steenhoff
D, Coletta A, Molter C, Duque R, de Schaetzen V, Weiss Solís DY,
Bersini H and Nowé A: Unlocking the potential of publicly available
microarray data using inSilicoDb and inSilicoMerging R/Bioconductor
packages. BMC Bioinformatics. 13:3352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R and Chu G:
Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing
radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:5116–5121. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methedol. 57:289–300.
1995.
|
|
23
|
Borgatti SP: Centrality and AIDS.
Connections. 18:112–115. 1995.
|
|
24
|
Otte E and Rousseau R: Social network
analysis: A powerful strategy, also for the information sciences. J
Info Sci. 28:441–453. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
da Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He D, Liu ZP, Honda M, Kaneko S and Chen
L: Coexpression network analysis in chronic hepatitis B and C
hepatic lesions reveals distinct patterns of disease progression to
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Mol Cell Biol. 4:140–152. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu ZP, Wang Y, Zhang XS and Chen L:
Network-based analysis of complex diseases. IET Syst Biol. 6:22–33.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabási AL and Oltvai
ZN: Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature.
411:41–42. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Teichmann SA and Babu MM: Gene regulatory
network growth by duplication. Nat Genet. 36:492–496. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de la Fuente A: From 'differential
expression' to 'differential networking'-identification of
dysfunctional regulatory networks in diseases. Trends Genet.
26:326–333. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Whitley GS, Dash PR, Ayling LJ, Prefumo F,
Thilaganathan B and Cartwright JE: Increased apoptosis in first
trimester extravillous trophoblasts from pregnancies at higher risk
of developing preeclampsia. Am J Pathol. 170:1903–1909. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Longtine MS, Chen B, Odibo AO, Zhong Y and
Nelson DM: Villous trophoblast apoptosis is elevated and restricted
to cytotrophoblasts in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia,
IUGR, or preeclampsia with IUGR. Placenta. 33:352–359. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fu JJ, Lin P, Lv XY, Yan XJ, Wang HX, Zhu
C, Tsang BK, Yu XG and Wang H: Low molecular mass polypeptide-2 in
human trophoblast: over-expression in hydatidiform moles and
possible role in trophoblast cell invasion. Placenta. 30:305–312.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hass R and Sohn C: Increased oxidative
stress in pre-eclamptic placenta is associated with altered
proteasome activity and protein patterns. Placenta. 24:979–984.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kugawa F and Aoki M: Expression of the
polyubiquitin gene early in the buprenorphine hydrochloride-induced
apoptosis of NG108-15 cells. DNA Seq. 15:237–245. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roberts JM and Hubel CA: The two stage
model of preeclampsia: variations on the theme. Placenta. 30(Suppl
A): S32–S37. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Heazell AE, Buttle HR, Baker PN and
Crocker IP: Altered expression of regulators of caspase activity
within trophoblast of normal pregnancies and pregnancies
complicated by preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 15:1034–1043. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Unek G, Ozmen A, Mendilcioglu I, Simsek M
and Korgun ET: The expression of cell cycle related proteins PCNA,
Ki67, p27 and p57 in normal and preeclamptic human placentas.
Tissue Cell. 46:198–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Atienza JM, Roth RB, Rosette C, Smylie KJ,
Kammerer S, Rehbock J, Ekblom J and Denissenko MF: Suppression of
RAD21 gene expression decreases cell growth and enhances
cytotoxicity of etoposide and bleomycin in human breast cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:361–368. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wong RW and Blobel G: Cohesin subunit SMC1
associates with mitotic microtubules at the spindle pole. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:15441–15445. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Birkenbihl RP and Subramani S: The rad21
gene product of Schizosaccharomyces pombe is a nuclear, cell
cycle-regulated phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 270:7703–7711. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guillou E, Ibarra A, Coulon V, Casado-Vela
J, Rico D, Casal I, Schwob E, Losada A and Méndez J: Cohesin
organizes chromatin loops at DNA replication factories. Genes Dev.
24:2812–2822. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kong X, Ball AR Jr, Sonoda E, Feng J,
Takeda S, Fukagawa T, Yen TJ and Yokomori K: Cohesin associates
with spindle poles in a mitosis-specific manner and functions in
spindle assembly in vertebrate cells. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1289–1301.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ulrich HD: SUMO modification: Wrestling
with protein conformation. Current Biol. 15:R257–R259. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Furness DL, Dekker GA, Hague WM, Khong TY
and Fenech MF: Increased lymphocyte micronucleus frequency in early
pregnancy is associated prospectively with pre-eclampsia and/or
intrauterine growth restriction. Mutagenesis. 25:489–498. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Baczyk D, Drewlo S and Kingdom J: Emerging
role of SUMOylation in placental pathology. Placenta. 34:606–612.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Branzei D, Sollier J, Liberi G, Zhao X,
Maeda D, Seki M, Enomoto T, Ohta K and Foiani M: Ubc9-and
mms21-mediated sumoylation counteracts recombinogenic events at
damaged replication forks. Cell. 127:509–522. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|