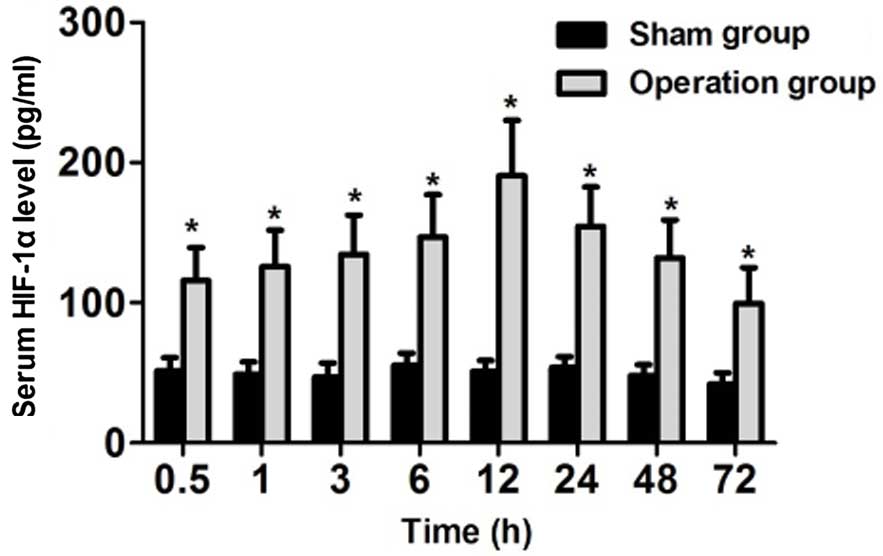
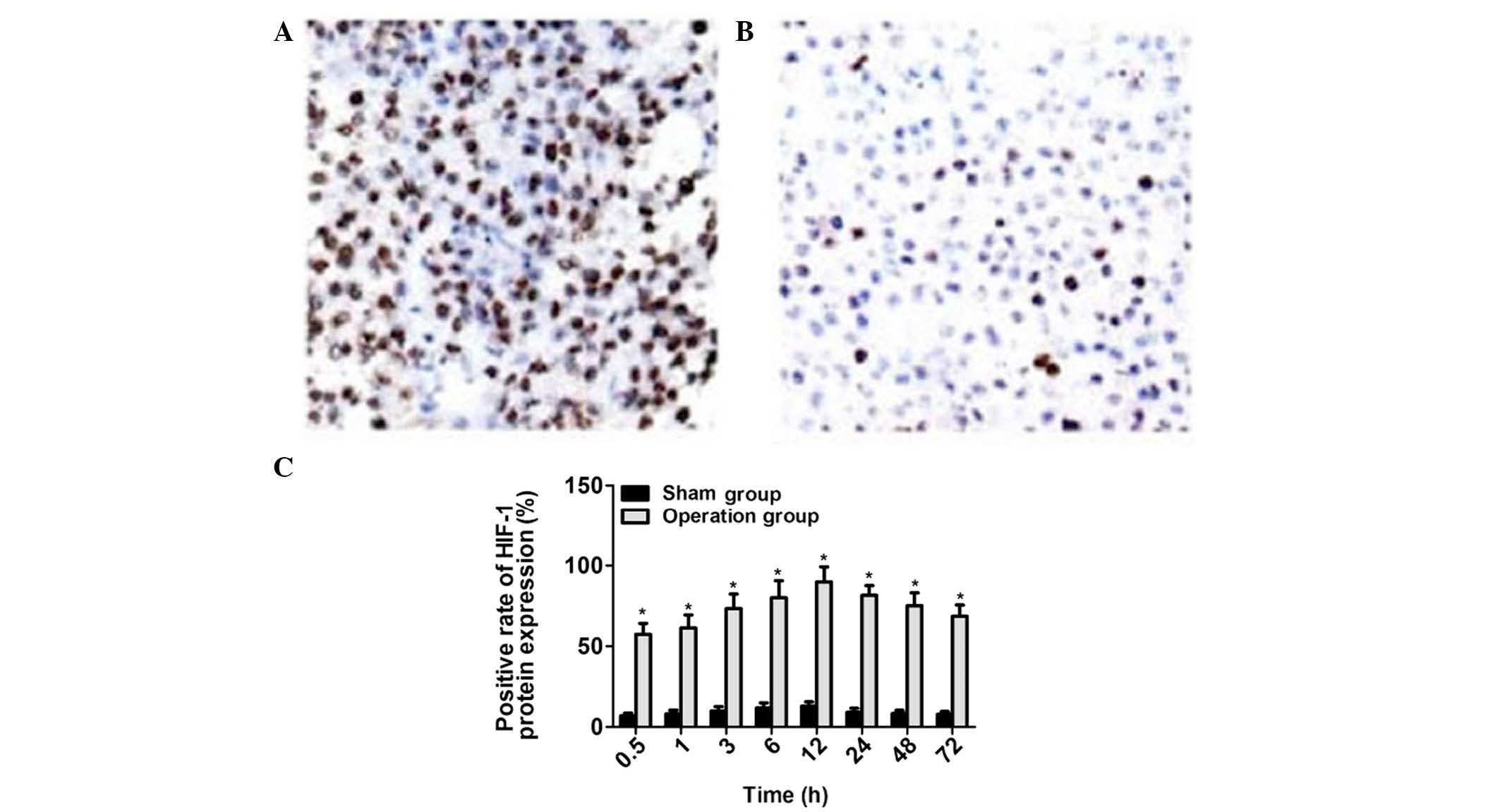
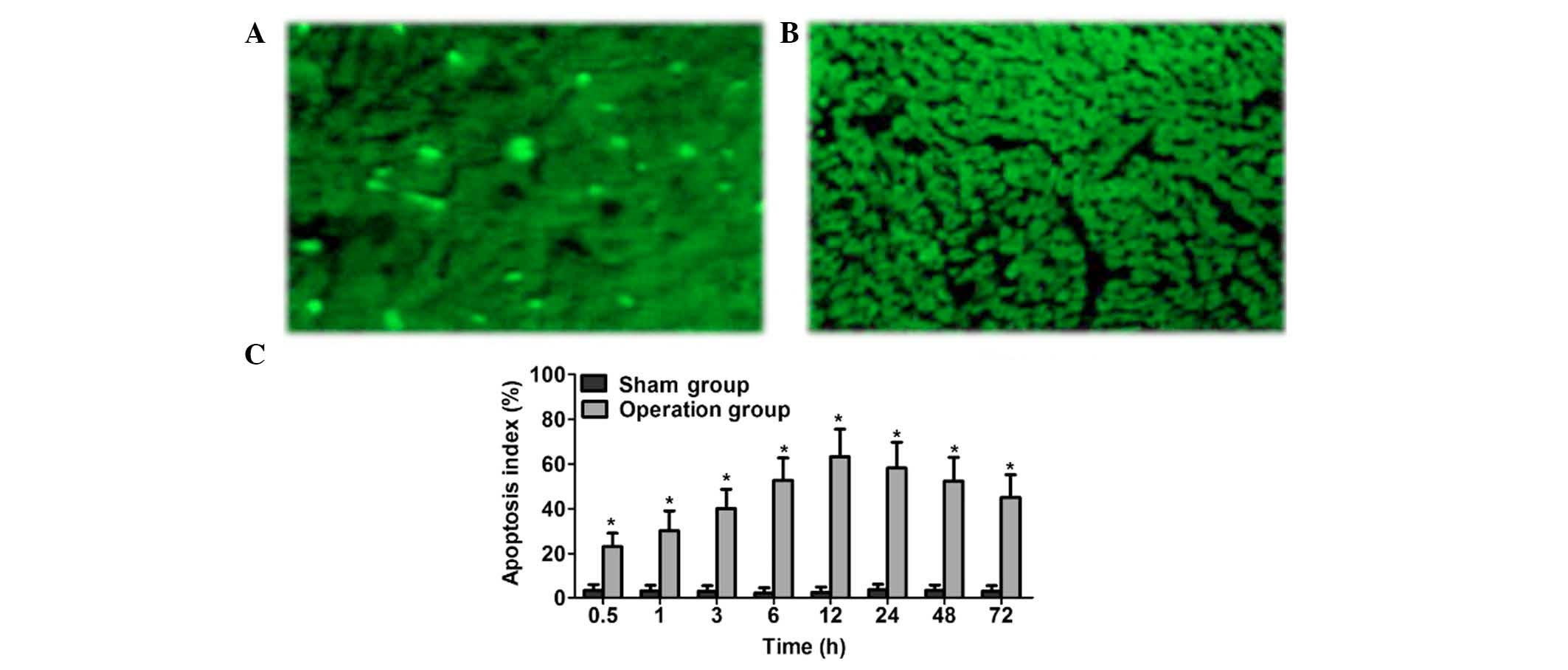
|
1
|
Wang J, An Z, Li B, Yang L, Tu J, Gu H,
Zhan C, Liu B, Su TC and Ning X: Increasing stroke incidence and
prevalence of risk factors in a low-income Chinese population.
Neurology. 84:374–381. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang H, Ju Z, Wang N, Zhang YF, Xu T and
Zhang YH: Pulse pressure and in-hospital mortality and morbidity in
acute stroke patients. Zhong Hua Gao Xue Ya Za Zhi. 16:633–636.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Wang SS, Wang JJ, Wang PX and Chen R:
Determinants of fatigue after first-ever ischemic stroke during
acute phase. PLoS One. 9:e1100372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wira CR III, Rivers E, Martinez-Capolino
C, Silver B, Iyer G, Sherwin R and Lewandowski C: Cardiac
complications in acute ischemic stroke. West J Emerg Med.
12:414–420. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J: Clinical characteristics observed in
elderly patients with cerebral infarction. Zhong Guo Shi Yong Shen
Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi. 14:59–60. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Fang H, Song B, Cheng B, Wong KS, Xu YM,
Ho SS and Chen XY: Compensatory patterns of collateral flow in
stroke patients with unilateral and bilateral carotid stenosis. BMC
Neurol. 16:392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saqqur M, Ibrahim M, Butcher K, Khan K,
Emery D, Manawadu D, Derksen C, Schwindt B and Shuaib A:
Transcranial Doppler and cerebral augmentation in acute ischemic
stroke. J Neuroimaging. 23:460–465. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iwata T: Current and future prospects of
endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Rinsho
Shinkeigaku. 54:1200–1202. 2014.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fan CG and Guo S: Effect of Ginkgo biloba
extract on acute cerebral infarction rats apoptosis genes. Zhong
Guo Yi Yuan Yao Xue Za Zhi. 35:902–907. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Teasell R, Rice D, Richardson M, Campbell
N, Madady M, Hussein N, Murie-Fernandez M and Page S: The next
revolution in stroke care. Expert Rev Neurother. 14:1307–1314.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li L, Candelario KM, Thomas K, Wang R,
Wright K, Messier A and Cunningham LA: Hypoxia inducible factor-1α
(HIF-1α) is required for neural stem cell maintenance and vascular
stability in the adult mouse SVZ. J Neurosci. 34:16713–16719. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen L, Pei H, Zhu S, Zhu J and Shi R:
Expression and significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in lung
tissues of obesity-asthma rat. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
30:1262–1265. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salva E, Turan SO, Eren F and Akbuğa J:
The enhancement of gene silencing efficiency with chitosan-coated
liposome formulations of siRNAs targeting HIF-1α and VEGF. Int J
Pharm. 478:147–154. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen C, Ostrowski RP, Zhou C, Tang J and
Zhang JH: Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and its
downstream genes reduces acute hyperglycemia-enhanced hemorrhagic
transformation in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res.
88:2046–2055. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources
(US). Committee on Care, Use of Laboratory Animals, and National
Institutes of Health (US). Division of Research Resources: Guide
for the care and use of laboratory animals (8th). National
Academies Press. (Washington, DC). 2011.
|
|
16
|
Walcott BP, Boehm KM, Stapleton CJ, Mehta
BP, Nahed BV and Ogilvy CS: Retrievable stent thrombectomy in the
treatment of acute ischemic stroke: Analysis of a revolutionizing
treatment technique. J Clin Neurosci. 20:1346–1349. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rahme R, Abruzzo TA and Ringer AJ: Acute
ischemic stroke in the setting of cervical carotid occlusion: A
proposed management strategy. World Neurosurg. 76(Suppl 6):
S60–S65. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Amar AP: Brain and vascular imaging of
acute stroke. World Neurosurg. 76(Suppl 6): S3–S8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu Y, Sun Y, Mao XO, Jin KL and Greenberg
DA: Expression of poly(C)-binding proteins is differentially
regulated by hypoxia and ischemia in cortical neurons.
Neuroscience. 110:191–198. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Donohue A, McLaughlin C, Crowe M and
Horgan F: Clinical guideline adherence by physiotherapists working
in acute stroke care. Ir Med J. 107:287–289. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
El-Koussy M, Schroth G, Brekenfeld C and
Arnold M: Imaging of acute ischemic stroke. Eur Neurol. 72:309–316.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bentovim L, Amarilio R and Zelzer E: HIF1α
is a central regulator of collagen hydroxylation and secretion
under hypoxia during bone development. Development. 139:4473–4483.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sharma S, Kapahi R, Sambyal V, Guleria K,
Manjari M, Sudan M, Uppal MS and Singh NR: No association of
hypoxia inducible factor-1α gene polymorphisms with breast cancer
in north-west indians. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:9973–9978. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tennant DA, Frezza C, MacKenzie ED, Nguyen
QD, Zheng L, Selak MA, Roberts DL, Dive C, Watson DG, Aboagye EO
and Gottlieb E: Reactivating HIF prolyl hydroxylases under hypoxia
results in metabolic catastrophe and cell death. Oncogene.
28:4009–4021. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng J, Huang Q, Wang Y, Shen P, Guan F,
Li J, Huang H and Shi C: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha regulates
autophagy to activate hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 454:328–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Botlagunta M: Neuronal pentraxin 1
expression is regulated by hypoxia inducible factor-1α. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 456:662–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu Q, Liang X, Chen D, Chen Y, Doycheva D,
Tang J, Tang J and Zhang JH: Delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy
promotes neurogenesis through reactive oxygen
species/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/β-catenin pathway in middle
cerebral artery occlusion rats. Stroke. 45:1807–1814. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma Y, Lovekamp-Swan T, Bekele W, Dohi A
and Schreihofer DA: Hypoxia-inducible factor and vascular
endothelial growth factor are targets of dietary soy during acute
stroke in female rats. Endocrinology. 154:1589–1597. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen L, Chen SH and Chen JY: Change
characteristics and relation study of serum HIF-1, VEGF factor on
acute stage cerebral infarction in SD rats. Leshan Shi Fan Xue Yuan
Xue Bao. 27:13–18. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Panchision DM: The role of oxygen in
regulating neural stem cells in development and disease. J Cell
Physiol. 220:562–568. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hua W, Zhou M, Liu W and Qi JP: Effect of
RhEPO to hypoxia-inducible factor-1α after cerebral ischemia. Ha Er
Bin Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 47:216–219. 2013.(In Chinese).
|