|
1.
|
Montfrans CV, Stok M and Geerkens M:
Biology of chronic wounds and new treatment strategies. Phlebology.
29(Suppl): 165–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Charbonneau L, Perrenoud B, Gallant S,
Lehn I and Champier V: Chronic wound management in hospital care
units - a literature review. Rech Soins Infirm. 96:58–68. 2009.(In
French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Fumimoto Y, Matsuyama A, Komoda H, et al:
Creation of a rich subcutaneous vascular network with implanted
adipose tissue-derived stromal cells and adipose tissue enhances
subcutaneous grafting of islets in diabetic mice. Tissue Eng Part C
Methods. 15:437–444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Ohmura Y, Tanemura M, Kawaguchi N, et al:
Combined transplantation of pancreatic islets and adipose
tissue-derived stem cells enhances the survival and insulin
function of islet grafts in diabetic mice. Transplantation.
90:1366–1373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K, Fan X, Ma X and Cui
Z: Adipose-derived stem cell: A better stem cell than BMSC. Cell
Biochem Funct. 26:664–675. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Han C, Zhang L, Song L, Liu Y, Zou W, Piao
H and Liu J: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A better
cell source for nervous system regeneration. Chin Med J (Engl).
127:329–337. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Nuschke A: Activity of mesenchymal stem
cells in therapies for chronic skin wound healing. Organogenesis.
10:29–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Das R, Jahr H, van Osch GJ and Farrell E:
The role of hypoxia in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells:
Considerations for regenerative medicine approaches. Tissue Eng
Part B Rev. 16:159–168. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Liu H, Xue W, Ge G, et al: Hypoxic
preconditioning advances CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression by activating
HIF-1α in MSCs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 401:509–515. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Shevchenko EK, Makarevich PI, Tsokolaeva
ZI, et al: Transplantation of modified human adipose derived
stromal cells expressing VEGF165 results in more efficient
angiogenic response in ischemic skeletal muscle. J Transl Med.
11:1382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
de Ruiz Almodovar C, Luttun A and
Carmeliet P: An SDF-1 trap for myeloid cells stimulates
angiogenesis. Cell. 124:18–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Togel FE and Westenfelder C: Role of SDF-1
as a regulatory chemokine in renal regeneration after acute kidney
injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 1:87–89. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Nakamura Y, Ishikawa H, Kawai K, Tabata Y
and Suzuki S: Enhanced wound healing by topical administration of
mesenchymal stem cells transfected with stromal cell-derived
factor-1. Biomaterials. 34:9393–9400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Herberg S, Shi X, Johnson MH, Hamrick MW,
Isales CM and Hill WD: Stromal cell-derived factor-1β mediates cell
survival through enhancing autophagy in bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 8:e582072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Liu H, Liu S, Li Y, et al: The role of
SDF-1-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in the therapeutic effects of
hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells for renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 7:e346082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ghadge SK, Mühlstedt S, Ozcelik C and
Bader M: SDF-1α as a therapeutic stem cell homing factor in
myocardial infarction. Pharmacol Ther. 129:97–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Wang K, Zhao X, Kuang C, et al:
Overexpression of SDF-1α enhanced migration and engraftment of
cardiac stem cells and reduced infarcted size via CXCR4/PI3K
pathway. PLoS One. 7:e439222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Li Q, Zhang A, Tao C, Li X and Jin P: The
role of SDF-1-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in biological behaviors of adipose
tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 441:675–680. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Li Q, Li PH, Hou DJ, et al: EGF enhances
ADSCs secretion via ERK and JNK pathways. Cell Biochem Biophys.
69:189–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Martínez-Santamaría L, Conti CJ, Llames S,
et al: The regenerative potential of fibroblasts in a new
diabetes-induced delayed humanised wound healing model. Exp
Dermatol. 22:195–201. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Li H and Fu X: Mechanisms of action of
mesenchymal stem cells in cutaneous wound repair and regeneration.
Cell Tissue Res. 348:371–377. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Gojo S, Gojo N, Takeda Y, et al: In vivo
cardiovasculogenesis by direct injection of isolated adult
mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 288:51–59. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Liu X, Zuo D, Fan H, et al:
Over-expression of CXCR4 on mesenchymal stem cells protect against
experimental colitis via immunomodulatory functions in impaired
tissue. J Mol Histol. 45:181–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
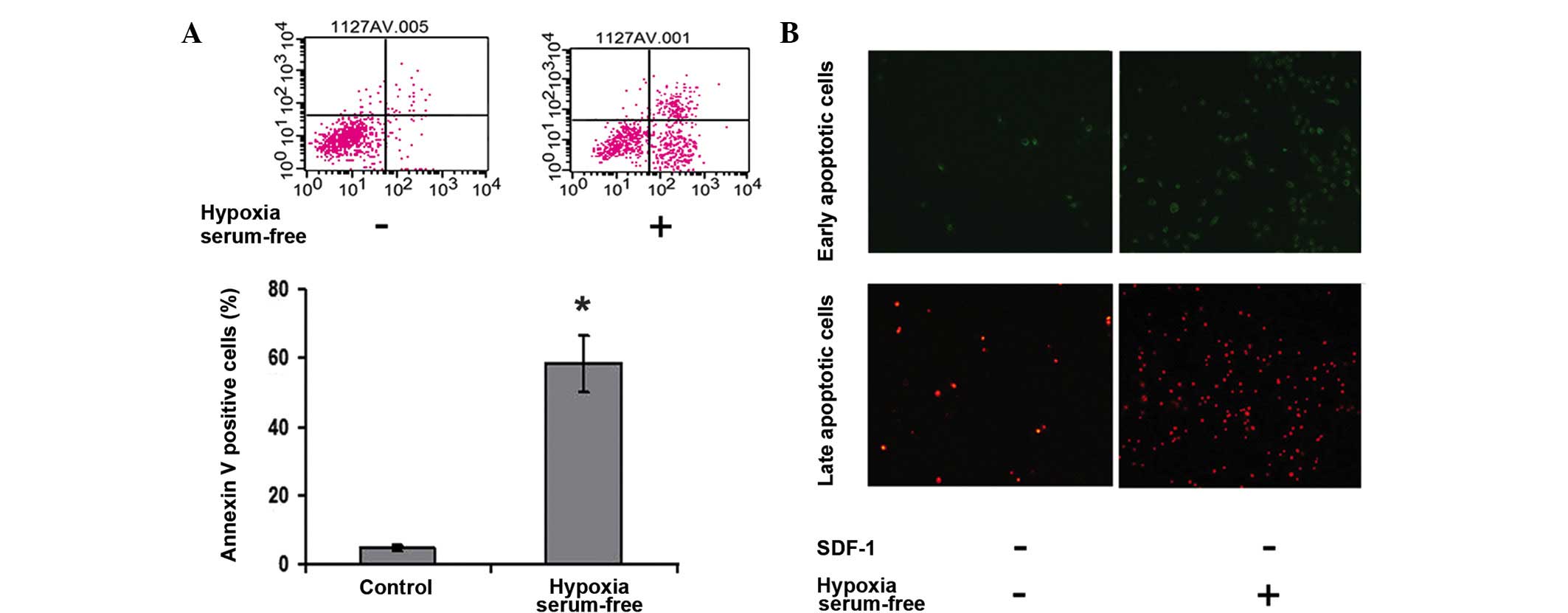
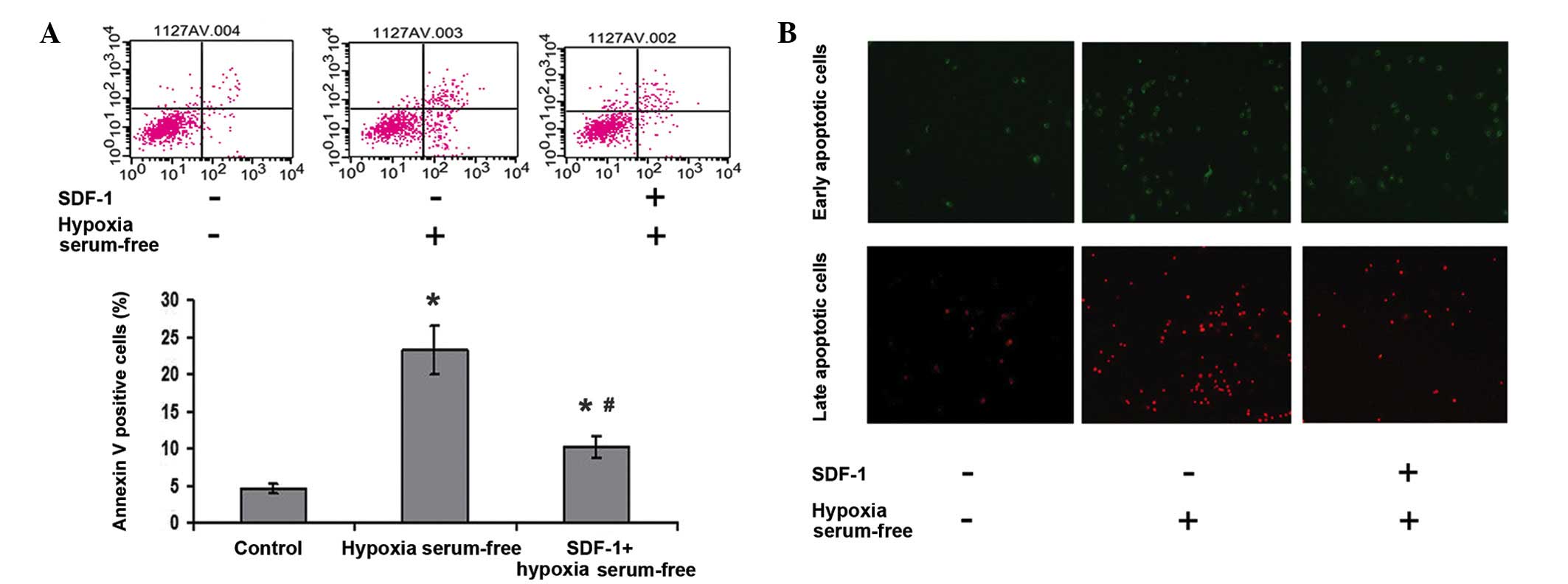
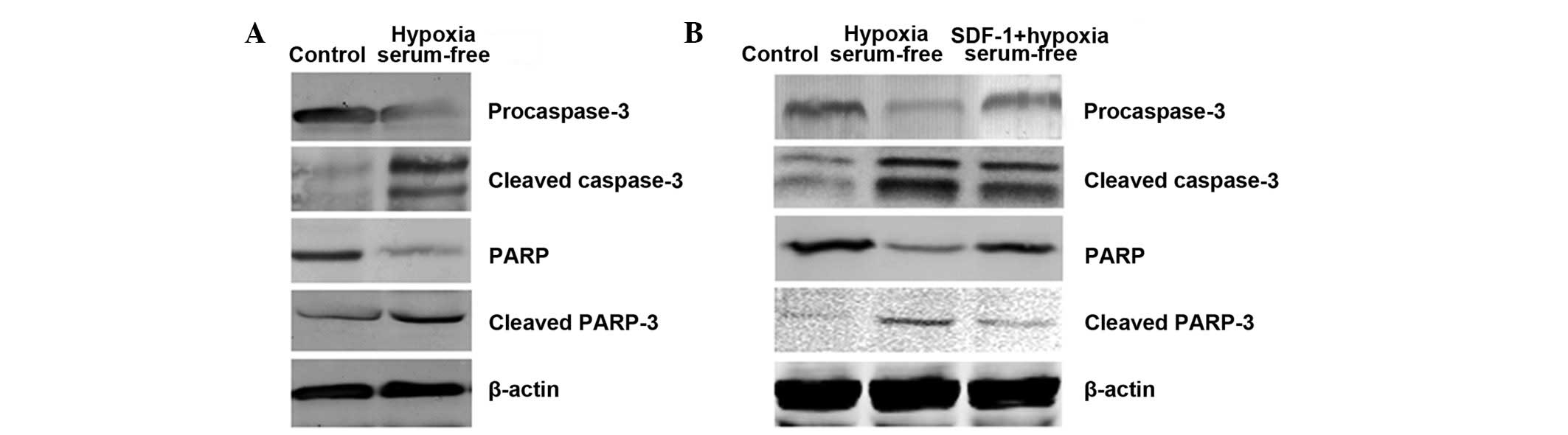
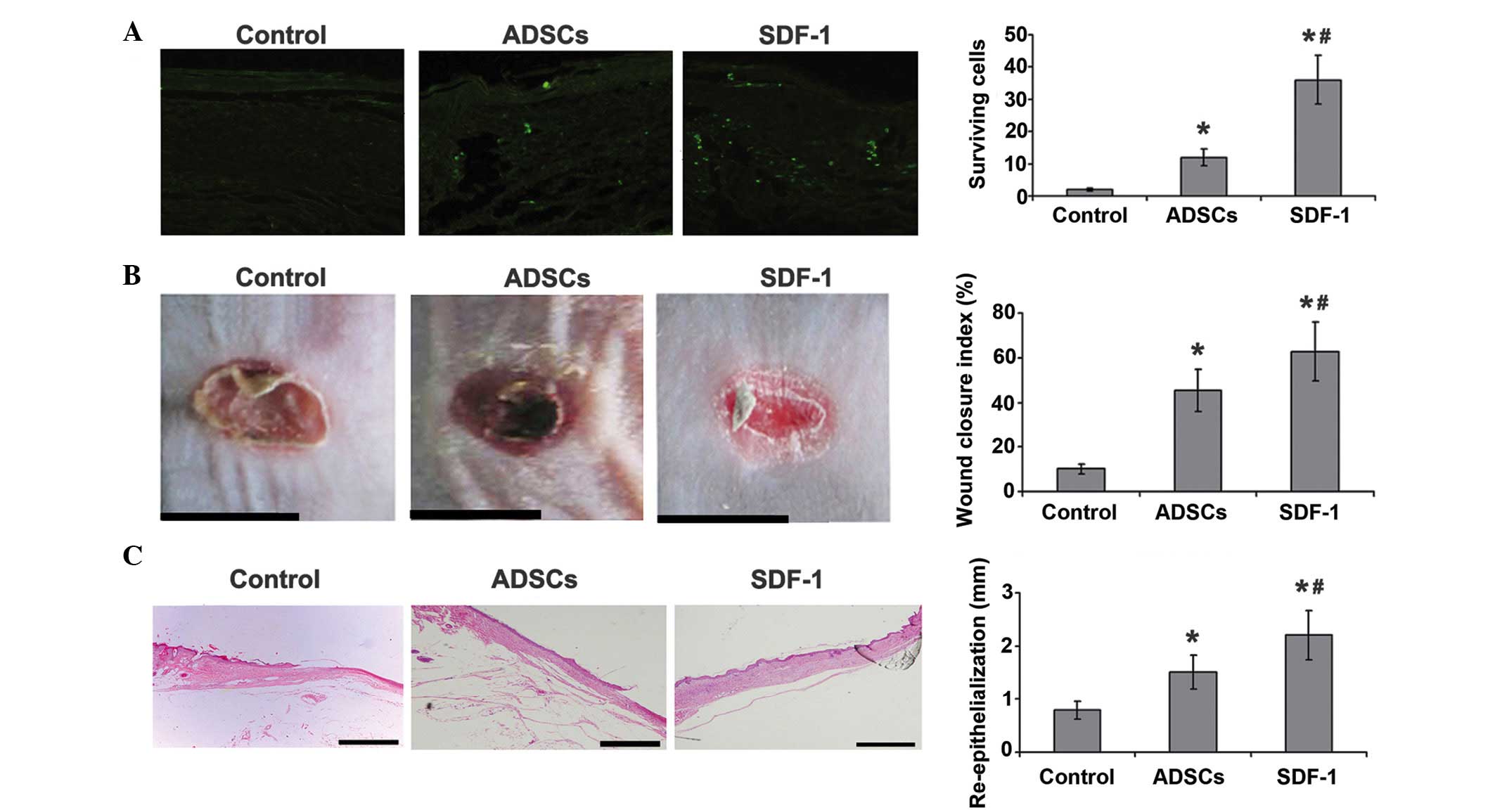
Yin Q, Jin P, Liu X, et al: SDF-1α
inhibits hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in
mesenchymal stem cells through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling
pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 38:9–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Zong ZW, Cheng TM, Su YP, et al: Crucial
role of SDF-1/CXCR4 interaction in the recruitment of transplanted
dermal multipotent cells to sublethally irradiated bone marrow. J
Radiat Res (Tokyo). 47:287–293. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Askari AT, Unzek S, Popovic ZB, et al:
Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor 1 on stem-cell homing and
tissue regeneration in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet.
362:697–703. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Brem H and Tomic-Canic M: Cellular and
molecular basis of wound healing in diabetes. J Clin Invest.
117:1219–1222. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Litwiniuk M, Bikowska B, Niderla-Bielińska
J, et al: Potential role of metalloproteinase inhibitors from
radiation-sterilized amnion dressings in the healing of venous leg
ulcers. Mol Med Rep. 6:723–728. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Khanna S, Biswas S, Shang Y, et al:
Macrophage dysfunction impairs resolution of inflammation in the
wounds of diabetic mice. PLoS ONE. 5:e95392010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Krisp C, Jacobsen F, McKay MJ, Molloy MP,
Steinstraesser L and Wolters DA: Proteome analysis reveals
antiangiogenic environments in chronic wounds of diabetes mellitus
type 2 patients. Proteomics. 13:2670–2681. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|