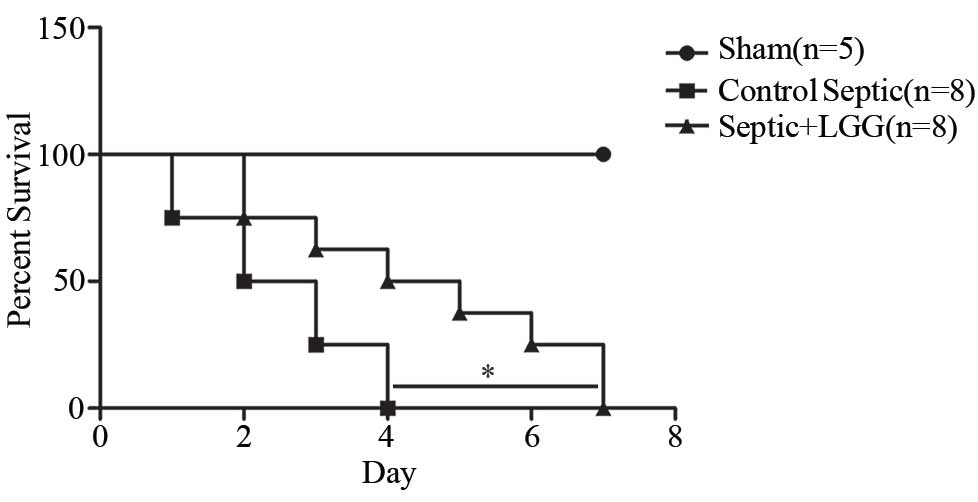
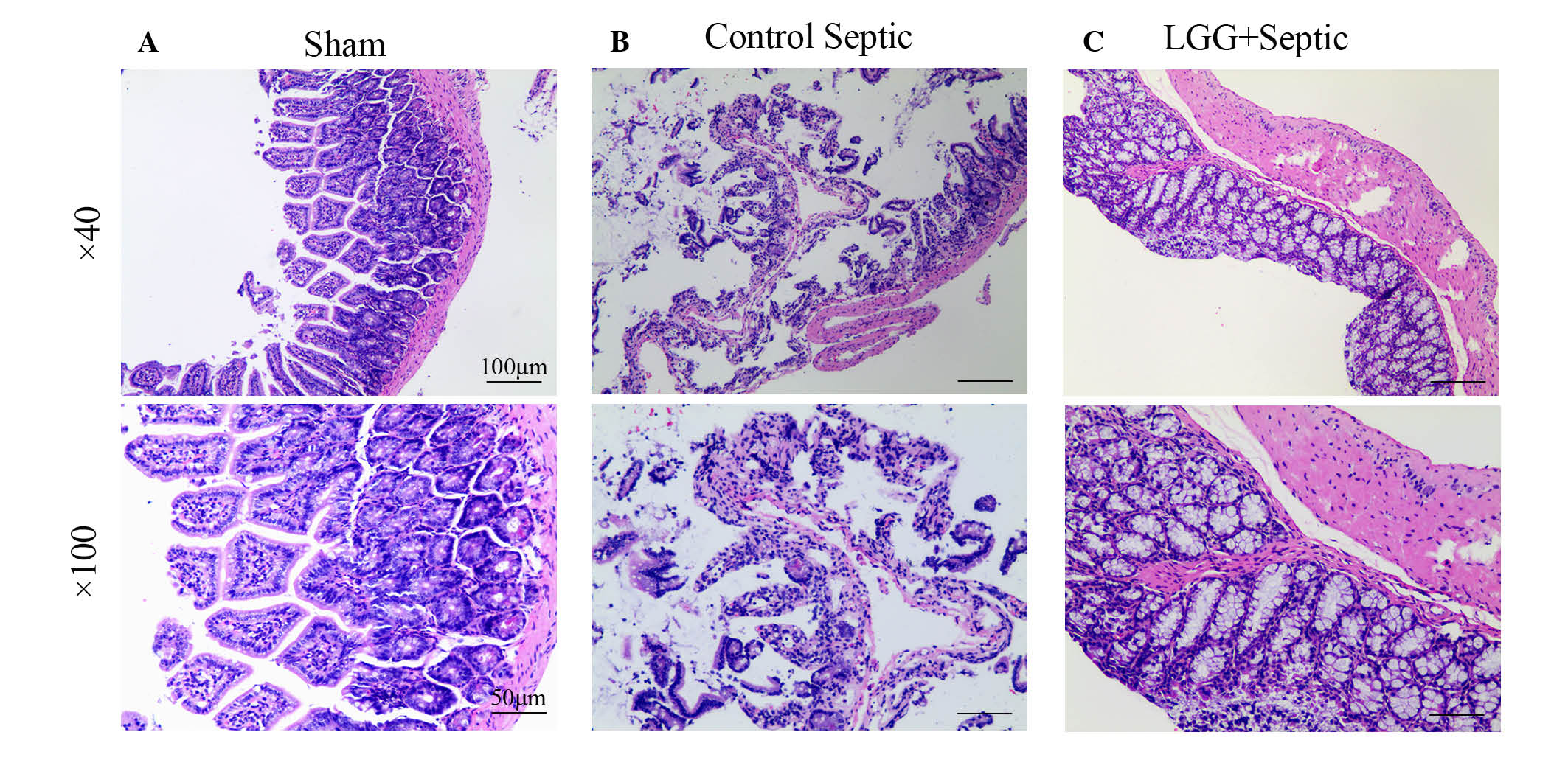
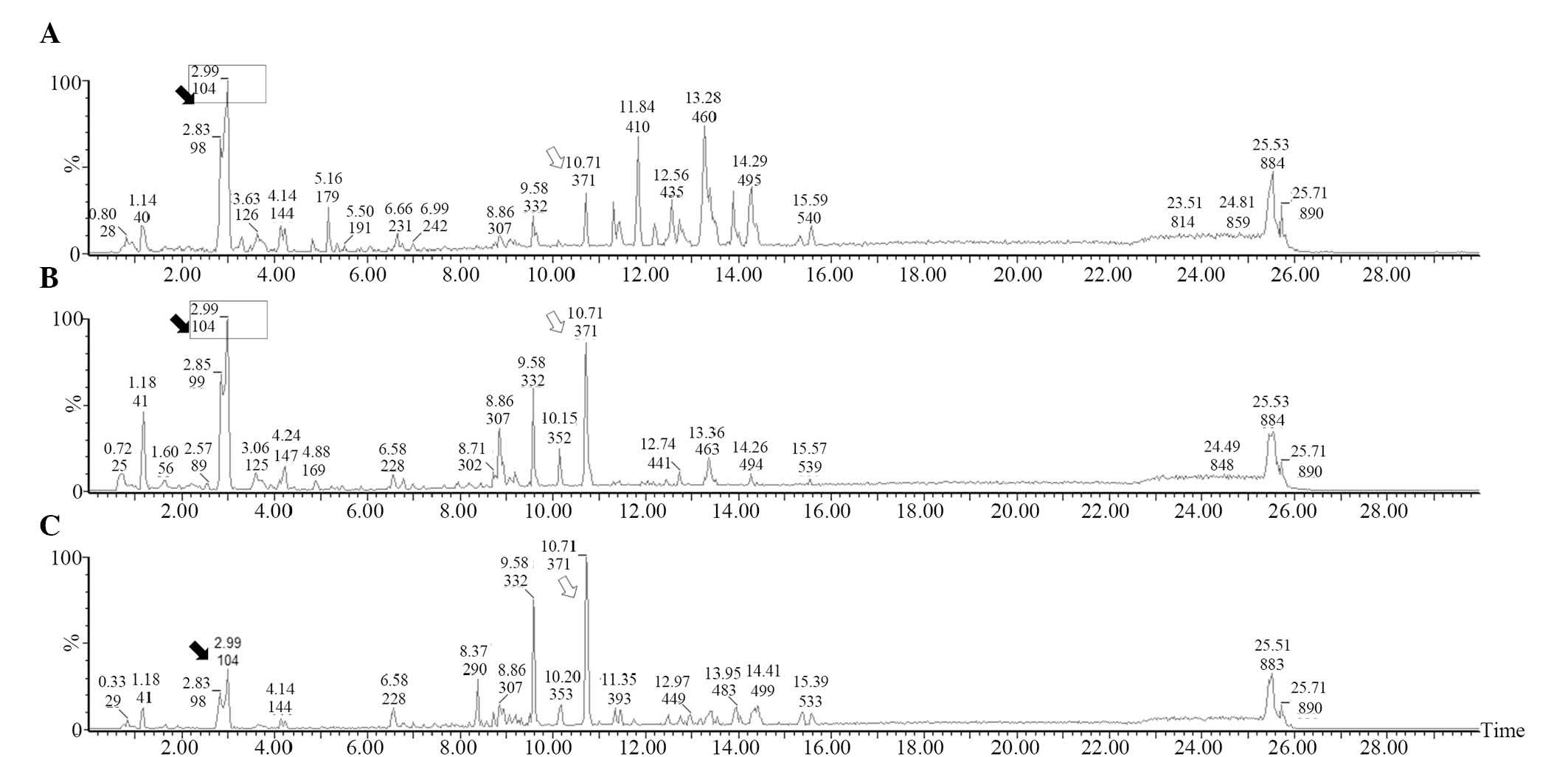
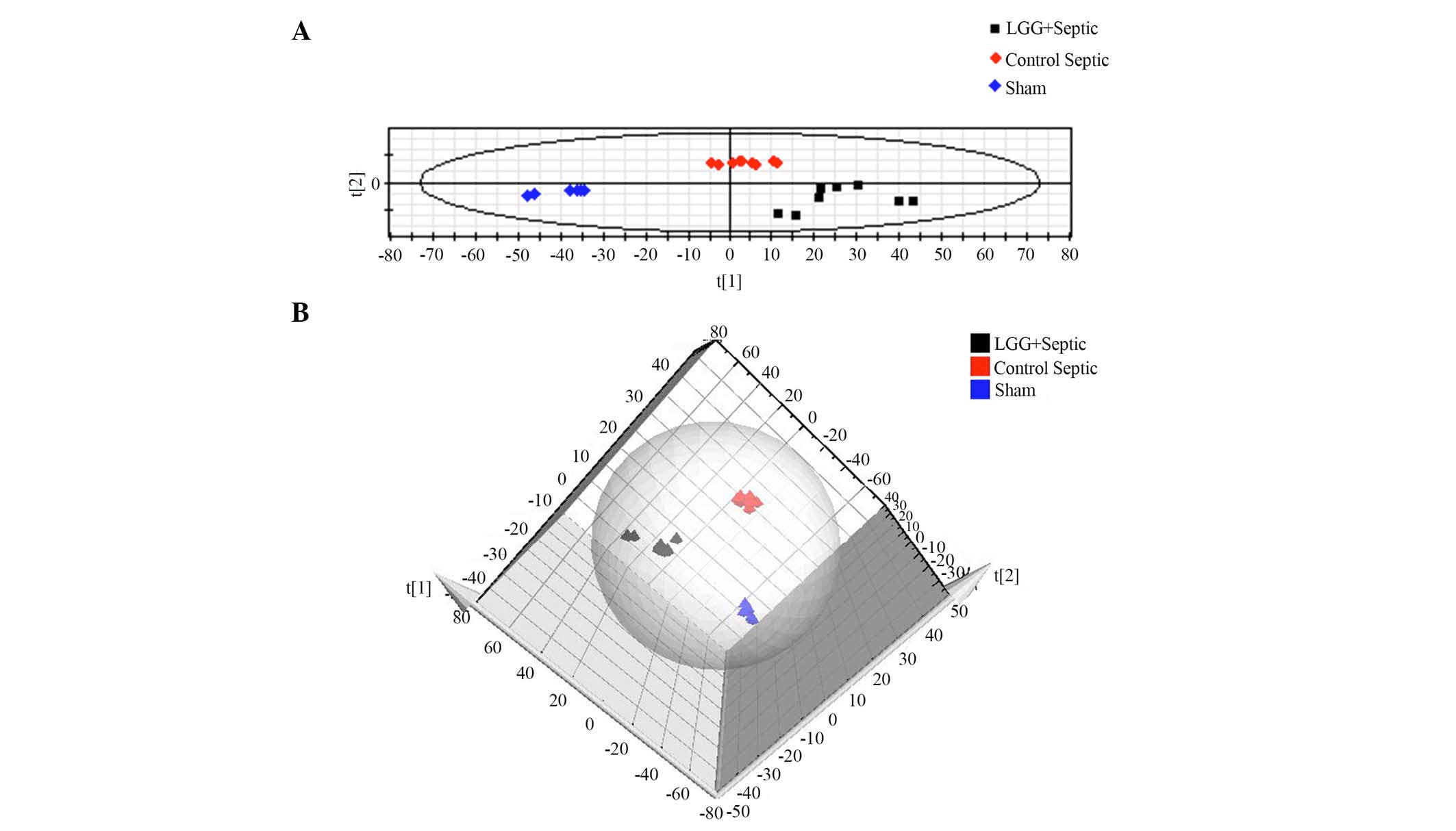
|
1
|
Bouza C, López-Cuadrado T, Saz-Parkinson Z
and Amate-Blanco JM: Epidemiology and recent trends of severe
sepsis in Spain: A nationwide population-based analysis
(2006-2011). BMC Infect Dis. 14:38632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khailova L, Frank DN, Dominguez JA and
Wischmeyer PE: Probiotic administration reduces mortality and
improves intestinal epithelial homeostasis in experimental sepsis.
Anesthesiology. 119:166–177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sokol H: Probiotics and Antibiotics in
IBD. Dig Dis. 32(Suppl 1): S10–S17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wan Y, Xin Y, Zhang C, Wu D, Ding D, Tang
L, Owusu L, Bai J and Li W: Fermentation supernatants of
Lactobacillus delbrueckii inhibit growth of human colon cancer
cells and induce apoptosis through a caspase 3-dependent pathway.
Oncol Lett. 7:1738–1742. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Plaza-Diaz J, Gomez-Llorente C, Fontana L
and Gil A: Modulation of immunity and inflammatory gene expression
in the gut, in inflammatory diseases of the gut and in the liver by
probiotics. World J Gastroenterol. 20:15632–15649. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dietrich CG, Kottmann T and Alavi M:
Commercially available probiotic drinks containing Lactobacillus
casei DN-114001 reduce antibiotic-associated diarrhea. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:15837–15844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu CT, Chen PJ, Lee YT, Ko JL and Lue KH:
Effects of immunomodulatory supplementation with Lactobacillus
rhamnosus on airway inflammation in a mouse asthma model. J
Microbiol Immunol Infect. Nov 11–2014.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Griffin JL and Bollard ME: Metabonomics:
Its potential as a tool in toxicology for safety assessment and
data integration. Curr Drug Metab. 5:389–398. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lahti L, Salonen A, Kekkonen RA, Salojärvi
J, Jalanka-Tuovinen J, Palva A, Orešič M and de Vos WM:
Associations between the human intestinal microbiota, Lactobacillus
rhamnosus GG and serum lipids indicated by integrated analysis of
high-throughput profiling data. Peer J. 1:e322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan F and Polk DB: Probiotics: Progress
toward novel therapies for intestinal diseases. Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 26:95–101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quigley EM: Gut Bacteria in health and
disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 9:560–569. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barraud D, Blard C, Hein F, Marçon O,
Cravoisy A, Nace L, Alla F, Bollaert PE and Gibot S: Probiotics in
the critically ill patient: A double blind, randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. 36:1540–1547. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Honeycutt TC, El Khashab M, Wardrop RM
III, McNeal-Trice K, Honeycutt AL, Christy CG, Mistry K, Harris BD,
Meliones JN and Kocis KC: Probiotic administration and the
incidence of nosocomial infection in pediatric intensive care: A
randomized placebo-controlled trial. Pediatr Crit Care Med.
8:452–458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gou S, Yang Z, Liu T, Wu H and Wang C: Use
of probiotics in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials. Crit Care. 18:R572014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barraud D, Bollaert PE and Gibot S: Impact
of the administration of probiotics on mortality in critically ill
adult patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Chest. 143:646–655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Treede I, Braun A, Sparla R, Kühnel M,
Giese T, Turner JR, Anes E, Kulaksiz H, Füllekrug J, Stremmel W, et
al: Anti-inflammatory effects of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem.
282:27155–27164. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stremmel W, Merle U, Zahn A, Autschbach F,
Hinz U and Ehehalt R: Retarded release phosphatidylcholine benefits
patients with chronic active ulcerative colitis. Gut. 54:966–971.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stremmel W: Mucosal protection by
phosphatidylcholine as new therapeutic concept in ulcerative
colitis. Z Gastroenterol. 51:384–389. 2013.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang H, Kovacs-Nolan J, Kodera T, Eto Y
and Mine Y: γ-Glutamyl cysteine and γ-glutamyl valine inhibit TNF-α
signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and reduce inflammation in
a mouse model of colitis via allosteric activation of the
calcium-sensing receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:792–804. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hsieh CY, Osaka T, Moriyama E, Date Y,
Kikuchi J and Tsuneda S: Strengthening of the intestinal epithelial
tight junction by Bifidobacterium bifidum. Physiol Rep. 3:pii.
e123272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barrenetxe J, Sánchez O, Barber A, Gascón
S, Rodríguez-Yoldi MJ and Lostao MP: TNFα regulates sugar
transporters in the human intestinal epithelial cell line Caco-2.
Cytokine. 64:181–187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goretsky T, Dirisina R, Sinh P, Mittal N,
Managlia E, Williams DB, Posca D, Ryu H, Katzman RB and Barrett TA:
P53 mediates TNF-induced epithelial cell apoptosis in IBD. Am J
Pathol. 181:1306–1315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao X, Qu H, Ai CZ, Cao YF, Huang T, Chen
JX, Zeng J, Sun XY, Hong M, Gonzalez FJ, et al: Regulation profile
of phosphatidylcholines (PCs) and lysophosphatidylcholines (LPCs)
components towards UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) isoforms.
Xenobiotica. 45:197–206. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu M, Subramanian VS and Subbaiah PV:
Modulation of the positional specificity of lecithin-cholesterol
acyltransferase by the acyl group composition of its
phosphatidylcholine substrate: Role of the sn-1-acyl group.
Biochemistry. 37:13626–13633. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miklishanskaia SV, Liakishev AA and
Kukharchuk VV: Clinical role of lipoprotein-associated
phospholipase A2. Kardiologiia. 53:59–70. 2013.(In Russian).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Domeij H, Hua X, Su J, Bäcklund A, Yan Z,
Frostegård AG, Haeggström JZ, Modéer T and Frostegård J: Annexin A5
inhibits atherogenic and pro-inflammatory effects of
lysophosphatidylcholine. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
106:72–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kajander K, Myllyluoma E, Kyrönpalo S,
Rasmussen M, Sipponen P, Mattila I, Seppänen-Laakso T, Vapaatalo H,
Oresic M and Korpela R: Elevated pro-inflammatory and lipotoxic
mucosal lipids characterise irritable bowel syndrome. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:6068–6074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang-Sattler R, Yu Z, Herder C, Messias
AC, Floegel A, He Y, Heim K, Campillos M, Holzapfel C, Thorand B,
et al: Novel biomarkers for pre-diabetes identified by
metabolomics. Mol Syst Biol. 8:6152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jantscheff P, Schlesinger M, Fritzsche J,
Taylor LA, Graeser R, Kirfel G, Fürst DO, Massing U and Bendas G:
Lysophosphatidylcholine pretreatment reduces VLA-4 and
P-Selectin-mediated b16.f10 melanoma cell adhesion in vitro and
inhibits metastasis-like lung invasion in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther.
10:186–197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Smani Y, Domínguez-Herrera J,
Ibáñez-Martínez J and Pachón J: Therapeutic efficacy of
lysophosphatidylcholine in severe infections caused by
Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agent Chemother.
59:3920–3924. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Croset M, Brossard N, Polette A and
Lagarde M: Characterization of plasma unsaturated
lysophosphatidylcholines in human and rat. Biochem J. 345:61–67.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou B, Ren J, Han G, Chen YAJ, Gu G, Chen
J, Wang G and Li J: Dynamics of albumin synthetic response to
intra-abdominal abscess in patients with gastrointestinal fistula.
Surg Infect (Larchmt). 15:111–117. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ruot B, Papet I, Bechereau F, Denis P,
Buffiere C, Gimonet J, Glomot F, Elyousfi M, Breuille D and Obled
C: Increased albumin plasma efflux contributes to hypoalbuminemia
only during early phase of sepsis in rats. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 284:R707–R713. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wiedermann CJ, Wiedermann W and Joannidis
M: Hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury: A meta-analysis of
observational clinical studies. Intensive Care Med. 36:1657–1665.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|