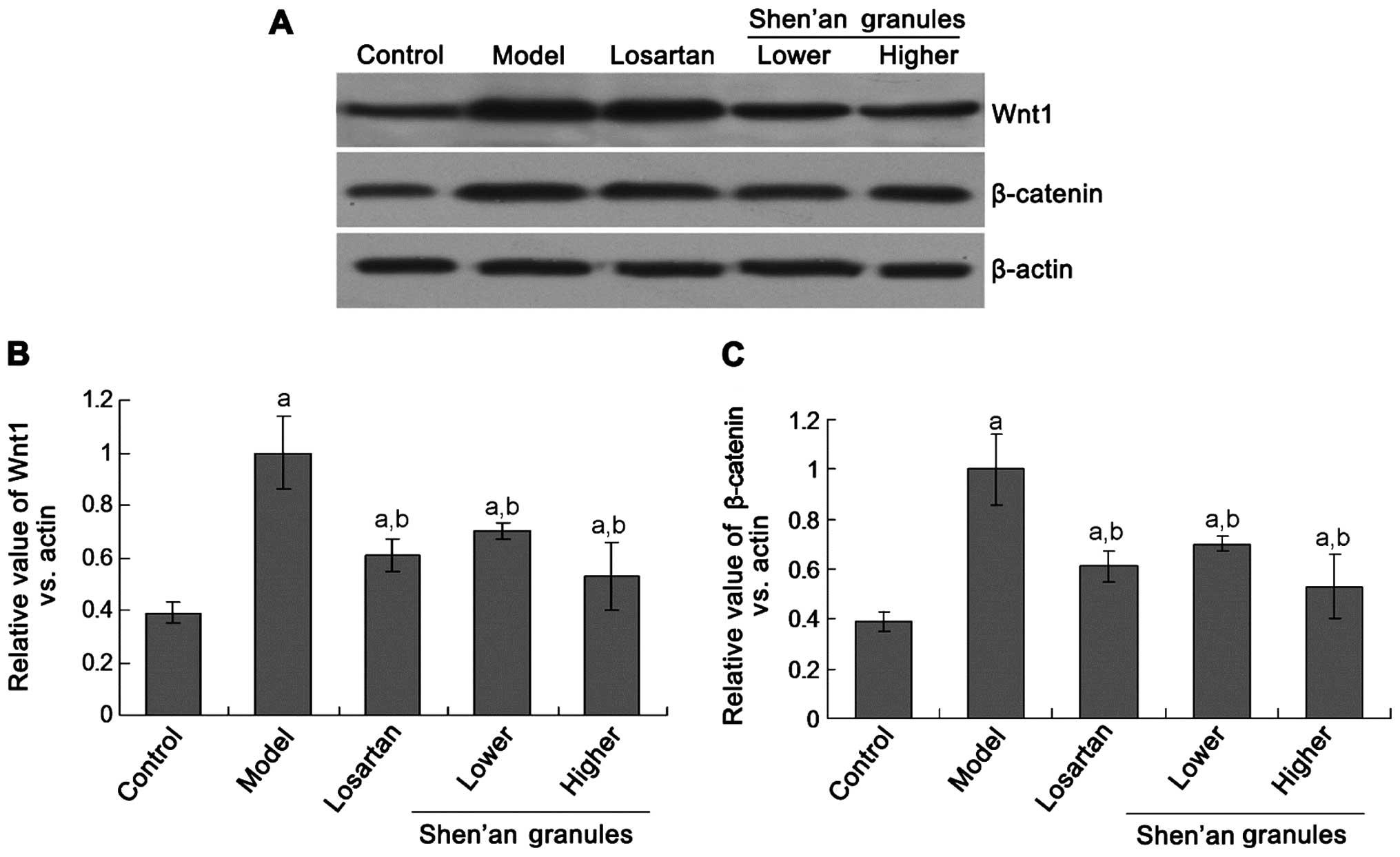
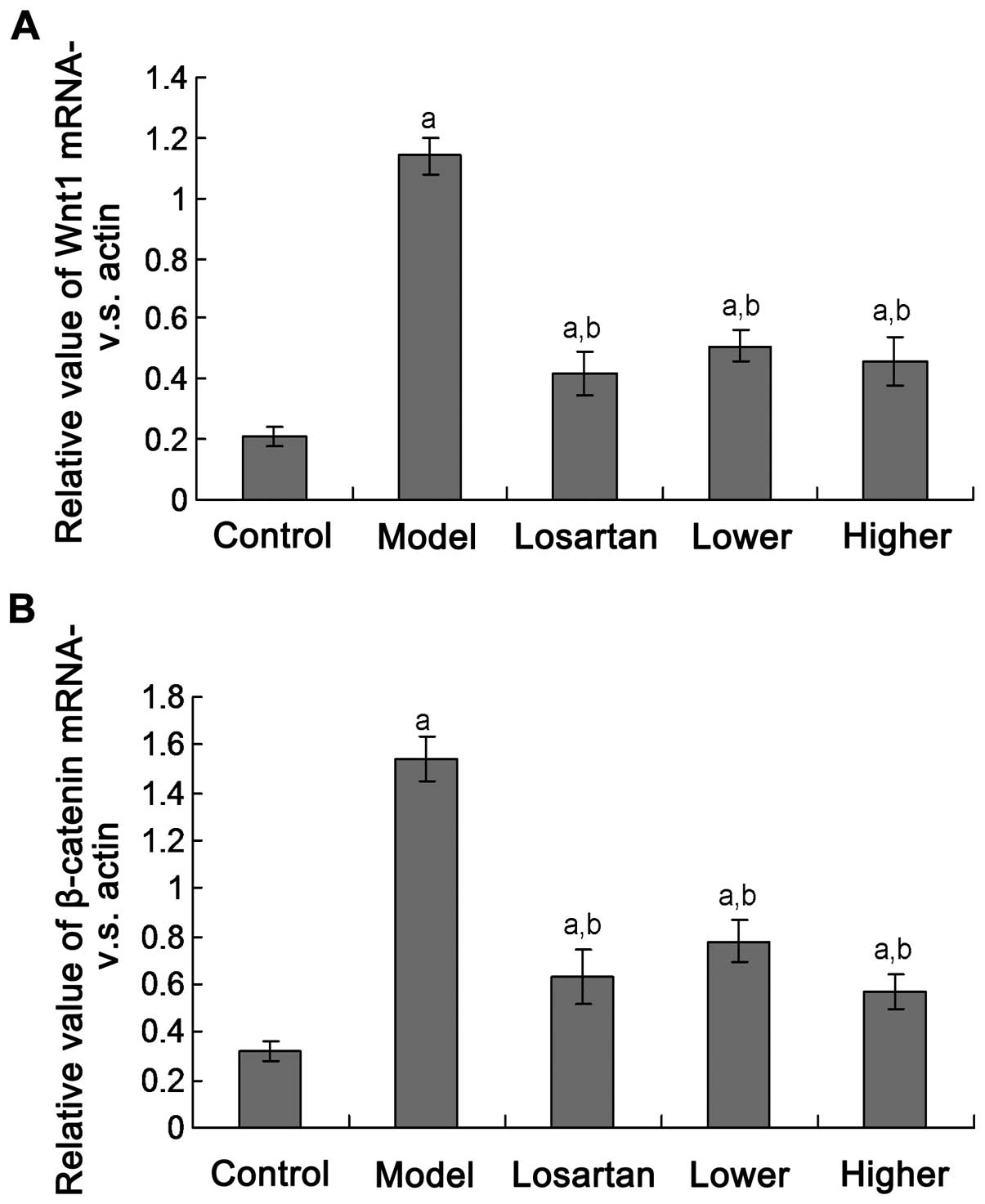
|
1
|
Chen C, Lu Y, Liu J, Li L, Zhao N and Lin
B: Genome-wide ChIP-seq analysis of TCF4 binding regions in
colorectal cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:4253–4259.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kawakami T, Ren S and Duffield JS: Wnt
signalling in kidney diseases: dual roles in renal injury and
repair. J Pathol. 229:221–231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kato H, Gruenwald A, Suh JH, Miner JH,
Barisoni-Thomas L, Taketo MM, Faul C, Millar SE, Holzman LB and
Susztak K: Wnt/β-catenin pathway in podocytes integrates cell
adhesion, differentiation, and survival. J Biol Chem.
286:26003–26015. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Auinger M, Edlinger R, Prischl F,
Kautzky-Willer A, Prager R, Rosenkranz AR, Roden M, Saemann M,
Clodi M and Schernthaner G: [Diabetic nephropathy - update 2012].
Wien Klin Wochenschr. 124:Suppl 2. 42–49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dalla VM, Masiero A, Roiter AM, Saller A,
Crepaldi G and Fioretto P: Is podocyte injury relevant in diabetic
nephropathy? Studies in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.
52:1031–1035. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou T, He X, Cheng R, Zhang B, Zhang RR,
Chen Y, Takahashi Y, Murray AR, Lee K, Gao G, et al: Implication of
dysregulation of the canonical wingless-type MMTV integration site
(WNT) pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia. 55:255–266.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He W, Dai C, Li Y, Zeng G, Monga SP and
Liu Y: Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes renal interstitial
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:765–776. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He W, Kang YS, Dai C and Liu Y: Blockade
of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by paricalcitol ameliorates proteinuria
and kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:90–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Woroniecka KI, Park AS, Mohtat D, Thomas
DB, Pullman JM and Susztak K: Transcriptome analysis of human
diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes. 60:2354–2369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Kiss LP, Monga SP,
Holzman LB and Liu Y: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte
dysfunction and albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1997–2008. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iglesias DM, Hueber PA, Chu L, Campbell R,
Patenaude AM, Dziarmaga AJ, Quinlan J, Mohamed O, Dufort D and
Goodyer PR: Canonical WNT signaling during kidney development. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 293:F494–F500. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He W, Tan RJ, Li Y, Wang D, Nie J, Hou FF
and Liu Y: Matrix metalloproteinase-7 as a surrogate marker
predicts renal Wnt/β-catenin activity in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol.
23:294–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang L, Xu L, Song Y, Li J, Mao J, Zhao
AZ, He W, Yang J and Dai C: Calmodulin-dependent protein
kinaseII/cAMP response element-binding protein/Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling cascade regulates angiotensin II-induced podocyte injury
and albuminuria. J Biol Chem. 288:23368–23379. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pozzi A, Jarad G, Moeckel GW, Coffa S,
Zhang X, Gewin L, Eremina V, Hudson BG, Borza DB, Harris RC, et al:
Beta1 integrin expression by podocytes is required to maintain
glomerular structural integrity. Dev Biol. 316:288–301. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin Y, Wang L, Duan Q, Gong Z, Yang F and
Song Y: Differential expression of 5-HT-related genes in
symptomatic pulmonary embolism patients. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:512–518. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lv J, Wang YX and Liu YN: Exploration of
heat treatment for diabetic nephropathy from the inflammation
pathogenesis. Chin J Integr Trad Western Nephrol. 15:60–61.
2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Wang YH, Pan Z and Wang YX: Molecular
pathological basis ofabdominal mass in Shen collaterals. J Beijing
Univ Trad Chin Med. 29:301–303. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Chen LJ, Wang XQ and Ping AY: Influence of
kidney-qi-nourishing therapy on T lymphocyte subgroup of spleen in
natural abortion model mice. Chin Archives Trad. Chin Med.
2012.
|
|
19
|
Qian H, Yang JJ, Pan DY, Tang WT, Xu KJ
and Qi MY: [Protective effectof total flavonoids of epimedium on
the kidney in experimental diabetic rats]. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng
Li Xue Za Zhi. 30:314–317. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ye D, Wu Z, Zhang T and Yue Y:
Experimental study of rhubarb and epimedium decoction in
counteracting hearing impairment due to chronic renal failure. Acta
Univ Trad Med Sin Pharmacol Shanghai. 1998.
|