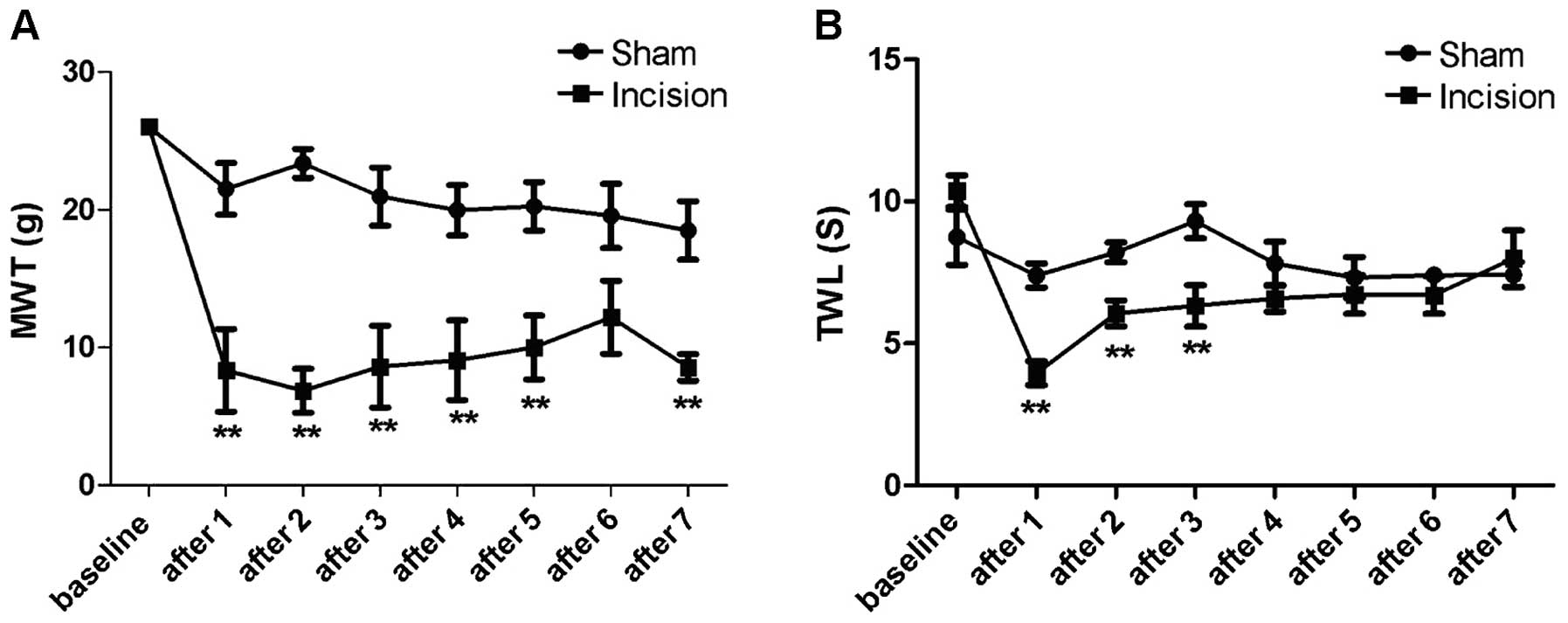
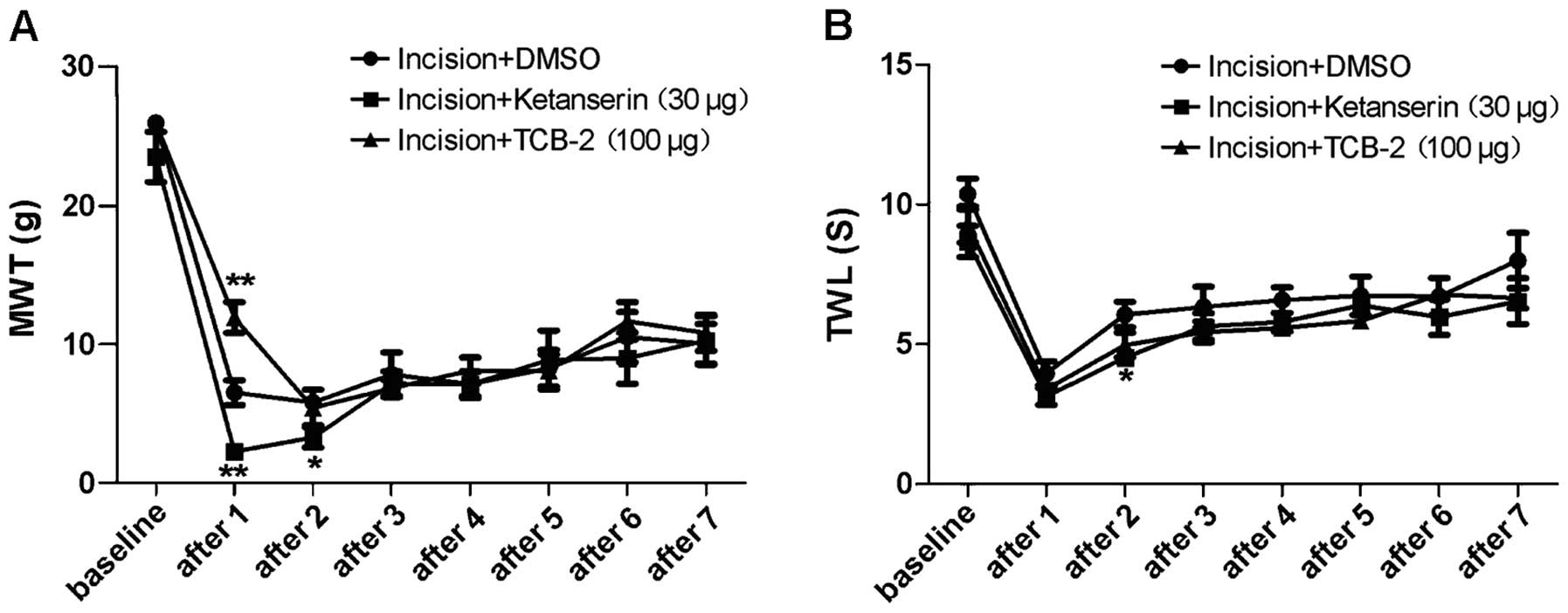
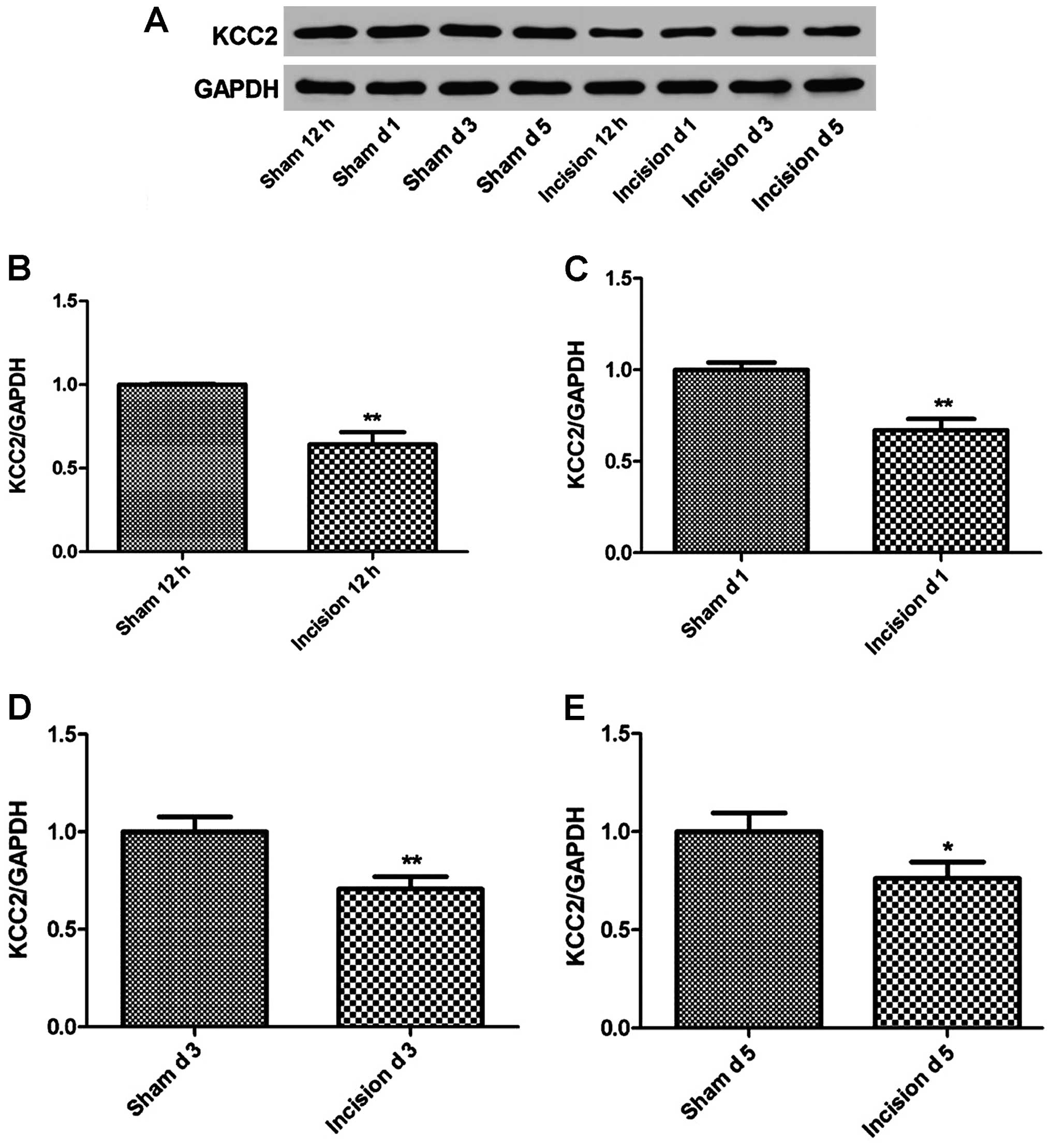
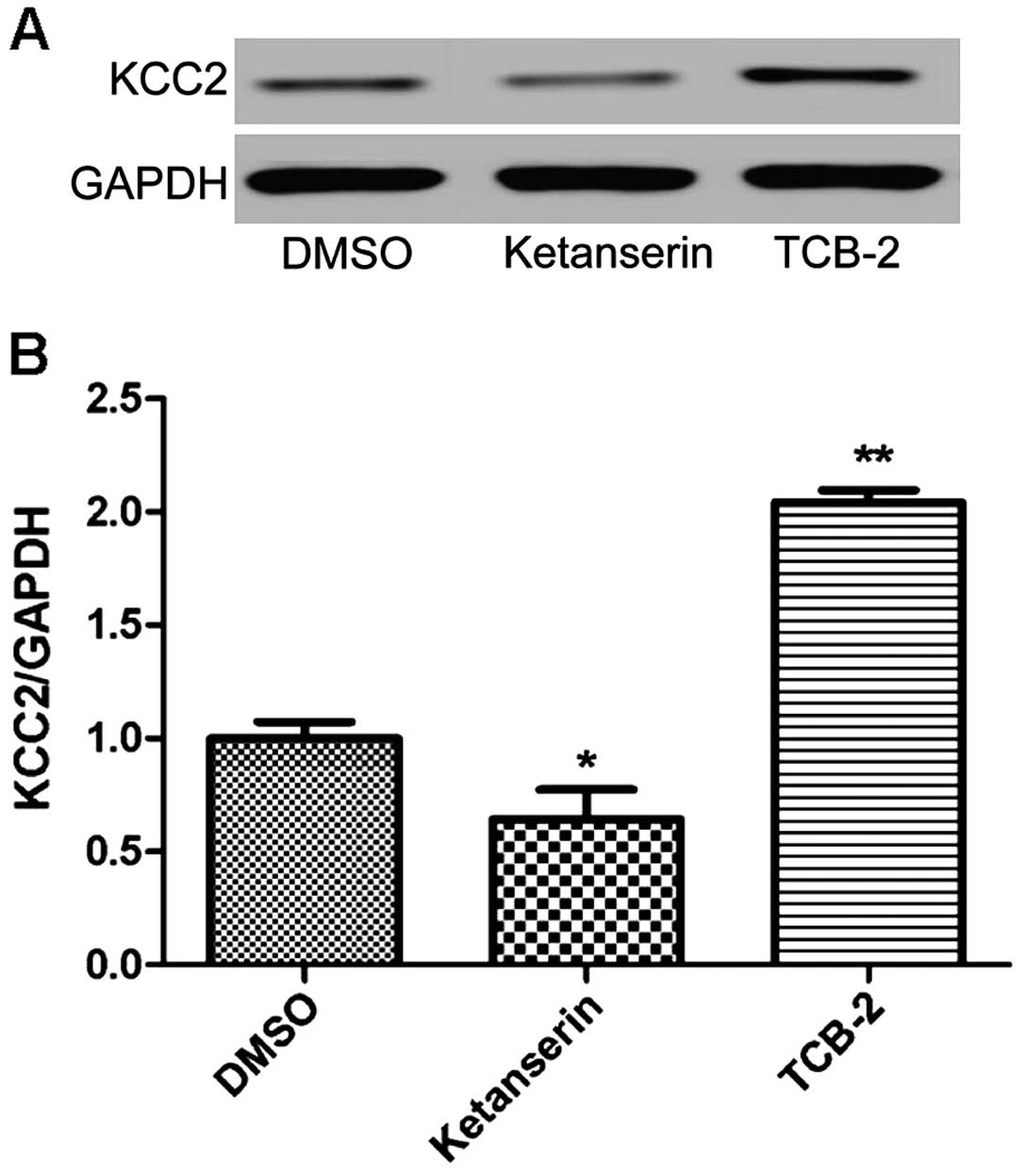
|
1
|
Macrae WA: Chronic post-surgical pain: 10
years on. Br J Anaesth. 101:77–86. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pavlin DJ, Chen C, Penaloza DA, Polissar
NL and Buckley FP: Pain as a factor complicating recovery and
discharge after ambulatory surgery. Anesth Analg. 95:627–634. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chou R, Gordon DB, de Leon-Casasola OA,
Rosenberg JM, Bickler S, Brennan T, Carter T, Cassidy CL,
Chittenden EH, Degenhardt E, et al: Management of postoperative
pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American Pain Society,
the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and
the American Society of Anesthesiologists Committee on Regional
Anesthesia, Executive Committee, and Administrative Council. J
Pain. 17:131–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dirks J, Møiniche S, Hilsted KL and Dahl
JB: Mechanisms of postoperative pain: Clinical indications for a
contribution of central neuronal sensitization. Anesthesiology.
97:1591–1596. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dostrovsky JO, Shah Y and Gray BG:
Descending inhibitory influences from periaqueductal gray, nucleus
raphe magnus, and adjacent reticular formation. II. Effects on
medullary dorsal horn nociceptive and nonnociceptive neurons. J
Neurophysiol. 49:948–960. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hosobuchi Y, Adams JE and Linchitz R: Pain
relief by electrical stimulation of the central gray matter in
humans and its reversal by naloxone. Science. 197:183–186. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie H, Ma F, Zhang YQ, Gao X and Wu GC:
Expression of 5-HT2A receptor mRNA in some nuclei of
brain stem enhanced in monoarthritic rats. Brain Res. 954:94–99.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okamoto K, Imbe H, Kimura A, Donishi T,
Tamai Y and Senba E: Activation of central 5HT2A
receptors reduces the craniofacial nociception of rats.
Neuroscience. 147:1090–1102. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Obata H, Saito S, Sasaki M and Goto F:
Interactions of 5-HT2 receptor agonists with
acetylcholine in spinal analgesic mechanisms in rats with
neuropathic pain. Brain Res. 965:114–120. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lavertu G, Côté SL and De Koninck Y:
Enhancing K-Cl co-transport restores normal spinothalamic sensory
coding in a neuropathic pain model. Brain. 137:724–738. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cramer SW, Baggott C, Cain J, Tilghman J,
Allcock B, Miranpuri G, Rajpal S, Sun D and Resnick D: The role of
cation-dependent chloride transporters in neuropathic pain
following spinal cord injury. Mol Pain. 4:362008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bos R, Sadlaoud K, Boulenguez P, Buttigieg
D, Liabeuf S, Brocard C, Haase G, Bras H and Vinay L: Activation of
5-HT2A receptors upregulates the function of the
neuronal K-Cl cotransporter KCC2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:348–353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blaesse P, Airaksinen MS, Rivera C and
Kaila K: Cation-chloride cotransporters and neuronal function.
Neuron. 61:820–838. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee HH, Walker JA, Williams JR, Goodier
RJ, Payne JA and Moss SJ: Direct protein kinase C-dependent
phosphorylation regulates the cell surface stability and activity
of the potassium chloride cotransporter KCC2. J Biol Chem.
282:29777–29784. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brennan TJ, Van der Meulen EP and Gebhart
GF: Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain.
64:493–501. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coull JA, Boudreau D, Bachand K, Prescott
SA, Nault F, Sík A, De Koninck P and De Koninck Y: Trans-synaptic
shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism
of neuropathic pain. Nature. 424:938–942. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Price TJ, Cervero F and de Koninck Y: Role
of cation-chloride-cotransporters (CCC) in pain and hyperalgesia.
Curr Top Med Chem. 5:547–555. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|