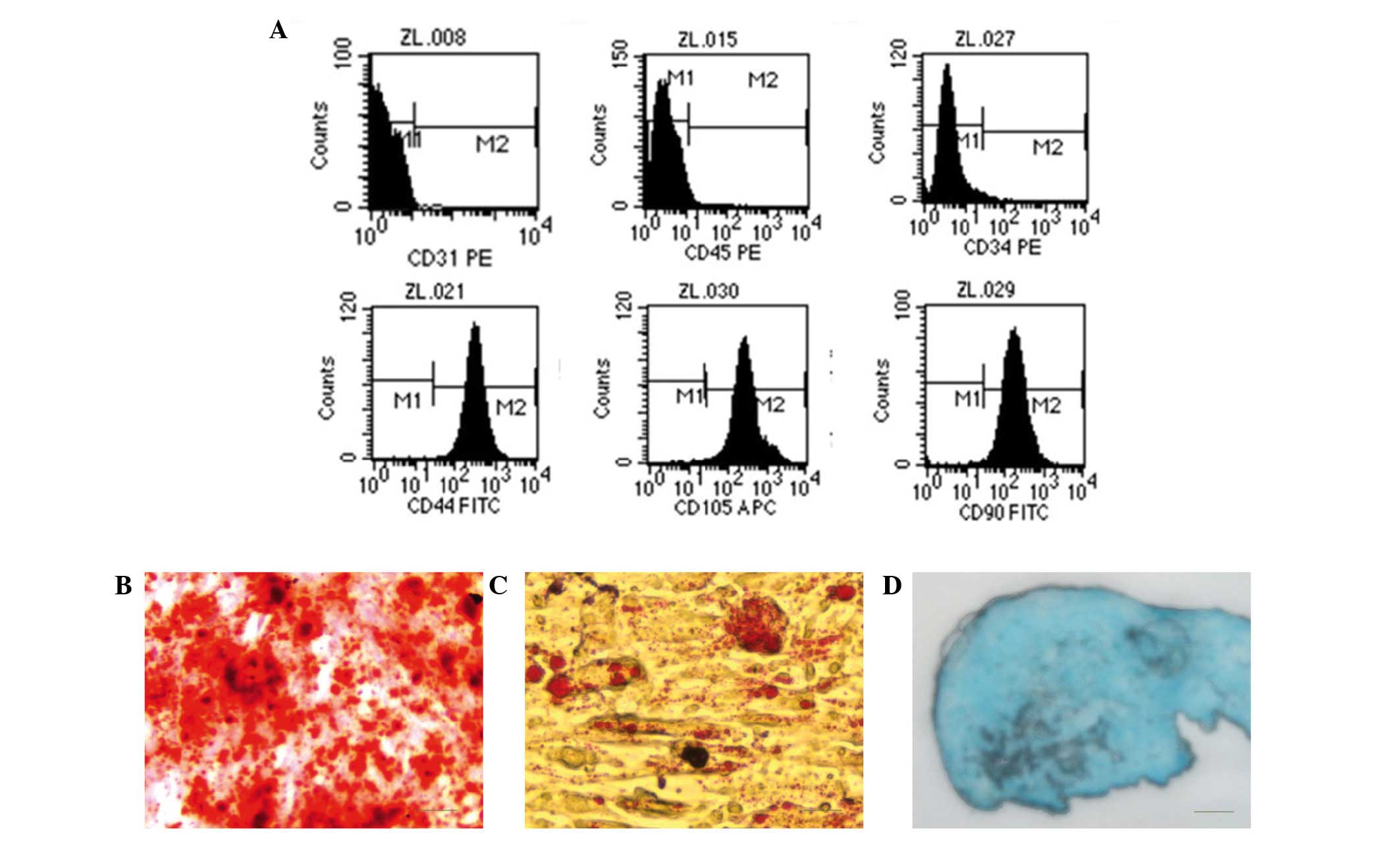
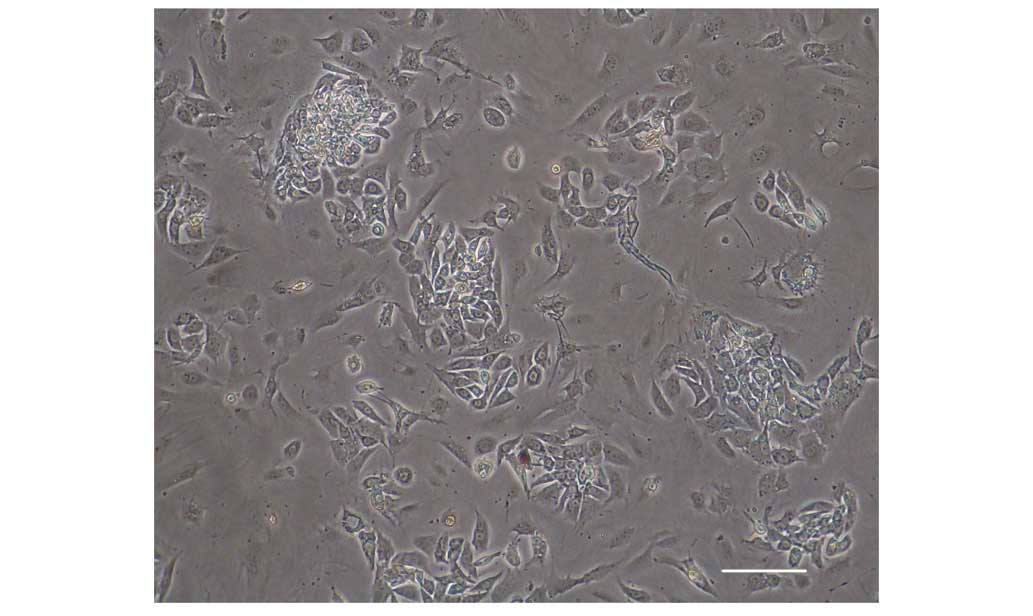
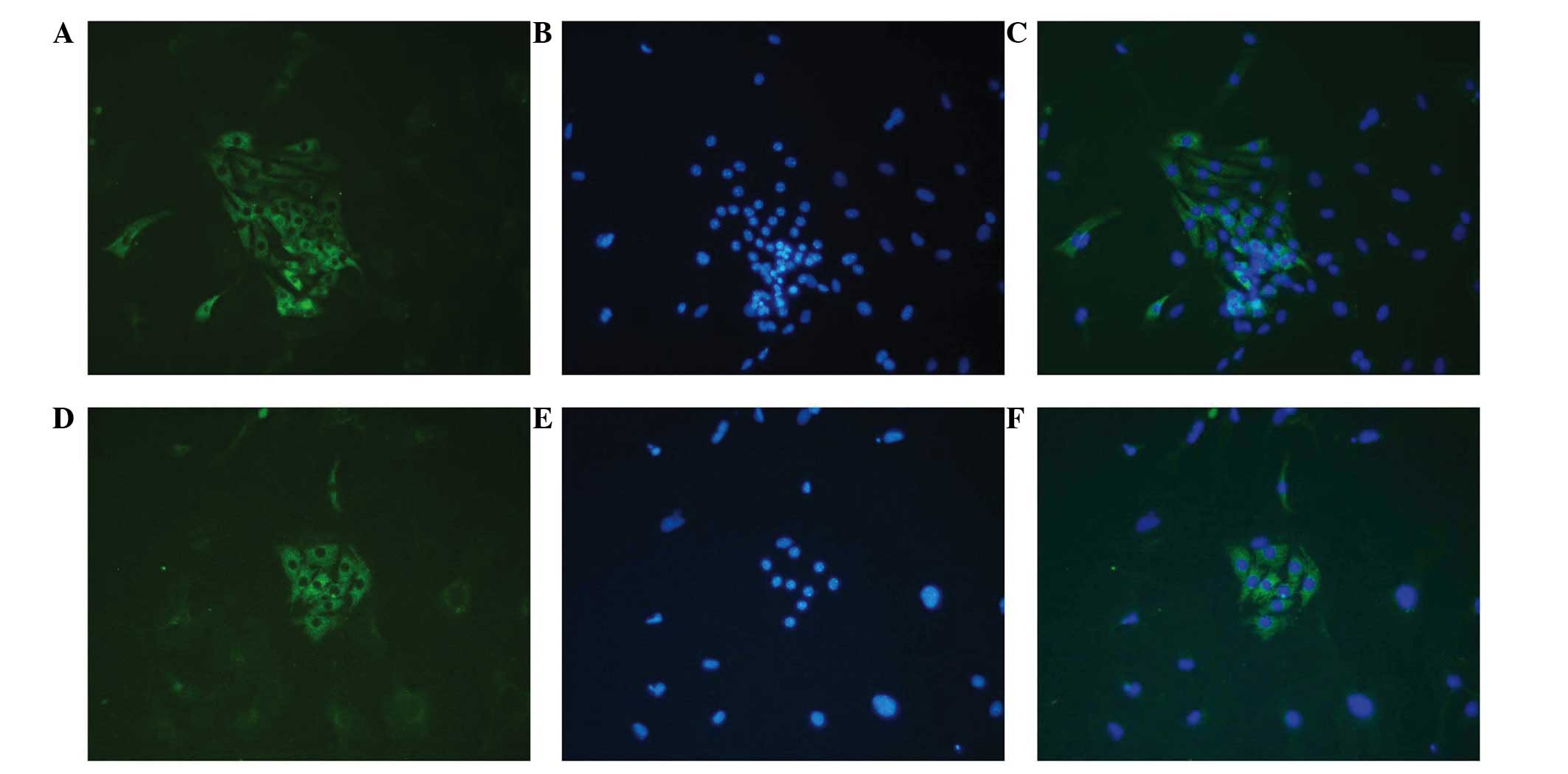
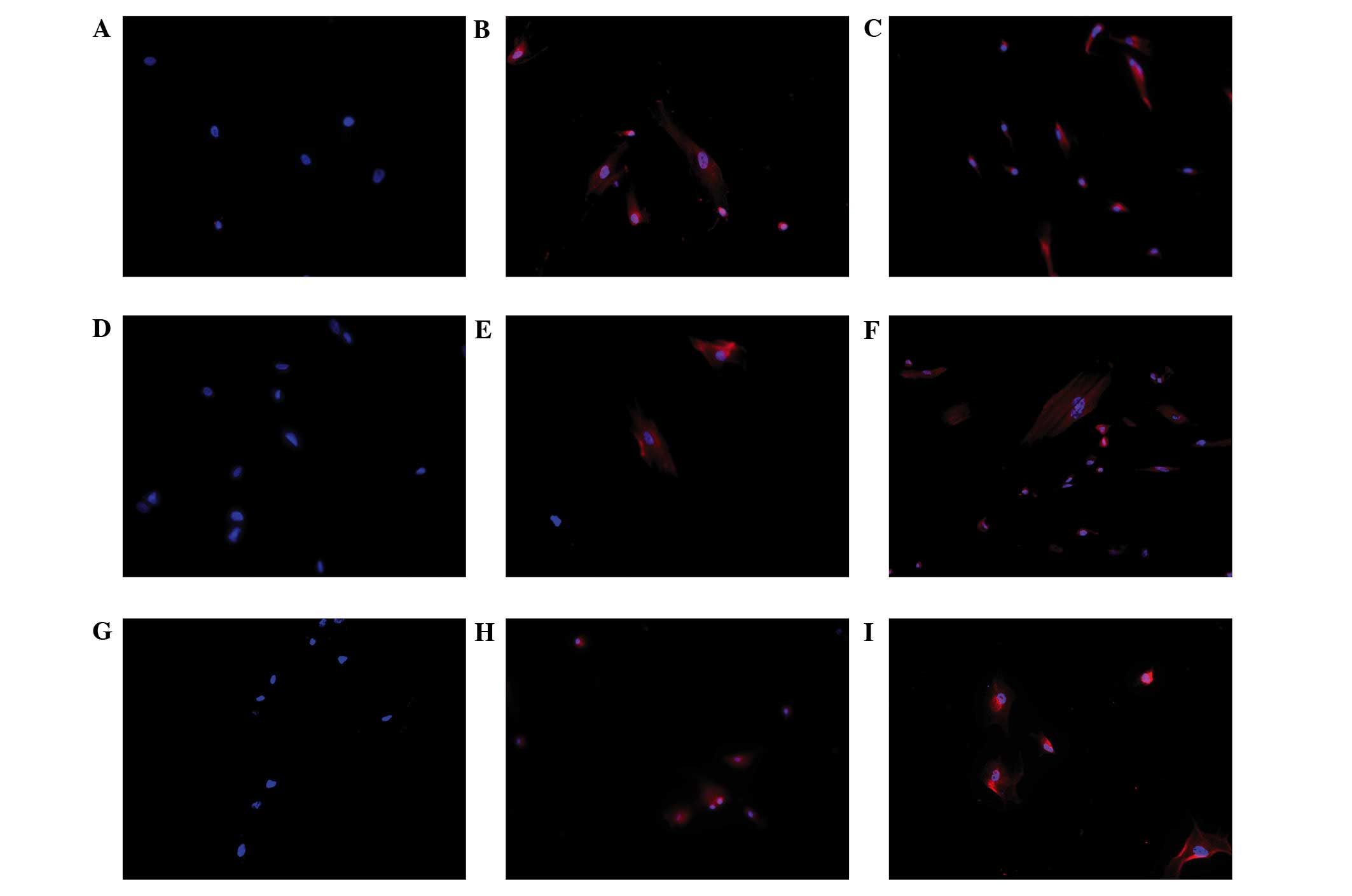
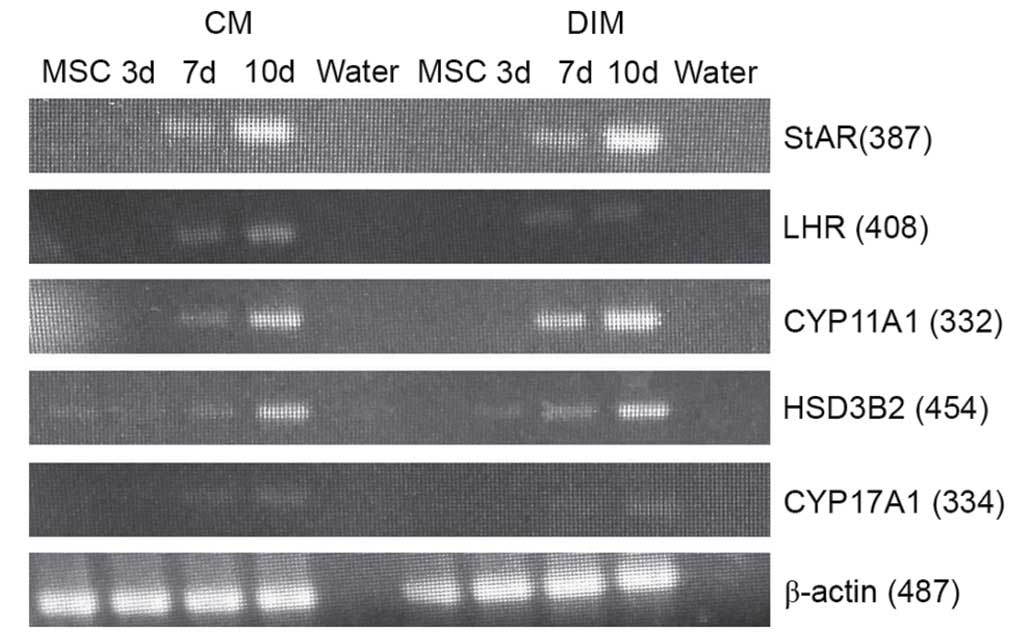
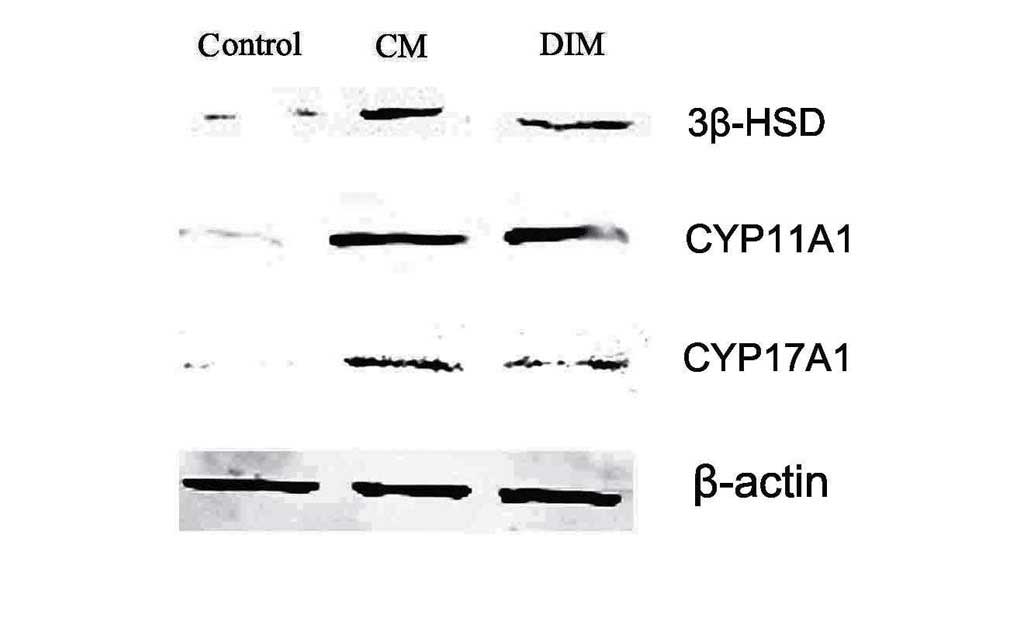
|
1
|
Wohlfahrt-Veje C, Main KM and Skakkebaek
NE: Testicular dysgenesis syndrome: Foetal origin of adult
reproductive problems. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 71:459–465. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meikle AW: The interrelationships between
thyroid dysfunction and hypogonadism in men and boys. Thyroid.
14:(Suppl 1). S17–S25. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun J, Xi YB, Zhang ZD, Shen P, Li HY, Yin
MZ, Li WY and Shi CR: Leydig cell transplantation restores androgen
production in surgically castrated prepubertal rats. Asian J
Androl. 11:405–409. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zirkin BR: Where do adult Leydig cells
come from? Biol Reprod. 82:1019–1020. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jahnukainen K, Ehmcke J, Hou M and Schlatt
S: Testicular function and fertility preservation in male cancer
patients. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 25:287–302. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lo KC, Lei Z, Rao ChV, Beck J and Lamb DJ:
De novo testosterone production in luteinizing hormone receptor
knockout mice after transplantation of leydig stem cells.
Endocrinology. 145:4011–4015. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mobasheri A, Csaki C, Clutterbuck AL,
Rahmanzadeh M and Shakibaei M: Mesenchymal stem cells in connective
tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Applications in
cartilage repair and osteoarthritis therapy. Histol Histopathol.
24:347–366. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Charbord P: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells: Historical overview and concepts. Hum Gene Ther.
21:1045–1056. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM, Lee KD, Hsieh SL
and Chen TH: Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from
umbilical cord blood. Blood. 103:1669–1675. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stenderup K, Justesen J, Clausen C and
Kassem M: Aging is associated with decreased maximal life span and
accelerated senescence of bone marrow stromal cells. Bone.
33:919–926. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST, Huang CC, Wei
HM, Guo YJ, Fu YS, Lai MC and Chen CC: Mesenchymal stem cells in
the Wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells.
22:1330–1337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsieh JY, Fu YS, Chang SJ, Tsuang YH and
Wang HW: Functional module analysis reveals differential osteogenic
and stemness potentials in human mesenchymal stem cells from bone
marrow and Wharton's jelly of umbilical cord. Stem Cells Dev.
19:1895–1910. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mitchell KE, Weiss ML, Mitchell BM, Martin
P, Davis D, Morales L, Helwig B, Beerenstrauch M, Abou-Easa K,
Hildreth T, et al: Matrix cells from Wharton's jelly form neurons
and glia. Stem Cells. 21:50–60. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang L, Ott L, Seshareddy K, Weiss ML and
Detamore MS: Musculoskeletal tissue engineering with human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells. Regen Med. 6:95–109.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen MY, Lie PC, Li ZL and Wei X:
Endothelial differentiation of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal
stem cells in comparison with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Exp Hematol. 37:629–640. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ge RS, Dong Q, Sottas CM, Papadopoulos V,
Zirkin BR and Hardy MP: In search of rat stem Leydig cells:
Identification, isolation, and lineage-specific development. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2719–2724. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wegman F, Oner FC, Dhert WJ and Alblas J:
Non-viral gene therapy for bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol
Genet Eng Rev. 29:206–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weiss ML, Medicetty S, Bledsoe AR,
Rachakatla RS, Choi M, Merchav S, Luo Y, Rao MS, Velagaleti G and
Troyer D: Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells: Preliminary
characterization and effect of transplantation in a rodent model of
Parkinson's disease. Stem cells. 24:781–792. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun J, Zhong L, Zhu Y and Liu G: Research
on the isolation of mouse Leydig cells using differential digestion
with a low concentration of collagenase. J Reprod Dev. 57:433–436.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du T, Cheng J, Zhong L, Zhao XF, Zhu J,
Zhu YJ and Liu GH: The alleviation of acute and chronic kidney
injury by human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells
triggered by ischemia-reperfusion injury via an endocrine
mechanism. Cytotherapy. 14:1215–1227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Teerds KJ and Huhtaniemi IT: Morphological
and functional maturation of Leydig cells: From rodent models to
primates. Hum Reprod Update. 21:310–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klinefelter GR, Hall PF and Ewing LL:
Effect of luteinizing hormone deprivation in situ on
steroidogenesis of rat Leydig cells purified by a multistep
procedure. Biol Reprod. 36:769–783. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shima Y, Miyabayashi K, Haraguchi S,
Arakawa T, Otake H, Baba T, Matsuzaki S, Shishido Y, Akiyama H,
Tachibana T, et al: Contribution of Leydig and Sertoli cells to
testosterone production in mouse fetal testes. Mol Endocrinology.
27:63–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li X, Bai J, Ji X, Li R, Xuan Y and Wang
Y: Comprehensive characterization of four different populations of
human mesenchymal stem cells as regards their immune properties,
proliferation and differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 34:695–704.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
De Bruyn C, Najar M, Raicevic G, Meuleman
N, Pieters K, Stamatopoulos B, Delforge A, Bron D and Lagneaux L: A
rapid, simple, and reproducible method for the isolation of
mesenchymal stromal cells from Wharton's jelly without enzymatic
treatment. Stem Cells Dev. 20:547–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen H, Ge RS and Zirkin BR: Leydig cells:
From stem cells to aging. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 306:9–16. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsuchida J, Dohmae K, Kitamura Y and
Nishimune Y: The role of the c-kit receptor in the regenerative
differentiation of rat Leydig cells. Int J Androl. 26:121–125.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ferlin A and Foresta C: Insulin-like
factor 3: A novel circulating hormone of testicular origin in
humans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1041:497–505. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qu JH, Fei J, Hong X, Chen JF, Gu AH, Sun
H, Xu XL, Song L, Wang SL and Wang XR: Involvement of IGF-I
signaling pathway in the regulation of steroidogenesis in mouse
Leydig cells treated with fenvalerate. Toxicology. 292:151–155.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luo L, Chen H and Zirkin BR: Leydig cell
aging: Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) and
cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme. J Androl. 22:149–156.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ariyaratne HB, Mills N, Mason JI and
Mendis-Handagama SM: Effects of thyroid hormone on Leydig cell
regeneration in the adult rat following ethane dimethane sulphonate
treatment. Biol Reprod. 63:1115–1123. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Luu-The V: Assessment of steroidogenesis
and steroidogenic enzyme functions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
137:176–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu X, Zhang N and Lee MM: Mullerian
inhibiting substance recruits ALK3 to regulate Leydig cell
differentiation. Endocrinology. 153:4929–4937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Svechnikov K, Landreh L, Weisser J, Izzo
G, Colón E, Svechnikova I and Söder O: Origin, development and
regulation of human Leydig cells. Horm Res Paediatr. 73:93–101.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stanley EL, Johnston DS, Fan J,
Papadopoulos V, Chen H, Ge RS, Zirkin BR and Jelinsky SA: Stem
Leydig cell differentiation: Gene expression during development of
the adult rat population of Leydig cells. Biol Reprod.
85:1161–1166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stocco DM, Wang X, Jo Y and Manna PR:
Multiple signaling pathways regulating steroidogenesis and
steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression: More complicated
than we thought. Mol Endocrinol. 19:2647–2659. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Teerds KJ, Rijntjes E, Veldhuizen-Tsoerkan
MB, Rommerts FF and de Boer-Brouwer M: The development of rat
Leydig cell progenitors in vitro: How essential is luteinising
hormone? J Endocrinol. 194:579–593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bjelic MM, Stojkov NJ, Baburski AZ,
Sokanovic SJ, Mihajlovic AI, Janjic MM, Kostic TS and Andric SA:
Molecular adaptations of testosterone-producing Leydig cells during
systemic in vivo blockade of the androgen receptor. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 396:10–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu S, Cheng Z, Liu G, Zhao X, Zhong L, Zhu
Y and Zhu J: Urothelial differentiation of human umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Anal Cell Pathol
(Amst). 36:63–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li TX, Yuan J, Chen Y, Pan LJ, Song C, Bi
LJ and Jiao XH: Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from
human umbilical cord tissue into odontoblast-like cells using the
conditioned medium of tooth germ cells in vitro. Biomed Res Int.
2013:2185432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fuchs E, Tumbar T and Guasch G:
Socializing with the neighbors: Stem cells and their niche. Cell.
116:769–778. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moore KA and Lemischka IR: Stem cells and
their niches. Science. 311:1880–1885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wei X, Peng G, Zheng S and Wu X:
Differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into
steroidogenic cells in comparison to bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells. Cell Prolif. 45:101–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sonoyama T, Sone M, Honda K, Taura D,
Kojima K, Inuzuka M, Kanamoto N, Tamura N and Nakao K:
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and human induced
pluripotent stem cells into steroid-producing cells. Endocrinology.
153:4336–4345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gondo S, Okabe T, Tanaka T, Morinaga H,
Nomura M, Takayanagi R, Nawata H and Yanase T: Adipose
tissue-derived and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells develop
into different lineage of steroidogenic cells by forced expression
of steroidogenic factor 1. Endocrinology. 149:4717–4725. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lue Y, Erkkila K, Liu PY, Ma K, Wang C,
Hikim AS and Swerdloff RS: Fate of bone marrow stem cells
transplanted into the testis: Potential implication for men with
testicular failure. Am J Pathol. 170:899–908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|