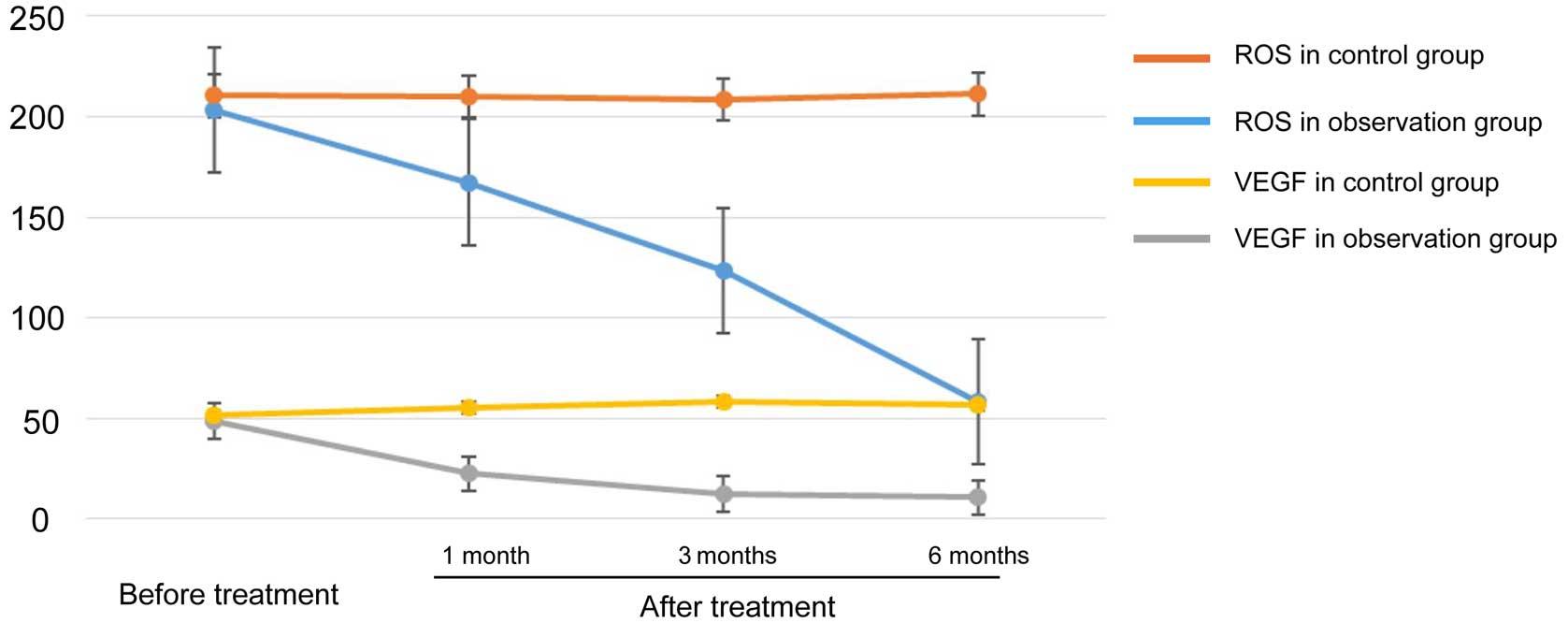
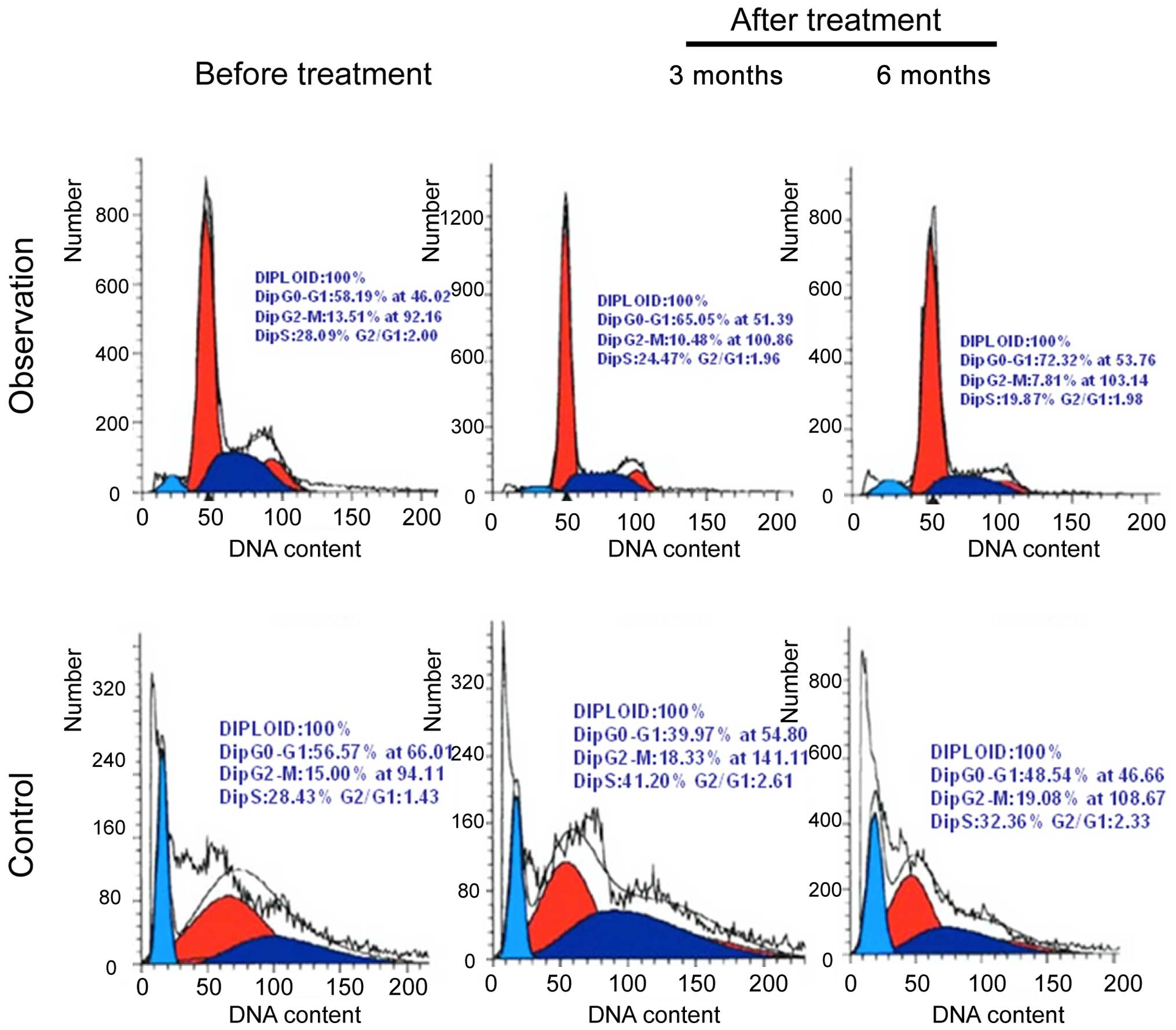
|
1
|
Blumenfeld Z and Evron A: Endocrine
prevention of chemotherapy-induced ovarian failure. Curr Opin
Obstet Gynecol. 28:223–229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mishra B, Ortiz L and Luderer U: Charged
iron particles, components of space radiation, destroy ovarian
follicles. Hum Reprod. 31:1816–1826. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roussev RG, Kaider BD, Price DE and Coulam
CB: Laboratory evaluation of women experiencing reproductive
failure. Am J Reprod Immunol. 35:415–420. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu X, Cai H, Kallianpur A, Li H, Yang G,
Gao J, Xiang YB, Ji BT, Yu-Tang, Zheng W and Shu XO: Impact of
premature ovarian failure on mortality and morbidity among Chinese
women. PLoS One. 2014.9:e89597 View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tamura H, Nakamura Y, Korkmaz A,
Manchester LC, Tan DX, Sugino N and Reiter RJ: Melatonin and the
ovary: physiological and pathophysiological implications. Fertil
Steril. 92:328–343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jang H, Lee OH, Lee Y, Yoon H, Chang EM,
Park M, Lee JW, Hong K, Kim JO, Kim NK, et al: Melatonin prevents
cisplatin-induced primordial follicle loss via suppression of
PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a pathway activation in the mouse ovary. J Pineal
Res. 60:336–347. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He H, Jiang DM, Kang B, Ma R, Bai L, Wang
X and Zhao L: Gene expression profiling of melatonin receptor
subtypes in the ovarian hierarchical follicles of the Sichuan white
goose. Anim Reprod Sci. 145:62–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma Q, Zhang T, Zhang P and Wang ZY:
Melatonin attenuates postharvest physiological deterioration of
cassava storage roots. J Pineal Res. 60:424–434. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gurer-Orhan H, Karaaslan C, Ozcan S,
Firuzi O, Tavakkoli M, Saso L and Suzen S: Novel indole-based
melatonin analogues: evaluation of antioxidant activity and
protective effect against amyloid β-induced damage. Bioorg Med
Chem. 24:1658–1664. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lohana CK and Samir N: Risk management of
osteoporosis in postmenopausal women; a study of women in a
teaching hospital. Glob J Health Sci. 8:555052016.
|
|
11
|
Vriend J and Reiter RJ: Melatonin and the
von Hippel-Lindau/HIF-1 oxygen sensing mechanism: a review. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1865:176–183. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu Y, Wang S, Jiang L, Wang H, Yang Y, Li
M, Wang X, Zhao X and Xie K: Identify melatonin as a novel
therapeutic reagent in the treatment of 1-bromopropane(1-BP)
intoxication. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e22032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rhee YH and Ahn JC: Melatonin attenuated
adipogenesis through reduction of the CCAAT/enhancer binding
protein beta by regulating the glycogen synthase 3 beta in human
mesenchymal stem cells. J Physiol Biochem. 72:145–155. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie JY, He W, Zhao LM, Chen M and Liang
ZQ: The changes of CD4− CD25− regulatory T
cells and changes of interferon gamma and expression of
transforming growth factor beta 1 in patients with premature
ovarian failure. West China Med J. 3:377–379. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Bodas M, Van Westphal C,
Carpenter-Thompson R, Mohanty KD and Vij N: Nicotine exposure
induces bronchial epithelial cell apoptosis and senescence via ROS
mediated autophagy-impairment. Free Radic Biol Med. 97:441–453.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mehrzadi S, Kamrava SK, Dormanesh B,
Motevalian M, Hosseinzadeh A, Tabatabaei SM Hosseini and Ghaznavi
H: Melatonin synergistically enhances protective effect of
atorvastatin against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rat
kidney. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 94:265–271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Check JH, Wilson C, DiAntonio G and
DiAntonio A: In vitro fertilization (IVF) outcome in women in overt
menopause attempting to induce follicular maturation by follicle
stimulating hormone (FSH) receptor down-regulation. Clin Exp Obstet
Gynecol. 43:181–183. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sundaresan NR, Leo MD Marcus, Subramani J,
Anish D, Sudhagar M, Ahmed KA, Saxena M, Tyagi JS, Sastry KV and
Saxena VK: Expression analysis of melatonin receptor subtypes in
the ovary of domestic chicken. Vet Res Commun. 33:49–56. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu T, Li Q, Wang S, Chen C and Zheng J:
Transplantation of ovarian granulosa-like cells derived from human
induced pluripotent stem cells for the treatment of murine
premature ovarian failure. Mol Med Rep. 13:5053–5058.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kleszczyñski K, Zillikens D and Fischer
TW: Melatonin enhances mitochondrial ATP synthesis, reduces ROS
formation and mediates translocation of the nuclear erythroid
2-related factor 2 resulting in activation of phase-2 antioxidant
enzymes (ã-GCS, HO-1, NQO1) in UVR-treated normal human epidermal
keratinocytes (NHEK). J Pineal Res. (In press). 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Benedict C, Thom B, N Friedman D,
Diotallevi D, M Pottenger E, Raghunathan JN and Kelvin JF: Young
adult female cancer survivors' unmet information needs and
reproductive concerns contribute to decisional conflict regarding
posttreatment fertility preservation. Cancer. 122:2101–2109. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Laisk-Podar T, Lindgren CM, Peters M,
Tapanainen JS, Lambalk CB, Salumets A and Mägi R: Ovarian
physiology and GWAS: biobanks, biology, and beyond. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 27:516–528. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|